Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tracheoesophageal
Tracheoesophageal
Uploaded by
Luigi GeduqueOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tracheoesophageal
Tracheoesophageal
Uploaded by
Luigi GeduqueCopyright:
Available Formats
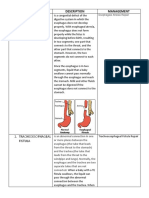
Tracheoesophageal allowed to dry out and crack
Atresia and Fistula Exposure of intestine to air also causes a rapid
loss of body heat
Between weeks 4 & 8 of intrauterine life, the
groove develops into larynx, trachea and Therefore immediately place the baby in a
beginning lung tissue. warmed incubator
A number of anomalies may occur if trachea
and esophagus are affected by some teratogen Do not leave infants under a radiant heat source
that does not allow the two organs to separate because this will quickly dry the exposed bowel
but remain connected
If a radiopaque catheter is used, it can be Assessment
demonstrated coiled in the blind end of the
esophagus on x ray It may be revealed by an elevated MSAFP
A newborn who has so much mucus in the examination during pregnancy
mouth that he or she appears to be blowing
bubbles If not, the presence of Omphalocele is obvious
The condition can be diagnosed with certainty if on inspection at birth
a catheter cannot be passed through the
esophagus to the stomach or the stomach When it is identified in utero, Cesarean birth may
contents cannot be aspirated be performed to protect the exposed intestine
Use of a firm catheter is necessary because a
soft one will curl in a blind end esophagus and Be sure to document the Omphalocele general
appear to have passed appearance and its size in centimeters at
birth
To keep the sac moist, cover it with either sterile
Therapeutic Management saline-soaked gauze or a sterile plastic bowel
bag until surgery
Emergency surgery for the infant with
tracheoesophageal fistula is essential to prevent Because of the large amount of exposed
the development of pneumonia from leakage intestinal surface, the saline used must be at
of stomach secretions into thE lungs or body temperature to prevent lowering body
dehydration or an electrolyte imbalance from temperature
lack of oral intake
A nasogastric tube is inserted at birth to prevent
Antibiotics may be prescribed to help prevent intestinal distention, which would enlarge the
infection bowel lumen, making it even more difficult to
replace
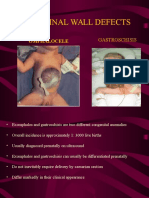
Omphalocele
Don't feed the infant orally or allow him or her
Is a protrusion of abdominal contents through to suck on a pacifier until the bowel repair is
the abdominal wall at the point of junction of the complete
umbilical cord and abdomen
Observe infants carefully for signs of
The herniated organs are usually the intestines, obstruction (abdominal distention,
but they may include stomach and liver constipation, diarrhea or vomiting)when they
begin oral feedings
They are usually covered and contained by a
thin transparent layer of peritoneum
GASTROSCHISIS
This condition occurs because at Is a condition similar to Omphalocele, except
approximately weeks 6 to 8 of intrauterine that the abdominal wall disorder is a distance
life, the fetal abdominal contents, growing faster from the umbilicus and abdominal organs
than the fetal abdomen, are extruded from the are not contained by peritoneal membrane
abdomen into the base of the umbilical cord but rather spill freely from the abdomen
At 7 to 10 weeks, when the abdomen has Also, a greater amount of intestinal contents
enlarged sufficiently, the intestine returns to tends to herniate, increasing the potential for
the abdomen Volvulus and obstruction
Omphalocele occurs when the abdominal The surgical procedure is the same as that for
contents fail to return in the usual way Omphalocele
Therapeutic Management Children with Gastric (soften have decreased
bowel mobility, and even after surgical correction
they may have difficulty with absorption of
Most infants will have immediate surgery to
nutrients and passage of stool
replace the bowel before the this peritoneal
membrane surrounding is ruptures or becomes
infected DOWN SYNDROME
If the Omphalocele large, infants may be The most common chromosomal abnormality
prescribed a topical application of a solution Seen as frequently as 1 in 800 livebirths
such as Silver Sulfadiazine to prevent infection
of the sac, followed by delayed surgical closure Most frequently in the pregnancies of women
who are over 35 years of age. The incidence is
Before Surgery high I in 100 live births
It is important that the lining of the peritoneum
covering the Omphalocele not be ruptured or
Paternal age (over 55) may also contribute to upward
the increased incidence
The iris of the eye may have white specks
Down syndrome called Brushfield's spots
- is a genetic disorder caused when abnormal •Even in the newborn, the tongue may
cell division results in an extra full or partial protrude from the mouth because the oral
copy of chromosome 21. This extra genetic cavity is smaller than normal
material causes the developmental changes and
physical features of Down syndrome. The back of the head is flat, the neck is short
and an extra pad of fat at the base of the head
Causes: causes the skin to be loose and can be lifted up
(like a puppy's neck)
Human cells normally contain 23 pairs of The ears may be low-set
chromosomes. One chromosome in each pair
comes from your father, the other from your Muscle tone is poor, giving the baby a rag-doll
mother. appearance
Down syndrome results when abnormal cell Fingers are short and thick and the little
division involving chromosome 21 occurs. finger is often curved inward
These cell division abnormalities result in an
extra partial or full chromosome 21. There may be a wide space between the first
and second toes and the first and second fingers
This extra genetic material is responsible for the
characteristic features and developmental
problems of Down syndrome. The palm of the hand shows a peculiar
Any one of three genetic variations can cause crease (a simian line) or a horizontal palm
Down syndrome: crease rather than the normal 3 creases in the
palm
Down syndrome varies in severity among
individuals, causing lifelong intellectual disability Have some degree of Cognitive challenge the
and developmental delays. degree can range from
that of less involvement (IQ 50 to 70) to one
It's the most common genetic chromosomal requiring total care (IQ less than 20)
disorder and cause of learning disabilities in
children. Appear to have altered immune function, making
them prone to respiratory infections
It also commonly causes other medical
abnormalities, including heart and COMMON DOWN SYNDROME:
gastrointestinal disorders.
l-lymphocytic leukemia
Infants with Down syndrome may be average
size, but typically they grow slowly and remain Congenital heart disorders esp. atrioventricular
shorter than other children the same age. disorders
Stenosis or atresia of the duodenum
Symptoms: Strabismus and cataract disorders
Each person with Down syndrome is an Their lifespan generally is only 50 to
individual — intellectual and developmental 60 years
problems may be mild, moderate or severe.
Some people are healthy while others have THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT
significant health problems such as serious heart
defects. Need to be exposed to early educational and
play opportunities
NOTE:
Sensible precautions such as good
Most of the time, Down syndrome isn't handwashing technique because they are prone
inherited. It's caused by a mistake in cell to infection infancy the enlarged tongue may
division during early development of the fetus. interfere with swallowing and cause choking
unless the child is fed slowly
Infants with Down syndrome may be average
size, but typically they grow slowly and remain Need physical examination at birth so that
shorter than other children the same age. genetic disorder can be detected and counseling
and support for parents and siblings can begin
Intellectual disabilities
Most children with Down syndrome have mild
to moderate cognitive impairment. Language is
delayed, and both short and long-term memory
is affected.
ASSESSMENT FINDINGS:
The nose is broad and flat
Eyelids have an extra fold of tissue at the inner
canthus (an fold), and the fissure (opening
between the eyelids)tends to slant laterally
You might also like
- Panic Away - Joe BarryDocument102 pagesPanic Away - Joe BarryPatrickNyenhuisNo ratings yet
- Omphalocele: 1 Baskaran NDocument5 pagesOmphalocele: 1 Baskaran Nதாசன் தமிழன்No ratings yet
- OmphaloceleDocument23 pagesOmphaloceleFred PupeNo ratings yet
- Maternal First Quiz ReviewerDocument15 pagesMaternal First Quiz ReviewerRay Ann BorresNo ratings yet
- Colic SyndromeDocument4 pagesColic SyndromeKenneth UbaldeNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Saint Louis UniversityDocument5 pagesGastrointestinal Disorders: Saint Louis UniversityAle SandraNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument6 pagesCarsVelado Alessandra Loraine B.No ratings yet
- Esophageal Atresia: Name of The Disease Description ManagementDocument4 pagesEsophageal Atresia: Name of The Disease Description ManagementAle SandraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Child Born With PhysicalDocument55 pagesNursing Care of The Child Born With PhysicalJoy kimmNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies of GiDocument94 pagesCongenital Anomalies of GiPadmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Child With Physical AND Developmental ChallengesDocument9 pagesNursing Care of A Child With Physical AND Developmental ChallengesAngelo ArabejoNo ratings yet
- CMCR-PART-4Document18 pagesCMCR-PART-4Alexandra AyneNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment For The Requirements in R.L.E: Submitted By: Elaine Blanche R. GonzalezDocument6 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment For The Requirements in R.L.E: Submitted By: Elaine Blanche R. GonzalezBlanche GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pediatric G.I Disorders FinalDocument53 pagesPediatric G.I Disorders FinalRashid Hussain0% (1)
- Esophageal AtresiaDocument21 pagesEsophageal AtresiaOktania Putri Kusnawan100% (2)
- CASE STUDY Quiane 1Document16 pagesCASE STUDY Quiane 1BeBs jai SelasorNo ratings yet
- Summary and Conclusion Esophageal Atresia (Or Oesophageal AtresiaDocument3 pagesSummary and Conclusion Esophageal Atresia (Or Oesophageal AtresiaSanket TelangNo ratings yet
- Physical and Developmental Disorders of The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument10 pagesPhysical and Developmental Disorders of The Gastrointestinal SystemJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- Congenital AnomaliesDocument10 pagesCongenital Anomaliesربيع ضياء ربيعNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Kongenital Sistem RespirasiDocument54 pagesKelainan Kongenital Sistem RespirasiBhima PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall Defects: Omphalocele GastroschisisDocument20 pagesAbdominal Wall Defects: Omphalocele GastroschisisYogi drNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument3 pagesNursing Care of A Family When A Child Has Gastrointestinal DisorderIan BathanNo ratings yet
- Repro Infant High RiskDocument10 pagesRepro Infant High Riskj UNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies in Newborn (Critical)Document46 pagesCongenital Anomalies in Newborn (Critical)Shereen Mohamed Soliman HammoudaNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula: A Guide For ParentsDocument4 pagesEsophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula: A Guide For ParentsMaya Asharie HarahapNo ratings yet
- Congenital Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument7 pagesCongenital Gastrointestinal DisorderDONA, Randel John T.No ratings yet
- GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS Cleft Palate - Esophageal Atresia - Oral MoniliasisDocument7 pagesGASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS Cleft Palate - Esophageal Atresia - Oral MoniliasisMikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Atresia: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesIntestinal Atresia: A Case ReportOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Omphalocele:exomphalosDocument10 pagesOmphalocele:exomphalosKhalilul AkbarNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall DefectsDocument5 pagesAbdominal Wall DefectsS GNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nurs GI DisordersDocument9 pagesPediatric Nurs GI DisordersVin Lorenzo CampbellNo ratings yet
- 70 Neonatal Anaesthesia 2 Anaesthesia For Neonates With Abdominal Wall DefectsDocument10 pages70 Neonatal Anaesthesia 2 Anaesthesia For Neonates With Abdominal Wall DefectsParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Imperforate AnusDocument17 pagesImperforate AnusNalzaro Emyril100% (1)
- OMPHALOCELEDocument11 pagesOMPHALOCELEPerpolNo ratings yet
- Surgery - Pediatric GIT, Abdominal Wall, Neoplasms - 2014ADocument14 pagesSurgery - Pediatric GIT, Abdominal Wall, Neoplasms - 2014ATwinkle SalongaNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip: Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (May Cause Ulceration and Destruction) and Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument2 pagesCleft Lip: Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (May Cause Ulceration and Destruction) and Chlamydia TrachomatisteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Ehp PDFDocument3 pagesEhp PDFIván Castellares RojasNo ratings yet
- Imperforate AnusDocument8 pagesImperforate AnusBâchtyăr Đ'jâckêrsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 NCMDocument3 pagesChapter 27 NCMGracian Vel AsocsomNo ratings yet
- Omphalocelevsgastroschisis 160810122732Document23 pagesOmphalocelevsgastroschisis 160810122732LNICCOLAIO100% (1)
- Prelims109 M1L1Document4 pagesPrelims109 M1L1MARY ROSE DOLOGUINNo ratings yet
- Omphalocele Omphalocele: Perceptor: DR. AMRAN SINAGA, SP.B AUTHOR: Ida Ayu Ratna W, S.Ked (G1A214018)Document17 pagesOmphalocele Omphalocele: Perceptor: DR. AMRAN SINAGA, SP.B AUTHOR: Ida Ayu Ratna W, S.Ked (G1A214018)Rully Riyan DikaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall DefectsDocument23 pagesAbdominal Wall DefectsJOSLIN100% (1)
- Abdominal Wall DefectsDocument16 pagesAbdominal Wall DefectsDesta FransiscaNo ratings yet
- Care of The New FoalDocument3 pagesCare of The New FoalCarlos Pedro VillaNo ratings yet
- Dlobasic Apr11Document27 pagesDlobasic Apr11Dr. T. BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Hirsch SprungDocument3 pagesHirsch SprungBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Choanal AtresiaDocument32 pagesChoanal AtresiaGreeshma ShajiNo ratings yet
- Gastroschisis BookletDocument4 pagesGastroschisis Bookletapi-381637629No ratings yet
- Hymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpDocument7 pagesHymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpSusan GachukiaNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Hernia - Wikipedia PDFDocument31 pagesUmbilical Hernia - Wikipedia PDFNeelamNo ratings yet
- H. Omphalocele: and Genitourinary System Infants Born With This Condition Often Have OtherDocument2 pagesH. Omphalocele: and Genitourinary System Infants Born With This Condition Often Have OthershakiraNo ratings yet
- B. Meckel's DiverticulumDocument3 pagesB. Meckel's DiverticulumClareen JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Pedia GiDocument10 pagesPedia GiCam IbardolasaNo ratings yet
- Common GI DiseasesDocument116 pagesCommon GI DiseasesmeleseNo ratings yet
- Day 12 - Ncm-109 7b InfancyDocument59 pagesDay 12 - Ncm-109 7b InfancySheena Patricia ArasulaNo ratings yet
- Pyloric Stenosis WDocument11 pagesPyloric Stenosis WKlaue Neiv CallaNo ratings yet
- 10th - Vaginal ProlapseDocument15 pages10th - Vaginal Prolapsenoor aineNo ratings yet
- Anorectal MalformationDocument8 pagesAnorectal Malformationgautami charingiaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 FinalsDocument9 pagesActivity 2 FinalsLuigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- Ncpfdardrug Study NotesDocument3 pagesNcpfdardrug Study NotesLuigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- Nebulization Pulse Oximetry 1Document2 pagesNebulization Pulse Oximetry 1Luigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- Research Group 4 FinalDocument20 pagesResearch Group 4 FinalLuigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- Imperforate AnusDocument2 pagesImperforate AnusLuigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument3 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeLuigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida: Types of DisordersDocument3 pagesSpina Bifida: Types of DisordersLuigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- Table of Comparison On Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation For Adul1Document1 pageTable of Comparison On Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation For Adul1Luigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- MN Geriatric Nursing - SET2Document15 pagesMN Geriatric Nursing - SET2dila punNo ratings yet
- Anscie-Lab ActivityDocument2 pagesAnscie-Lab ActivityKim Tian TigbabaoNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Krisis Hipertensi - Dr. Saugi AbduhDocument29 pages1.1. Krisis Hipertensi - Dr. Saugi AbduhdmaulidaNo ratings yet
- Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension: ReviewDocument6 pagesNoncirrhotic Portal Hypertension: ReviewIsrael BlancoNo ratings yet
- Gorlin-Goltz Syndrome Report of Two CasesDocument6 pagesGorlin-Goltz Syndrome Report of Two CasesNidhiNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Modification: Asterlyn T. Coniendo Bsn-IvDocument4 pagesLifestyle Modification: Asterlyn T. Coniendo Bsn-IvAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Ankle SprainDocument3 pagesAnkle SpraindrakbarbabNo ratings yet
- Sle 2010-2Document12 pagesSle 2010-2mahi_elsemary7011No ratings yet
- Antithrombotic DrugsDocument11 pagesAntithrombotic DrugsKatyBrnNo ratings yet
- Med Surg AnswersDocument23 pagesMed Surg Answersedoble67% (3)
- HypoparathyroidismDocument2 pagesHypoparathyroidismLorelyn Santos Corpuz0% (1)
- Report 2108432430 1Document1 pageReport 2108432430 1bilalbhai vahoraNo ratings yet
- Fatima Ishaq Adam MLT Project CompleteDocument37 pagesFatima Ishaq Adam MLT Project CompleteCapitallink cafeNo ratings yet
- A Look at Your Child's NutritionDocument2 pagesA Look at Your Child's NutritionAslul KhitanNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy in Children With Cerebral PalsyDocument6 pagesEpilepsy in Children With Cerebral PalsyTiara Renita LestariNo ratings yet
- (Impetigo) : Erbil Polythecnic University Soran Technical Insititute Nuraing Department First StageDocument14 pages(Impetigo) : Erbil Polythecnic University Soran Technical Insititute Nuraing Department First StageKubra ĖdrisNo ratings yet
- Assesing A Casualty Vital SignsDocument19 pagesAssesing A Casualty Vital SignsCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Tatiana BennettDocument7 pagesChapter 2 - Tatiana BennettEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- IFU Wondfo SARS CoV 2 Antibody Test (Lateral Flow Method) PDFDocument2 pagesIFU Wondfo SARS CoV 2 Antibody Test (Lateral Flow Method) PDFEndrio R HartonoNo ratings yet
- 21 AdisaDocument6 pages21 AdisaTri UtariNo ratings yet
- PDF Understanding Pathophysiology Canadian Edition Sue E Huether Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Understanding Pathophysiology Canadian Edition Sue E Huether Ebook Full Chaptermiriam.thornberg849100% (2)
- 31 Acid Base Imbalances ABGs II - 230110 - 004938Document2 pages31 Acid Base Imbalances ABGs II - 230110 - 004938JanaNo ratings yet
- Health: Ielts Thematic VocabDocument3 pagesHealth: Ielts Thematic VocabNguyễn Bông Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAko Si Vern ÖNo ratings yet
- Preoperative PreparationDocument53 pagesPreoperative PreparationBir Mohammad Sonet0% (1)
- Heat Stroke and Heat ExhausDocument46 pagesHeat Stroke and Heat ExhausDewi Pertiwi Pertiwi0% (1)
- ICD-10 CM All Diagnosis and Trigger Codes - Revised 9-17-2015Document6,507 pagesICD-10 CM All Diagnosis and Trigger Codes - Revised 9-17-2015Puskesmas MakaleNo ratings yet
- Feline Nonregenerative Anemia Pathophysiology and ErilologiesDocument7 pagesFeline Nonregenerative Anemia Pathophysiology and ErilologiesTORRES GUTIERREZ JOYNY RAQUEL catedraticoNo ratings yet
- PichosisDocument3 pagesPichosisalexandraNo ratings yet