Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C - 11 - Exp - 1 - V.C. - To Find Volume of Cylinder
C - 11 - Exp - 1 - V.C. - To Find Volume of Cylinder
Uploaded by
Mudit KaushikCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- AP - Lab 01 - Measurement Using Vernier CalliperDocument4 pagesAP - Lab 01 - Measurement Using Vernier Callipersaliha50% (4)
- Matriculation Physics Experiment 2 (Malaysia)Document5 pagesMatriculation Physics Experiment 2 (Malaysia)Muhammad Syahir Asyraf63% (8)
- Physics PracticalsDocument86 pagesPhysics PracticalsGvns Reddy100% (1)
- Class 11 ExperimentsDocument25 pagesClass 11 ExperimentsSoham Nag100% (1)
- Applied Physics Lab ManualDocument28 pagesApplied Physics Lab ManualJulie MaxNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Objective: Vernier Callipers, A Spherical Body (It Can Be A Pendulum Bob), A Beaker or A CalorimeterDocument2 pagesExperiment No. 1 Objective: Vernier Callipers, A Spherical Body (It Can Be A Pendulum Bob), A Beaker or A CalorimeterShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Experiments (1 - 4)Document8 pagesExperiments (1 - 4)Aditya YadavNo ratings yet
- The Theory: Das2102 Applied Science Lab - (Iind - Sem) Experiment No. 1. AimDocument6 pagesThe Theory: Das2102 Applied Science Lab - (Iind - Sem) Experiment No. 1. AimKashish shrivastwaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi - Practicals - R - RecDocument26 pagesClass Xi - Practicals - R - RecDivyashekogNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Practicals - Expts 1&2Document7 pagesClass 11 Practicals - Expts 1&2ARAVIND SANTHOSHNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Physics - Practical - Booklet - 2022-23Document40 pagesGR 11 Physics - Practical - Booklet - 2022-23Hunter OfficialNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document5 pagesExperiment 3bhagwatsunil100No ratings yet
- Class - 11 Physics PracticalDocument14 pagesClass - 11 Physics PracticalAvenger Gaming ZoneNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1: Aim: To Determine The Least Count of The Vernier Callipers and Measure The Length and Diameter of A Small Cylinder. ApparatusDocument7 pagesExperiment - 1: Aim: To Determine The Least Count of The Vernier Callipers and Measure The Length and Diameter of A Small Cylinder. Apparatusunknown 1593No ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document2 pagesExperiment 1ISMART STUDY POINTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2bhagwatsunil100No ratings yet
- Practical, Class - IxDocument10 pagesPractical, Class - Ixunknown 1593No ratings yet
- Class Xi - Practicals 2024Document24 pagesClass Xi - Practicals 2024pillisathwik2No ratings yet
- Experiment 1 (I) : To Measure Diameter of A Small Cylindrical Bod Using Vernier CallipersDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 (I) : To Measure Diameter of A Small Cylindrical Bod Using Vernier CallipersBaichitra MondalNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 VernierDocument13 pagesExpt 1 VernierIbrahim Ali RizviNo ratings yet
- Practical 123Document16 pagesPractical 123tbf06720No ratings yet
- Physics - Practical Record Writing - Class XI-2024Document35 pagesPhysics - Practical Record Writing - Class XI-2024Soha TamkeenNo ratings yet
- Vernier Scale Reading Vernier Division Coinciding With Main Scale Division × Least Count (In CM) Total Reading Main Scale Reading + Vernier Scale Reading I.e., Diameter (In CM)Document30 pagesVernier Scale Reading Vernier Division Coinciding With Main Scale Division × Least Count (In CM) Total Reading Main Scale Reading + Vernier Scale Reading I.e., Diameter (In CM)Cdt varun rana 44No ratings yet
- Vernier CalliperDocument5 pagesVernier CalliperWahyu FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- MBD 2 SO84 P6 XRQ WF V1 ApnDocument3 pagesMBD 2 SO84 P6 XRQ WF V1 ApnAneeshNo ratings yet
- COMMEDIA - Labmanual XIPHY24 25 v1 - 20240611220307Document64 pagesCOMMEDIA - Labmanual XIPHY24 25 v1 - 20240611220307Balaji MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Computer Laboratory ManualDocument34 pagesApplied Physics: Computer Laboratory ManualYousha AbbasNo ratings yet
- 27092023060932VC-27 Practicals Class 9 With ReadingDocument7 pages27092023060932VC-27 Practicals Class 9 With ReadingatharvNo ratings yet
- XI Physics ManualDocument10 pagesXI Physics Manualkiranpatel0100% (3)
- Physics Practical Manual Class Xi-1Document32 pagesPhysics Practical Manual Class Xi-1Debajyoti SunariNo ratings yet
- Class - 11 Physics PracticalDocument5 pagesClass - 11 Physics PracticalAhana PoddarNo ratings yet
- Vernier CalipersDocument6 pagesVernier CalipersRani JahnaviNo ratings yet
- Practical Experiments 1 To 7Document9 pagesPractical Experiments 1 To 7Moses Samuel SukdularyNo ratings yet
- Newtons Ring Experiment1Document4 pagesNewtons Ring Experiment1Mahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab - 1: Ma'am FaizaDocument5 pagesPhysics Lab - 1: Ma'am FaizaJamshaid khanNo ratings yet
- Vernier Calipers-2Document4 pagesVernier Calipers-2warriorNo ratings yet
- Fybsc ManualDocument46 pagesFybsc ManualnNo ratings yet
- Vernier - ActivityDocument9 pagesVernier - ActivityCherry LimNo ratings yet
- Lab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperDocument3 pagesLab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- XI Physics Lab. Work 2023-24 Only For CBSEDocument13 pagesXI Physics Lab. Work 2023-24 Only For CBSEMohammed RizwanNo ratings yet
- Grade Xi Physics Manual-22-23Document18 pagesGrade Xi Physics Manual-22-23Poop MasterNo ratings yet
- VernierDocument8 pagesVernierMophato KhachanaNo ratings yet
- Ekya Itpl Lab ManualDocument4 pagesEkya Itpl Lab ManualKriday JangraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: PhysicsDocument76 pagesLaboratory Manual: PhysicsMURUGAN SUBRAMANIANNo ratings yet
- Lab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperDocument4 pagesLab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- BASIC PHYSICS G-2 Practical Manual FinalDocument27 pagesBASIC PHYSICS G-2 Practical Manual FinalPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vernier Caliper FinalDocument7 pagesVernier Caliper FinalRajesh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Class 9Document6 pagesPhysics Practical Class 9shagufta yaseenNo ratings yet
- Physics Manual XIDocument23 pagesPhysics Manual XIAnonymous ExAwm00UPNo ratings yet
- Expt-PH-OP-02 Newton - S Ring - OdtDocument3 pagesExpt-PH-OP-02 Newton - S Ring - OdtSnehasishNo ratings yet
- PHY 107 Experiment 1Document6 pagesPHY 107 Experiment 1Aisha AwaisuNo ratings yet
- 1 PUC Manual-17Document22 pages1 PUC Manual-17shyla100% (1)
- Physics - Practical Record Writing - Class XIDocument83 pagesPhysics - Practical Record Writing - Class XISara Wolf100% (1)
- Vernier Calipers-I-BCJDocument2 pagesVernier Calipers-I-BCJtrail7488No ratings yet
- 1.1micrometer Screw Gauge: Pitch of The Screw Totalnumber of Divisions On Thecircular ScaleDocument3 pages1.1micrometer Screw Gauge: Pitch of The Screw Totalnumber of Divisions On Thecircular ScaleShairryal AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Grade - 11 - Study Material - Practical Exam - 23-24Document17 pagesGrade - 11 - Study Material - Practical Exam - 23-24monishchess2468No ratings yet
- 9physics Practical - (2020-2021)Document14 pages9physics Practical - (2020-2021)chaitusangaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
C - 11 - Exp - 1 - V.C. - To Find Volume of Cylinder
C - 11 - Exp - 1 - V.C. - To Find Volume of Cylinder
Uploaded by
Mudit KaushikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C - 11 - Exp - 1 - V.C. - To Find Volume of Cylinder
C - 11 - Exp - 1 - V.C. - To Find Volume of Cylinder
Uploaded by
Mudit KaushikCopyright:
Available Formats
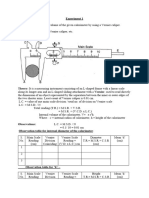
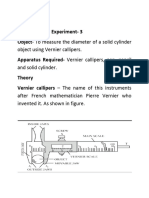
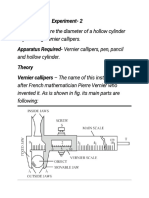
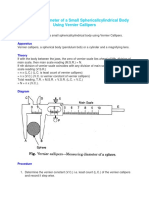
Experiment- 1
Object-
To measure the internal diameter and depth of a given beaker by vernier calliper and hence find its
volume.
Apparatus-
Vernier calliper, a spherical body (pendulum bob) or a cylindrical rod, beaker.
Theory-
Volume of a cylindrical rod =
Where r is the radius and l is the length of the rod.
One main scale division = 1 mm
One vernier scale division = 0.9 mm
V.C. = 1MSD – 1VSD = (1 – 0.9)mm = 0.1mm = 0.01cm
Observations –
- Least count of vernier calliper = 0.01cm
- Zero correction = Zero
Observation Table –
1. Observation table for depth
S.No. M .S. R.(cm) V. S. R. (cm) Total reading Average
(x) n n x L. C.=y (x + y) (cm) reading (cm)
1
2
3
2. Observation table for internal diameter-
S.No. M .S. R.(cm) V. S. R. (cm) Total reading Average
(x) n n x L. C.=y (x + y) (cm) reading (cm)
1
2
3
Calculation –
1. Average depth = = ………cm
2. Average diameter = = …….cm
3. Radius = = ………..cm
4. Volume of beaker = = ………….cm3
Result –
Volume of the given cylindrical beaker = ………… cm3
Precautions-
1. Oil the vernier if its motion is not smooth.
2. The zero error should be noted carefully with sign and taken into account.
3. The jaws should not be pressed too hard.
Source of Error –
1. None of the vernier divisions may be exactly coincident.
2. Vernier jaws may not be at right angle to main scale.
3. The vernier scale may be loose.
You might also like
- AP - Lab 01 - Measurement Using Vernier CalliperDocument4 pagesAP - Lab 01 - Measurement Using Vernier Callipersaliha50% (4)
- Matriculation Physics Experiment 2 (Malaysia)Document5 pagesMatriculation Physics Experiment 2 (Malaysia)Muhammad Syahir Asyraf63% (8)
- Physics PracticalsDocument86 pagesPhysics PracticalsGvns Reddy100% (1)
- Class 11 ExperimentsDocument25 pagesClass 11 ExperimentsSoham Nag100% (1)
- Applied Physics Lab ManualDocument28 pagesApplied Physics Lab ManualJulie MaxNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Objective: Vernier Callipers, A Spherical Body (It Can Be A Pendulum Bob), A Beaker or A CalorimeterDocument2 pagesExperiment No. 1 Objective: Vernier Callipers, A Spherical Body (It Can Be A Pendulum Bob), A Beaker or A CalorimeterShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Experiments (1 - 4)Document8 pagesExperiments (1 - 4)Aditya YadavNo ratings yet
- The Theory: Das2102 Applied Science Lab - (Iind - Sem) Experiment No. 1. AimDocument6 pagesThe Theory: Das2102 Applied Science Lab - (Iind - Sem) Experiment No. 1. AimKashish shrivastwaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi - Practicals - R - RecDocument26 pagesClass Xi - Practicals - R - RecDivyashekogNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Practicals - Expts 1&2Document7 pagesClass 11 Practicals - Expts 1&2ARAVIND SANTHOSHNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Physics - Practical - Booklet - 2022-23Document40 pagesGR 11 Physics - Practical - Booklet - 2022-23Hunter OfficialNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document5 pagesExperiment 3bhagwatsunil100No ratings yet
- Class - 11 Physics PracticalDocument14 pagesClass - 11 Physics PracticalAvenger Gaming ZoneNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1: Aim: To Determine The Least Count of The Vernier Callipers and Measure The Length and Diameter of A Small Cylinder. ApparatusDocument7 pagesExperiment - 1: Aim: To Determine The Least Count of The Vernier Callipers and Measure The Length and Diameter of A Small Cylinder. Apparatusunknown 1593No ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document2 pagesExperiment 1ISMART STUDY POINTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2bhagwatsunil100No ratings yet
- Practical, Class - IxDocument10 pagesPractical, Class - Ixunknown 1593No ratings yet
- Class Xi - Practicals 2024Document24 pagesClass Xi - Practicals 2024pillisathwik2No ratings yet
- Experiment 1 (I) : To Measure Diameter of A Small Cylindrical Bod Using Vernier CallipersDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 (I) : To Measure Diameter of A Small Cylindrical Bod Using Vernier CallipersBaichitra MondalNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 VernierDocument13 pagesExpt 1 VernierIbrahim Ali RizviNo ratings yet
- Practical 123Document16 pagesPractical 123tbf06720No ratings yet
- Physics - Practical Record Writing - Class XI-2024Document35 pagesPhysics - Practical Record Writing - Class XI-2024Soha TamkeenNo ratings yet
- Vernier Scale Reading Vernier Division Coinciding With Main Scale Division × Least Count (In CM) Total Reading Main Scale Reading + Vernier Scale Reading I.e., Diameter (In CM)Document30 pagesVernier Scale Reading Vernier Division Coinciding With Main Scale Division × Least Count (In CM) Total Reading Main Scale Reading + Vernier Scale Reading I.e., Diameter (In CM)Cdt varun rana 44No ratings yet
- Vernier CalliperDocument5 pagesVernier CalliperWahyu FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- MBD 2 SO84 P6 XRQ WF V1 ApnDocument3 pagesMBD 2 SO84 P6 XRQ WF V1 ApnAneeshNo ratings yet
- COMMEDIA - Labmanual XIPHY24 25 v1 - 20240611220307Document64 pagesCOMMEDIA - Labmanual XIPHY24 25 v1 - 20240611220307Balaji MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Computer Laboratory ManualDocument34 pagesApplied Physics: Computer Laboratory ManualYousha AbbasNo ratings yet
- 27092023060932VC-27 Practicals Class 9 With ReadingDocument7 pages27092023060932VC-27 Practicals Class 9 With ReadingatharvNo ratings yet
- XI Physics ManualDocument10 pagesXI Physics Manualkiranpatel0100% (3)
- Physics Practical Manual Class Xi-1Document32 pagesPhysics Practical Manual Class Xi-1Debajyoti SunariNo ratings yet
- Class - 11 Physics PracticalDocument5 pagesClass - 11 Physics PracticalAhana PoddarNo ratings yet
- Vernier CalipersDocument6 pagesVernier CalipersRani JahnaviNo ratings yet
- Practical Experiments 1 To 7Document9 pagesPractical Experiments 1 To 7Moses Samuel SukdularyNo ratings yet
- Newtons Ring Experiment1Document4 pagesNewtons Ring Experiment1Mahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab - 1: Ma'am FaizaDocument5 pagesPhysics Lab - 1: Ma'am FaizaJamshaid khanNo ratings yet
- Vernier Calipers-2Document4 pagesVernier Calipers-2warriorNo ratings yet
- Fybsc ManualDocument46 pagesFybsc ManualnNo ratings yet
- Vernier - ActivityDocument9 pagesVernier - ActivityCherry LimNo ratings yet
- Lab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperDocument3 pagesLab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- XI Physics Lab. Work 2023-24 Only For CBSEDocument13 pagesXI Physics Lab. Work 2023-24 Only For CBSEMohammed RizwanNo ratings yet
- Grade Xi Physics Manual-22-23Document18 pagesGrade Xi Physics Manual-22-23Poop MasterNo ratings yet
- VernierDocument8 pagesVernierMophato KhachanaNo ratings yet
- Ekya Itpl Lab ManualDocument4 pagesEkya Itpl Lab ManualKriday JangraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: PhysicsDocument76 pagesLaboratory Manual: PhysicsMURUGAN SUBRAMANIANNo ratings yet
- Lab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperDocument4 pagesLab 2, 3 Vernier CaliperWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- BASIC PHYSICS G-2 Practical Manual FinalDocument27 pagesBASIC PHYSICS G-2 Practical Manual FinalPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vernier Caliper FinalDocument7 pagesVernier Caliper FinalRajesh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Class 9Document6 pagesPhysics Practical Class 9shagufta yaseenNo ratings yet
- Physics Manual XIDocument23 pagesPhysics Manual XIAnonymous ExAwm00UPNo ratings yet
- Expt-PH-OP-02 Newton - S Ring - OdtDocument3 pagesExpt-PH-OP-02 Newton - S Ring - OdtSnehasishNo ratings yet
- PHY 107 Experiment 1Document6 pagesPHY 107 Experiment 1Aisha AwaisuNo ratings yet
- 1 PUC Manual-17Document22 pages1 PUC Manual-17shyla100% (1)
- Physics - Practical Record Writing - Class XIDocument83 pagesPhysics - Practical Record Writing - Class XISara Wolf100% (1)
- Vernier Calipers-I-BCJDocument2 pagesVernier Calipers-I-BCJtrail7488No ratings yet
- 1.1micrometer Screw Gauge: Pitch of The Screw Totalnumber of Divisions On Thecircular ScaleDocument3 pages1.1micrometer Screw Gauge: Pitch of The Screw Totalnumber of Divisions On Thecircular ScaleShairryal AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Grade - 11 - Study Material - Practical Exam - 23-24Document17 pagesGrade - 11 - Study Material - Practical Exam - 23-24monishchess2468No ratings yet
- 9physics Practical - (2020-2021)Document14 pages9physics Practical - (2020-2021)chaitusangaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet