Professional Documents
Culture Documents
002 - Periodic Table Class Notes Low
002 - Periodic Table Class Notes Low
Uploaded by
Emad AlomariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
002 - Periodic Table Class Notes Low
002 - Periodic Table Class Notes Low
Uploaded by
Emad AlomariCopyright:
Available Formats
Class Notes
Introduction
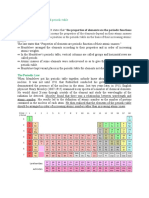
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic
number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties, whose structure shows
periodic trends. Generally, within one row (period) the elements are metals to the left, and non-
metals to the right, with the elements having similar chemical behaviors placed in the same column.
Table rows are commonly called periods and columns are called groups. Six groups have accepted names
as well as assigned numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18 are the
noble gases. Also displayed are four simple rectangular areas or blocks associated with the filling of
different atomic orbitals.
Electronic Structure of Atoms
The organization of the periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the various element
properties, but also the predicted chemical properties and behaviors of undiscovered or newly
synthesized elements. Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev was the first to publish a recognizable periodic
table in 1869, developed mainly to illustrate periodic trends of the then-known elements. He also
predicted some properties of unidentified elements that were expected to fill gaps within the table. Most
of his forecasts proved to be correct. Mendeleev's idea has been slowly expanded and refined with the
discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain
chemical behavior. The modern periodic table now provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical
reactions, and continues to be widely used in chemistry, nuclear physics and other sciences.
Atomic Theory
The organization of the periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the various element
properties, but also the predicted chemical properties and behaviors of undiscovered or newly
synthesized elements. Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev was the first to publish a recognizable periodic
table in 1869, developed mainly to illustrate periodic trends of the then-known elements. He also
predicted some properties of unidentified elements that were expected to fill gaps within the table. Most
of his forecasts proved to be correct. Mendeleev's idea has been slowly expanded and refined with the
discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain
chemical behavior. The modern periodic table now provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical
reactions, and continues to be widely used in chemistry, nuclear physics and other sciences.
Periodic Table Structure
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic
number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties, whose structure shows
periodic trends. Generally, within one row (period) the elements are metals to the left, and non-
metals to the right, with the elements having similar chemical behaviors placed in the same column.
Table rows are commonly called periods and columns are called groups. Six groups have accepted names
as well as assigned numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18 are the
noble gases. Also displayed are four simple rectangular areas or blocks associated with the filling of
different atomic orbitals
You might also like
- The Periodic Table: Grade 10 (ICSE)Document21 pagesThe Periodic Table: Grade 10 (ICSE)Kirthika SNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 7.2.3.5 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine A UDP DNS Capture - ILMDocument6 pages7.2.3.5 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine A UDP DNS Capture - ILMRuy Pequeno CidNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument13 pagesPeriodic TablesemantotanzimahmedNo ratings yet
- 001 Periodic Table ArabicDocument2 pages001 Periodic Table ArabicEmad AlomariNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic TableNorbert MedvésNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document58 pagesChapter 13oninNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Is A Tabular Arrangement of The Chemical ElementsDocument1 pageThe Periodic Table Is A Tabular Arrangement of The Chemical ElementsKaycin Duzon SorianoNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument70 pagesPeriodic TableRicardo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Element and Periodicity in PropertiseDocument27 pagesClassification of Element and Periodicity in PropertiseAditya chauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry T1U3 EssayDocument3 pagesChemistry T1U3 EssaymwgthrowawayaccNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table of Elementsmichael tenajerosNo ratings yet
- 1stch-5 Chem PartiDocument19 pages1stch-5 Chem PartiShaheen parweenNo ratings yet
- On Chemistry Sidpreet Singh Class XDocument24 pagesOn Chemistry Sidpreet Singh Class XSidpreet SandhuNo ratings yet
- MendeleevDocument25 pagesMendeleevapi-239694539No ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Atomic Number Electron Configurations Chemical Properties BlocksDocument1 pageChemical Elements Atomic Number Electron Configurations Chemical Properties BlocksLudmila GoguNo ratings yet
- Who Invented The Periodic TableDocument1 pageWho Invented The Periodic TableJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument11 pagesPeriodic Table of Elementsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Notesnitin kapriNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Perodic Classification Chapter 5 NotesDocument13 pagesClass 10 Science Perodic Classification Chapter 5 NotescxsdvNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic Table PPT 1Document17 pagesChemistry Periodic Table PPT 1Hazel ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2 - Module 2 Periodic Table of ElementsDocument4 pagesCHEM 2 - Module 2 Periodic Table of ElementsMicah BlazaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocument3 pagesPeriodic Table and PeriodicityEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument3 pagesPeriodic TableMurali SambhuNo ratings yet
- International: India SchoolDocument18 pagesInternational: India SchoolAkash MondalNo ratings yet
- Early Attempts To Arrange ElementsDocument4 pagesEarly Attempts To Arrange ElementsJaninah Ali PirogonganNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic TableAdrian YangaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument47 pagesPeriodic Table of Elementsbrent tobiasNo ratings yet
- History of Peiodic Table - Gen ChemDocument2 pagesHistory of Peiodic Table - Gen ChemSai Adrienne RealubitNo ratings yet
- The History of The Periodic Table of Elements: Gwyneth D. GocoDocument16 pagesThe History of The Periodic Table of Elements: Gwyneth D. GocoMelissa MalicdemNo ratings yet
- 1 STEC Periodicity of The ElementsDocument20 pages1 STEC Periodicity of The ElementsPrince HasanNo ratings yet
- The Modern Periodic Table: Cosmic Chemistry: Understanding ElementsDocument1 pageThe Modern Periodic Table: Cosmic Chemistry: Understanding ElementsHarshaNo ratings yet
- History of Periodic Table DevelopmentDocument5 pagesHistory of Periodic Table Developmenthafizah_90No ratings yet
- Lectures Part 1Document87 pagesLectures Part 1anomaniNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Revision NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 5 Revision NotesRaman TiwariNo ratings yet
- ? Lesson 1Document10 pages? Lesson 1Chrisshalyn Sy PinedaNo ratings yet
- The Development of The Periodic Table (Updated)Document23 pagesThe Development of The Periodic Table (Updated)Mariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4:the Periodic Table of Elements: Group 1 - Afiq Rifqal - Nicole Ho - Raihan - Bharath - Tuck HoeDocument11 pagesChapter 4:the Periodic Table of Elements: Group 1 - Afiq Rifqal - Nicole Ho - Raihan - Bharath - Tuck HoeShafeeqah FadzilNo ratings yet
- Scientist: The Contributions of The in The Development of The PeriodicDocument16 pagesScientist: The Contributions of The in The Development of The PeriodicSiti Nurul AmirahNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument38 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsLia Marlia100% (2)
- Dmitri Ivanovich MendeleevDocument4 pagesDmitri Ivanovich MendeleevEmmanuel OfforNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic Table PPT 1Document17 pagesChemistry Periodic Table PPT 1Hazel ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Tel/Fax No.: (047) 811-1683 The Historical Development of The Periodic TableDocument8 pagesTel/Fax No.: (047) 811-1683 The Historical Development of The Periodic TableCarl PaduaNo ratings yet
- Del MarDocument3 pagesDel MarDelmar DucayNo ratings yet
- Intrototheperiodictablepre ApDocument11 pagesIntrototheperiodictablepre ApvishakhshuklaNo ratings yet
- Döbereiner, Johann Wolfgang (Germany, 1780-1849)Document6 pagesDöbereiner, Johann Wolfgang (Germany, 1780-1849)Andrea May IntiaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 P 1 Class 10 Sci MSBSHSE NotesDocument13 pagesCH 2 P 1 Class 10 Sci MSBSHSE NotesIrganesh MadagundiNo ratings yet
- The Life of Dmitri MendeleevDocument1 pageThe Life of Dmitri MendeleevIvan chester QuejadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Periodic Law PDFDocument38 pagesChapter 5 The Periodic Law PDFTranscendental MindNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table History and ArrangementDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table History and ArrangementDeekshitha KameshNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic Tablepanda catNo ratings yet
- Module - 2: 4.1 Early AttemptsDocument1 pageModule - 2: 4.1 Early Attemptsabhijeet_sangwanNo ratings yet
- 1 Development of The Periodic Table UpdatedDocument11 pages1 Development of The Periodic Table UpdatednurulhudaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of The Element - Lesson - 1Document15 pagesPeriodic Classification of The Element - Lesson - 1samsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument15 pagesUnit 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiescpverma2811100% (1)
- Groups or FamiliesDocument2 pagesGroups or FamiliesvarshaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Unit 3Document26 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Unit 3kamaraj8@rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 4Document2 pagesQ3 Module 4jillianjalbuena80No ratings yet
- History of Periodic TableDocument2 pagesHistory of Periodic TableSukrit KhannaNo ratings yet
- CHEM Grade 10 WK 6Document14 pagesCHEM Grade 10 WK 6Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- 800 X ADocument16 pages800 X Abigsteve9088No ratings yet
- Programming HP48GXDocument14 pagesProgramming HP48GXRodolfo Sergio Cruz FuentesNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions Models Xtri-S / Xtri-D / Xtri-R: Building Technologies DivisionDocument8 pagesInstallation Instructions Models Xtri-S / Xtri-D / Xtri-R: Building Technologies DivisionPrabu KhayanganNo ratings yet
- Final Demo DLPDocument7 pagesFinal Demo DLPAljohaila GulamNo ratings yet
- EZR ManualDocument40 pagesEZR Manualdancuk99No ratings yet
- High-Resolution Spectroscopic Analysis of Four Unevolved Barium StarsDocument29 pagesHigh-Resolution Spectroscopic Analysis of Four Unevolved Barium Starsl2j89zxwNo ratings yet
- Open Ended LabDocument11 pagesOpen Ended LabM. TahmanNo ratings yet
- Ludwig Polarization DefinitionsDocument5 pagesLudwig Polarization DefinitionsSandrine GallardNo ratings yet
- Advanced Survey MethodsDocument83 pagesAdvanced Survey MethodsMarcel MhuruNo ratings yet
- EC3354 Signals and SystemsDocument58 pagesEC3354 Signals and SystemsheraldNo ratings yet
- Trouble ShootingDocument22 pagesTrouble ShootingBitstream SurferNo ratings yet
- Aqa 74012 MS Nov21Document18 pagesAqa 74012 MS Nov21Addan AddanNo ratings yet
- Digital 3 Phase Voltage Relay: DSP-DVR, DVR-M Main FeaturesDocument2 pagesDigital 3 Phase Voltage Relay: DSP-DVR, DVR-M Main FeaturesAngel MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Kelemahan Pengendalian InternalDocument13 pagesKelemahan Pengendalian InternalSetio van HaostenNo ratings yet
- Student CertificationDocument4 pagesStudent CertificationGegeyz1028No ratings yet
- What Caused The Accident at The Sayano - Shushenskaya Hydroelectric Power Plant (SSHPP) : A Seismologist 'S Point of ViewDocument8 pagesWhat Caused The Accident at The Sayano - Shushenskaya Hydroelectric Power Plant (SSHPP) : A Seismologist 'S Point of ViewStefan FleancuNo ratings yet
- Tugas Akhir Modul 2: Soal 1Document8 pagesTugas Akhir Modul 2: Soal 1AnggriantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Traditional and Behavioral FinanceDocument22 pagesChapter 2: Traditional and Behavioral FinanceGeeta RanjanNo ratings yet
- Uper RO: The Wonder DropDocument1 pageUper RO: The Wonder DropEkollo Narcisse100% (1)
- RRLDocument3 pagesRRLEmmanuel RapadaNo ratings yet
- Tollefson Pattern Drafting 1 AssignmentsDocument10 pagesTollefson Pattern Drafting 1 Assignmentstauqeer_141No ratings yet
- Piston Engine QuestionsDocument33 pagesPiston Engine QuestionsSky Patel100% (1)
- Wittkower Architectural Principles in The Age of HumanismDocument6 pagesWittkower Architectural Principles in The Age of HumanismSunday Heavycloth Jr.33% (3)
- 2024 Grade 12 Term 2 Baseline TestDocument7 pages2024 Grade 12 Term 2 Baseline Testamandashabalala1237No ratings yet
- SIMSCI Component Data Input ManualDocument152 pagesSIMSCI Component Data Input Manualarmando0212-1100% (1)
- rr320106 Transportation EngineeringDocument5 pagesrr320106 Transportation EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Shabeer Et Al-2018-Journal of PerinatologyDocument8 pagesShabeer Et Al-2018-Journal of PerinatologyrenataNo ratings yet
- TLS2 Serial Interface ManualDocument113 pagesTLS2 Serial Interface Manualjose moralesNo ratings yet
- B PH 1 S EnglishDocument19 pagesB PH 1 S Englishnifty.vedNo ratings yet