Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circulatory System - Deliver Oxygen and Nutrients - Carries Waste Products - Circulates Electrolytes (Na, K, Ca) and
Circulatory System - Deliver Oxygen and Nutrients - Carries Waste Products - Circulates Electrolytes (Na, K, Ca) and
Uploaded by
yoonie cat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesThe circulatory system delivers oxygen and nutrients throughout the body and removes waste via the heart and blood vessels. The heart has four chambers and four valves that ensure one-way blood flow. Blood travels from the heart to the lungs to become oxygenated, then to the organs and tissues before returning to the heart. The heart's electrical conduction system coordinates contractions and pumping. Blood vessels include arteries, which carry blood away from the heart, and veins, which carry blood back to the heart. The circulatory system works closely with other body systems to sustain life.
Original Description:
Original Title
CIRCULATORY-SYSTEM-Handouts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe circulatory system delivers oxygen and nutrients throughout the body and removes waste via the heart and blood vessels. The heart has four chambers and four valves that ensure one-way blood flow. Blood travels from the heart to the lungs to become oxygenated, then to the organs and tissues before returning to the heart. The heart's electrical conduction system coordinates contractions and pumping. Blood vessels include arteries, which carry blood away from the heart, and veins, which carry blood back to the heart. The circulatory system works closely with other body systems to sustain life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesCirculatory System - Deliver Oxygen and Nutrients - Carries Waste Products - Circulates Electrolytes (Na, K, Ca) and
Circulatory System - Deliver Oxygen and Nutrients - Carries Waste Products - Circulates Electrolytes (Na, K, Ca) and
Uploaded by
yoonie catThe circulatory system delivers oxygen and nutrients throughout the body and removes waste via the heart and blood vessels. The heart has four chambers and four valves that ensure one-way blood flow. Blood travels from the heart to the lungs to become oxygenated, then to the organs and tissues before returning to the heart. The heart's electrical conduction system coordinates contractions and pumping. Blood vessels include arteries, which carry blood away from the heart, and veins, which carry blood back to the heart. The circulatory system works closely with other body systems to sustain life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The Heart Valves:
- Deliver oxygen and nutrients Atrioventricular Valve
- Carries waste products - composed of 3 cusps
- Circulates electrolytes (Na, K, Ca) and - separates right atrium from right
hormones ventricle.
Tricuspid and Mitral/bicuspid
HEART valve
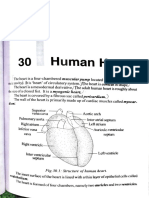
- Hollow muscular organ located in the - composed of 2 cusps
center of the thorax, where it occupies the - separates left atrium from
space between the large (mediastinum) and ventricle.
the rests on the diaphragm. Pulmonic Valve
Composed of 3 layers: - composed of 3 half-moons like
Endocardium leaflets Between the right ventricle
- inner layer; consist of endothelial and pulmonary artery.
tissue Aortic Valve
Endocarditis - composed of 3 half-moons like
- inflammation of the leaflets Between the left ventricle
endocardium and aorta.
Myocardium PATHWAY OF BLOOD THROUGH THE HEART
- middle layer; made up of muscle A. Systemic Circulation
fibers responsible for pumping - flow of blood from the heart to the
action of the heart body organs and back to the heart.
Myocarditis B. Pulmonic Circulation
- inflammation of the - flow of blood from the heart to the
myocardium lungs and back to the heart.
Epicardium - unoxygenated blood
- exterior layer C. Coronary Circulation
Epicarditis - flow of blood that nourishes the cells
- inflammation of the in the heart.
epicardium - within the heart
Parts of the Heart: D. Fetal Circulation
Visceral Pericardium - path of blood between the mother
- exterior layer; thin transparent and child in the womb.
layer that is actually part of the - happens in fetal stage
heart.
Parietal Pericardium CARDIAC CYCLE
- fibrous layers helps protect the Pulmonary Circulation
heart and anchors it to the - smaller functions as low pressure
diaphragm and sternum. system
Pericardial Cavity MAP= 12mmHg
- contains a 50 ml pericardial fluid Systemic Circulation
that reduces friction and erosion of - functions as high pressure system
tissue between these membrane as MAP= 90- 100mmHg
the heart expands and contracts
during a cardiac cycle.
Formula: Cardiac volume
- amount of blood the heart pumps with
Diastolic Pressure x 2 + Systemic Pressure
MAP =
each minute
3 CO = SV x HR
Cardiac Output = Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
MAP – Mean Arterial Pressure
Mean Arterial Pressure
Flow of Blood (Systemic Circulation) - represents the average pressure in the
IF – SV RA TV RV PA Lungs atrial system during ventricular and
Artery LA LV Aorta relaxation
Tetralogy of Falot
- 4 abnormalities in the heart Oxygenated HEART RATE
and non-oxygenated blood is mixed. - normal- 60-100 beat per minute
- blue baby presence of cyanosis BRADYCARDIA – slow heart beat
Coronary Arteries TACHYCARDIA – fast heart beat
- the heart is nourished not by the blood HEART SOUNDS
passing through its chambers but by a S1 – First Associated with tricuspid and
specialized network of blood vessels. mitral closure
- known as coronary arteries. These blood S2 – Associated with aortic and pulmonic
vessels encircle the heart like a crown. valve closure
ELECTRICAL CELLS HAVE 3 CHARACTERISTICS The first heart sound is generally
Automaticity longer than second producing heart
- Ability to initiate electrical impulse beat that sounds like lub-dup, lub-
Excitability Ability dup, lub-dup
rd
- to respond an electric stimuli S3 – 3 heart sound; Ventricular gallop
Conductivity Ability S4 – 4th heart sound; Atrial gallop
- to transmit electrical impulse from ECG – Electrocardiograph
one cell to another
CONDUCTION SYSTEM FETAL CIRCULATION
- continuous functioning 2 arteries – carry carbon dioxide to placenta
Sinoatrial Node Atrioventricular node AV from fetus
bundle of his right and left bundle branch 1 vein – carry oxygen to fetus from placenta
purkinje fiber
BLOOD VESSELS
TERMS: - any of the veins, arteries and capillaries that
Preload transport blood through the body
- amount of blood that a heart must pump - keep up waste between 2 blood vessels
with each beat Artery
After load - tubular vessels that conveys blood
- pressure that the heart must generate to from the heart to the tissues of the
move blood into the aorta body.
Stroke volume
- amount of blood ejected from each
ventricle beat
- difficulty to pass through and to be
Two arteries have connection with the heart: circulated
1. Aorta - very fatal
- which with its branches, conveys - heart attack
oxygenated blood from the left ventricle - obstruction
to every part of the body. Angina
2. Pulmonary Artery - type of temporary chest pain,
- blood from the right ventricle to the pressure or discomfort
lungs.
3 Layers of Artery: narrowed artery
a. Tunica Media
- smooth muscle Ischemia
b. Tunica Externa - death of the tissues of the heart
- white fibrous connective tissue - can cause malfunctioning of the
c. Tunica Intima specific part of the heart
- direct connection to the blood - not receiving enough oxygen due
- endothelial cells to a narrowed common artery
Vein
- conducts the deoxygenated blood HEMATOLOGIC SYSTEM
from the capillaries back to the heart - blood is the only liquid connective tissue
- pour the blood through superior and found in the body
inferior vena cava into right atrium of Function of the Blood:
the heart. Their coats are similar to a. Transports oxygen, carbon dioxide,
those of the arteries, but thinner and nutrients, heat, wastes and hormones
often transparent. b. It helps regulate pH level, body temp,
and water content of cells
Capillary c. It prevents blood loss through clotting
- one of the minute blood vessels that and combats toxins and microbes
form the connection between the through certain phagocytic white blood
arteries and the veins cells
- they are surrounded by lymph Blood
- facilitate the processes of nutrition and - average total volume:
elimination and enables the exchange of Men: 75.5 ml/kg
oxygen and carbon dioxide to take Female: 66.5 ml/kg
place. Lymph capillaries assist the blood - 7-8% of person’s total weight
capillaries in this process. Blood cells – 45%
Blood Plasma – 55%
Arteriosclerosis – narrowing of artery; fats Arterial blood pH – 7.25-7.45
surrounded the blood vessels COMPONENTS:
a. Plasma
CIRCLE OF WILLIS - complex aqueous liquid containing
- blood circulation in the nervous system several organic & inorganic elements
Myocardial Infraction Functions of Plasma:
- narrowing of the passage way of - maintain the intravascular volume
the blood - contribute to blood viscosity
PLASMA PROTEINS - contain enzymes and
1.) Serum Albumin other antibacterial
- main component of plasma substances
protein - life span of 10 hours
- maintaining blood pressure and Eosinophils
blood volume - 1 – 3% of WBC
- serves as a carrier molecule - contain a protein that
2.) Serum Globulin is highly toxic to large
- Alpha Fraction parasitic worms
- Beta Fraction Basophils
- Gamma Fraction - 3 - .5% of WBC
3.) Fibrinogen - contain histamine and
b. Cellular Components other bioactive
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cell) mediators of
- normal concentration: 4.2 – inflammation
6.2 millions/mm3 Agranulocytes
- 4.8% of blood in men Monocytes
- 4.2 % of blood in women (Macrophage)
- A small unique disk with 2 - 3 – 8% of WBC
unique properties: - Largest of the
BICONCAVITY circulating WBC
REVERSIBLE - 2nd to arrive at the site
DEFORMABILITY - Engulf large
2 Main Function of RBC: microorganisms
1.) Transporting oxygen to - Life span: 3 – 4x
tissues longer than neutrophil
2.) Removing carbon dioxide Platelets
from tissues - normal value: 150,000 –
o LIFESPAN: 120 days 400,000/mm3
o MAIN COMPONENT: - function to form a platelet
hemoglobin plug to control bleeding after
Leukocytes injury to a vessel wall
- normal value: 5,000 – ERYTHROPOIETIN
10,000/mm3 - Also called as erythropoietic factor
- FUNCTION: protect from - Regulates RBC production in bone marrow
infection - RBC production takes place in the:
- white blood cells involved in Bone of the vertebrae
inflammation Sternum
Granulocytes Ribs
Neutrophils Pelvis
- 60 – 70% of WBC
- Primary phagocytes;
1st to arrive;
- 6 – 12 hours after
initial injury
You might also like
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular Systemsurviving nursing school100% (2)
- Food Security EssayDocument7 pagesFood Security EssayNeil Clelland100% (3)
- Choudhry FTP Principles Jan 2018Document133 pagesChoudhry FTP Principles Jan 2018James BestNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Heart ReviewerDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System Heart ReviewerImmanuel Cris PalasigueNo ratings yet
- 9 - Urban & Rural Development in BangladeshDocument21 pages9 - Urban & Rural Development in BangladeshMd Omar Kaiser MahinNo ratings yet
- A Validation Approach For LIMSDocument9 pagesA Validation Approach For LIMSFred100% (1)
- ANATOMY Final pt.1Document26 pagesANATOMY Final pt.1Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- CARDIOLOGYDocument15 pagesCARDIOLOGYPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- Anaph111 - FinalsDocument7 pagesAnaph111 - FinalsUwen NalpNo ratings yet
- The Human HeartDocument4 pagesThe Human HeartFrama Intan MiguelNo ratings yet
- A C.A.R. On P.B., 69 Y.O., Female, Diagnosed With Right Thalamic Infarction, and Hypertensive Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument8 pagesA C.A.R. On P.B., 69 Y.O., Female, Diagnosed With Right Thalamic Infarction, and Hypertensive Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseasefebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesLec 3 - Circulatory SystemJewel Jehd AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1Document54 pagesLecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1hafiz patah100% (1)
- CHAP11Document12 pagesCHAP11Crystal ARIETANo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASDocument3 pagesCARDIOVASFrama Intan MiguelNo ratings yet
- SB0024 Transport in Animals and Plant (DFN)Document80 pagesSB0024 Transport in Animals and Plant (DFN)jmyphjmrdnNo ratings yet
- 0.8 Sec. The HeartDocument9 pages0.8 Sec. The Heartmary lee gumapacNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 11 The Cardiovascular SystemunknownNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System NotesDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System NotesMichaela ManacmulNo ratings yet
- Heart External AnatomyDocument6 pagesHeart External AnatomyKrissia BaasisNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular / Circulatory System: Upper Chambers or Receiving ChambersDocument2 pagesCardiovascular / Circulatory System: Upper Chambers or Receiving ChambersRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- MS Term 1Document7 pagesMS Term 1Abegail QuintoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 CARDIO (Pretest)Document6 pagesCHAPTER 11 CARDIO (Pretest)unknownNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Cardiovascular SystemluaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesCardiovascular SystemPurple Ivy GuarraNo ratings yet
- 8 CardiovascularDocument44 pages8 CardiovascularleonardodataguroNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 5Document13 pagesBiology Chapter 5Shahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System WordDocument18 pagesCardiovascular System WordLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- CARDIODocument17 pagesCARDIORayana Ubas100% (1)
- Ana CardioDocument3 pagesAna CardioFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Layers:: Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesLayers:: Cardiovascular SystemCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSDocument56 pagesPhysiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSDocument56 pagesPhysiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSDocument56 pagesPhysiology of The Cardiovascular System-CVSAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyKIRSTEN CHAVEZ100% (1)
- Anaphy HeartDocument6 pagesAnaphy HeartAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- #3 Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pages#3 Cardiovascular SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument3 pagesCardiovascular DrugsLaurente, Patrizja Ysabel B. BSN-2DNo ratings yet
- Heart Finals ReviewerDocument7 pagesHeart Finals ReviewershannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesAnaphy Cardiovascular SystemFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument5 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesLec 3 - Circulatory SystemJewel Jehd AlegriaNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument8 pagesHEARTJoyce OmegaNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsDocument7 pagesPRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Heart and Blood Vessels, BloodDocument13 pagesHeart and Blood Vessels, BloodDaniel DanielNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Lecture 3-2018-2019 PDFDocument27 pagesCardiovascular System - Lecture 3-2018-2019 PDFMary100% (1)
- Ms - CardiovascularDocument70 pagesMs - CardiovascularMark OngNo ratings yet
- CARDIO 1. Assessment and Diagnostic - ReviewerDocument21 pagesCARDIO 1. Assessment and Diagnostic - ReviewerMark OngNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio MC1Document12 pagesAnaphysio MC1KRISTINE CHAD NAVALES CANTALEJONo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System ZooDocument9 pagesThe Circulatory System Zoopierre TritzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology NotesDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology NotesChristina Gonez100% (2)
- Lecture Notes NCM 102: Union Christian College College of NursingDocument77 pagesLecture Notes NCM 102: Union Christian College College of Nursingnarswiponshistoryan100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System ReviewerDocument7 pagesCardiovascular System ReviewerVictoria Ellex TiomicoNo ratings yet
- 8.cardiovascular SystemDocument13 pages8.cardiovascular Systempodki gurungNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Electrical SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System - Electrical SystemRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Cardio 1Document7 pagesCardio 1Moon KillerNo ratings yet
- LIFS1902 Heart and CVS Revision NotesDocument6 pagesLIFS1902 Heart and CVS Revision NotesmystudylifechloeNo ratings yet
- Pericardium: Chambers and Associated Great VesselsDocument3 pagesPericardium: Chambers and Associated Great VesselsJocelyn AlunanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 HeartDocument9 pagesLesson 12 HeartEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Scan Dec 12, 2022Document6 pagesScan Dec 12, 2022Saktheeswaran VNo ratings yet
- Biology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryDocument13 pagesBiology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryMa. Teresa M. AbainzaNo ratings yet
- MS CVS ReviewDocument41 pagesMS CVS ReviewShayesra-Radina Laja SahibadNo ratings yet
- CMCADocument3 pagesCMCAyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Health Education Teaching MethodsDocument6 pagesHealth Education Teaching Methodsyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching Purposes of Clinical Laboratory: ST NDDocument3 pagesClinical Teaching Purposes of Clinical Laboratory: ST NDyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Calories, Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrition - Finals Lesson 12Document12 pagesCalories, Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrition - Finals Lesson 12yoonie catNo ratings yet
- LEARNING THEORY (Determinants of Learning) Determinants of LearningDocument6 pagesLEARNING THEORY (Determinants of Learning) Determinants of Learningyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Dorothy JohnsonDocument2 pagesDorothy Johnsonyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis in Children of The World: What Needs To Be Done?Document8 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis in Children of The World: What Needs To Be Done?yoonie catNo ratings yet
- Lit 101 Notes FormatDocument10 pagesLit 101 Notes Formatyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio BibleDocument139 pagesPathophysio Bibleyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Final Examination SEMESTER 2, SESSION 2017/2018: Instruction To CandidatesDocument7 pagesFinal Examination SEMESTER 2, SESSION 2017/2018: Instruction To CandidatesusssNo ratings yet
- Roof Safety C/o OSHADocument4 pagesRoof Safety C/o OSHAAlejo Raquel Jr.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Person With Croup Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Person With Croup Nursing DiagnosisMonica Rivera100% (1)
- The Little Match Girl Analysis and ThemeDocument3 pagesThe Little Match Girl Analysis and ThemejyothigkrishnanNo ratings yet
- Module 1: An Introduction To Psychology: What You Will LearnDocument16 pagesModule 1: An Introduction To Psychology: What You Will LearnDiana PascuNo ratings yet
- Siemon Catalogue - XGLO Fibre Optic Cable (MM) Indoor - Outdoor Loose Tube - EMEADocument6 pagesSiemon Catalogue - XGLO Fibre Optic Cable (MM) Indoor - Outdoor Loose Tube - EMEASantiago PugaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundations of Classroom Management in Special Education Module 2Document27 pagesTheoretical Foundations of Classroom Management in Special Education Module 2XERXA BILLONES100% (1)
- Plastic Pallet 1219 X 1016 MMDocument1 pagePlastic Pallet 1219 X 1016 MMANANo ratings yet
- Disease Detectives C ExamDocument34 pagesDisease Detectives C ExamGustavo Pacheco0% (1)
- Organic Farming and Waste Management: Presented By: Nikhitha H 4MH21CS06 2 C' Sec TionDocument8 pagesOrganic Farming and Waste Management: Presented By: Nikhitha H 4MH21CS06 2 C' Sec Tionnikhitha HNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Planning and Disaster Recovery PlanDocument55 pagesBusiness Continuity Planning and Disaster Recovery PlanNeeraj Kohli100% (2)
- CESC - Lesson 2 - Community DynamicsDocument25 pagesCESC - Lesson 2 - Community DynamicsZaharaNo ratings yet
- Telescopic-Cranes-Operations Safety S3 20170309Document98 pagesTelescopic-Cranes-Operations Safety S3 20170309Design NarayanawindpowerNo ratings yet
- Special Power of Attorney Pag Ibig Housing LoanDocument2 pagesSpecial Power of Attorney Pag Ibig Housing LoanRnel Manalo100% (1)
- TACA Times Sept/Oct 2010Document6 pagesTACA Times Sept/Oct 2010Bruce WileyNo ratings yet
- Tea and CocktailsDocument5 pagesTea and Cocktailsapplejak100% (2)
- 152 Experiment 3Document2 pages152 Experiment 3Earl CañoneroNo ratings yet
- BCHEDocument3 pagesBCHERolando AmadNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Ansys 2Document13 pagesPressure Vessel Ansys 2Bruna Macedo100% (1)
- Design of Pile and Pile Cap FinalDocument39 pagesDesign of Pile and Pile Cap FinalMahendra Suryavanshi100% (1)
- Ambrosia PDFDocument103 pagesAmbrosia PDFJanani ChanderNo ratings yet
- Introduction Related Literature MethodologyDocument12 pagesIntroduction Related Literature MethodologyEllaiza LopezNo ratings yet
- Pregnant Workers Fairness ActDocument5 pagesPregnant Workers Fairness ActGabriel StarkNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 English Achievement TestDocument4 pagesGrade 10 English Achievement TestJelaica Alarilla - GerminoNo ratings yet
- Bias-Free Language in TranslationDocument48 pagesBias-Free Language in TranslationNoeliaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Use in HemostasisDocument47 pagesDrugs Use in HemostasiskadibhaNo ratings yet