Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foundation Engineering
Foundation Engineering
Uploaded by
fitri zohriatunCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- List of Industries in and Around ChennaiDocument5 pagesList of Industries in and Around Chennaijayvee75% (4)
- Design of Reinforced Concrete ChamberDocument10 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete ChamberVan BGNo ratings yet
- Tutorials Pad Footing Nta 5 (2012&2013)Document3 pagesTutorials Pad Footing Nta 5 (2012&2013)Host FredyNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering Assignment - 1 Shallow Foundation: Department of Civil EngineeringDocument2 pagesFoundation Engineering Assignment - 1 Shallow Foundation: Department of Civil EngineeringYash MehtaNo ratings yet
- 07a70101 Geotechnical Engineering-IiDocument7 pages07a70101 Geotechnical Engineering-IiSamiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Marks: With: Autumri. S LTL - Ester Suitabl Req:uii D.F,' Properti S.of 1Document2 pagesMarks: With: Autumri. S LTL - Ester Suitabl Req:uii D.F,' Properti S.of 1Suman SahaNo ratings yet
- University of Mauritius Faculty of EngineeringDocument6 pagesUniversity of Mauritius Faculty of EngineeringAvinaash VeeramahNo ratings yet
- Question Paper - GIAN - 19 - ModifiedDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper - GIAN - 19 - Modifiedsayan mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment ECEC-4120 Unit-1 (2021)Document2 pagesHome Assignment ECEC-4120 Unit-1 (2021)Arbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Geotech Engg QuestionsDocument2 pagesGeotech Engg QuestionsYashasviNo ratings yet
- RT32012112019Document2 pagesRT32012112019ruchika sahuNo ratings yet
- Rev PapersDocument3 pagesRev PapersRotich VincentNo ratings yet
- R7410101 Geotechnical Engineering-IIDocument8 pagesR7410101 Geotechnical Engineering-IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Light Weight ConcreteDocument5 pagesComparative Study of Light Weight ConcreteAmulyaRajbharNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIIDocument4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIIElvis MutsvangaNo ratings yet
- Foundation EngineeringDocument2 pagesFoundation EngineeringqwfqefwqefgefqeNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment-1Document1 pageGroup Assignment-1etrimageoffreyNo ratings yet
- Water Table at Depth 3m From Ground Level: Marks CO R.B.T. LevelDocument3 pagesWater Table at Depth 3m From Ground Level: Marks CO R.B.T. LevelRitesh SonarNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Geotechnical Engineering - IiDocument1 pageWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Geotechnical Engineering - IimaheshNo ratings yet
- Soil Geotechnical Engineering - IIDocument5 pagesSoil Geotechnical Engineering - IIabmsd2No ratings yet
- Advanced Foundation Engineering Rr420101Document8 pagesAdvanced Foundation Engineering Rr420101Andronico BintiNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document4 pagesHomework 2Ali AratNo ratings yet
- Test-Foundation Desiga: ConditionsDocument1 pageTest-Foundation Desiga: ConditionsBlessingNo ratings yet
- Cl449 - Dos-II - Unit Test - I - Question PaperDocument2 pagesCl449 - Dos-II - Unit Test - I - Question PaperNirpex PatelNo ratings yet
- CE - 303 - GE - End Sem-1Document3 pagesCE - 303 - GE - End Sem-1Anudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- CE366 2017-2018 SPRING HW1 QUESTIONS v1.0Document4 pagesCE366 2017-2018 SPRING HW1 QUESTIONS v1.0Bahri AkhanNo ratings yet
- Geo Technical Engineering Ii July 2023Document8 pagesGeo Technical Engineering Ii July 2023Sobha Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Apj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksDocument2 pagesApj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksirshadNo ratings yet
- 2020 10 19SupplementaryCE364CE364 F Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 10 19SupplementaryCE364CE364 F Ktu QbankRoshiya FathimaNo ratings yet
- CT II QP Sep'11Document4 pagesCT II QP Sep'11Rajha RajeswaranNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics IIDocument2 pagesSoil Mechanics IIqwfqefwqefgefqeNo ratings yet
- UI-004 - Design Calculation ReportDocument34 pagesUI-004 - Design Calculation ReportwesleynjNo ratings yet
- r5410101 Foundation EngineeringDocument4 pagesr5410101 Foundation EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper (CBCS Scheme)Document2 pagesModel Question Paper (CBCS Scheme)Veeresh PattarNo ratings yet
- 15CV53Document2 pages15CV53Vijay KulkarniNo ratings yet
- CE - 321: Foundation Engineering 6 Semester (Spring-2021) : Final Term Paper ExamDocument2 pagesCE - 321: Foundation Engineering 6 Semester (Spring-2021) : Final Term Paper ExamBilal SaifNo ratings yet
- Geotech - 2Document2 pagesGeotech - 2Sanket AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering and SurveyingDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering and SurveyingWataNo ratings yet
- ENG1001 Civil Set 1Document4 pagesENG1001 Civil Set 1Christopher AngNo ratings yet
- Nov2017 Re-Exam FE 100%Document2 pagesNov2017 Re-Exam FE 100%kirtiNo ratings yet
- Ce 342 Tutorial 2Document5 pagesCe 342 Tutorial 2Deus IrechoNo ratings yet
- Geo Tech EngineeringDocument1 pageGeo Tech EngineeringVishal yadavNo ratings yet
- Ce 441 Foundation Engineering - 2021 Fall Homework 1Document2 pagesCe 441 Foundation Engineering - 2021 Fall Homework 1Yusuf DuranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsNametso MoatsheNo ratings yet
- FE Imp QuestionsDocument8 pagesFE Imp QuestionsYeswanth PaluriNo ratings yet
- GT 2 QBDocument6 pagesGT 2 QBPrajakta ShindeNo ratings yet
- CIVE09016 Geotechical Engineering 3 - December 2016Document9 pagesCIVE09016 Geotechical Engineering 3 - December 2016Praise Okoro ResLifeNo ratings yet
- 0753.PLAXIS - 2D - CEV22.02 - Tutorial - 4 - Settlements Due To Tunnel ConstructionDocument16 pages0753.PLAXIS - 2D - CEV22.02 - Tutorial - 4 - Settlements Due To Tunnel ConstructionErolNo ratings yet
- TR 335 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTR 335 Tutorial 1Deus IrechoNo ratings yet
- Questions FinalDocument9 pagesQuestions FinalRavindra JagadaleNo ratings yet
- r7410101 Geotechnical Engineering IIDocument4 pagesr7410101 Geotechnical Engineering IISiva SankarNo ratings yet
- M. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesM. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil Engineeringjay shankar prabhatNo ratings yet
- CE407S1 ESem Question Paper Nov 28 2020Document4 pagesCE407S1 ESem Question Paper Nov 28 2020SonuNo ratings yet
- University of ExaminationDocument4 pagesUniversity of Examinationforplayinggame120No ratings yet
- Foundation EnggDocument2 pagesFoundation EnggS M Mozakkir QuadriNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Elevated TanksDocument64 pagesSeismic Design of Elevated TanksMahadev Sastry100% (3)
- Ecv 403: Foundation Engineering 1-Year 2020/2021 Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesEcv 403: Foundation Engineering 1-Year 2020/2021 Tutorial QuestionsEdwin KaranjqNo ratings yet
- Flexible Glass: Enabling Thin, Lightweight, and Flexible ElectronicsFrom EverandFlexible Glass: Enabling Thin, Lightweight, and Flexible ElectronicsSean M. GarnerNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AluCo-Wood Profiles & AccessoriesDocument4 pagesAluCo-Wood Profiles & AccessoriesAlif AliffahNo ratings yet
- Design Basis:: 1a. MATERIAL: Sectional Steel Fy 240 N/mm2Document3 pagesDesign Basis:: 1a. MATERIAL: Sectional Steel Fy 240 N/mm2Feroz Khan PatthanNo ratings yet
- Restrained Joints For Iron Pipe LinesDocument34 pagesRestrained Joints For Iron Pipe LinesAlberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: SwensonDocument12 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Swensonkaspersky2009No ratings yet
- Rockwool Fire Barrier PDFDocument8 pagesRockwool Fire Barrier PDFcodefinderNo ratings yet
- TLE-EIM9 - Q4M3WEEK3 - OKDocument26 pagesTLE-EIM9 - Q4M3WEEK3 - OKglazykimjorquiaNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Jan 2023Document2 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Jan 2023ssmbsuperstar022No ratings yet
- Ytg A 0616Document108 pagesYtg A 0616Mechanical PowerNo ratings yet
- Detail of Septic Tank: Plan SectionDocument1 pageDetail of Septic Tank: Plan Sectionar. berna quiambaoNo ratings yet
- Asbestos Management ProcedureDocument6 pagesAsbestos Management Procedureh4rajukuNo ratings yet
- Plate No. I. Design of A One-Way SlabDocument11 pagesPlate No. I. Design of A One-Way Slabdela rosaNo ratings yet
- Design Strategies For Hot Dry ClimateDocument9 pagesDesign Strategies For Hot Dry ClimatemariyaNo ratings yet
- 2008 ASPE Plumbing System Spec GuideDocument31 pages2008 ASPE Plumbing System Spec GuidePao Hwa Yu0% (1)
- Classroom AcousticsDocument21 pagesClassroom AcousticsSham Salonga Pascual100% (1)
- Stormwater System Management: Best Practices ManualDocument35 pagesStormwater System Management: Best Practices ManualErnest NavarroNo ratings yet
- 4 3 1Document3 pages4 3 1rahulmnm007No ratings yet
- Thermal Management of Power ElectronicsDocument6 pagesThermal Management of Power Electronicsh4n5_chr1sNo ratings yet
- PWHT ProceduresDocument15 pagesPWHT Proceduresmd quasid rabbaniNo ratings yet
- Foul Sewer Design ReportDocument7 pagesFoul Sewer Design ReportmeenhonNo ratings yet
- Is List For Plastic PipesDocument4 pagesIs List For Plastic PipesSunil Devdutt ThakoreNo ratings yet
- How2 Flat SlabsDocument8 pagesHow2 Flat SlabsTim DanNo ratings yet
- Soak-Pit: Floor LatrineDocument3 pagesSoak-Pit: Floor LatrineAbijithNo ratings yet
- Metal Weather Proof SocketDocument5 pagesMetal Weather Proof SocketIbrahim SNo ratings yet
- Cemento Weld On 724Document2 pagesCemento Weld On 724luis claudio c, vieiraNo ratings yet
- OFC - VILLA Hydraulics - General Catalogue 2016 - 03Document286 pagesOFC - VILLA Hydraulics - General Catalogue 2016 - 03МихаилNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Buckling and Stress Stiffening 1Document9 pagesChapter 10 Buckling and Stress Stiffening 1Quân TrịnhNo ratings yet
- CPVC Fire Sprinkler SystemsDocument55 pagesCPVC Fire Sprinkler SystemsNam NguyenNo ratings yet
- DBSTDocument118 pagesDBSTBihanChathuranga100% (6)
Foundation Engineering
Foundation Engineering
Uploaded by
fitri zohriatunOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Foundation Engineering
Foundation Engineering
Uploaded by
fitri zohriatunCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.
np
method and Terzaghi’s method. The soil properties are
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY unit weight above water table is 18 KN/m3, unit weight
VI SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2003
below water table is 18 KN/m3, unit weight above
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil)
below water table is 20KN/m3, conesion 20 KN/m2 and
SUBJECT: BEG359CI, Foundation Engineering.
internal friction zero. Water table is located 2m below
Full Marks: 80
the ground level. [8]
TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32
Q. [3] [a] What are the various loads to be considered while
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as designing spread foundation? Also explain the factor
far as practicable. affecting footing depth selection. [8]
All questions carry equal marks. The marks allotted for each sub- [b] In what circumstances is a mat foundation more
question is specified along its side. suitable than other shallow foundations? Also describe
Attempt any FIVE questions. the various types of mat foundation. [8]
Q. [4] [a] What are various components of a well foundation?
Q. [1] [a] Why is site investigation important? Describe various Also explain their functions. How well foundation is
stages of site investigation. [8] sunk? [8]
[b] The details of solids retained behind a masonry wall is [b] A concrete pile of diameter 0.3 m is driven into the
given in Fig 1[b]. The block of wall is vertical and ground where the upper layer is 3m thick soft clay and
smooth. Check the stability of the retaining wall the lower layer is stiff clay. The properties of soft clay
against sliding for a factor of safety of 2.0. The unit are unit weight 18 KN/m3, unconfined compressive
weight of the wall is 24.0 kN/m3 and coefficient of base strength 50 kN/m2 and adhesion factor is 0.45. The
friction is 0.65. [8] properties of stiff-clay are unit weight 20 KN/m3,
unconfined compressive strength 150 KN/m2 and
0.5m adhesion factor is 0.9. Determine total length of the pile
if the designed load on pile top is 100KN and factor
γ = 18kN/m3 safety is 3.0. [8]
φ = 30o , C = 0 Q. [5] [a] Describe pile load test. How bearing cap….determined
γ = 20kN/m3 by pile load test?
φ = 0o , C = 10kN/m2 [b] An anchored sheet pile is shown in Fig. 5[b]. Compute
the embedded length of the sheet pile below dredge line
1.5m
assuming free earth support.
Q. [2] [a] What assumptions are made by coulomb while
determining earth pressure theory ………explain how
active earth pressure is determined by coulomb’s wedge
theory. [8]
[b] A rectangular footing size 1m×2m is placed at a depth
of 1.5m below ground level. Calculate safe being
capacity for a factor of safety 3.0, using Skempton’s
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /1
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Figure: it is not clear
Q. [6] [a] What do you mean by bearing capability and net
bearing capability? Derive Terazag ….bearing
capability equation for a strip foundation.
[b] Calculate the earth pressure per unit length against a 6m
high retaining wall when it is pushed towards the
backfill. The soil …………….the wall has unit weight
of 18 KN/m2 above water able and ……KN/m2 below
water table. Take ø = 30o, …..= 25 KN/m2. The backfill
carries a surcharge of 10KN/m2. Also draw earth
pressure diagram. Water table is at depth of 2m below
ground level.
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /2
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Q. [2] [a] What are the assumption in Coulomb’s theory? Briefly
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY compare rankine’s theory and Coulomb’s theory.
VI SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2004
Discuss Culmann’s method for the determining of
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil)
active earth pressure. [8]
SUBJECT: BEG359CI, Foundation Engineering.
y
Full Marks: 80
TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Qu γ = 18kN/m3
φ’= 30o
e=0.1m c’=0
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as 1m
far as practicable.
All questions carry equal marks. The marks allotted for each sub-
question is specified along its side.
Assume necessary data if missing.
Attempt any FIVE questions. 0.1m x
1.5m
Q. [1] [a] Describe about the site investigation with its purposes.
What are distributed and undistributed samples? [8]
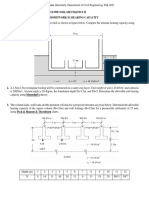
[b] A frictionless wall is shown in the fig. 1[b]. Determine 1m
the active force, Pa and the location of pa after the
tensile crack occurs. Also calculate the passive Q. [3] [a] A concrete pile, 30cm diameter, is driven into a
resistance, pp on the backfill and the location of the medium dense sand (ø’ = 35o, γ = 21 kN/m3, K = 1.0,
resultant passive force. [8] tanδ = 0.70) for a depth of 8m. If the water table is 2m
below the ground surface, estimate the safe load taking
q = 15 kN/m2
a factor of safety of 2.50. Take γw = 10 kN/m3. [8]
[b] Describe various methods for the construction of drilled
..
.......... Q. [4]
piers.
[a] What are different types of shallow foundation?
[8]
...... Explain the procedure for the design of a spread
.. γ = 16.6kN/m3
..............
φ’ = 26o , C’ = 10kN/m2 footing. [8]
6m
[b] The plane of a mat foundation with 9 columns is shown
........ in the Fig. 3[b]. Assume that the mat is rigid, determine
...... the soil pressure distribution. All the columns are of the
size 0.6m ×0.6m. [8]
................
...........
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /3
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
[b] Determine the active earth pressure and the total active
force on the retaining wall shown in the Fig. 6[b] using
400kN 500kN 300kN Rankine’s theory. [8]
y
8m
x 1200kN
x
L=16.6m γ = 16kN/m3
1500kN 2000kN φ’=30
8m c’=0kN/m2
500kN 600kN
400kN
6m 6m
γ = 18kN/m3
B=12.6m φ’=35
c’=0
Q. [5] [a] What is negative skin friction? What is its effect on the
pile? [7]
[b] Determine the depth of embedment ‘d’ for the
cantilever sheet pile shown in the Fig. 5[b]. [9]
γ = 16kN/m3
φ’= 30o
5m
p1
γ = 19kN/m3
d φ ’=0
c’=50kN/m2
p2 p3
Q. [6] [a] What are the assumptions made in the derivation of
Terzaghi’s bearing capacity theory? Write the equation
for the ultimate bearing capacity. [8]
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /4
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY Q. [2] [a] Derive the relation between the horizontal and vertical
VI SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2005
intergrandular pressures for the Rankine’s active state. [8]
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil)
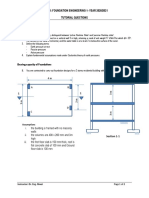
[b] A column foundation fig. 2[b] is 3m×2m plan. Given:
SUBJECT: BEG359CI, Foundation Engineering.
Depth of foundation , Df = 1.5m, angle of internal
Full Marks: 80
friction, ø = 25o, cohesion, c = 50 kN/m2. Using
TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32
general bearing capacity equation and factor of safety
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as equal to 4, determine the net allowable load the
far as practicable. foundation could carry. [8]
All questions carry equal marks. The marks allotted for each sub-
question is specified along its side. 1m γ = 16.8kN/m3
Assume necessary data if missing.
Attempt any FIVE questions. 0.5m
3m*2m γ m = 19.4kN/m3
Q. [1] [a] Kathmandu municipality is planning to construct an
outer ring road in the valley. For the purpose, a detailed Q. [3] [a] Where do you provide a combined footing? Discuss the
soil survey has to be conducted. As a geotechnical procedure for the design of the trapezoidal footing. [8]
engineer, what will be your recommendation regarding [b] The mat has dimension 18m ×30m as shown in fig 3[b].
the types of sample to be collected during subsurface The dead load and live load acting vertically and axially
exploration? What kind of tests you are going to on each column are also shown in the same figure. The
perform with the recommended soil samples in the mat is placed on the saturated clay having a unit weight
laboratory for the design of ring road? [8] of 18.90kN/m3 and cu = 134kN/m2 . If the depth of fond
[b] Details of smooth and vertical retaining walls are dation is equal to 1.50m, determine the factor of safety
shown in fig 1[b]. The horizontal stress in the soil is against bearing capacity failure. [8]
such that it is always less then the vertical stress
through out the height of the retaining wall. Estimate Column DL LL 1 2
the total force per meter acting behind the wall. [8] (kN) (kN)
1 100 60
2 180 120
30m
γ = 20.5kN/m3
φ’=26
3 190 130 4 5 6
5m c’=8kN/m2 4 180 120
Water Table 5 360 200
6 400 240 7 8 9
γ = 18.0kN/m3 7 190 120
3m φ’=38o
c’=0 8 400 250 18m
1m 9 440 300
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /5
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Q. [4] [a] What are the various components of a well foundation
? Describe their uses in detail. [8] Q. [6] [a] Explain what do you mean by soil stabilization?
[b] A group pile in clay is shown in fig. 4[b]. Determine Discuss the various methods of soil stabilization. [8]
the consolidation settlement of the, pile groups. All clay [b] A long footing is placed over a homogeneous soil mass
layers are normally consolidated. Assume suitable data, at some depth. It is assumed that as the load on the
if necessary. [8] footing increases, the failure surface in the soil below
the foundation extends upto the ground surface. By
50 kN/m 2
Pile Cap Size 3m*3m appropriately dividing the failure area into elastic zone,
3m
radial shear zones and Rankine passive shear zones,
0.5m Clay Layer 1
derive the equation that can be used to determine
γ = 18.02kN/m3 bearing capacity of the long footing. [8]
3m e0=0.88
Clay Layer 2 cc=0.35
5m
γ = 18.86kN/m3 Clay Layer 3
e0=0.70
cc=0.2
Q. [5] [a] What do you mean by anchored sheet piled wall?
Explain with neat sketch. Obtained an expression for
the determination of penetration depth of an anchored
sheet pile in sandy soil using free earth support method.
[8]
[b] The section of a 3×4 group pile in a layered saturated
clay is shown in fig. 5[b]. The piles are square in cross-
section (350mm ×350mm). The center to center spacing
of the piles is 890mm. Determine the allowable load
bearing capacity of the pile group. Use factor of safety
equals to 4. [8]
50 kN/m 2
4.5m Cu =50.20kN/m2
13.5m Cu = 85.00kN/m 2
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /6
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
Q. [2] [a] What are the factors that affect the bearing capacity of
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY the soil? What will be the change in the bearing
VI SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2006
capacity of the soil with change in the water table?
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil)
Describe with the help of bearing capacity equation. [8]
SUBJECT: BEG359CI, Foundation Engineering.
[b] How does an active state of earth pressure differ form
Full Marks: 80
its passive state? Derive the theoretical expression for
TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32
the calculation of active and passive lateral earth
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as pressures using Mohr’s envelope. [8]
far as practicable. Q. [3] [a] Describe the design procedure of designing the mat
All questions carry equal marks. The marks allotted for each sub- foundation. [8]
question is specified along its side. [b] A client wants to construct a circular footing of 1m
Assume necessary data if missing. diameters to transfer the load of 1200KN with the
Attempt any FIVE questions. safety factor of 2.5 to soil strata with an angle of
shearing resistance 30oC, cohesion 10KN/m2 and unit
Q. [1] [a] Sketch the longitudinal section of an undisturbed weight of 18kN/m3. Suggest the client what should be
sampling tube and indicate the different parts of the the depth of footing. Take Terzaghi’s bearing capacity
tube. State the necessary requirement of an undisturbed Nc, Nq and Nγ as 37.2, 22.5, 19.7 respectively.
sampling tube. [7] Q. [4] [a] A concrete pile of 0.3m diameter is driven into the
[b] Determine the maximum and minimum pressure under ground where the upper layer is cohesionless sand of
the base of the cantilever retaining wall as shown in 4m thickness and the lower layer is stiff clay. The
figure and also the factor of safety against sliding and friction angle of sand is 32o and the bulk unit weight is
overturning. The appropriate shear strength parameters 19KN/m3. Coefficient of lateral earth pressure (k) is 1.0
for soil are c=0 , ø = 40o. The unit weight of soil and and friction angle between pipe and soil is 0.75 times
concrete are 18KN/m3 and 24 KN/m3 respectively. the friction angle of soil. The unconfined compressive
Take δ = 25o. [9] strength of stiff clay is constant through out the depth,
equal to 120KN/m2 and bulk unit weight is 20KN/m3.
50 kN/m 2 Using the adhesion factor of 0.8 determine the total
0.3m length of pile if the allowable load on the pile is
designed to be 100KN and safety factor is 2.5. The
water table is 1m below the ground surface. [8]
4.45m 0.9m [b] What are the differences between piers and cassions?
0.45m How can the piers be constructed by manual method?
0.45m [8]
Q. [5] [a] ……15m….12m in plan has its base 2m below surface
2.8m of deposit of clay with a unit weight of 16KN/m3. The
unconfined compressive strength of clay is 100kN/m3.
The factor of safety against bearing capacity failure
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /7
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
must be 3.0. What total weight of building plus the
foundation can safely by supported by the raft? [8]
[b] How do you classify the pile foundation on the basis of
(a) materials (b) method of installation (c) load transfer
? Define negative skin friction with its effect on the
piles. [8]
Q. [6] [a] What are the various methods of removing ground
water form construction sites ? Describe three
prominent methods of foundation soil stabilization. [8]
[b] A cantilever sheet pile wall is driven into sand deposit
having friction angle 35o and bulk unit weight of
22KN/m3. Once side of the sheet pile was backfilled to
3m height. The backfill material is cohensionless sand
having friction angle 32o and bulk unit weight of
18KN/m3. Using simplified method determine the
deposit of penetration needed for the sheet pile to retain
backfill. Provide the safety factor of 2.0 for the passive
region. The water table is below the base of the sheet
pile. [8]
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /8
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY Q. [2] [a] What are the assumptions of Rankine earth pressure
VI SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2007
theory? Derive the relation for active earth pressure in
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil)
cohesive soil. [8]
SUBJECT: BEG359CI, Foundation Engineering.
[b] A building owner has planned to construct his house
Full Marks: 80
with framed structure with square columns at a depth of
TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32
1.5m below the ground. If the column has to carry a
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as load of 800KN, determine the size of the footing
far as practicable. required to transfer the load to a soil strata with
All questions carry equal marks. The marks allotted for each sub- cohesion 10KN/m2, angle of internal friction 30o and
question is specified along its side. unit weight of 20KN/m3. Use a factor of safety as 3.
Assume necessary data if missing. Take Terzaghi’s bearing capacity factors Ne, Nq, Nγ
Attempt any FIVE questions. are 37.20, 22.50 and 19.70 respectively. [8]
Q. [3] [a] What is soil stabilization? What are various methods of
Q. [1] [a] What are the objectives of site investigation ? Describe soil stabilization? Describe soil-cement stabilization in
the various stages of site investigation. [8] brief. [8]
[b] The proposed Retaining wall of top width 0.6m and [b] A building has to be supported on a R.C raft foundation
bottom width 4m shown below is to be constructed in of dimensions 12m×18m. The subsoil is clay having
masonary of unit weight 24kN/m3. Determine the average undrained shear strength of 60KN/m2. the
minimum pressure under the base of the wall as shown pressure on soil due to the weight of building and the
in figure and also the factor of safety against sliding, loads that it will carry will be 140KN/m2 at the base of
overturning and bearing. The safe bearing capacity of raft. If the unit weight of the excavated soil is 20kN/m3,
soil is 150KN/m2 and coefficient of base friction = 0.6. at what depth should the bottom of raft be placed to
Assume that water table is at 3m from base of retaining provide a factor of safety of 3 against shear failure? [8]
wall. [8] Q. [4] [a] What are the various components of a well foundation?
Mention the functions of each component with a neat
20 kN/m 2 sketch. [8]
[b] A pile group consists of 9 friction piles of 30cm
diameter and 10m length is driven in clay (Undrained
γ = 16kN/m3 shear strength =100 kN/m2 and γ = 20kN/m3). [8]
3m φ’=30
c’=0
γ 18kN/m3
= The piles are arranged in square pattern and centre to
3m φ’=28
c’=8kN/m2 centre spacing is kept 750mm. Determine the safe load
for the pile group. Take factor of safety = 3.0 and
adhesion factor = 0.60. [8]
Q. [5] [a] Describe the various stages of failure mechanism of
foundation soil. Derive an expression for the ultimate
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /9
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
bearing capacity of a strip footing suggested by
Terzaghi. [8]
[b] A retaining wall is 7m high, with its back face smooth
and vertical. It retains sand with its top surface
horizontal. Using Rankiines’s theory, determine active
earth pressure at the base when the backfill is (a) dry
and (b) submerged, with water table at the surface.
Take γ = 18KN/m3, ø = 30o and γsat = 21 kN/m3. [8]
Q. [6] [a] Describe the pile load test. How bearing capacity is
determined by pile load test? [8]
[b] Determine the depth of embedment for the cantilever
sheet pile shown in the figure. [8]
A
2m Sand
γ = 15kN/m3
φ’=32
WT c’= 0 WT
Sand
3.5m γsat = 19kN/m3
φ’=32
E c’= 0
Clay
D
γ = 19kN/m3
φ’=0o
B c’=50kN/m2
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /10
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
based on the function and material with brief
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY description of any three major types. [8]
VI SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2008
[b] Explain the design method of mat foundation by using
LEVEL : B. E. (Civil)
conventional method.
SUBJECT: BEG359CI, Foundation Engineering.
Q. [4] [a] Write the assumption made by Karl Terzaghi during the
Full Marks: 80
analysis of Bearing Capacity Equation for strip footing. [6]
TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32
[b] Check the stability of RCC Retaining wall supporting
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as cohesionless backfill as shown in below fig. Take ø =
far as practicable. 34o, δ = 25o, γ = 18kN/m3 and allowable bearing
All questions carry equal marks. The marks allotted for each sub- pressure of 500kpa. Unit weight of R.C.C is 25kN/m3.
question is specified along its side. Assume necessary data if missing. [10]
Attempt any FIVE questions. 50 kN/m 2
0.4m
Q. [1] [a] What are the essential requirement of a good
foundation? Write the types of foundation and brief it
with neat sketch. [4+4] 5.6m 2.3m
[b] A Retaining wall of 8.0 m high has a smooth vertical 0.6m
back. It supports a horizontal backfill with angle of 0.6m
internal friction of 35oC, cohesion of 10 kPa. The water
table is at a depth of 3.0m below the surface of backfill. 3.5m
The unit weight of backfill is 17 kN/m3 above the water
table and 19kN/m3 below the water table. The backfill
supports a surcharge of 20kpa. Determine the Q. [5] [a] Write short notes on
magnitude and point of action of active earth pressure. [8] [i] Coffer Dam and its type [ii] Retaining wall.
Q. [2] [a] What are the factors affecting the bearing capacity of [b] In a group of 12 piles each having a diameter of 500mm
the soil? Describe the effect of water table on bearing and 30.0m long. The piles are arranged in 3-rows and
capacity of soil with the help of bearing capacity spaced at 1.25m. Centre to centre. Take unit weith of
equation. [3+5] soil y’ = 11 kN/m3, unconfined compressive strength qu
[b] A foundation to carry a column load of 10000 kN is = 75kpa, angle of internal friction, ø = 0o, adhesion
placed 1.0m below the ground level on uniform sand factor, α = 0.8 and factor of safety, F = 2.5. Determine
having unit weight, γ = 16 kN/m3, angle of internal the safe load carrying capacity of the pile group. [8]
friction, ø = 40o. Take factor of safety of 3.0. Determine Q. [6] [a] What is well foundation? Write types of well
the size of square foundation. Take Nq = 80, Nγ = 100. foundation. Describe the various components (parts) of
[8] the open caisson with neat sketch. [2+2+6]
Q. [3] [a] What are the major differences between pile foundation [b] A 2.5m deep excavation of a trench is carried out in
and pier foundation? Write the types of pile foundation sand is supported by cantilever sheet pile wall. The
water table at both side of the sheet pile wall is found at
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /11
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np
the bottom of excavation. The bulk unit weight of sand
above the water table is 18kN/m3 and below water table
it is 20kN/m3, ø = 35oC, considering a safety factor as
2.0 for the passive resistance, determine required depth
of embedment of the sheet pile. [8]
Downloaded from www.jayaram.com.np /12
You might also like
- List of Industries in and Around ChennaiDocument5 pagesList of Industries in and Around Chennaijayvee75% (4)
- Design of Reinforced Concrete ChamberDocument10 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete ChamberVan BGNo ratings yet
- Tutorials Pad Footing Nta 5 (2012&2013)Document3 pagesTutorials Pad Footing Nta 5 (2012&2013)Host FredyNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering Assignment - 1 Shallow Foundation: Department of Civil EngineeringDocument2 pagesFoundation Engineering Assignment - 1 Shallow Foundation: Department of Civil EngineeringYash MehtaNo ratings yet
- 07a70101 Geotechnical Engineering-IiDocument7 pages07a70101 Geotechnical Engineering-IiSamiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Marks: With: Autumri. S LTL - Ester Suitabl Req:uii D.F,' Properti S.of 1Document2 pagesMarks: With: Autumri. S LTL - Ester Suitabl Req:uii D.F,' Properti S.of 1Suman SahaNo ratings yet
- University of Mauritius Faculty of EngineeringDocument6 pagesUniversity of Mauritius Faculty of EngineeringAvinaash VeeramahNo ratings yet
- Question Paper - GIAN - 19 - ModifiedDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper - GIAN - 19 - Modifiedsayan mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment ECEC-4120 Unit-1 (2021)Document2 pagesHome Assignment ECEC-4120 Unit-1 (2021)Arbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Geotech Engg QuestionsDocument2 pagesGeotech Engg QuestionsYashasviNo ratings yet
- RT32012112019Document2 pagesRT32012112019ruchika sahuNo ratings yet
- Rev PapersDocument3 pagesRev PapersRotich VincentNo ratings yet
- R7410101 Geotechnical Engineering-IIDocument8 pagesR7410101 Geotechnical Engineering-IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Light Weight ConcreteDocument5 pagesComparative Study of Light Weight ConcreteAmulyaRajbharNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIIDocument4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIIElvis MutsvangaNo ratings yet
- Foundation EngineeringDocument2 pagesFoundation EngineeringqwfqefwqefgefqeNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment-1Document1 pageGroup Assignment-1etrimageoffreyNo ratings yet
- Water Table at Depth 3m From Ground Level: Marks CO R.B.T. LevelDocument3 pagesWater Table at Depth 3m From Ground Level: Marks CO R.B.T. LevelRitesh SonarNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Geotechnical Engineering - IiDocument1 pageWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Geotechnical Engineering - IimaheshNo ratings yet
- Soil Geotechnical Engineering - IIDocument5 pagesSoil Geotechnical Engineering - IIabmsd2No ratings yet
- Advanced Foundation Engineering Rr420101Document8 pagesAdvanced Foundation Engineering Rr420101Andronico BintiNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document4 pagesHomework 2Ali AratNo ratings yet
- Test-Foundation Desiga: ConditionsDocument1 pageTest-Foundation Desiga: ConditionsBlessingNo ratings yet
- Cl449 - Dos-II - Unit Test - I - Question PaperDocument2 pagesCl449 - Dos-II - Unit Test - I - Question PaperNirpex PatelNo ratings yet
- CE - 303 - GE - End Sem-1Document3 pagesCE - 303 - GE - End Sem-1Anudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- CE366 2017-2018 SPRING HW1 QUESTIONS v1.0Document4 pagesCE366 2017-2018 SPRING HW1 QUESTIONS v1.0Bahri AkhanNo ratings yet
- Geo Technical Engineering Ii July 2023Document8 pagesGeo Technical Engineering Ii July 2023Sobha Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Apj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksDocument2 pagesApj Abdul Kalam Technological University: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksirshadNo ratings yet
- 2020 10 19SupplementaryCE364CE364 F Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 10 19SupplementaryCE364CE364 F Ktu QbankRoshiya FathimaNo ratings yet
- CT II QP Sep'11Document4 pagesCT II QP Sep'11Rajha RajeswaranNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics IIDocument2 pagesSoil Mechanics IIqwfqefwqefgefqeNo ratings yet
- UI-004 - Design Calculation ReportDocument34 pagesUI-004 - Design Calculation ReportwesleynjNo ratings yet
- r5410101 Foundation EngineeringDocument4 pagesr5410101 Foundation EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper (CBCS Scheme)Document2 pagesModel Question Paper (CBCS Scheme)Veeresh PattarNo ratings yet
- 15CV53Document2 pages15CV53Vijay KulkarniNo ratings yet
- CE - 321: Foundation Engineering 6 Semester (Spring-2021) : Final Term Paper ExamDocument2 pagesCE - 321: Foundation Engineering 6 Semester (Spring-2021) : Final Term Paper ExamBilal SaifNo ratings yet
- Geotech - 2Document2 pagesGeotech - 2Sanket AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering and SurveyingDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering and SurveyingWataNo ratings yet
- ENG1001 Civil Set 1Document4 pagesENG1001 Civil Set 1Christopher AngNo ratings yet
- Nov2017 Re-Exam FE 100%Document2 pagesNov2017 Re-Exam FE 100%kirtiNo ratings yet
- Ce 342 Tutorial 2Document5 pagesCe 342 Tutorial 2Deus IrechoNo ratings yet
- Geo Tech EngineeringDocument1 pageGeo Tech EngineeringVishal yadavNo ratings yet
- Ce 441 Foundation Engineering - 2021 Fall Homework 1Document2 pagesCe 441 Foundation Engineering - 2021 Fall Homework 1Yusuf DuranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsNametso MoatsheNo ratings yet
- FE Imp QuestionsDocument8 pagesFE Imp QuestionsYeswanth PaluriNo ratings yet
- GT 2 QBDocument6 pagesGT 2 QBPrajakta ShindeNo ratings yet
- CIVE09016 Geotechical Engineering 3 - December 2016Document9 pagesCIVE09016 Geotechical Engineering 3 - December 2016Praise Okoro ResLifeNo ratings yet
- 0753.PLAXIS - 2D - CEV22.02 - Tutorial - 4 - Settlements Due To Tunnel ConstructionDocument16 pages0753.PLAXIS - 2D - CEV22.02 - Tutorial - 4 - Settlements Due To Tunnel ConstructionErolNo ratings yet
- TR 335 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTR 335 Tutorial 1Deus IrechoNo ratings yet
- Questions FinalDocument9 pagesQuestions FinalRavindra JagadaleNo ratings yet
- r7410101 Geotechnical Engineering IIDocument4 pagesr7410101 Geotechnical Engineering IISiva SankarNo ratings yet
- M. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesM. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil Engineeringjay shankar prabhatNo ratings yet
- CE407S1 ESem Question Paper Nov 28 2020Document4 pagesCE407S1 ESem Question Paper Nov 28 2020SonuNo ratings yet
- University of ExaminationDocument4 pagesUniversity of Examinationforplayinggame120No ratings yet
- Foundation EnggDocument2 pagesFoundation EnggS M Mozakkir QuadriNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Elevated TanksDocument64 pagesSeismic Design of Elevated TanksMahadev Sastry100% (3)
- Ecv 403: Foundation Engineering 1-Year 2020/2021 Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesEcv 403: Foundation Engineering 1-Year 2020/2021 Tutorial QuestionsEdwin KaranjqNo ratings yet
- Flexible Glass: Enabling Thin, Lightweight, and Flexible ElectronicsFrom EverandFlexible Glass: Enabling Thin, Lightweight, and Flexible ElectronicsSean M. GarnerNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AluCo-Wood Profiles & AccessoriesDocument4 pagesAluCo-Wood Profiles & AccessoriesAlif AliffahNo ratings yet
- Design Basis:: 1a. MATERIAL: Sectional Steel Fy 240 N/mm2Document3 pagesDesign Basis:: 1a. MATERIAL: Sectional Steel Fy 240 N/mm2Feroz Khan PatthanNo ratings yet
- Restrained Joints For Iron Pipe LinesDocument34 pagesRestrained Joints For Iron Pipe LinesAlberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: SwensonDocument12 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Swensonkaspersky2009No ratings yet
- Rockwool Fire Barrier PDFDocument8 pagesRockwool Fire Barrier PDFcodefinderNo ratings yet
- TLE-EIM9 - Q4M3WEEK3 - OKDocument26 pagesTLE-EIM9 - Q4M3WEEK3 - OKglazykimjorquiaNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Jan 2023Document2 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Jan 2023ssmbsuperstar022No ratings yet
- Ytg A 0616Document108 pagesYtg A 0616Mechanical PowerNo ratings yet
- Detail of Septic Tank: Plan SectionDocument1 pageDetail of Septic Tank: Plan Sectionar. berna quiambaoNo ratings yet
- Asbestos Management ProcedureDocument6 pagesAsbestos Management Procedureh4rajukuNo ratings yet
- Plate No. I. Design of A One-Way SlabDocument11 pagesPlate No. I. Design of A One-Way Slabdela rosaNo ratings yet
- Design Strategies For Hot Dry ClimateDocument9 pagesDesign Strategies For Hot Dry ClimatemariyaNo ratings yet
- 2008 ASPE Plumbing System Spec GuideDocument31 pages2008 ASPE Plumbing System Spec GuidePao Hwa Yu0% (1)
- Classroom AcousticsDocument21 pagesClassroom AcousticsSham Salonga Pascual100% (1)
- Stormwater System Management: Best Practices ManualDocument35 pagesStormwater System Management: Best Practices ManualErnest NavarroNo ratings yet
- 4 3 1Document3 pages4 3 1rahulmnm007No ratings yet
- Thermal Management of Power ElectronicsDocument6 pagesThermal Management of Power Electronicsh4n5_chr1sNo ratings yet
- PWHT ProceduresDocument15 pagesPWHT Proceduresmd quasid rabbaniNo ratings yet
- Foul Sewer Design ReportDocument7 pagesFoul Sewer Design ReportmeenhonNo ratings yet
- Is List For Plastic PipesDocument4 pagesIs List For Plastic PipesSunil Devdutt ThakoreNo ratings yet
- How2 Flat SlabsDocument8 pagesHow2 Flat SlabsTim DanNo ratings yet
- Soak-Pit: Floor LatrineDocument3 pagesSoak-Pit: Floor LatrineAbijithNo ratings yet
- Metal Weather Proof SocketDocument5 pagesMetal Weather Proof SocketIbrahim SNo ratings yet
- Cemento Weld On 724Document2 pagesCemento Weld On 724luis claudio c, vieiraNo ratings yet
- OFC - VILLA Hydraulics - General Catalogue 2016 - 03Document286 pagesOFC - VILLA Hydraulics - General Catalogue 2016 - 03МихаилNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Buckling and Stress Stiffening 1Document9 pagesChapter 10 Buckling and Stress Stiffening 1Quân TrịnhNo ratings yet
- CPVC Fire Sprinkler SystemsDocument55 pagesCPVC Fire Sprinkler SystemsNam NguyenNo ratings yet
- DBSTDocument118 pagesDBSTBihanChathuranga100% (6)