Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integ App3
Integ App3
Uploaded by
Dem BQOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Integ App3
Integ App3
Uploaded by
Dem BQCopyright:
Available Formats
Thursday, 15 April 2021 6:16 am
INTEGRAL CALCULUS
INDEFINITE INTEGRAL
1. Evaluate
DEFINITE INTEGRAL
New Section 207 Page 1
2.
3. Evaluate:
f. g.
New Section 207 Page 2
APPLICATIONS
New Section 207 Page 3
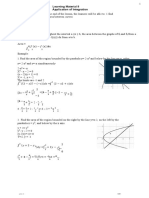
4. Find the area of the region bounded by:
a.
b. &
c. &
New Section 207 Page 4
d.
e.
f. ,
New Section 207 Page 5
5. An industrial machine generates revenue at the rate R(x) =
5000 – 20x2 pesos per year and results in cost that accumulates
at the rate of C(x) = 2000 + 10x 2 pesos per year. For how many
years (x) is the use of this machine profitable? Compute also
that net earnings generated by the machine at this period.
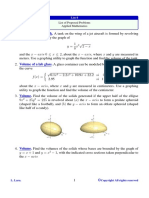
6. Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region
bounded by about (a) and (b)
.
7. Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region
bounded by about (a) and (b) .
New Section 207 Page 6
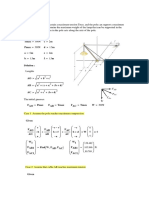
8. Find the volume formed by revolving the hyperbola xy = 6 , x =
2 and x = 4 about the x axis.
New Section 207 Page 7
9. Find the centroid of the region bounded by:
a.
b. &
New Section 207 Page 8
b. &
10. Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region
bounded by (a) about and
(b) 4 about and (c)
& about
New Section 207 Page 9
11. Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region
bounded by
a. xy =2 , x =1, x =3 and y = 0 about 2x+y+4=0.
b. +6=0 about y axis.
New Section 207 Page 10
c. =1about [a] minor axis and [b] major axis
12. Find the volume of:
a. ellipsoid =1
b. prolate spheroid =1
c. oblate spheroid =1
New Section 207 Page 11
c. oblate spheroid =1
d. sphere =1
13. Find the centroid of the solid formed by revolving the region
bounded by and about the (a)
(b)
New Section 207 Page 12
14. Find the moment of inertia and radius of gyration of the region
bounded by and with respect to (a)
15. Find the moment of inertia and radius of gyration of the
solid formed by revolving the region bounded by and
about the (a) (b) with respect to
axis of revolution.
New Section 207 Page 13
16. Find the length of the arc of the curves:
3/2
(a) from to
(b) from to
(c) from to
17. Find the area of the surface generated by revolving the arcs
(a) from from to
(b) from to
about the x and y axis.
New Section 207 Page 14
(a) from from to
(b) from to
about the x and y axis.
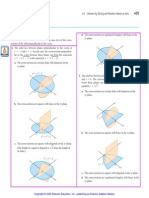
18. Find the area enclosed by:
(a)
New Section 207 Page 15
(b)
New Section 207 Page 16
(c)
19. A right triangular plate of legs 6m and 8 m is submerged
vertically in water with 6 m leg in the surface. Find the force on
one side of the plate.
20. A plate in the form of parabolic segment of base 8m and height
5m is submerged in a liquid of specific weight . If the vertex is
in the liquid surface, find the force on a face of the plate.
New Section 207 Page 17
in the liquid surface, find the force on a face of the plate.
21. The natural length of a spring is 10 cm. A force of10N will
stretch it to total length of 12cm. Find the work done in
starching it from its natural length to a total length of 18cm.
22. A conical tank of radius 4m and altitude 8m is full of liquid of
sp. weight . Determine the work done in pumping the liquid
to the top of the tank and to a point 2m above the top of the
tank.
23. A hemispherical tank of radius 8 m is full of liquid of specific
weight . Find the work done in pumping the liquid on the top
of the tank.
24. A 100 N monkey is attached to a 10m hanging rope
that weighs 4 N/m. If the monkey climbs to the rope up to the
top, find the work by the monkey.
25. A bucket weighing 20N when empty is loaded with 100N sand
and then lifted to a height of 2m at constant speed. Sand leaks
out of a hole in a bucket at a uniform rate and ¼ of this sand is
New Section 207 Page 18
25. A bucket weighing 20N when empty is loaded with 100N sand
and then lifted to a height of 2m at constant speed. Sand leaks
out of a hole in a bucket at a uniform rate and ¼ of this sand is
lost by the end of the lifting. Find the work done in the lifting
process in joules.
26. Evaluate the following:
a. 16.5 b. 15.5 c. 17.5 d. 14.5
27. Evaluate
28. A solid has a circular base of radius 4 units. Find the volume of
the solid if every plane section perpendicular to a particular
fixed diameter is
a. an equilateral triangle.
New Section 207 Page 19
b. an isosceles right triangle
New Section 207 Page 20
c. Square
and (first octant)
and
New Section 207 Page 21
29. Find the volume in the first octant under the plane x + y + z = 4
and inside the cylinder x 2+y=1.
30. Find the volume of the solid by the following surfaces
a. y+2x = 4, z = 3 and the coordinate planes.
b. x2+y=1, z= y and z = 0
New Section 207 Page 22
c. x2+z2=4 and y2+z2=4
New Section 207 Page 23
You might also like
- Class 2 Maths AssessmentDocument19 pagesClass 2 Maths Assessmentthird100% (1)
- Exercises 1 Continuum MechanicsDocument2 pagesExercises 1 Continuum MechanicsankurNo ratings yet
- Statics Problet SetDocument26 pagesStatics Problet SetXyNo ratings yet
- 20 - Volume of Revolution Disk MethodDocument2 pages20 - Volume of Revolution Disk MethodNini LobzhanidzeNo ratings yet
- Chap 7Document4 pagesChap 7김민균No ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument4 pagesIntegral CalculusCGD ReviewNo ratings yet
- CH - 6) Applications of Definite IntegralsDocument19 pagesCH - 6) Applications of Definite Integrals,冰果No ratings yet
- Handouts - Integral CalculusDocument4 pagesHandouts - Integral CalculusLexter Quitara100% (1)
- Lab 15 - Centroids of Solids and Surfaces of RevolutionDocument8 pagesLab 15 - Centroids of Solids and Surfaces of RevolutionMike JawNo ratings yet
- Volumes of RevolutionDocument7 pagesVolumes of RevolutionDegresFernandezPalomaNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus Refresher SetDocument4 pagesIntegral Calculus Refresher SetChristian Dela Vega100% (1)
- 6.4 Lecture NotesDocument3 pages6.4 Lecture NotesDevil InsideNo ratings yet
- RCD Integral Calculus 2 May 2017Document1 pageRCD Integral Calculus 2 May 2017jj012586No ratings yet
- Section 6-4: Volumes of Solids of Revolution / Method of CylindersDocument3 pagesSection 6-4: Volumes of Solids of Revolution / Method of Cylindersblack bloodNo ratings yet
- Math Chapter 6 ReviewDocument5 pagesMath Chapter 6 ReviewYena CheonNo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument4 pagesIntegral CalculusJoevhin Patrice BambicoNo ratings yet
- ClassWork1 AdvDocument4 pagesClassWork1 Advebrahimipour1360No ratings yet
- Tsu m7 Practice Problems Integral CalculusDocument1 pageTsu m7 Practice Problems Integral CalculusJAMNo ratings yet
- Volumes of Solids of Revolution PDFDocument7 pagesVolumes of Solids of Revolution PDFhamxafarrukhNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument18 pagesQuestion PaperPoovizhi ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 22Document6 pagesProblem Set 22Reynaldo Martin Coloma Jr.No ratings yet
- (Integration Course 1) SUP-4C: Solved Problem Set Sub-Topic 3Document7 pages(Integration Course 1) SUP-4C: Solved Problem Set Sub-Topic 3Aly DTNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Assignment 6Document2 pagesInstructions: Assignment 6nikko reloxNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document11 pagesUnit 3lg481476114No ratings yet
- Tutorial 12 Rev01Document6 pagesTutorial 12 Rev01Fiq DenNo ratings yet
- Geometry AppsDocument3 pagesGeometry Appsmasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Volume of A Fuel Tank.: List of Proposed Problems Applied MathematicsDocument11 pagesVolume of A Fuel Tank.: List of Proposed Problems Applied MathematicsEstrella M Correa VertizNo ratings yet
- Volume of Revolution WorksheetDocument4 pagesVolume of Revolution WorksheetWati KaNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus Refresher SetDocument4 pagesIntegral Calculus Refresher SetVincent Oriana100% (1)
- Calculus Session 2 Volume of Solid RevolutionDocument4 pagesCalculus Session 2 Volume of Solid RevolutionJennie Gail RigorNo ratings yet
- Mat 1Document16 pagesMat 1mutuvi.12231No ratings yet
- Take Home Exam in Integral Calculus Part IIDocument3 pagesTake Home Exam in Integral Calculus Part IIGing FreecsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 5 PDFDocument1 pageTutorial Week 5 PDFNaiker KaveetNo ratings yet
- Homework Integral May 2020Document7 pagesHomework Integral May 2020Jelianne Kyla TanpianNo ratings yet
- Math BookDocument5 pagesMath BookKoyel SahaNo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument2 pagesIntegral CalculusJhema RosieNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 (Answer)Document10 pagesChapter9 (Answer)Mateo FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 8 - Math 2Document3 pagesSheet 8 - Math 2Shehab Eldin SaidNo ratings yet
- Into, Lee Warren A. Id 2015-22533 Problem Set 3 - Integral CalculusDocument48 pagesInto, Lee Warren A. Id 2015-22533 Problem Set 3 - Integral CalculusLee Warren IntoNo ratings yet
- Math Work p2Document7 pagesMath Work p2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- 28 Degrees 29 MinDocument14 pages28 Degrees 29 Minkheem esconde0% (1)
- Calculus 2 Exam 1 Review (Avila)Document3 pagesCalculus 2 Exam 1 Review (Avila)Ehsan HaltermanNo ratings yet
- Surface Areas and Volumes: 11.1 Surface Area of A Right Circular ConeDocument14 pagesSurface Areas and Volumes: 11.1 Surface Area of A Right Circular ConeBhagya OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering: Pre-Board Examination (Final Exam)Document5 pagesCollege of Engineering: Pre-Board Examination (Final Exam)elijames locabaNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 - Tutorial Student SM015 2022-2023Document5 pagesTopic 10 - Tutorial Student SM015 2022-2023四叶草No ratings yet
- Ch9 Volume and Surface Area of Pyramids Cones and SpheresDocument16 pagesCh9 Volume and Surface Area of Pyramids Cones and SpheresJKNo ratings yet
- Seri Omega Private & International School: To View The Video For This Worksheet, ClickDocument26 pagesSeri Omega Private & International School: To View The Video For This Worksheet, ClickShean LimNo ratings yet
- CH (11)Document14 pagesCH (11)Md KaifNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0002 Math Module 2 PRC 3Document1 pageIMG - 0002 Math Module 2 PRC 3ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Tomas CalculatorDocument5 pagesTomas CalculatorPablo NortonNo ratings yet
- April 4 Difcal IntecalDocument2 pagesApril 4 Difcal IntecalJazz SicatNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - VolumeDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 - VolumeArianNo ratings yet
- Volumes by Integration1 TRIGONOMETRYDocument8 pagesVolumes by Integration1 TRIGONOMETRYChristopherOropelNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus RefreshDocument3 pagesDifferential Calculus RefreshKevin Pontillas100% (2)
- Integralcalcvol ExfinDocument1 pageIntegralcalcvol ExfinMaria Deborah BaluranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 5 PDFSarwan NerwayNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Mathematics Revision Exercises 1: Section ADocument10 pagesForm 2 Mathematics Revision Exercises 1: Section AJimei TanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document1 pageTutorial 8me230003066No ratings yet
- Watch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyFrom EverandWatch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyNo ratings yet
- Euclidean Geometry MemoDocument99 pagesEuclidean Geometry Memomanamelakoketso81No ratings yet
- Survey 22 Chapter Two (2) CURVEDocument22 pagesSurvey 22 Chapter Two (2) CURVENura GuyoNo ratings yet
- Circle Vocabulary PDFDocument4 pagesCircle Vocabulary PDFAngel VanzuelaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics-Units 2 and 3Document48 pagesDynamics-Units 2 and 3BaranikumarNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Geometry: Rick MirandaDocument11 pagesAlgebraic Geometry: Rick MirandaNestor Armando Marin SolanoNo ratings yet
- Nav 2 Prelim QuistionaireDocument2 pagesNav 2 Prelim QuistionaireDexter Paquibot UdtoNo ratings yet
- Dover. N. J.: Bruce BarnettDocument65 pagesDover. N. J.: Bruce BarnettNEsNo ratings yet
- ICSE Sample Paper Class 9 - Mathematics - # 1 Questions - Topperlearning PDFDocument5 pagesICSE Sample Paper Class 9 - Mathematics - # 1 Questions - Topperlearning PDFAvinash Dubey100% (1)
- SL Analysis Formula Booklet PDFDocument14 pagesSL Analysis Formula Booklet PDFMATHVISION STUDY MATERIALNo ratings yet
- Fowles 08Document18 pagesFowles 08jjmaldonisNo ratings yet
- Year 9 5.3 Mathematics Major Assessment TaskDocument8 pagesYear 9 5.3 Mathematics Major Assessment TaskHenry ChenNo ratings yet
- String Theory NotesDocument38 pagesString Theory NotesMoataz EmamNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument18 pagesMaths Projectsujay giriNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument11 pagesAlgebraPRAKHAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- ME320 Professor John M. Cimbala: Recall Our Fluid Statics EquationDocument9 pagesME320 Professor John M. Cimbala: Recall Our Fluid Statics EquationSudesh PowarNo ratings yet
- Caed PDF Notes I SemDocument161 pagesCaed PDF Notes I SemjovanNo ratings yet
- 12 AngiDocument4 pages12 AngiGunjee GunjeeNo ratings yet
- Spherical MirrorsDocument14 pagesSpherical Mirrorssyaoran26No ratings yet
- 16 LM9 Integral Calculus Area Between CurvesDocument2 pages16 LM9 Integral Calculus Area Between CurvesDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Functions and Graphs: Basic Techniques of Sketching The Graph and Some Real Life ApplicationsDocument15 pagesFunctions and Graphs: Basic Techniques of Sketching The Graph and Some Real Life ApplicationsMarian GhuzlanNo ratings yet
- 11.1: Rolling Motion - Physics LibreTextsDocument8 pages11.1: Rolling Motion - Physics LibreTextsAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- FGvolume7 (Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 2007) PDFDocument254 pagesFGvolume7 (Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 2007) PDFTirtharaj BasuNo ratings yet
- 11 Rotation and TorqueDocument94 pages11 Rotation and TorquePutri S100% (1)
- Lowk Persp Interp TechrepDocument2 pagesLowk Persp Interp TechrepAnand BalajiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Exercise: y I W y C X I W W WDocument2 pagesModule 2 - Exercise: y I W y C X I W W WTrigger DineshNo ratings yet
- TurboCad PDFDocument730 pagesTurboCad PDFKawuma AbelNo ratings yet
- ACT Math Formula Cheat Sheet 2021Document14 pagesACT Math Formula Cheat Sheet 2021AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- ch03c PDFDocument36 pagesch03c PDFAnonymous rpcAOp0% (1)