Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A) B) C) D) : Chemical Effect of Electric Current-Critical Thinking Questions
A) B) C) D) : Chemical Effect of Electric Current-Critical Thinking Questions
Uploaded by
Aadil Muhammed SajiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Ngee Ann SecondaryDocument35 pages2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Ngee Ann SecondaryDORA SIN YU KWOKNo ratings yet
- Aisi 4130Document3 pagesAisi 4130Rajesh R BhavsarNo ratings yet
- .Ws Ionic Bonding Activity KeyDocument4 pages.Ws Ionic Bonding Activity KeyrajaijahNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Electrolysis: A B C DDocument30 pagesWork Sheet Electrolysis: A B C DAhmadNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument33 pagesElectrolysisborglingchompersNo ratings yet
- Jar 1 Jar 1 Lid Air: A B C DDocument7 pagesJar 1 Jar 1 Lid Air: A B C DaaryavaminNo ratings yet
- UQr BW Ae OH3 ZP DV M6 VBJFDocument4 pagesUQr BW Ae OH3 ZP DV M6 VBJFgoodvp05No ratings yet
- Eletrolysis NotesDocument34 pagesEletrolysis NotesGoogle Drive shahNo ratings yet
- NL MCQ Challenge 03Document5 pagesNL MCQ Challenge 03Alvin Lee100% (1)
- Electricity ND ChemistryDocument23 pagesElectricity ND ChemistryFilza SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4 Electrolysis QP Level Cie For Class 10 11Document24 pagesChemistry 4 Electrolysis QP Level Cie For Class 10 11Maryam KhanNo ratings yet
- Klks 9 Test-LatihanDocument6 pagesKlks 9 Test-LatihankrisnuNo ratings yet
- 4 - Electrolysis MCQ SolutionsDocument4 pages4 - Electrolysis MCQ SolutionsNasreen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Read These Instructions FirstDocument7 pagesRead These Instructions FirstSalman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Q & ADocument8 pagesElectrochemistry Q & AYash JoshiNo ratings yet
- SUB CHEMISTRY Date27-03-2024Document2 pagesSUB CHEMISTRY Date27-03-2024shankarbannu143No ratings yet
- SS2 CHEMISTRY TEST ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesSS2 CHEMISTRY TEST Electrolysisforthland consultingNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Section A (15 Marks)Document7 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Section A (15 Marks)chee pin wongNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 Full Notes 2Document81 pagesSem 1 Full Notes 2Shravani PakhaleNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 19 MC PracticeDocument18 pagesTopic 9 19 MC PracticeDharmesh Ramnarayan Yadav100% (1)
- SULIT 4541/1 Chemistry Paper 1 Mei 2007Document22 pagesSULIT 4541/1 Chemistry Paper 1 Mei 2007AMINNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North (2022 - 23)Document4 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North (2022 - 23)itz gamerNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document15 pagesPaper 1SitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis QuestionsDocument53 pagesElectrolysis QuestionsAahaan ShethNo ratings yet
- Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentDocument4 pagesChemical Effects of Electric Currentyuvaneshsridhar2No ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 3 (10)Document6 pagesWorksheet Chapter 3 (10)Satyam DeoraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry RevisionDocument9 pagesChemistry RevisionHING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- Class X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyDocument4 pagesClass X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyToshiGMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Read These Instructions FirstDocument6 pagesRead These Instructions FirstSalman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Electrolysisspurohit1991No ratings yet
- Class X ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesClass X ElectrolysisvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Notes On ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesNotes On Electrolysisapi-3819012No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Paper 2Document9 pagesMultiple Choice Paper 2lsstr1e2no2No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry With AnswersDocument27 pagesElectrochemistry With AnswersKris CruzNo ratings yet
- WS4,5,6,7 WK 16-20 Aug Energy and Chemicals Class 10 ZoyaDocument18 pagesWS4,5,6,7 WK 16-20 Aug Energy and Chemicals Class 10 ZoyaUsman AsmatullahNo ratings yet
- Gems Genesis: 9caieDocument4 pagesGems Genesis: 9caieBhavya darjiNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument41 pagesCHEMISTRYLindsayyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Presentation: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument118 pagesChemistry Presentation: Multiple Choice QuestionsKhiZra ShahZadNo ratings yet
- Exemplar - Chemical Effects of CurrentDocument14 pagesExemplar - Chemical Effects of CurrentnitikaNo ratings yet
- Test Topic: Atomic Structure, Formula Writing and Balancing Equation, Bonding and Structure, Redox, ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesTest Topic: Atomic Structure, Formula Writing and Balancing Equation, Bonding and Structure, Redox, ElectrolysisArham Tamim100% (1)
- Pre IG 0.14 (Night), Chemistry, Monthly TestDocument8 pagesPre IG 0.14 (Night), Chemistry, Monthly TestHtet Wai Yan AungNo ratings yet
- 2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersDocument9 pages2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersThanabalan MunuswamyNo ratings yet
- CHS Paper Final ExamDocument10 pagesCHS Paper Final Examabdulhadisaqib290No ratings yet
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current (Grade 8 CBSE)Document2 pagesChemical Effects of Electric Current (Grade 8 CBSE)mithlikesfun2No ratings yet
- Regents Review Chemical Bonding KeyDocument7 pagesRegents Review Chemical Bonding Keycitation04No ratings yet
- Chem Prac 2 (Voltaic Cell, Danielle Cell)Document7 pagesChem Prac 2 (Voltaic Cell, Danielle Cell)Joshua WeeNo ratings yet
- Cie QDocument17 pagesCie Qinternationalmakkhayar100% (1)
- HanksDocument20 pagesHanksRia MandasariNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2006 45 MinutesDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2006 45 MinutesVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Bahagian A 1. The Melting Point of A Substance X Is - 2: Diagram 3Document12 pagesBahagian A 1. The Melting Point of A Substance X Is - 2: Diagram 3ndianaoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemicalsDocument6 pagesElectricity and ChemicalsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- 5.electricity and Chemistry PDFDocument15 pages5.electricity and Chemistry PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry (Multiple Choice) QPDocument29 pagesElectricity & Chemistry (Multiple Choice) QPGunay OmarovaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 110: Paper 1 Name: - Class: - Date: - A. Multiple Choice Questions. 1Document26 pagesLesson 110: Paper 1 Name: - Class: - Date: - A. Multiple Choice Questions. 1Siapa Al AhbashiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 ElectrolysisJayadevi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- APEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFDocument2 pagesAPEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- APEF - Electrochemistry - Multiple Choice Questions - Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesAPEF - Electrochemistry - Multiple Choice Questions - Page 1 of 2alyaa sheirNo ratings yet
- APEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFDocument2 pagesAPEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFFirdausia Rahma PutriNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis MasteryDocument8 pagesElectrolysis MasteryDonald ZhuoNo ratings yet
- CHEM ASM FOR L-3 and L-4 (X)Document8 pagesCHEM ASM FOR L-3 and L-4 (X)Arsh KhanNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument4 pagesBiology NotesAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- G-7 - The Hunt NotesDocument3 pagesG-7 - The Hunt NotesAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- Mughal Empire 2Document2 pagesMughal Empire 2Aadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- General Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesGeneral Practice WorksheetAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- Module1 Cyber SafetyDocument2 pagesModule1 Cyber SafetyAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- Oil BleedingDocument3 pagesOil BleedingDhananjay B KNo ratings yet
- Test Report of PVC Water Stop: Customer: Address: Batch No.: Na Description: Size & Quantity: StandardDocument1 pageTest Report of PVC Water Stop: Customer: Address: Batch No.: Na Description: Size & Quantity: StandardR.ThangarajNo ratings yet
- TLE M15 Learning Material For Week 10Document4 pagesTLE M15 Learning Material For Week 10ALLY ۦۦNo ratings yet
- SikaPlast 2014 NS BDDocument2 pagesSikaPlast 2014 NS BDTaposh Paul100% (1)
- Gulf Precast GRCDocument12 pagesGulf Precast GRCmujeebscribdNo ratings yet
- Tivar 882 UHMWPE PF E 02122014 PDFDocument1 pageTivar 882 UHMWPE PF E 02122014 PDFCristhian Guerrero AsmadNo ratings yet
- QC Qustion and AnswerDocument32 pagesQC Qustion and Answerrajum465100% (2)
- Bayferrox Iron Oxide PigmentDocument9 pagesBayferrox Iron Oxide PigmentMuzammal HussainNo ratings yet
- Materials Research Bulletin: Activated Carbon Aerogel Containing Graphene As Electrode Material For SupercapacitorDocument8 pagesMaterials Research Bulletin: Activated Carbon Aerogel Containing Graphene As Electrode Material For SupercapacitornagatozzNo ratings yet
- Iesc 102Document17 pagesIesc 102ecdmrcNo ratings yet
- Me Elective ModulesDocument141 pagesMe Elective ModulesBenedictus Torres MoldesNo ratings yet
- Guide For The Use of Polymers in Concrete: ACI 548.1R-97Document29 pagesGuide For The Use of Polymers in Concrete: ACI 548.1R-97Control de calidad Antamina100% (1)
- Solution 1176952Document4 pagesSolution 1176952arb88279No ratings yet
- Sotrafer-Quality Observation Complaince Tracking Record.Document63 pagesSotrafer-Quality Observation Complaince Tracking Record.mitendra singhNo ratings yet
- Shubham+Report Abcdpdf PDF To WordDocument46 pagesShubham+Report Abcdpdf PDF To WordGond AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Wa0023Document10 pagesWa0023kevin iyeseNo ratings yet
- A Bright Future For Copper Electrowinning: Michael Moats and Michael FreeDocument3 pagesA Bright Future For Copper Electrowinning: Michael Moats and Michael Freealexis diazNo ratings yet
- Plant Visits and Seminar MEGAWIDEDocument5 pagesPlant Visits and Seminar MEGAWIDEEngr SantosNo ratings yet
- D&D 5E - Metals - Dungeon Master AssistanceDocument25 pagesD&D 5E - Metals - Dungeon Master AssistanceSamuel JouveNo ratings yet
- 1 4509Document2 pages1 4509Umesh KotadiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Iron Making (PCMT4303) - 6th Sem BTech (Metallurgy)Document158 pagesLecture Notes Iron Making (PCMT4303) - 6th Sem BTech (Metallurgy)mandakini baskey100% (2)
- Coating PaintingDocument8 pagesCoating Paintingdeva0170% (2)
- 1 2 2 5 2 PDFDocument16 pages1 2 2 5 2 PDFSrinivas VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Koh Pich Construction Company Cambodia-China Polytechnic University Daily Activities ReportDocument7 pagesKoh Pich Construction Company Cambodia-China Polytechnic University Daily Activities ReportNhoek RenNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document55 pagesChem 1vishnupatel7112006No ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 5 Electricity and Chemistry - CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument65 pagesFlashcards - Topic 5 Electricity and Chemistry - CIE Chemistry IGCSEBhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- Block Elements Class 12Document15 pagesBlock Elements Class 12Åmìßhã PŕãťãpNo ratings yet
- Adobe90 3 PDFDocument150 pagesAdobe90 3 PDFDorinha AlvarengaNo ratings yet
A) B) C) D) : Chemical Effect of Electric Current-Critical Thinking Questions
A) B) C) D) : Chemical Effect of Electric Current-Critical Thinking Questions
Uploaded by
Aadil Muhammed SajiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A) B) C) D) : Chemical Effect of Electric Current-Critical Thinking Questions
A) B) C) D) : Chemical Effect of Electric Current-Critical Thinking Questions
Uploaded by
Aadil Muhammed SajiCopyright:
Available Formats
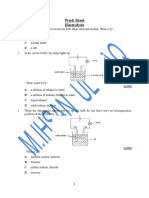
Chemical effect of Electric Current-Critical thinking Questions
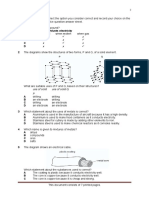
1. In which one of the following situations does a conventional electric current flow due
north?
A) Protons in a beam are moving due south.
B) A water molecule is moving due north.
C) Electrons in a beam are moving due south.
D) None of these
2. Which of the following circuits gives the correct way of connecting an LED to light
it up? A)
B)
C)
D)
3.What are insulators?
A) Materials that conduct electricity
B) Materials that do not conduct electricity
C) Materials that conduct electricity only at low temperatures
D) Materials that conduct electricity at room temperature
4.Which of the following is an insulator?
A) Wood
B) Iron
C) Graphite
D) Silver
5.Adding common salt to distilled water makes it
a.Conductor
b.Insulator
c.None of the above.
6.In electrolytic solutions, which of the following acts as carrier of charge?
A) Protons
B) Electrons
C) Neutrons
D) Ions
7.Which of the following are the characteristics of an electrolyte?
A) It has a positive charge.
B) It has a negative charge.
C) It conducts charge without dissociating.
D) It forms positive and negative ions.
8.What happens when electric current is made to flow through a conductor?
A) Some amount of electrical energy is converted into heat energy.
B) Some amount of electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy.
C) Some amount of mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy.
D) Some amount of heat energy is converted into electrical energy.
9.Which of the following liquids is a bad conductor of electricity?
A) Lemon juice
B) Vinegar
C) Sea water D) Distilled water
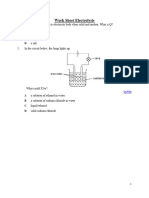
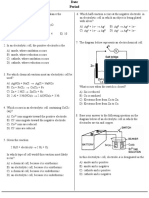
10..
In the given figure, electrolyte, anode and cathode respectively are
A) A, B and C
B) B, A and C
C) B, C and A
D) A, C and B
11..An electric current is passed through a conducting solution. Following are the some
observations:
(i) Deposits of metal may be seen on electrodes
(ii) Solution may get heated
(iii) Bubbles of gas may be formed on the electrodesA) Only (ii) is true.
B) Only (i) and (ii) are true.
C) Only (i) and (iii) are true.
D) All (i), (ii) and (iii) are true.
12.Which of the following is correct?
A) Water can be used for extinguishing fires caused due to electrical faults.
B) Carbon is a non-metal so it cannot be used in an electrolytic cell.
C) A liquid conducts electricity because of the presence of ions.
D) Pure water forms ions to conduct electricity.
13.Which of the following cells use(s) electric current to produce a chemical reaction? A)
Dry cell
B) Solar cell
C) Electrolytic cell
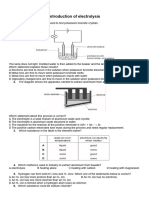
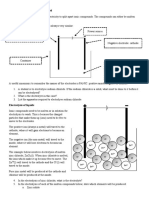
D) Both dry cell and electrolytic cell14.
Direction: Four substances were tested for their electrical conductivity. The results are shown in the
table. Study the table and answer the following questions.
Substance Bulb Substance at Cathode Substance at Anode
P Lights up Aluminium Oxygen
Q Lights up Nothing Nothing
R Does not light up Nothing Nothing
S Lights up Hydrogen Carbon dioxide
In substance Q, bulb lights up but no substance is found either at cathode or at anode,
why?
A) Because Q is non-electrolyte.
B) Because Q is an element which remains unchanged when it conducts electricity.
C) Because Q is an electrolyte that conducts electricity when it is in the molten state.
D) Because Q is a poor conductor of electricity.
15.What is the splitting of a compound using electricity called?
A) Electrolysis
B) Electrolyte
C) Electrokinesis
D) Electrochemistry
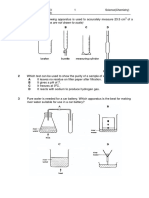
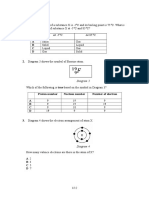
16.There are two different solutions in set up P and Q as shown in figure. The bulb in
the set up P glows more brightly as compared to that of the set up Q. What are the
possible causes for this?
(i) The connections of the circuit Q may be loose.
(ii) The liquid in Q may have small conductivity.
(iii) Liquid in P is equivalent to a battery while liquid in Q is equivalent to a cell of the
battery of liquid P.
A) Only (i) and (ii)
B) Only (ii) and (iii)
C) Only (i)
D) Only (ii)
17.To protect iron from corrosion and rust, it is coated with
A) Tin
B) CopperC) Mercury
D) Zinc.
************************************************************s************
You might also like
- 2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Ngee Ann SecondaryDocument35 pages2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Ngee Ann SecondaryDORA SIN YU KWOKNo ratings yet
- Aisi 4130Document3 pagesAisi 4130Rajesh R BhavsarNo ratings yet
- .Ws Ionic Bonding Activity KeyDocument4 pages.Ws Ionic Bonding Activity KeyrajaijahNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Electrolysis: A B C DDocument30 pagesWork Sheet Electrolysis: A B C DAhmadNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument33 pagesElectrolysisborglingchompersNo ratings yet
- Jar 1 Jar 1 Lid Air: A B C DDocument7 pagesJar 1 Jar 1 Lid Air: A B C DaaryavaminNo ratings yet
- UQr BW Ae OH3 ZP DV M6 VBJFDocument4 pagesUQr BW Ae OH3 ZP DV M6 VBJFgoodvp05No ratings yet
- Eletrolysis NotesDocument34 pagesEletrolysis NotesGoogle Drive shahNo ratings yet
- NL MCQ Challenge 03Document5 pagesNL MCQ Challenge 03Alvin Lee100% (1)
- Electricity ND ChemistryDocument23 pagesElectricity ND ChemistryFilza SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4 Electrolysis QP Level Cie For Class 10 11Document24 pagesChemistry 4 Electrolysis QP Level Cie For Class 10 11Maryam KhanNo ratings yet
- Klks 9 Test-LatihanDocument6 pagesKlks 9 Test-LatihankrisnuNo ratings yet
- 4 - Electrolysis MCQ SolutionsDocument4 pages4 - Electrolysis MCQ SolutionsNasreen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Read These Instructions FirstDocument7 pagesRead These Instructions FirstSalman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Q & ADocument8 pagesElectrochemistry Q & AYash JoshiNo ratings yet
- SUB CHEMISTRY Date27-03-2024Document2 pagesSUB CHEMISTRY Date27-03-2024shankarbannu143No ratings yet
- SS2 CHEMISTRY TEST ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesSS2 CHEMISTRY TEST Electrolysisforthland consultingNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Section A (15 Marks)Document7 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Section A (15 Marks)chee pin wongNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 Full Notes 2Document81 pagesSem 1 Full Notes 2Shravani PakhaleNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 19 MC PracticeDocument18 pagesTopic 9 19 MC PracticeDharmesh Ramnarayan Yadav100% (1)
- SULIT 4541/1 Chemistry Paper 1 Mei 2007Document22 pagesSULIT 4541/1 Chemistry Paper 1 Mei 2007AMINNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North (2022 - 23)Document4 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North (2022 - 23)itz gamerNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document15 pagesPaper 1SitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis QuestionsDocument53 pagesElectrolysis QuestionsAahaan ShethNo ratings yet
- Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentDocument4 pagesChemical Effects of Electric Currentyuvaneshsridhar2No ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 3 (10)Document6 pagesWorksheet Chapter 3 (10)Satyam DeoraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry RevisionDocument9 pagesChemistry RevisionHING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- Class X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyDocument4 pagesClass X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyToshiGMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Read These Instructions FirstDocument6 pagesRead These Instructions FirstSalman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Electrolysisspurohit1991No ratings yet
- Class X ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesClass X ElectrolysisvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Notes On ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesNotes On Electrolysisapi-3819012No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Paper 2Document9 pagesMultiple Choice Paper 2lsstr1e2no2No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry With AnswersDocument27 pagesElectrochemistry With AnswersKris CruzNo ratings yet
- WS4,5,6,7 WK 16-20 Aug Energy and Chemicals Class 10 ZoyaDocument18 pagesWS4,5,6,7 WK 16-20 Aug Energy and Chemicals Class 10 ZoyaUsman AsmatullahNo ratings yet
- Gems Genesis: 9caieDocument4 pagesGems Genesis: 9caieBhavya darjiNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument41 pagesCHEMISTRYLindsayyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Presentation: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument118 pagesChemistry Presentation: Multiple Choice QuestionsKhiZra ShahZadNo ratings yet
- Exemplar - Chemical Effects of CurrentDocument14 pagesExemplar - Chemical Effects of CurrentnitikaNo ratings yet
- Test Topic: Atomic Structure, Formula Writing and Balancing Equation, Bonding and Structure, Redox, ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesTest Topic: Atomic Structure, Formula Writing and Balancing Equation, Bonding and Structure, Redox, ElectrolysisArham Tamim100% (1)
- Pre IG 0.14 (Night), Chemistry, Monthly TestDocument8 pagesPre IG 0.14 (Night), Chemistry, Monthly TestHtet Wai Yan AungNo ratings yet
- 2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersDocument9 pages2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersThanabalan MunuswamyNo ratings yet
- CHS Paper Final ExamDocument10 pagesCHS Paper Final Examabdulhadisaqib290No ratings yet
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current (Grade 8 CBSE)Document2 pagesChemical Effects of Electric Current (Grade 8 CBSE)mithlikesfun2No ratings yet
- Regents Review Chemical Bonding KeyDocument7 pagesRegents Review Chemical Bonding Keycitation04No ratings yet
- Chem Prac 2 (Voltaic Cell, Danielle Cell)Document7 pagesChem Prac 2 (Voltaic Cell, Danielle Cell)Joshua WeeNo ratings yet
- Cie QDocument17 pagesCie Qinternationalmakkhayar100% (1)
- HanksDocument20 pagesHanksRia MandasariNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2006 45 MinutesDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2006 45 MinutesVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Bahagian A 1. The Melting Point of A Substance X Is - 2: Diagram 3Document12 pagesBahagian A 1. The Melting Point of A Substance X Is - 2: Diagram 3ndianaoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemicalsDocument6 pagesElectricity and ChemicalsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- 5.electricity and Chemistry PDFDocument15 pages5.electricity and Chemistry PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry (Multiple Choice) QPDocument29 pagesElectricity & Chemistry (Multiple Choice) QPGunay OmarovaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 110: Paper 1 Name: - Class: - Date: - A. Multiple Choice Questions. 1Document26 pagesLesson 110: Paper 1 Name: - Class: - Date: - A. Multiple Choice Questions. 1Siapa Al AhbashiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 ElectrolysisJayadevi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- APEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFDocument2 pagesAPEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- APEF - Electrochemistry - Multiple Choice Questions - Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesAPEF - Electrochemistry - Multiple Choice Questions - Page 1 of 2alyaa sheirNo ratings yet
- APEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFDocument2 pagesAPEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFFirdausia Rahma PutriNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis MasteryDocument8 pagesElectrolysis MasteryDonald ZhuoNo ratings yet
- CHEM ASM FOR L-3 and L-4 (X)Document8 pagesCHEM ASM FOR L-3 and L-4 (X)Arsh KhanNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument4 pagesBiology NotesAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- G-7 - The Hunt NotesDocument3 pagesG-7 - The Hunt NotesAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- Mughal Empire 2Document2 pagesMughal Empire 2Aadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- General Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesGeneral Practice WorksheetAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- Module1 Cyber SafetyDocument2 pagesModule1 Cyber SafetyAadil Muhammed SajiNo ratings yet
- Oil BleedingDocument3 pagesOil BleedingDhananjay B KNo ratings yet
- Test Report of PVC Water Stop: Customer: Address: Batch No.: Na Description: Size & Quantity: StandardDocument1 pageTest Report of PVC Water Stop: Customer: Address: Batch No.: Na Description: Size & Quantity: StandardR.ThangarajNo ratings yet
- TLE M15 Learning Material For Week 10Document4 pagesTLE M15 Learning Material For Week 10ALLY ۦۦNo ratings yet
- SikaPlast 2014 NS BDDocument2 pagesSikaPlast 2014 NS BDTaposh Paul100% (1)
- Gulf Precast GRCDocument12 pagesGulf Precast GRCmujeebscribdNo ratings yet
- Tivar 882 UHMWPE PF E 02122014 PDFDocument1 pageTivar 882 UHMWPE PF E 02122014 PDFCristhian Guerrero AsmadNo ratings yet
- QC Qustion and AnswerDocument32 pagesQC Qustion and Answerrajum465100% (2)
- Bayferrox Iron Oxide PigmentDocument9 pagesBayferrox Iron Oxide PigmentMuzammal HussainNo ratings yet
- Materials Research Bulletin: Activated Carbon Aerogel Containing Graphene As Electrode Material For SupercapacitorDocument8 pagesMaterials Research Bulletin: Activated Carbon Aerogel Containing Graphene As Electrode Material For SupercapacitornagatozzNo ratings yet
- Iesc 102Document17 pagesIesc 102ecdmrcNo ratings yet
- Me Elective ModulesDocument141 pagesMe Elective ModulesBenedictus Torres MoldesNo ratings yet
- Guide For The Use of Polymers in Concrete: ACI 548.1R-97Document29 pagesGuide For The Use of Polymers in Concrete: ACI 548.1R-97Control de calidad Antamina100% (1)
- Solution 1176952Document4 pagesSolution 1176952arb88279No ratings yet
- Sotrafer-Quality Observation Complaince Tracking Record.Document63 pagesSotrafer-Quality Observation Complaince Tracking Record.mitendra singhNo ratings yet
- Shubham+Report Abcdpdf PDF To WordDocument46 pagesShubham+Report Abcdpdf PDF To WordGond AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Wa0023Document10 pagesWa0023kevin iyeseNo ratings yet
- A Bright Future For Copper Electrowinning: Michael Moats and Michael FreeDocument3 pagesA Bright Future For Copper Electrowinning: Michael Moats and Michael Freealexis diazNo ratings yet
- Plant Visits and Seminar MEGAWIDEDocument5 pagesPlant Visits and Seminar MEGAWIDEEngr SantosNo ratings yet
- D&D 5E - Metals - Dungeon Master AssistanceDocument25 pagesD&D 5E - Metals - Dungeon Master AssistanceSamuel JouveNo ratings yet
- 1 4509Document2 pages1 4509Umesh KotadiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Iron Making (PCMT4303) - 6th Sem BTech (Metallurgy)Document158 pagesLecture Notes Iron Making (PCMT4303) - 6th Sem BTech (Metallurgy)mandakini baskey100% (2)
- Coating PaintingDocument8 pagesCoating Paintingdeva0170% (2)
- 1 2 2 5 2 PDFDocument16 pages1 2 2 5 2 PDFSrinivas VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Koh Pich Construction Company Cambodia-China Polytechnic University Daily Activities ReportDocument7 pagesKoh Pich Construction Company Cambodia-China Polytechnic University Daily Activities ReportNhoek RenNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document55 pagesChem 1vishnupatel7112006No ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 5 Electricity and Chemistry - CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument65 pagesFlashcards - Topic 5 Electricity and Chemistry - CIE Chemistry IGCSEBhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- Block Elements Class 12Document15 pagesBlock Elements Class 12Åmìßhã PŕãťãpNo ratings yet
- Adobe90 3 PDFDocument150 pagesAdobe90 3 PDFDorinha AlvarengaNo ratings yet