Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment
Assignment
Uploaded by
TONICopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lecture Notes in Intro. To Philosophy Weeks 1-3Document3 pagesLecture Notes in Intro. To Philosophy Weeks 1-3Lorie Mae Domingo100% (1)
- Introduction To The Study of Logic: Lesson 1: Philosophy: Its Meaning and NatureDocument163 pagesIntroduction To The Study of Logic: Lesson 1: Philosophy: Its Meaning and NatureJuditha100% (3)
- World History - Modern TimesDocument372 pagesWorld History - Modern TimesKristine Joy Perez - CapiliNo ratings yet
- The Branches of PhilosophyDocument23 pagesThe Branches of Philosophyvicente ferrer100% (1)
- Important Summary Notices: Please NoteDocument37 pagesImportant Summary Notices: Please NotegrgaprgaNo ratings yet
- Europe and Western Civilization in The Modern Age (Guidebook) PDFDocument177 pagesEurope and Western Civilization in The Modern Age (Guidebook) PDFjames whiteNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentMark Anthony Telan PitogoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy - Final PDFDocument252 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy - Final PDFnyre aceNo ratings yet
- Philo of Man Calayan 20191Document36 pagesPhilo of Man Calayan 20191Catherine Mae MacailaoNo ratings yet
- Jhonshello Philosophy 1 1Document27 pagesJhonshello Philosophy 1 1juvelyn.aclaoNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Is The Study of General and Fundamental Problems, Such As ThoseDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Is The Study of General and Fundamental Problems, Such As ThoseGail Eunice MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Its Importance...Document23 pagesPhilosophy and Its Importance...Haika MariamNo ratings yet
- Logic Chapter 1Document6 pagesLogic Chapter 1Laine QuijanoNo ratings yet
- ARAO2Document4 pagesARAO2nuguitnorelyn30No ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy Chapter 3 4Document53 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy Chapter 3 4Georgess Murithi Gitonga94% (18)
- The Nature of Philosophy As An Autonomous Branch of KnowledgeDocument7 pagesThe Nature of Philosophy As An Autonomous Branch of KnowledgeAnn CelineNo ratings yet
- Branches of PhilosophyDocument20 pagesBranches of PhilosophyArlene Amistad AbingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 What Is PhilosophyDocument35 pagesLesson 1 What Is PhilosophyRyca Obnial100% (1)
- Philosophy: English Dictionary)Document4 pagesPhilosophy: English Dictionary)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- Branches of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesBranches of Philosophyyvette18latagNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Philosopy of Ethics PDFDocument5 pagesLecture-Philosopy of Ethics PDFMUHAMMAD SALEEM RAZANo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Philosophy and Its NatureDocument5 pagesUnit 1 - Philosophy and Its NatureKim ChiNo ratings yet
- PhiloDocument17 pagesPhiloJudy PatenoNo ratings yet
- Topic 1..Document14 pagesTopic 1..Małgorzata KosiórNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhilosophyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To PhilosophyMichelle Gonzales CaliuagNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of ManDocument2 pagesPhilosophy of ManCassandra LeeNo ratings yet
- Philos Q1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesPhilos Q1 ReviewerelieanetactaquinNo ratings yet
- Нұрғали РабиғаDocument6 pagesНұрғали РабиғаKyroko FairyNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Quarter1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Quarter1 ReviewerCristine Mae MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Nature of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesDiscuss The Nature of PhilosophyUrbana RaquibNo ratings yet
- MC 4 Prelim ReviewerDocument15 pagesMC 4 Prelim Reviewernuguitnorelyn30No ratings yet
- Ethics - : KnowledgeDocument4 pagesEthics - : KnowledgeCarlo EmilNo ratings yet
- MODULE in ETHICS 1Document6 pagesMODULE in ETHICS 1Jyrill Dyne P LannaonNo ratings yet
- Philosophy - WikipediaDocument390 pagesPhilosophy - Wikipediasalobei2213No ratings yet
- Good Governance and Social ResponsibilityModule-1-Lesson-2Document17 pagesGood Governance and Social ResponsibilityModule-1-Lesson-2Elyn PasuquinNo ratings yet
- GST 107Document7 pagesGST 107wisdomdurojaiyeNo ratings yet
- Logic CompleteDocument26 pagesLogic CompleteDanielle MerlinNo ratings yet
- Philo Week 1 4Document3 pagesPhilo Week 1 4Mikaela Sai ReynesNo ratings yet
- Arnie A. Valdez AR-5A "Assignment in Philosophy"Document4 pagesArnie A. Valdez AR-5A "Assignment in Philosophy"Joshua SantosNo ratings yet
- Philos 118 - Logic and Critical ThinkingDocument89 pagesPhilos 118 - Logic and Critical ThinkingMargie Villas Prayco50% (2)
- Logic: True, and More With What Kinds of Meanings Can Be True or FalseDocument4 pagesLogic: True, and More With What Kinds of Meanings Can Be True or FalseminmorNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (A)Document10 pagesModule 1 (A)Freddie ColladaNo ratings yet
- The Philosophical Background of Business EthicsDocument35 pagesThe Philosophical Background of Business EthicsRimuru TempestNo ratings yet
- 1 Fundamentals of Philosophy and LogicDocument2 pages1 Fundamentals of Philosophy and Logicdaniel chuaNo ratings yet
- The Word PhilosDocument4 pagesThe Word PhilosLovely PeñaredondoNo ratings yet
- TFN Worksheet No. 3: 1. Define Philosophy?Document3 pagesTFN Worksheet No. 3: 1. Define Philosophy?Faatoots FatsNo ratings yet
- Logic NotesDocument19 pagesLogic NotesCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Ip PointersDocument14 pagesIp PointersmkfolaesNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument16 pagesCritical ThinkingAbemelek tNo ratings yet
- Philosophy-Module 1Document6 pagesPhilosophy-Module 1gericj7dsNo ratings yet
- Fatima Assignment PhilosophyDocument27 pagesFatima Assignment PhilosophyAbdullah HabibNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhilosophyDocument4 pagesReviewer in PhilosophyrayacvnwiajNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Characterization of PhilosophyDocument13 pagesLesson 4 Characterization of PhilosophyRALPH JOSEPH SANTOSNo ratings yet
- EDU 08101 Lecture ppt-1Document14 pagesEDU 08101 Lecture ppt-1Swax BoyNo ratings yet
- Ethics and PhilosophyDocument20 pagesEthics and PhilosophyJulia Marie LlonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document59 pagesChapter 2Jay MenonNo ratings yet
- ShortDocument1 pageShortAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Artikel Filsafat IlmuDocument10 pagesArtikel Filsafat IlmuSasuke BonboruNo ratings yet
- Major of PhilosophyDocument6 pagesMajor of PhilosophyJames FulgencioNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION OF PHILOSOPHY TO THE HUMAN PERSON Week 1Document13 pagesINTRODUCTION OF PHILOSOPHY TO THE HUMAN PERSON Week 1janeNo ratings yet
- Reason and Emotion: Essays on Ancient Moral Psychology and Ethical TheoryFrom EverandReason and Emotion: Essays on Ancient Moral Psychology and Ethical TheoryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Philosophy: Sound smarter without trying harderFrom EverandPhilosophy: Sound smarter without trying harderRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Research On Datsu A RonDocument70 pagesResearch On Datsu A RonNguyen Luong Hai KhoiNo ratings yet
- Tor Tor DanceDocument5 pagesTor Tor DanceYuniazlinaNo ratings yet
- Phoenicia and The Phoenician CivilizationDocument12 pagesPhoenicia and The Phoenician CivilizationErdal Kam100% (1)
- 臺灣傳統木工鉋刀種類及其變異性Document12 pages臺灣傳統木工鉋刀種類及其變異性CiouZih-YanNo ratings yet
- List of Publications: Books & Book ChaptersDocument3 pagesList of Publications: Books & Book ChapterssaurabhshubhamNo ratings yet
- History of DentistryDocument5 pagesHistory of DentistryEdgar CortezNo ratings yet
- Controversy 1st MassDocument11 pagesControversy 1st MassRYAN JEREZNo ratings yet
- Beckett, Greg - The Ontology of Freedom The Unthinkable Miracle of HaitiDocument22 pagesBeckett, Greg - The Ontology of Freedom The Unthinkable Miracle of HaitiBethania PereiraNo ratings yet
- Wa0000Document142 pagesWa0000Speedie recordsNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument17 pagesGeographyRodel AlicanteNo ratings yet
- Class 11 History Mind MapsDocument11 pagesClass 11 History Mind Mapsmishraanushka405No ratings yet
- Tony BennetDocument9 pagesTony BennetMaría Jesus MontesNo ratings yet
- Wallerstein - World System Analysis PDFDocument65 pagesWallerstein - World System Analysis PDFJoão Ricardo Boechat Sales100% (1)
- Polybius: Polybios Sau Polibiu - Cca 201 - Cca 120 Î.hr., Fiul Lui Lycortas. OmDocument7 pagesPolybius: Polybios Sau Polibiu - Cca 201 - Cca 120 Î.hr., Fiul Lui Lycortas. OmElena100% (1)
- Tachev DionysopolisDocument8 pagesTachev DionysopolisJasmina TachevaNo ratings yet
- Sargon The Grea-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesSargon The Grea-WPS OfficeJustine Lawrenz BaracenaNo ratings yet
- Sex in The Empire - Book Review PDFDocument4 pagesSex in The Empire - Book Review PDFPaul ChanNo ratings yet
- CO de Literatura Engleza - Mohor-Ivan IoanaDocument50 pagesCO de Literatura Engleza - Mohor-Ivan IoanaGabriel BotezatuNo ratings yet
- Kabbalah UnveiledDocument185 pagesKabbalah UnveiledVictoria Generao100% (2)
- Brenner Property and Progress 2007Document32 pagesBrenner Property and Progress 2007Virgilio Urbina LazardiNo ratings yet
- Terry Cook Novos Usos PDFDocument22 pagesTerry Cook Novos Usos PDFCharlley LuzNo ratings yet
- Acara II Principles DatingDocument32 pagesAcara II Principles DatingSunrise HomeNo ratings yet
- Special Program in The Arts ThesisDocument27 pagesSpecial Program in The Arts ThesisDianne GealonNo ratings yet
- Readingsineurope005820mbp PDFDocument587 pagesReadingsineurope005820mbp PDFAlexandru CiocazanuNo ratings yet
- HellenisticArt PDFDocument35 pagesHellenisticArt PDFpostiraNo ratings yet
- Hidden Lebanon PDFDocument28 pagesHidden Lebanon PDFfjabaraNo ratings yet
- HerodotusDocument13 pagesHerodotusNicéphore JüngeNo ratings yet
Assignment
Assignment
Uploaded by
TONIOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment
Assignment
Uploaded by
TONICopyright:
Available Formats
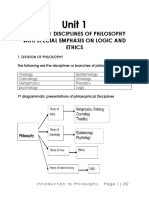
1.
Give the definition of the following:
a. Science- From latin scientia it means knowledge is a systematic
enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable
explanations and predictions about the universe. Scientific methodology
includes the following:
Objective observation: Measurement and data (possibly
although not necessarily using mathematics as a tool).
Evidence
Experiment and/or observation as benchmarks for testing
hypothesis
Induction: reasoning to establish general rules or conclusions
drawn from facts or example
Repetition
Critical analysis
Verification and testing: critical exposure to scrutiny, peer
review and assessment
b. History- from greek iotopia, historia, meaning “inquiry; knowledge
acquired by investigation” is the study of the past. Events before the
invention of writing systems are considered prehistory. History is an
umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery,
collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events.
Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as
written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological
markers.
c. Philosophy- from Greek, by way of Latin, philosophia, “love of wisdom”.
The rational, abstract, and methodical consideration of reality as a whole
or of fundamental dimensions of human existence and experience.
Philosophical inquiry is a central element in the intellectual history of many
civilizations. The subject of philosophy is treated in a number of articles.
For discussion of major system of Eastern philosophy,see Buddhism;
Chinese philosophy; Confucianism; Daoism; Hinduism;Indian philosophy;
Jainism; Japanese philosophy; Shinto; Sikhism.
d. Ontology- is the branch of philosophy that studies concepts such as
existence, being, becoming, and reality. It includes the questions of how
entities are grouped into basic categories and which of these entities exist
on the most fundamental level. Ontology is sometimes referred to as the
science of being and belongs to the major branch of philosophy known as
metaphysics. Ontologist often try to determine what the categories or
highest kinds are and how they form a system of categories that provides
an encompassing classification of all entities.
e. Metaphysics- The word “metaphysics” comes from the two Greek words
that, together, literally mean “ after or behind or among the study of the
natural. It is the branch of philosophy that studies the first principles of
being, identity and change, space and time, causality, necessity and
possibility. It includes questions about the nature of consciousness and the
relationship between mind and matter.Whatever the reasons may be, the
set of problems to which the word metaphysics now applies is so diverse
that it very hard to frame a definition that adequately expresses the nature
and scope of the discipline.
f. Epistemology – The term “ epistemology” comes from the Greek words “
episteme” and “logos”. Episteme can be translated as knowledge or
understanding or acquaintance while logos can be translated as account
or argument or reason.Just as each of these different translations captures
some facet of the meaning of these Greek terms, so too does each
translation capture some facet of the meaning of these Greek terms, so
too does each translation capture a different facet of epistemology itself.
g. Axiology- From Greek word axia means “value, worth’’; and logia it
means “study of ”- is the philosophical study of value. It includes questions
about the nature and classification of values and about what kinds of
things have value. It is intimately connected with various other
philosophical fields that crucially depend on the notion of value, like ethics,
aesthetics or philosophy of religion. It is also closely related to value theory
and methaethics. The term was first used by Paul Lapie, in 1902, and
Eduard von Hartmann, in 1908.
h. Logic- is an interdisciplinary field which studies truth and reasoning.
Informal logic seeks to characterize valid arguments informally, for
instance by listing varieties of fallacies. Formal logic represents statements
and argument patterns symbolically, using formal systems such as first
order logic.. Within formal logic, mathematical logic, studies the
mathematical characteristics of logical system, while philosophical logic
applies them to philosophical problems such as the nature of meaning,
knowledge, and existence. Systems of formal logic are also applied in
other fields including linguistics, cognitive science, and computer science.
You might also like
- Lecture Notes in Intro. To Philosophy Weeks 1-3Document3 pagesLecture Notes in Intro. To Philosophy Weeks 1-3Lorie Mae Domingo100% (1)
- Introduction To The Study of Logic: Lesson 1: Philosophy: Its Meaning and NatureDocument163 pagesIntroduction To The Study of Logic: Lesson 1: Philosophy: Its Meaning and NatureJuditha100% (3)
- World History - Modern TimesDocument372 pagesWorld History - Modern TimesKristine Joy Perez - CapiliNo ratings yet
- The Branches of PhilosophyDocument23 pagesThe Branches of Philosophyvicente ferrer100% (1)
- Important Summary Notices: Please NoteDocument37 pagesImportant Summary Notices: Please NotegrgaprgaNo ratings yet
- Europe and Western Civilization in The Modern Age (Guidebook) PDFDocument177 pagesEurope and Western Civilization in The Modern Age (Guidebook) PDFjames whiteNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentMark Anthony Telan PitogoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy - Final PDFDocument252 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy - Final PDFnyre aceNo ratings yet
- Philo of Man Calayan 20191Document36 pagesPhilo of Man Calayan 20191Catherine Mae MacailaoNo ratings yet
- Jhonshello Philosophy 1 1Document27 pagesJhonshello Philosophy 1 1juvelyn.aclaoNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Is The Study of General and Fundamental Problems, Such As ThoseDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Is The Study of General and Fundamental Problems, Such As ThoseGail Eunice MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Its Importance...Document23 pagesPhilosophy and Its Importance...Haika MariamNo ratings yet
- Logic Chapter 1Document6 pagesLogic Chapter 1Laine QuijanoNo ratings yet
- ARAO2Document4 pagesARAO2nuguitnorelyn30No ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy Chapter 3 4Document53 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy Chapter 3 4Georgess Murithi Gitonga94% (18)
- The Nature of Philosophy As An Autonomous Branch of KnowledgeDocument7 pagesThe Nature of Philosophy As An Autonomous Branch of KnowledgeAnn CelineNo ratings yet
- Branches of PhilosophyDocument20 pagesBranches of PhilosophyArlene Amistad AbingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 What Is PhilosophyDocument35 pagesLesson 1 What Is PhilosophyRyca Obnial100% (1)
- Philosophy: English Dictionary)Document4 pagesPhilosophy: English Dictionary)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- Branches of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesBranches of Philosophyyvette18latagNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Philosopy of Ethics PDFDocument5 pagesLecture-Philosopy of Ethics PDFMUHAMMAD SALEEM RAZANo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Philosophy and Its NatureDocument5 pagesUnit 1 - Philosophy and Its NatureKim ChiNo ratings yet
- PhiloDocument17 pagesPhiloJudy PatenoNo ratings yet
- Topic 1..Document14 pagesTopic 1..Małgorzata KosiórNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhilosophyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To PhilosophyMichelle Gonzales CaliuagNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of ManDocument2 pagesPhilosophy of ManCassandra LeeNo ratings yet
- Philos Q1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesPhilos Q1 ReviewerelieanetactaquinNo ratings yet
- Нұрғали РабиғаDocument6 pagesНұрғали РабиғаKyroko FairyNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Quarter1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Quarter1 ReviewerCristine Mae MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Nature of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesDiscuss The Nature of PhilosophyUrbana RaquibNo ratings yet
- MC 4 Prelim ReviewerDocument15 pagesMC 4 Prelim Reviewernuguitnorelyn30No ratings yet
- Ethics - : KnowledgeDocument4 pagesEthics - : KnowledgeCarlo EmilNo ratings yet
- MODULE in ETHICS 1Document6 pagesMODULE in ETHICS 1Jyrill Dyne P LannaonNo ratings yet
- Philosophy - WikipediaDocument390 pagesPhilosophy - Wikipediasalobei2213No ratings yet
- Good Governance and Social ResponsibilityModule-1-Lesson-2Document17 pagesGood Governance and Social ResponsibilityModule-1-Lesson-2Elyn PasuquinNo ratings yet
- GST 107Document7 pagesGST 107wisdomdurojaiyeNo ratings yet
- Logic CompleteDocument26 pagesLogic CompleteDanielle MerlinNo ratings yet
- Philo Week 1 4Document3 pagesPhilo Week 1 4Mikaela Sai ReynesNo ratings yet
- Arnie A. Valdez AR-5A "Assignment in Philosophy"Document4 pagesArnie A. Valdez AR-5A "Assignment in Philosophy"Joshua SantosNo ratings yet
- Philos 118 - Logic and Critical ThinkingDocument89 pagesPhilos 118 - Logic and Critical ThinkingMargie Villas Prayco50% (2)
- Logic: True, and More With What Kinds of Meanings Can Be True or FalseDocument4 pagesLogic: True, and More With What Kinds of Meanings Can Be True or FalseminmorNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (A)Document10 pagesModule 1 (A)Freddie ColladaNo ratings yet
- The Philosophical Background of Business EthicsDocument35 pagesThe Philosophical Background of Business EthicsRimuru TempestNo ratings yet
- 1 Fundamentals of Philosophy and LogicDocument2 pages1 Fundamentals of Philosophy and Logicdaniel chuaNo ratings yet
- The Word PhilosDocument4 pagesThe Word PhilosLovely PeñaredondoNo ratings yet
- TFN Worksheet No. 3: 1. Define Philosophy?Document3 pagesTFN Worksheet No. 3: 1. Define Philosophy?Faatoots FatsNo ratings yet
- Logic NotesDocument19 pagesLogic NotesCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Ip PointersDocument14 pagesIp PointersmkfolaesNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument16 pagesCritical ThinkingAbemelek tNo ratings yet
- Philosophy-Module 1Document6 pagesPhilosophy-Module 1gericj7dsNo ratings yet
- Fatima Assignment PhilosophyDocument27 pagesFatima Assignment PhilosophyAbdullah HabibNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhilosophyDocument4 pagesReviewer in PhilosophyrayacvnwiajNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Characterization of PhilosophyDocument13 pagesLesson 4 Characterization of PhilosophyRALPH JOSEPH SANTOSNo ratings yet
- EDU 08101 Lecture ppt-1Document14 pagesEDU 08101 Lecture ppt-1Swax BoyNo ratings yet
- Ethics and PhilosophyDocument20 pagesEthics and PhilosophyJulia Marie LlonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document59 pagesChapter 2Jay MenonNo ratings yet
- ShortDocument1 pageShortAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Artikel Filsafat IlmuDocument10 pagesArtikel Filsafat IlmuSasuke BonboruNo ratings yet
- Major of PhilosophyDocument6 pagesMajor of PhilosophyJames FulgencioNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION OF PHILOSOPHY TO THE HUMAN PERSON Week 1Document13 pagesINTRODUCTION OF PHILOSOPHY TO THE HUMAN PERSON Week 1janeNo ratings yet
- Reason and Emotion: Essays on Ancient Moral Psychology and Ethical TheoryFrom EverandReason and Emotion: Essays on Ancient Moral Psychology and Ethical TheoryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Philosophy: Sound smarter without trying harderFrom EverandPhilosophy: Sound smarter without trying harderRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Research On Datsu A RonDocument70 pagesResearch On Datsu A RonNguyen Luong Hai KhoiNo ratings yet
- Tor Tor DanceDocument5 pagesTor Tor DanceYuniazlinaNo ratings yet
- Phoenicia and The Phoenician CivilizationDocument12 pagesPhoenicia and The Phoenician CivilizationErdal Kam100% (1)
- 臺灣傳統木工鉋刀種類及其變異性Document12 pages臺灣傳統木工鉋刀種類及其變異性CiouZih-YanNo ratings yet
- List of Publications: Books & Book ChaptersDocument3 pagesList of Publications: Books & Book ChapterssaurabhshubhamNo ratings yet
- History of DentistryDocument5 pagesHistory of DentistryEdgar CortezNo ratings yet
- Controversy 1st MassDocument11 pagesControversy 1st MassRYAN JEREZNo ratings yet
- Beckett, Greg - The Ontology of Freedom The Unthinkable Miracle of HaitiDocument22 pagesBeckett, Greg - The Ontology of Freedom The Unthinkable Miracle of HaitiBethania PereiraNo ratings yet
- Wa0000Document142 pagesWa0000Speedie recordsNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument17 pagesGeographyRodel AlicanteNo ratings yet
- Class 11 History Mind MapsDocument11 pagesClass 11 History Mind Mapsmishraanushka405No ratings yet
- Tony BennetDocument9 pagesTony BennetMaría Jesus MontesNo ratings yet
- Wallerstein - World System Analysis PDFDocument65 pagesWallerstein - World System Analysis PDFJoão Ricardo Boechat Sales100% (1)
- Polybius: Polybios Sau Polibiu - Cca 201 - Cca 120 Î.hr., Fiul Lui Lycortas. OmDocument7 pagesPolybius: Polybios Sau Polibiu - Cca 201 - Cca 120 Î.hr., Fiul Lui Lycortas. OmElena100% (1)
- Tachev DionysopolisDocument8 pagesTachev DionysopolisJasmina TachevaNo ratings yet
- Sargon The Grea-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesSargon The Grea-WPS OfficeJustine Lawrenz BaracenaNo ratings yet
- Sex in The Empire - Book Review PDFDocument4 pagesSex in The Empire - Book Review PDFPaul ChanNo ratings yet
- CO de Literatura Engleza - Mohor-Ivan IoanaDocument50 pagesCO de Literatura Engleza - Mohor-Ivan IoanaGabriel BotezatuNo ratings yet
- Kabbalah UnveiledDocument185 pagesKabbalah UnveiledVictoria Generao100% (2)
- Brenner Property and Progress 2007Document32 pagesBrenner Property and Progress 2007Virgilio Urbina LazardiNo ratings yet
- Terry Cook Novos Usos PDFDocument22 pagesTerry Cook Novos Usos PDFCharlley LuzNo ratings yet
- Acara II Principles DatingDocument32 pagesAcara II Principles DatingSunrise HomeNo ratings yet
- Special Program in The Arts ThesisDocument27 pagesSpecial Program in The Arts ThesisDianne GealonNo ratings yet
- Readingsineurope005820mbp PDFDocument587 pagesReadingsineurope005820mbp PDFAlexandru CiocazanuNo ratings yet
- HellenisticArt PDFDocument35 pagesHellenisticArt PDFpostiraNo ratings yet
- Hidden Lebanon PDFDocument28 pagesHidden Lebanon PDFfjabaraNo ratings yet
- HerodotusDocument13 pagesHerodotusNicéphore JüngeNo ratings yet