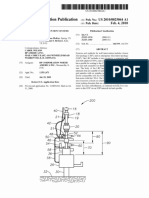
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EDP & LRP - Modeling
EDP & LRP - Modeling
Uploaded by
Jerome LIKIBIOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EDP & LRP - Modeling
EDP & LRP - Modeling
Uploaded by
Jerome LIKIBICopyright:
Available Formats
SubSea Modeling Example
by Gerrit Muller University of South-Eastern Norway-NISE
e-mail: gaudisite@gmail.com
www.gaudisite.nl
Abstract
This presentation provides an example of modeling in the subsea domain.
perform
assembly,
workover
functional test
operations
1 7 rig
retrieve coil
run
tubing and
EDP/LRP TF
wireline BOP
2 wireline
unhook coil coil tubing BOP
run risers tubing and
wireline BOP SFT WOCS
3 8
hook up SFT ROV assisted vessel or
Distribution and TF disconnect platform
August 21, 2020
4
move away from
move above well
well
riser
5 9
ROV assisted retrieve SFT and
This article or presentation is written as part of the Gaudí project. The Gaudí project
status: preliminary
connect TF
10
hook up coil
philosophy is to improve by obtaining frequent feedback. Frequent feedback is pursued by an 6
tubing and
wireline BOP
system function
retrieve risers
11
EDP
LRP
draft
retrieve
open creation process. This document is published as intermediate or nearly mature version and connection
seal test
EDP/LRP
12
XT
well
head
run coil tubing
to get feedback. Further distribution is allowed as long as the document remains complete 7
and wireline
disassembly
well
and unchanged. version: 0.5
Colophon
The examples in this presentation are based on the work of
SEMA participants: Martin Moberga, Tormod Stranda, Vazgen
Karlsenf, and Damien Weef, and the master project paper by
Dag Jostein Kleverf. Sensitive and confidential information is
removed or obfuscated.
All mistakes are to be blamed to the author.
Gunnar Berge stimulated the creation of a subsea example.
a
Aker Solutions
f
FMC Technologies
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
2 Gerrit Muller SSMEcolophon
Story: Workover Anno 2015
On September 4, Captain Frode Johansen was discussing the plans for the
upcoming workover of South Gulfaks (see http://www.npd.no/en/Publications/
Facts/Facts-2011/Chapter-10/Gullfaks-Sor-/) with his crew. Their vessel had been
well 1 out of operation for recertification of the equipment much longer than anticipated,
so there was a lot of pressure from Statoil on their schedule. Statoil sees
harbor diminishing production in several of the wells, so workover operations are urgent.
With the upcoming fall and winter storms, Frode hopes to finish the next three
workover operations in a new record time. The equipment supplier had not only
recertified all equipment, but also renovated parts of the riser system allowing for
faster deployment and retrieval. The supplier tested and installed equipment in
Horten. Tomorrow they will arrive in Sotra, their company support station. Here
they will stock their fuel, food, coiled tubing, and other material.
The weather forecast shows a depression close to Iceland that moves slowly in
Norway’s direction. If they can start deployment of the riser on September 7, then
they probably finish the workover before the storm associated with the depression
is too severe.
Since the schedule is so tight, the captain proposes to preassemble the riser
system as far as possible while traveling. In addition, the accumulators can already
be charged. The captain asks the foreman to make a schedule and to allocate
tasks to the crew. Safety will be a key attention point, since working with such
equipment with sea state 3 provides risks.
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
3 Gerrit Muller SSMEstory
Annotated Physical Diagram of WorkOver System
rig
tension frame connects TF wireline
riser to rig tension system
coil tubing BOP
provides well control
surface flow tree
provides well control SFT WOCS work over control system
monitoring and control
vessel or of subsea installation
platform
riser
conduit for running
tools to well
ROV remotely operated vehicle
one for observation
emergency disconnect package
ROV one for operation
provides disconnect function EDP
lower riser package
LRP provides well control function
Xmas tree
provides well control XT
well structural and pressure-
head containing interface
well
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
4 Gerrit Muller SSMEworkoverPhysicalAnnotated
Typical Workover Operation
perform
assembly,
workover
functional test
operations
1 7 rig
retrieve coil
run
tubing and
EDP/LRP TF
wireline BOP
2 wireline
unhook coil coil tubing BOP
run risers tubing and
wireline BOP SFT WOCS
3 8
hook up SFT ROV assisted vessel or
and TF disconnect platform
4
move away from
move above well
well
riser
5 9
ROV assisted retrieve SFT and
connect TF
10
hook up coil
tubing and retrieve risers EDP
wireline BOP
6 11 LRP
system function
retrieve
and connection XT
EDP/LRP
seal test well
12
head
run coil tubing
disassembly
and wireline
7 well
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
5 Gerrit Muller SSMEtypicalWorkoverOperation
Typical Workover Operation as Cartoon
rig rig rig rig rig rig
1 TF 2 TF 3 TF 4 5 6
TF TF TF
EDP SFT SFT SFT
LRP WOCS WOCS WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS
vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or
platform platform platform platform platform platform
EDP
LRP
riser riser
EDP EDP
LRP LRP EDP ROV EDP
LRP LRP
ROV
XT XT XT XT XT XT
well well well well well well
head head head head head head
well well well well well well
7 rig
8 rig 9 rig
10 rig
TF 11 rig
TF 12 rig
TF
TF TF TF
SFT SFT EDP SFT
SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS WOCS WOCS LRP WOCS
vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or
platform platform platform platform platform platform
EDP
LRP
riser riser
EDP EDP
EDP EDP LRP LRP
LRP LRP ROV
XT XT XT XT XT XT
well well well well well well
head head head head head head
well well well well well well
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
6 Gerrit Muller SSMEtypicalWorkoverOperationCartoon
Typical Workover Operation on Timeline
assumptions:
running and retrieving risers: 50m/hr
running and retrieving coiled tubing/wireline: 100m/hr
depth: 300m
hook up coiled tubing/wireline
retrieve coiled tubing/wireline
run coiled tubing/wireline
ROV assisted connect
function and seal test
move away from well
hook up SFT and TF
retrieve SFT and TF
assembly and test
retrieve EDP/LRP
move above well
retrieve risers
run EDP/LRP
disassembly
run risers
actual workover operation
48 hrs
preparation 36 hrs finishing 27 hrs
resume
stop production deferred operation 62 hrs
production
24 48 72 96
hours
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
7 Gerrit Muller SSMEtypicalWorkoverOperationTimeline
Typical Workover Operation Context
zero order model
tworkover =
ttransportation + tpreparation+ tworkover+
well 3
well 2 tfinishing
well 1 first order model
tworkover =
harbor ttransportation + tpreparation+ tworkover+
tdisruption + tfinishing
workover well 1 workover well 2
finishing 24 hrs
finishing 24 hrs
transportation
transportation
preparation
preparation
actual
reconnect
continued
workover
workover
24 hrs
32 hrs
24 hrs
32 hrs
storm
workover
operation
48 hrs
disruption
5 10
days
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
8 Gerrit Muller SSMEtypicalWorkoverOperationContext
0-order Cost Model Workover Operation
workover cost per day assumed cost (MNoK) workover duration estimated duration (hours)
platform, rig 2 transportation 24 production loss
equipment 0.2 preparation 36 6
crew 0.1 workover 48 48
total 2.3 MNoK/day finishing 27 8
total 135 (5.6 days) 62 (2.6 days)
deferred operation per day assumed cost (MNoK)
production delay 0.1
ongoing cost operation 0.2
total 0.3 MNoK/day
cost = costworkover/day * tworkover + costdeferred op./day * tdeferred op.
~= 2.3 * 5.6 + 0.3 * 2.6 ~= 14 MNoK / workover
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
9 Gerrit Muller SSMEcostModelWorkoverOperation
Disruption Workover Operation
rig rig rig
disruption, 7 rig
7a 7b 7c
e.g. storm TF TF TF TF
7 SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS
vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or
platform platform platform platform
retract wireline
shut down valves riser riser riser riser
control t&p well
7a EDP EDP EDP
EDP
disconnect EDP LRP LRP LRP
ROV
LRP
XT XT XT XT
move away well well well well
perform 7b head head head head
workover wait well well well well
operations
wait for resolution
continue workover
move above well
move above well
of disruption
reconnect EDP
disruption
move away
workover
reconnect
control t&p well
open valves
7c
run wireline
24 48
hours
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
10 Gerrit Muller SSMEdisruptionWorkoverOperation
1st order Cost Model Workover Operation
workover cost per day assumed cost (MNoK) workover duration estimated duration (hours)
platform, rig 2 production loss
workover 0-order 135 (5.6 days) 62 (2.6 days)
equipment 0.2
average disruption
crew 0.1 duration 72
total 2.3 MNoK/day overhead 11
disruption frequency 0.3
deferred operation per day assumed cost (MNoK) 1st order disruption 83*0.3=
production delay 0.1 correction 27 27
ongoing cost operation 0.2
total 162 (6.7 days) 89 (3.7 days)
total 0.3 MNoK/day
1st order cost = costworkover/day * tworkover + costdeferred op./day * tdeferred op.
~= 2.3 * 6.7 + 0.3 * 3.7 ~= 16.5 MNoK / workover
0-order cost ~= 14 MNoK ; disruption cost ~= 2.5 MNoK
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
11 Gerrit Muller SSMEcostModelWorkoverOperation1stOrder
A3 Architecture Overview
This A3 based on the work of SEMA participants: Martin Moberga, Tormod Stranda, Vazgen Karlsenf, and Damien Weef,
Workover operation; architecture overview and the master project paper by Dag Jostein Kleverf. aAker Solutions, f FMC Technologies version 2.2 Gerrit Muller
workover workover workflow
workflow 1 rig
TF 2 rig
TF 3 rig
TF 4 rig 5 rig 6 rig 7 rig 8 rig 9 rig 10 rig
TF
11 rig
TF
12 rig
TF
TF TF TF TF TF TF
EDP SFT SFT SFT SFT SFT EDP SFT
LRP WOCS WOCS WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS WOCS WOCS LRP WOCS
assembly, vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or
functional test platform platform platform platform platform platform platform platform platform platform platform platform
EDP EDP
1 LRP LRP
riser riser riser riser
run
EDP/LRP EDP EDP
EDP EDP
2 LRP LRP EDP ROV EDP EDP EDP LRP LRP
LRP LRP LRP LRP ROV
ROV
XT XT XT XT XT XT XT XT XT XT XT XT
run risers well well well well well well well well well well well well
head head head head head head head head head head head head
3 well well well well well well well well well well well well
hook up SFT and
TF disruption physical model rig
7 rig 7a rig 7b rig 7c rig
4 workflow TF TF TF
TF
move above well tension frame connects TF
SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS SFT WOCS
riser to rig tension system wireline
retract wireline vessel or vessel or vessel or vessel or
5 platform platform platform platform
coil tubing BOP
provides well control
ROV assisted shut down valves
connect riser riser riser surface flow tree
provides well control SFT WOCS work over control system
control t&p well monitoring and control
hook up coil tubing 7a EDP EDP EDP EDP vessel or of subsea installation
ROV
and wireline BOP disconnect EDP LRP LRP LRP LRP platform
XT XT XT XT
well well well well
6 head head head
system function head
move away well well well well
and connection
seal test 7b disruption workflow riser
wait conduit for running
run coil tubing and tools to well
wireline move above well disruption timeline
resolution of
7
move above
disruption
disruption
ROV
move away
workover
remotely operated vehicle
wait for
workover
continue
reconnect EDP
reconnect
perform workover
well
operations
one for observation
emergency disconnect package one for operation
control t&p well ROV
7 provides disconnect function EDP
retrieve coil tubing lower riser package
and wireline BOP open valves LRP provides well control function
7c Xmas tree
run wireline provides well control XT
unhook coil tubing
and wireline BOP 24 48 well
hours structural and pressure-
8 head containing interface
ROV assisted
workover timeline
hook up coiled tubing/wireline
retrieve coiled tubing/wireline
disconnect well
assumptions:
run coiled tubing/wireline
ROV assisted connect
move away from running and retrieving risers: 50m/hr
function and seal test
move away from well
hook up SFT and TF
retrieve SFT and TF
well running and retrieving coiled tubing/wireline: 100m/hr
0-order workover cost estimate
assembly and test
retrieve EDP/LRP
move above well
9
depth: 300m workover cost per day assumed cost (MNoK) workover duration estimated duration (hours)
retrieve risers
run EDP/LRP
retrieve SFT and
disassembly
platform, rig 2 transportation 24 production loss
TF
run risers
10 equipment 0.2 preparation 36 6
actual workover operation crew 0.1 workover 48
48
retrieve risers 48 hrs
total 2.3 MNoK/day finishing 27 8
11 deferred operation per day assumed cost (MNoK) total 135 (5.6 days) 62 (2.6 days)
retrieve production delay 0.1
EDP/LRP preparation 36 hrs finishing 27 hrs
ongoing cost operation 0.2
12 resume
stop production deferred operation 62 hrs total 0.3 MNoK/day
production
disassembly
cost = costworkover/day * tworkover + costdeferred op./day * tdeferred op.
24 48 72 96 ~= 2.3 * 5.6 + 0.3 * 2.6 ~= 14 MNoK / workover
hours
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
12 Gerrit Muller SSMEoverviewA3
Levels of A3s
contextual workover
A3AO operations
workover workover
workover A3AO topic
duration health safety
robustness of interest
and cost environment
navigation
A3AOs aspect ROV connect and barrier and
and
elaboration handling disconnect containment
positioning
SubSea Modeling Example version: 0.5
August 21, 2020
13 Gerrit Muller SSMElevelsOfA3s
You might also like
- Characters of Wisdom - Taoist Tales of The Acupuncture Points (PDFDrive) PDFDocument563 pagesCharacters of Wisdom - Taoist Tales of The Acupuncture Points (PDFDrive) PDFProf. Ivo Sampaio100% (3)
- Digitronf Single Connectors Rev4Document42 pagesDigitronf Single Connectors Rev4zym3344No ratings yet
- Barry S. Fogel, Donna B. Greenberg-Psychiatric Care of The Medical Patient-Oxford University Press (2015) PDFDocument1,813 pagesBarry S. Fogel, Donna B. Greenberg-Psychiatric Care of The Medical Patient-Oxford University Press (2015) PDFhalamadrid77100% (2)
- MS-700 Subsea Wellhead System Nov 11Document108 pagesMS-700 Subsea Wellhead System Nov 11New Auto TV100% (1)
- CJ46-X100-D: Platform ParticularsDocument3 pagesCJ46-X100-D: Platform ParticularsAshwani YadavNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Education of NursingDocument33 pagesOutcome Based Education of NursingAndrea Bone100% (1)
- Oilfield Services - Convention - 2018Document71 pagesOilfield Services - Convention - 2018Jerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Lamprell Rig Services CatalogDocument2 pagesLamprell Rig Services CatalogtxcrudeNo ratings yet
- IWOCS Brochure Landscape A4Document11 pagesIWOCS Brochure Landscape A4魏永涛No ratings yet
- Horizontalbore: Subsea TreeDocument8 pagesHorizontalbore: Subsea TreeJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- EDP & LRP - DescriptionDocument22 pagesEDP & LRP - DescriptionJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- ATWOOD Advantage BrochureDocument2 pagesATWOOD Advantage Brochurespong1ertzNo ratings yet
- Seaharvest BrochureDocument6 pagesSeaharvest BrochurealaddinNo ratings yet
- Santos Sole: Location: Gippsland BasinDocument6 pagesSantos Sole: Location: Gippsland BasinKaruppasamy GurusamyNo ratings yet
- Oss Subsea Connectors BRDocument12 pagesOss Subsea Connectors BRVISHNU GAIDHANINo ratings yet
- Well Intervention - Systems & MethodesDocument19 pagesWell Intervention - Systems & MethodesJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Rig Selection and Comparison of Top Drive and Rotary Table Drive Systems For Cost Effective Drilling Projects in Kenya UNU-GTP-2009-08Document20 pagesRig Selection and Comparison of Top Drive and Rotary Table Drive Systems For Cost Effective Drilling Projects in Kenya UNU-GTP-2009-08zouke2002No ratings yet
- VetcoGray S-Series SVXTDocument2 pagesVetcoGray S-Series SVXTarchitectintxNo ratings yet
- Prem Singh ResumeDocument3 pagesPrem Singh ResumezeeshanNo ratings yet
- Subsea EngineeringDocument16 pagesSubsea EngineeringMae JoyceNo ratings yet
- DX ConnectorDocument8 pagesDX ConnectorpooNo ratings yet
- Through-Tubing Rotary Drilling (TTRD) PDFDocument27 pagesThrough-Tubing Rotary Drilling (TTRD) PDFAnwarNo ratings yet
- Ga AhtsDocument1 pageGa AhtsMuhammad Elvan NawawiNo ratings yet
- SubSea Controls InspectorDocument2 pagesSubSea Controls Inspectorxiexienin23No ratings yet
- Challenges, Lessons Learned, and Successful Implementations of Multilateral Completion Technology Offshore Abu DhabiDocument10 pagesChallenges, Lessons Learned, and Successful Implementations of Multilateral Completion Technology Offshore Abu Dhabimoh kadNo ratings yet
- Subsea Single Bolt ConnectorsDocument12 pagesSubsea Single Bolt ConnectorsPedro DutraNo ratings yet
- IWOCSDocument4 pagesIWOCSrcaletaNo ratings yet
- PROSERV Subsea Control ModuleDocument12 pagesPROSERV Subsea Control ModuleJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- STREICHER Datenblatt Tiefbohranlage VDD 200 RUDocument4 pagesSTREICHER Datenblatt Tiefbohranlage VDD 200 RUShuriqqNo ratings yet
- Kongsberg Subsea Storage UnitDocument18 pagesKongsberg Subsea Storage UnitZhiyong ShanNo ratings yet
- Jack Up Drilling RigDocument2 pagesJack Up Drilling RigMaría MarquinaNo ratings yet
- 003 - Presentation From Nabors Drilling PDFDocument16 pages003 - Presentation From Nabors Drilling PDFVi Et100% (1)
- EXP Subsea A4Document12 pagesEXP Subsea A4Martinus LuckyantoNo ratings yet
- Expro CoilHose Well Intervention - 29april2021Document19 pagesExpro CoilHose Well Intervention - 29april2021Tong ChaipanyakulNo ratings yet
- Equinor Capping StackDocument5 pagesEquinor Capping StackHumisar Alprialdus SinagaNo ratings yet
- National Oilwell Varco v. Omron Oilfield & MarineDocument4 pagesNational Oilwell Varco v. Omron Oilfield & MarinePriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power Unit (HPU) : Product DefinitionDocument4 pagesHydraulic Power Unit (HPU) : Product DefinitionJay JayNo ratings yet
- Agito Simulation of Deep Water SystemsDocument3 pagesAgito Simulation of Deep Water Systemsiky77No ratings yet
- C200-047-09-Man Mha 2.125Document18 pagesC200-047-09-Man Mha 2.125Virnando Nainggolan100% (1)
- ST&R ROV Workover Control System (RWOCS)Document2 pagesST&R ROV Workover Control System (RWOCS)魏永涛No ratings yet
- Optimisaton of Static Characteristics of A Lazy Wave RizerDocument23 pagesOptimisaton of Static Characteristics of A Lazy Wave RizerAbiodunAremuOliyideNo ratings yet
- The Hytorc Nut Replaces Fasteners, Minimizes Stresses, and Covers A Wide Range of Sizes and Applications Tn-Series Hytorc NutDocument4 pagesThe Hytorc Nut Replaces Fasteners, Minimizes Stresses, and Covers A Wide Range of Sizes and Applications Tn-Series Hytorc NutRajiv GandhiNo ratings yet
- MHD55148 BOP Catalog 052008Document20 pagesMHD55148 BOP Catalog 052008jlmunozv100% (4)
- Deepwater Pipelay Capabilities: Company UpdateDocument21 pagesDeepwater Pipelay Capabilities: Company Updatecontenido100% (1)
- PROSERV Subsea Ctrls Project RefDocument81 pagesPROSERV Subsea Ctrls Project RefJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- OTC 24461 Advances in Autonomous Deepwater InspectionDocument9 pagesOTC 24461 Advances in Autonomous Deepwater InspectionThomas ThomasNo ratings yet
- 2340 Drilling Bu PresenDocument19 pages2340 Drilling Bu Presenmr3478No ratings yet
- SDX Connector System PDFDocument8 pagesSDX Connector System PDFRavi Chaitanya VelamarthyNo ratings yet
- BilcoDocument16 pagesBilcoruloNo ratings yet
- T 19Document1 pageT 19Richard EVNo ratings yet
- APS Rotary PulserDocument2 pagesAPS Rotary PulserWajid KhattakNo ratings yet
- Specialty Connectors PipeDocument19 pagesSpecialty Connectors PipeBhai RamaNo ratings yet
- 151 - GustoMSC 08.107 - Hydr. Jacking System HPEDocument2 pages151 - GustoMSC 08.107 - Hydr. Jacking System HPEAdarsh D. Karki100% (1)
- Drill Bits: Types and SelectionsDocument54 pagesDrill Bits: Types and SelectionssatyajitchowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Drawwing RigDocument31 pagesDrawwing Rigfarikh ibnuNo ratings yet
- Subsea Ngee Ann Primer CourseDocument6 pagesSubsea Ngee Ann Primer CoursescribdmingNo ratings yet
- Cementing Equipments 2017 CMT 001 REVDocument19 pagesCementing Equipments 2017 CMT 001 REVahada putratamaNo ratings yet
- Subsea MPFMDocument15 pagesSubsea MPFMTg TarroNo ratings yet
- Abb Jacking ControlDocument4 pagesAbb Jacking ControlAleksey Bondar100% (1)
- 30 Urban CruiserDocument1 page30 Urban CruiserHEMIL ROBERTO RODRIGUEZ HERRERANo ratings yet
- Comptector & Chiller (Cdu) Controller (Fx32C Series) : Precaution For UseDocument5 pagesComptector & Chiller (Cdu) Controller (Fx32C Series) : Precaution For UseFcma0903100% (1)
- Subsea Drilling SystemsDocument12 pagesSubsea Drilling SystemsJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Esanda 2020 Course CalendarDocument5 pagesEsanda 2020 Course CalendarJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- PROSERV Subsea Ctrls Project RefDocument81 pagesPROSERV Subsea Ctrls Project RefJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- 3 - RCM - An Intro To RCM by Ali Reza ManiDocument35 pages3 - RCM - An Intro To RCM by Ali Reza ManiJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Well Intervention - Systems & MethodesDocument19 pagesWell Intervention - Systems & MethodesJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Well Intervention - WOS Technical SafetyDocument11 pagesWell Intervention - WOS Technical SafetyJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Well Intervention - WorkOver PresentationDocument20 pagesWell Intervention - WorkOver PresentationJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- EDP & LRP - DescriptionDocument22 pagesEDP & LRP - DescriptionJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- PROSERV Subsea Control ModuleDocument12 pagesPROSERV Subsea Control ModuleJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- EHCS - Variable Displacement MachinesDocument9 pagesEHCS - Variable Displacement MachinesJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Introduction Offshore EngineeringDocument58 pagesIntroduction Offshore EngineeringJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- EHCS - Flying Vehicle Under Failure ConditionsDocument17 pagesEHCS - Flying Vehicle Under Failure ConditionsJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Horizontalbore: Subsea TreeDocument8 pagesHorizontalbore: Subsea TreeJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Integrated Formation Evaluation Clastic Carbonate ReservoirsDocument4 pagesIntegrated Formation Evaluation Clastic Carbonate ReservoirsJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Applied Technology Petroleum Engineering: N/A N/ADocument2 pagesBachelor of Applied Technology Petroleum Engineering: N/A N/AJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Wireline Operations Techniques: Approach Into Slick, Braided & Electrical Line Equipment, Tools & ApplicationsDocument4 pagesWireline Operations Techniques: Approach Into Slick, Braided & Electrical Line Equipment, Tools & ApplicationsJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Certificate in Subsea EngineeringDocument6 pagesSyllabus: Certificate in Subsea EngineeringJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Oilfield Services - Salary Rate - 2018Document1 pageOilfield Services - Salary Rate - 2018Jerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Advanced Well Log InterpretationDocument4 pagesAdvanced Well Log InterpretationJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Well Interventions: Completion Design & Slick Line/Coiled Tubing Well Interventions TechniquesDocument4 pagesWell Interventions: Completion Design & Slick Line/Coiled Tubing Well Interventions TechniquesJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- Army TM 9-2320-289-20P Air Force To 36a12-1a-2084-1 Marine Corps TM 2320-20P/3Document724 pagesArmy TM 9-2320-289-20P Air Force To 36a12-1a-2084-1 Marine Corps TM 2320-20P/3Albaro AguirreNo ratings yet
- Isp 3520oasDocument2 pagesIsp 3520oashekele9111No ratings yet
- M CHAT ScoringDocument4 pagesM CHAT ScoringClaritaNo ratings yet
- Specification For Solid Surfacing Welding Rods and ElectrodesDocument23 pagesSpecification For Solid Surfacing Welding Rods and ElectrodesDmitriyNo ratings yet
- Cosh CERT - FACILITATORDocument7 pagesCosh CERT - FACILITATORRedentor B. Rayla100% (1)
- RNA PowerPointDocument20 pagesRNA PowerPointAnki0391100% (1)
- Quiz AssessmentDocument5 pagesQuiz Assessmentshandy92No ratings yet
- Field Trip Permission Slip FillableDocument1 pageField Trip Permission Slip Fillabletvtcf286v9No ratings yet
- Vocabulary BuildingDocument5 pagesVocabulary BuildingSaima AbediNo ratings yet
- Compliance PDFDocument20 pagesCompliance PDFSUBHANKAR PALNo ratings yet
- PPS Steam Boiler Operation and AuxiliariesDocument9 pagesPPS Steam Boiler Operation and AuxiliariesAraNo ratings yet
- Nepal Macroeconomic Update 202209 PDFDocument30 pagesNepal Macroeconomic Update 202209 PDFRajendra NeupaneNo ratings yet
- GE Compact-Airway-Modules-Caiovx-And-CovxDocument4 pagesGE Compact-Airway-Modules-Caiovx-And-CovxmalucNo ratings yet
- Test Reliability 2Document47 pagesTest Reliability 2Mary Ann AmbitaNo ratings yet
- 7" Woc TRSCSSSV Subassemblies Make Up and Test Procedure: Doc. No. SP19-3Y-00-CP-PR-001-00Document7 pages7" Woc TRSCSSSV Subassemblies Make Up and Test Procedure: Doc. No. SP19-3Y-00-CP-PR-001-00Mehdi NorouziNo ratings yet
- X350 ManualDocument40 pagesX350 Manualdika anggaraNo ratings yet
- Oxygen MSDSDocument9 pagesOxygen MSDSariNo ratings yet
- Educational Pre-Testing (KROK-2) : Quiz NavigationDocument1 pageEducational Pre-Testing (KROK-2) : Quiz NavigationMohammad MohyeddienNo ratings yet
- ADD2407217Document2 pagesADD2407217SUMIT PATELNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ielts 15 - Test 1 Reading VocabularyDocument3 pagesCambridge Ielts 15 - Test 1 Reading Vocabularynhq010607No ratings yet
- Managing Remuneration MCQDocument5 pagesManaging Remuneration MCQlol100% (1)
- Role of Microorganisms in Petroleum IndustryDocument4 pagesRole of Microorganisms in Petroleum Industrysidraali786137No ratings yet
- Simon IeltsDocument16 pagesSimon IeltsNga Hương Sô ThịNo ratings yet
- Developing and Using HR Audit ToolsDocument32 pagesDeveloping and Using HR Audit ToolsJablack Angola MugabeNo ratings yet
- MCCB Catalogue PDFDocument84 pagesMCCB Catalogue PDFSudipta ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument23 pagesSpecial Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActMyk Rthur DavidNo ratings yet
- Ufc 3 600 01Document132 pagesUfc 3 600 01Juan RomeroNo ratings yet