Professional Documents
Culture Documents
13a Palate DR Gosai
13a Palate DR Gosai
Uploaded by
Dr.B.B.GosaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
13a Palate DR Gosai
13a Palate DR Gosai
Uploaded by
Dr.B.B.GosaiCopyright:
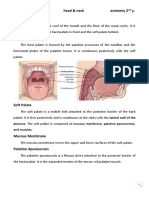
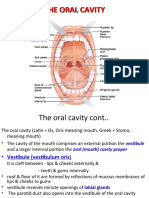
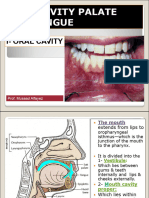
Palate
Introduction:
Palate is horizontal partition between oral cavity and Nasal cavity.
• It forms floor of nasal cavity and roof of oral cavity.
Palate is divided in to two parts:
• Hard (bony) palate, anteriorly
• Soft (muscular) palate, posteriorly
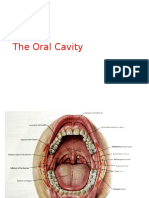
Hard Palate
Lies in the roof of the oral cavity and forms the floor of the nasal cavity
It is formed by: (Viva)
Palatine processes of maxillae in front
Horizontal plates of palatine bones behind
Bounded on sides by alveolar arches
Posteriorly, it is continuous with soft palate.
Its undersurface covered by mucoperiosteum
Shows transverse ridges in the anterior parts.
Ojvensha E learning Resources-Prepared by Dr.B.B.Gosai
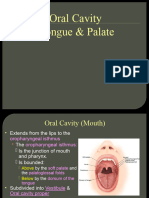
SOFT PALATE
(***Important Short Note)
(No need to draw this diagram- only for understanding)
(Draw this Diagram for the short note)
Ojvensha E learning Resources-Prepared by Dr.B.B.Gosai
(Draw this Diagram for the short note)
Introduction: It is movable muscular fold suspended from post border of hard palate.
It separates nasopharynx from oropharynx
It is like traffic controller
Features:
2 surfaces: Anterioinferior surface related to tongue and Posterosuperior surface is facing
towards pharynx.
2 borders: Superior border attached to posterior border of hard palate and Inferior border is
free.
2 folds of mucous membrane:
Palatoglossal fold from plate to tongue formed by Palatoglossus muscle
Palatopharyngeal fold from palate to lateral wall of pharynx formed by
palatopharyngeus muscle.
Ojvensha E learning Resources-Prepared by Dr.B.B.Gosai
Muscles of soft palate: (Viva and short Questions)
Palatine aponeurosis
(No need to draw this diagram- only for understanding)
(Draw this Diagram for the short note)
Ojvensha E learning Resources-Prepared by Dr.B.B.Gosai
Tensor veli palatini (Tensor palati)
Origin: spine of sphenoid, scaphoid fossa, auditory tube
Insertion: forms palatine aponeurosis which is attached to(a) Posterior border of hard
palate(b)Inf surface of palate behind palatine crest
(Palatine Aponeurosis is fibrous sheath attached to posterior border of hard palate. It is
flattened tendon of tensor vellipalatini. It splits to enclose musculusuvulae and gives origin &
insertion to palatine muscles.)
Action: Tenses soft palate, opens auditory tube
Levator veli palatini (Levator palati)
Origin: petrous temporal bone, auditory tube, Enters pharynx by passing over the upper
concave margin of sup constrictor
Insertion: palatine aponeurosis
Action: Raises soft palate also dilates auditory tube
Musculus uvulae
Origin: posterior nasal spine
Insertion: mucosa of uvula
Action: Elevates uvula
Palatopharyngeus
2 fasciculi (Parts)
Origin: Anterior Fasciculus Post border of hard palate and Posterior fasciculus: palatine
aponeurosis
Insertion: posterior border of thyroid cartilage
Action: Elevates wall of the pharynx
Palatoglossus
Origin: palatine aponeurosis
Insertion: side of tongue
Action: pulls root of tongue upward, narrowing oropharyngeal isthmus
All the muscles, except tensor veli palatini, are supplied by the Pharyngeal plexus
Ojvensha E learning Resources-Prepared by Dr.B.B.Gosai
Tensor veli palatini is supplied by Nerve to medial pterygoid, a branch of the mandibular
division of the trigeminal nerve.
(Draw this Diagram for the short note)
Blood Supply:
ARTERIES:
Greater palatine branch of the maxillary artery
Ascending palatine, branch of the facial artery
Palatine br of Ascending pharyngeal, branch of the external carotid artery
VEINS:
Pterygoid and tonsillar plexus of veins
LYMPHATICS:
Upper deep cervical & retropharyngeal lymphnodes
Sensory Nerve Supply
General Sensory: Mostly by the maxillary nerve through its branches: Middle lesser palatine
nerve, Posterior lesser palatine nerve
Special Sensory: For taste sensations: lesser palatine nerves>> greater petrosal nerve>>
geniculate ganglion >>facial nerve >>nucleus of solitary tract.
Ojvensha E learning Resources-Prepared by Dr.B.B.Gosai
Secretomotor: Lesser palatine nerves .Derived from sup salivatory nucleus Travel through
greater petrosal nerves branch of facial nerve
Motor Nerve Supply:
All the muscles, except tensor veli palatini, are supplied by the Pharyngeal plexus
Tensor veli palatini supplied by the:Nerve to medial pterygoid, a branch of the mandibular
division of the trigeminal nerve
Passavants Ridge: Upper fibres of palatopharyngeus raises a ridge.
Morphology: It is undescended part of palatopharyngeus: Best developed in cleft palate
patient to compensate the gap in palate.
Movements & functions of Soft palate:
Controls 2 gates oral cavity and pharynx
Isolates mouth from Oropharynx during chewing
Separates Oropharynx from nasopharynx
Vary degree of closure of pharyngeal isthmus to modify quality of voice
Helps dividing force during coughing and sneezing
Clinical Notes:
Cleft palate: may be associated with cleft lip (Most important applied aspect)
Unilateral, Bilateral, Median cleft palate
Paralysis of the soft palate: The pharyngeal isthmus can not be closed during swallowing and
speech. It leads to nasal regurgitation, nasal twang in voice and flattening of Palatoglossal arch
Perforation of hard palate in Tertiary syphilis
(No need to draw this diagram- only for understanding)
Ojvensha E learning Resources-Prepared by Dr.B.B.Gosai
(No need to draw this diagram- only for understanding)
==================X================
Ojvensha E learning Resources-Prepared by Dr.B.B.Gosai
You might also like
- Maxillofacial Prosthetics Theory and PracticeDocument305 pagesMaxillofacial Prosthetics Theory and PracticeMostafa Fayad100% (11)
- Paper The Five SensesDocument13 pagesPaper The Five SensesAlfiyyah TsuroyyaNo ratings yet
- 19 Norma Basalis DR GosaiDocument24 pages19 Norma Basalis DR GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity & Oropharynx (GIT-A-001) by MedicneticDocument14 pagesOral Cavity & Oropharynx (GIT-A-001) by MedicneticMuhammad Hammad ZiaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Mouth Cavity & PharynxDocument10 pagesMouth Cavity & PharynxBoody KhalilNo ratings yet
- General AnatomyDocument30 pagesGeneral Anatomyassilshelig5No ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- Y. Head & Neck Anatomy 2 DR - Ban I.S. Lec (11) The PalateDocument7 pagesY. Head & Neck Anatomy 2 DR - Ban I.S. Lec (11) The PalateAaaNo ratings yet
- Y. Head & Neck Anatomy 2 DR - Ban I.S. Lec (11) The PalateDocument7 pagesY. Head & Neck Anatomy 2 DR - Ban I.S. Lec (11) The PalateAaaNo ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Week 1Document8 pagesAnatomy Week 1zahraaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of GitDocument79 pagesAnatomy of Gitgaserhany3No ratings yet
- 12 Pharynx DR GosaiDocument9 pages12 Pharynx DR GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 1Document31 pagesLecture 2 1zahraaNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia TreatmentDocument122 pagesDysphagia TreatmentTiffani WallaceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 Palate NewDocument53 pagesChapter 29 Palate NewMohan PalanimalaiNo ratings yet
- 14 Oral CavityDocument41 pages14 Oral Cavityhamokimo65No ratings yet
- Mouth Cavity, Muscle of Soft PalateDocument4 pagesMouth Cavity, Muscle of Soft PalateameerabestNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument105 pagesOral CavityAisha AbbasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFshagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- Special Senses - Oral Cavity Etc.Document18 pagesSpecial Senses - Oral Cavity Etc.Dunkin DonutNo ratings yet
- Hard & Soft Palate + InnervationDocument7 pagesHard & Soft Palate + InnervationSahrish IqbalNo ratings yet
- Cavum OrisDocument40 pagesCavum OrisharisNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology 2Document63 pagesAnatomical Terminology 2blackamir385No ratings yet
- Oral Cavity Salivary GlandsDocument36 pagesOral Cavity Salivary GlandsSaifNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument59 pagesOral CavityshaisidroNo ratings yet
- Anatomi MenelanDocument74 pagesAnatomi MenelanAnonymous KrEomRrNo ratings yet
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (19)
- 14-Oral CavityDocument37 pages14-Oral CavitySajid AliNo ratings yet
- The MouthDocument23 pagesThe MouthgcamaymayanNo ratings yet
- H, NDocument20 pagesH, NNada Atef KoraitemNo ratings yet
- Head NeckDocument99 pagesHead NeckElena NazâruNo ratings yet
- Tongue, Palate, Palatine Tonsils PDFDocument10 pagesTongue, Palate, Palatine Tonsils PDFChristopher PhilipsNo ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument36 pages14-Oral CavitykavindukarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity Hard & Soft Palate: Dr. Bashir Ahmed ShaikhDocument19 pagesOral Cavity Hard & Soft Palate: Dr. Bashir Ahmed ShaikhHamza IqbalNo ratings yet
- Head Features: SkullDocument41 pagesHead Features: SkullAnne-Sophie BeduNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity585689409Document37 pagesOral Cavity585689409mittal.shubham0007No ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument30 pages14-Oral CavityNeeta ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Role of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTDocument18 pagesRole of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTashoorocksNo ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument23 pagesThe Oral CavityHamzaNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument57 pagesOral CavityArif NabeelNo ratings yet
- B-M of Human Teeth - 1Document10 pagesB-M of Human Teeth - 1Magd NabilNo ratings yet
- Palate: Sanjoy Dutta PG1 Year Dept of Prosthodontics Kothiwal Dental College and Research CentreDocument268 pagesPalate: Sanjoy Dutta PG1 Year Dept of Prosthodontics Kothiwal Dental College and Research CentreDr.Ragini PandeyNo ratings yet
- Med 1 Block 3 Wet Lab Notes Paul Couto1Document18 pagesMed 1 Block 3 Wet Lab Notes Paul Couto1luckyNo ratings yet
- GIT Anatomy Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesGIT Anatomy Learning ObjectivesangrypandasaredangerousNo ratings yet
- 7 Submandibular Region-Dr - GosaiDocument14 pages7 Submandibular Region-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Dental AnatomyDocument73 pagesDental Anatomykajojo joyNo ratings yet
- 8.2-Introduction To Oral CavityDocument57 pages8.2-Introduction To Oral CavityfaristhehackerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nose and TongueDocument40 pagesAnatomy of Nose and TongueDanial SharizulNo ratings yet
- 8a Temporal & Infratemporal Fossa I-DrDocument15 pages8a Temporal & Infratemporal Fossa I-DrDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity and PalateDocument1 pageOral Cavity and PalateCarlo BarriosNo ratings yet
- Osteology of Maxilla & Mandible Muscles of MasticationDocument26 pagesOsteology of Maxilla & Mandible Muscles of MasticationJaveria KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture (2) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueDocument11 pagesLecture (2) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueReem ZohairNo ratings yet
- ThroatDocument100 pagesThroatChekole AdaneNo ratings yet
- 16 The Mouth (Done)Document9 pages16 The Mouth (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- PalateDocument48 pagesPalateilagernischit321No ratings yet
- GIT TempDocument13 pagesGIT Tempdrahmed1028No ratings yet
- Plastic Surgery Board NotesDocument69 pagesPlastic Surgery Board Notesseandarcy600100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Classification of Joints-Dr - GosaiDocument10 pagesClassification of Joints-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Lecturing Guidelines - PIMSR 18-7-2023Document3 pagesLecturing Guidelines - PIMSR 18-7-2023Dr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Epiphysis DR - GosaiDocument4 pagesEpiphysis DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bones-Dr - GosaiDocument6 pagesClassification of Bones-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- An 1.1 - Introduction Anatomical Terminology DR - GosaiDocument46 pagesAn 1.1 - Introduction Anatomical Terminology DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 27 - Development of Skeletal SystemDocument28 pages27 - Development of Skeletal SystemDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy-Nervous System Lec 1-Dr - GosaiDocument18 pagesGeneral Anatomy-Nervous System Lec 1-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 16 - Development of Venous System and Fetal Circulation-Dr - GosaiDocument34 pages16 - Development of Venous System and Fetal Circulation-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Large Intestine PIMSR-Dr - Gosai 2022Document40 pagesLarge Intestine PIMSR-Dr - Gosai 2022Dr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 26 - Development of Muscular SystemDocument12 pages26 - Development of Muscular SystemDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels of Abdomen-PIMSR DR - Gosai 2022Document32 pagesBlood Vessels of Abdomen-PIMSR DR - Gosai 2022Dr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Reflection For Students PIMSRDocument5 pagesReflection For Students PIMSRDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 21 - Development of Kidney and Its AnomaliesDocument39 pages21 - Development of Kidney and Its AnomaliesDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 25 - Development of Head and NeckDocument43 pages25 - Development of Head and NeckDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 23 - Development of Genital SystemDocument67 pages23 - Development of Genital SystemDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 24 - Pharyngeal Arches and Its DerivativesDocument32 pages24 - Pharyngeal Arches and Its DerivativesDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 22 - Development of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocument14 pages22 - Development of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 20 - Development of Respiratory SystemDocument33 pages20 - Development of Respiratory SystemDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 17 - Development of Foregut-Derivatives and AnomaliesDocument22 pages17 - Development of Foregut-Derivatives and AnomaliesDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 10 Placenta DR - GosaiDocument29 pages10 Placenta DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 19 - Development of Hindgut-Derivatives and AnomaliesDocument14 pages19 - Development of Hindgut-Derivatives and AnomaliesDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 12 - Congenital Anomalies & Teratogens-Dr - GosaiDocument43 pages12 - Congenital Anomalies & Teratogens-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 14 - Development of CVS-II (Heart) - DR - GosaiDocument52 pages14 - Development of CVS-II (Heart) - DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 11 Fetal Period-Dr - GosaiDocument23 pages11 Fetal Period-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 13 - Development of CVS-I (Heart) - DR - GosaiDocument60 pages13 - Development of CVS-I (Heart) - DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 15 - Development of Arterial System-Dr - GosaiDocument27 pages15 - Development of Arterial System-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 9 Fetal Membranes-Dr - GosaiDocument22 pages9 Fetal Membranes-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 8 - Derivatives of Germ Layers-Dr - GosaiDocument35 pages8 - Derivatives of Germ Layers-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 6 - 2nd Week of Devlt.-Dr - GosaiDocument22 pages6 - 2nd Week of Devlt.-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Fertilization Cleavage Implantation-Dr - GosaiDocument41 pages5 - Fertilization Cleavage Implantation-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Head N Neck Guidelines by Mbbs CafeteriaDocument11 pagesHead N Neck Guidelines by Mbbs CafeteriaFarah Khan100% (1)
- Maxillofacial Notes DR - Mahmoud RamadanDocument83 pagesMaxillofacial Notes DR - Mahmoud Ramadanaziz200775% (4)
- Food Colloids Under Oral Conditions: George A. Van Aken, Monique H. Vingerhoeds, Els H.A. de HoogDocument12 pagesFood Colloids Under Oral Conditions: George A. Van Aken, Monique H. Vingerhoeds, Els H.A. de HoogGabriel GabiNo ratings yet
- Tongue IiDocument15 pagesTongue Iigajendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment in Tabular Form (Repaired) To Be Placed!@#%$!@# #@ @Document5 pagesNursing Assessment in Tabular Form (Repaired) To Be Placed!@#%$!@# #@ @Leo Buquiran AcabalNo ratings yet
- Landmarks For Maxilla and MandibleDocument25 pagesLandmarks For Maxilla and Mandibleوجيه الوجيهNo ratings yet
- In Intervention For Speech Sound Disorders - Lateralize SDocument5 pagesIn Intervention For Speech Sound Disorders - Lateralize SSaraOliveiraNo ratings yet
- Physical ExaminationDocument53 pagesPhysical ExaminationTrisha Mae BalladNo ratings yet
- Mouth Assessment RubricDocument5 pagesMouth Assessment RubricChris SmithNo ratings yet
- Palatine TonsilsDocument19 pagesPalatine TonsilsSiddarth DmNo ratings yet
- Tips and Tools To Vocal FreedomDocument10 pagesTips and Tools To Vocal FreedomasifNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument63 pagesMuscles of Facial Expressionraphaelyohana140No ratings yet
- Cases of Oral PathologyDocument7 pagesCases of Oral PathologyGilPeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Tongue PositioningDocument3 pagesTongue PositioningMyrna AzizNo ratings yet
- Retention of Complete DentureDocument43 pagesRetention of Complete DentureDrShweta SainiNo ratings yet
- Histology of Oral Mucous Membrane and GingivaDocument86 pagesHistology of Oral Mucous Membrane and GingivahazeemmegahedNo ratings yet
- 261 Lecture 18 Sensory Evaluation (White) 3-2-2011Document33 pages261 Lecture 18 Sensory Evaluation (White) 3-2-2011widianingsih100% (1)
- L1) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueDocument39 pagesL1) Oral Cavity, Palate and Tongue3amroooni.a.aNo ratings yet
- Oral Health Among Junior High School Student in Saints John and Paul Educational FoundationDocument15 pagesOral Health Among Junior High School Student in Saints John and Paul Educational FoundationDat boiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 4 PDFDocument1 pageAnatomy 4 PDFJihan SalsabillaNo ratings yet
- ActinobacillosisDocument16 pagesActinobacillosisMd Shamim AhasanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Resperatory SystemDocument5 pagesParts of Resperatory SystemPeysbukan Cyber CafeNo ratings yet
- Davis Modified Lingual Split 1983Document7 pagesDavis Modified Lingual Split 1983ArchanaShenoyNo ratings yet
- Glossitis and Other Tounge Disorder PDFDocument12 pagesGlossitis and Other Tounge Disorder PDFMuhammad Iqbal Al-ayyubiNo ratings yet
- Soal Try Out 1 B Anak2Document12 pagesSoal Try Out 1 B Anak2Tony YusuefNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueDocument33 pagesUnit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueBONGISIPHO HLOPHENo ratings yet
- Anatomical Considerations For Dental ImplantDocument74 pagesAnatomical Considerations For Dental ImplantsonalitalkeNo ratings yet
- Post Insertion Problems in Complete DenturesDocument51 pagesPost Insertion Problems in Complete DenturesKiarra Vashti NadiraNo ratings yet
- ASHA Presentation 2008 HandoutDocument5 pagesASHA Presentation 2008 HandoutlblessingerNo ratings yet