Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Curriculum Guide: Instructional Planning
Curriculum Guide: Instructional Planning
Uploaded by
Bowina KhoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Iplan TemplateDocument9 pagesIplan TemplateeyadcampNo ratings yet
- Chapter V: Curriculum Evaluation: A. Purposes of EvaluationDocument11 pagesChapter V: Curriculum Evaluation: A. Purposes of Evaluationvea verzonNo ratings yet
- Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesCurriculum GuideBowina Kho100% (1)
- Earth & Life Science DLP 15Document3 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 15Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- List of Behavioral Verbs - Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesList of Behavioral Verbs - Lesson PlanncplmrsNo ratings yet
- DLP ELS 1Q Origin of The UniverseDocument6 pagesDLP ELS 1Q Origin of The Universekathleen b. cabacabaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- S11-12 ES-Id-20Document5 pagesS11-12 ES-Id-20Hannisch Anne SakuraNo ratings yet
- DLP 2Document5 pagesDLP 2Raquel DomingoNo ratings yet
- DLP Earth and Life Science 1st QuarterDocument6 pagesDLP Earth and Life Science 1st Quarterkathleen b. cabacaba67% (3)
- Curriculum Guide: 1. Objectives The Learners Should Be Able To: Nowledge EmemberingDocument3 pagesCurriculum Guide: 1. Objectives The Learners Should Be Able To: Nowledge EmemberingAngielo LabajoNo ratings yet
- Blanco DLP FormatDocument5 pagesBlanco DLP FormatEdmundSeronBlanco100% (1)
- Earth & Life Science DLP 11Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 11Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- DLP Format Blank SheetDocument25 pagesDLP Format Blank SheetRhea Rose PelaezNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 13Document5 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 13Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan 02Document5 pagesIplan 02Jay Ed NamzugNo ratings yet
- DLP 3Document6 pagesDLP 3Baby YanyanNo ratings yet
- 2.4 How World Religions BeganDocument5 pages2.4 How World Religions BeganRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Ipan) Tool - V.05Document11 pagesInstructional Plan (Ipan) Tool - V.05Jesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Kojiki Creation TheoryDocument32 pagesUnderstanding The Kojiki Creation TheoryShyrra AndersonNo ratings yet
- 21st Century-LC-Q124Document5 pages21st Century-LC-Q124Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLP PE6 - 1.1 The Learner Describes The Philippines Physical Activity Pyramid.Document15 pagesDLP PE6 - 1.1 The Learner Describes The Philippines Physical Activity Pyramid.Farah Torreta75% (4)
- SIPP Tool - v.05 IPlan 2019Document12 pagesSIPP Tool - v.05 IPlan 2019Jesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- DLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarDocument4 pagesDLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarHayee TyNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Curriculum GuideDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Curriculum GuideJade ViloriaNo ratings yet
- DLP WRB 10 2Document5 pagesDLP WRB 10 2ironickNo ratings yet
- I PlanDocument12 pagesI PlanJovie Ababon BellitaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningHelen LaurelNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- DLP DemoDocument7 pagesDLP Demoves100% (2)
- DLP ELS 1Q Origin of The UniverseDocument7 pagesDLP ELS 1Q Origin of The Universekathleen b. cabacabaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAnngela Arevalo BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Iplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 1Document4 pagesIplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 1Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLP 2Document5 pagesDLP 2Baby YanyanNo ratings yet
- C1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Document4 pagesC1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Jonathan Gabriel Nario Jr.No ratings yet
- iPLAN COOKERY TENDocument5 pagesiPLAN COOKERY TENVhernaAveltPiezasNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionDocument5 pages3.3 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionDocument5 pages3.2 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- SIPP-Tool v.05Document9 pagesSIPP-Tool v.05Rose Mae TecsonNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAhbby LaureaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningEdgar Jr. SenarloNo ratings yet
- DLP Per DevDocument8 pagesDLP Per DevJeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- Final Dlp222Document8 pagesFinal Dlp222Pauline Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Blank Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesBlank Detailed Lesson PlanJames Arnold PanilagaoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Curriculum GuideDocument5 pagesInstructional Planning: Curriculum GuideAnngela Arevalo BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Iplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 3Document4 pagesIplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 3Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLP Ucsp 30Document5 pagesDLP Ucsp 30Jeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- PE 9 Week 1 Group 1 DLPDocument16 pagesPE 9 Week 1 Group 1 DLPJoyce SollestaNo ratings yet
- DLP TemplateDocument4 pagesDLP TemplateAcilla Mae BongoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideDocument20 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideJerwin MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Iplan English Q1W1Document5 pagesIplan English Q1W1jesannilpenas1985No ratings yet
- 21st Century Q2 LC24Document4 pages21st Century Q2 LC24Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning (Iplan)Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning (Iplan)Nathalie Yvonne AliserNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJoel MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Michael KitNo ratings yet
- DLP DemoDocument7 pagesDLP Demoartjill printingNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatJulia Maria LoviteNo ratings yet
- Final Curriculum Implementation Matrix Cim World ReligionDocument5 pagesFinal Curriculum Implementation Matrix Cim World ReligionBaby YanyanNo ratings yet
- Iplan English Q1W1Document5 pagesIplan English Q1W1jesannilpenas1985No ratings yet
- Ip Etech 10TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 10TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 9TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 9TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 8TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 8TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 7TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 7TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 2ND WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 2ND WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 4TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 4TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 13Document5 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 13Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 1ST WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 1ST WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 3RD WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 3RD WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 5TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 5TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 11Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 11Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 14Document4 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 14Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 15Document3 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 15Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) in Earth & Life Science: S11/12ES-Ia-e-4Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) in Earth & Life Science: S11/12ES-Ia-e-4Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan - 38 - People Media (Lec)Document2 pagesIplan - 38 - People Media (Lec)Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 12Document4 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 12Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan 37 Debate2Document2 pagesIplan 37 Debate2Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Explain That The Earth Consists of Four Subsystems, Across Whose Boundaries Matter and Energy Flow. CodeDocument3 pagesExplain That The Earth Consists of Four Subsystems, Across Whose Boundaries Matter and Energy Flow. CodeBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan - 35 - Uses of Social MediaDocument2 pagesIplan - 35 - Uses of Social MediaBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesCurriculum GuideBowina Kho100% (1)
- Lesson 5 SlideDocument11 pagesLesson 5 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan 36 Debate1Document2 pagesIplan 36 Debate1Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 SlideDocument25 pagesLesson 2 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 SlideDocument24 pagesLesson 4 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 SlideDocument16 pagesLesson 3 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 SlideDocument23 pagesLesson 1 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Educ 106 Q2L1Document3 pagesEduc 106 Q2L1Keith Ernest AbalosNo ratings yet
- BestColleges College Planning ChecklistDocument2 pagesBestColleges College Planning ChecklistSiangNo ratings yet
- Syllabus COMM 230-Fall 2021Document6 pagesSyllabus COMM 230-Fall 2021RUDR MATNo ratings yet
- NTA JEE Main Test 2Document74 pagesNTA JEE Main Test 2Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World Course Guide 1st Sem 2020-2021Document10 pagesContemporary World Course Guide 1st Sem 2020-2021Chelsea Duazo EncinaresNo ratings yet
- Philosophy College Vision: Course Syllabus in Catering ManagementDocument7 pagesPhilosophy College Vision: Course Syllabus in Catering ManagementCristy Lansangan Mejia100% (1)
- Faculty Peer Online Classroom Observations: PhilosophyDocument9 pagesFaculty Peer Online Classroom Observations: PhilosophyAmparo Christine Recon-PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Holy Angel University School of Education Angeles City: 2platrigoDocument12 pagesHoly Angel University School of Education Angeles City: 2platrigoJoshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Utsav Shrestha AcademicWritingDocument14 pagesUtsav Shrestha AcademicWritingBulls GhimireNo ratings yet
- Advt No. I - 28 - 1 To 7 - Rectt - 2023-24 - Corrected 4.11.23Document11 pagesAdvt No. I - 28 - 1 To 7 - Rectt - 2023-24 - Corrected 4.11.23animeshprasad30No ratings yet
- Fermator Premium Landing Door Lock CE Certificate PDFDocument8 pagesFermator Premium Landing Door Lock CE Certificate PDFHabibulla BavajiNo ratings yet
- Zou and Zhang 2017Document16 pagesZou and Zhang 2017Erda BakarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2023: Introduction To Development StudiesDocument16 pagesTutorial Letter 101/3/2023: Introduction To Development StudiesMatlhodi Pholoso MashapaNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection (BAHRM322) : Dr. Adoree A. RamosDocument9 pagesRecruitment and Selection (BAHRM322) : Dr. Adoree A. RamosAdoree RamosNo ratings yet
- General Science, Quantitative Reasoning & Analysis and Research Aptitude. These Can Be Further Divided Into Below TopicsDocument2 pagesGeneral Science, Quantitative Reasoning & Analysis and Research Aptitude. These Can Be Further Divided Into Below TopicsXam HemaNo ratings yet
- CalenderDocument1 pageCalenderEman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mdms in Nepal - Mdms in Nepal Apply - Mdms in Study - Study Mdms in NepalDocument6 pagesMdms in Nepal - Mdms in Nepal Apply - Mdms in Study - Study Mdms in NepalOfficial Global Dream EducationNo ratings yet
- New York State - NclexDocument5 pagesNew York State - NclexBia KriaNo ratings yet
- Mantiquil Masaligan High School: Senen Priscillo P. Paulin, Ceso VDocument3 pagesMantiquil Masaligan High School: Senen Priscillo P. Paulin, Ceso VMars TubatoNo ratings yet
- SBU Commercial Law Review (6 FEBRUARY 2024)Document16 pagesSBU Commercial Law Review (6 FEBRUARY 2024)Susanna Martha B. IbeNo ratings yet
- ANSWER SHEET PRC LogoDocument2 pagesANSWER SHEET PRC LogoRii Rii100% (1)
- Assessment of The English Remedial Programme at ADocument17 pagesAssessment of The English Remedial Programme at Aishaqzai evisaNo ratings yet
- Resume Format PDF For TeachersDocument6 pagesResume Format PDF For Teachersfskt032h100% (1)
- Edu 533 Sas#17Document8 pagesEdu 533 Sas#17Lalaine Villamar DizonNo ratings yet
- Annabelle EDUC 204 Evaluating The Result of School Administration and SupervisionDocument26 pagesAnnabelle EDUC 204 Evaluating The Result of School Administration and SupervisionCristhel MacajetoNo ratings yet
- English Literature: Grade 12Document68 pagesEnglish Literature: Grade 12Kirran Khumar GollaNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis GuidelinesDocument31 pagesItem Analysis GuidelinesLuna Ledezma100% (1)
- Intersummer 2021 Course Offerings: Arts, Humanities, Soc ScienceDocument15 pagesIntersummer 2021 Course Offerings: Arts, Humanities, Soc ScienceRamkumar HaridossNo ratings yet
- FASH2002 Sustainable Fashion Semester 1 2022 Bentley Perth Campus INTDocument12 pagesFASH2002 Sustainable Fashion Semester 1 2022 Bentley Perth Campus INTArchVFXNo ratings yet
Curriculum Guide: Instructional Planning
Curriculum Guide: Instructional Planning
Uploaded by
Bowina KhoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Curriculum Guide: Instructional Planning
Curriculum Guide: Instructional Planning
Uploaded by
Bowina KhoCopyright:
Available Formats
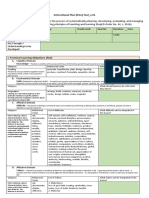
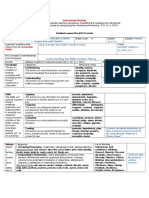
Instructional Planning
(The process of systematically planning, developing, evaluating and managing the instructional
process by using principles of teaching and learning - D.O. 42, s. 2016)
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format
DLP No.:2 Learning Area: Earth Grade Level: 11 Quarter: 2 Duration: 1 hour Date:
and Life Science
Learning Competency/ies: Describe the different hypotheses explaining the origin of the solar system Code: S11/12ES-Ia-e-2
(Taken from the Curriculum
Guide)
Key Concepts / The different hypotheses explaining the origin of the solar system.
Understandings to be
Developed
Domain Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions (D.O. No. 8, s. 2015) 1. Objectives
Knowledge Categories: Behavioral Verbs: The Learners shall be able to:
The fact or condition Remembering identify, retrieve, recognize, duplicate,
of knowing list, memorize, repeat, describe,
something with reproduce
familiarity gained Understanding interpret, exemplify, classify, summarize, Classify the different hypotheses
through experience infer, compare, explain, paraphrase, as to catastrophic or evolutionary
or association discuss theories
explain the different hypotheses
on the origin of the solar system,
Skills Applying execute, implement, demonstrate, dramatize, illustrate at least one hypotheses on the
The ability and interpret, solve, use, illustrate, convert, origin of the solar system,
capacity acquired discover
through deliberate, Analyzing differentiate, distinguish, compare, contrast,
systematic, and organize, outline, attribute, deconstruct
sustained effort to Evaluating coordinate, measure, detect, defend, judge,
smoothly and argue, debate, describe, critique, appraise,
adaptively carryout evaluate
complex activities or Creating generate, hypothesize, plan, design, develop,
the ability, coming produce, construct, formulate, assemble, devise
from one’s
knowledge, practice,
aptitude, etc., to do
something
Attitude Categories: List of Attitudes:
Growth in feelings or emotional 1. Receiving Self-esteem, Self-confidence, Wellness,
areas. Phenomen Respect, Honesty, Personal discipline,
A settled way of thinking or feeling a Perseverance, Sincerity, Patience,
about someone or something, 2. Respondin Critical thinking, Open-mindedness,
typically one that is reflected in a g to Interest, Courteous, Obedience, Hope,
person’s behavior Phenomen Charity, Fortitude, Resiliency, Positive
a vision, Acceptance, Determined,
Independent , Gratitude, Tolerant,
3. Valuing Cautious, Decisive, Self-Control,
Calmness, Responsibility, Accountability,
Industriousness, Industry, Cooperation,
4. Organizati
on Optimism, Satisfaction, Persistent,
Cheerful, Reliable, Gentle, Appreciation
display open-mindedness to the
of one’s culture, Globalism, Compassion,
different hypotheses on the origin
Work Ethics, Creativity, Entrepreneurial
of the universe,
Spirit, Financial Literacy, Global,
Solidarity, Making a stand for the good,
5. Voluntariness of human act,
Internalizin Appreciation of one’s rights,
g values Inclusiveness, Thoughtful, Seriousness,
Generous, Happiness, Modest, Authority,
Hardworking, Realistic, Flexible,
Considerate,
Sympathetic, Frankness
Values Categories: List of Values: demonstrate love of God for an
A learner’s principles or standards 1. Receiving 1. Maka-Diyos orderly solar system.
of behavior; one’s judgment of Phenomena
what is important in life. – 2. Maka-tao
Go beyond learner’s life on earth, 2.
include more than wealth and Responding 3. Makakalikasan
fame, and would affect the eternal to
destiny of millions Phenomena 4. Makabansa
3. Valuing
4.
Organizatio
n
5.
Internalizin
g
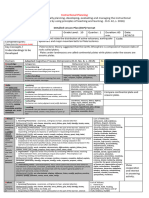
2. Content Universe and the Solar System
3. Learning Resources Printed material
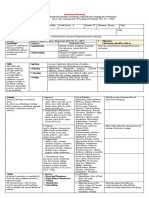
4. Procedures
4.1 Introductory Activity (5minutes). Students view the video entitled “The Birth of the Solar System”
What are the different concepts of the video?
What are the different hypotheses that you know about the origin of the
universe.
4.2 Activity (15minutes) (Collaborative Learning)
Students will go to their respective groups and they will pick one hypothesis.
Representatives explain the hypothesis assigned to them based on what they have
researched.
Define catastrophic and evolutionary theory.
4.3 Analysis (5minutes) Students classify the different hypotheses as to evolutionary or catastrophic.
4.4 Abstraction (12minutes) The Solar System started from dust sized particles.
Discussion of the different theories explaining the origin of the solar system
through a power point presentation.
4.5 Application (10minutes)
Illustrate at least one hypotheses on the origin of the solar system.
4.6 Assessment (10minutes)
Assessment Method Possible Activities
a) Observation Investigation, Role Play, Oral Presentation,
Dance, Musical Performance, Skill
Demonstration, Group Activity (e.g. Choral
Reading), Debate, Motor & Psychomotor
Games, Simulation Activities, Science
Experiment
b) Talking to Learners / Hands-on Math Activities, Written Work and
Conferencing Essay, Picture Analysis, Comic Strip, Panel
Discussion, Interview, Think-Pair-Share,
Reading
c) Analysis of Learners’ Worksheets for all subjects, Essay, Concept
Products Maps/Graphic Organizer, Project, Model, Demonstrate love of God for an orderly solar
Artwork, Multi-media Presentation, Product system through an essay.
made in technical-vocational subjects
d) Tests Skill Performance Test, Open-Ended
Question, Practicum, Pen and Paper Test,
Pre and Post Test, Diagnostic Test, Oral
Test, Quiz
4.7 Assignment (3minutes). Fill-in below any of the four purposes:
Reinforcing / strengthening the day’s lesson
Enriching / inspiring the day’s lesson
Enhancing / improving the day’s lesson
Preparing for the new lesson Study about our planet, Earth
4.8 Concluding Activity (5 minutes). “When there was nothing, there was the word and
This is usually a brief but affective closing activity such as a strong quotation, a the word dwelleth in us”
short song, an anecdote, parable or a letter that inspires the learners to do
something to practice their new learning.
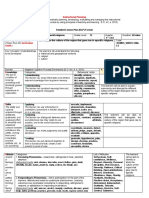
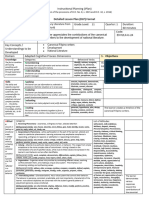
5. Remarks Indicate below special cases including but not limited to continuation of lesson plan to the
following day in case of re-teaching or lack of time, transfer of lesson to the following day, in cases
of class suspension, etc.
6. Reflections Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your student’s progress this
week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your
instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant
questions. Indicate below whichever is/are appropriate.
A.No. of learners who earned 80%
in the evaluation.
B.No. of learners who require
additional activities for
remediation.
C. Did the remedial lessons
work? No. of learners who have
caught up with the lesson.
D. No. of learners who
continue to require remediation.
E.Which of my learning strategies
worked well? Why did these
work?
F.What difficulties did I encounter
which my principal or supervisor
can help me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials did I
use/discover which I wish to
share with other teachers?
Prepared by:
Name: KENNY Y. ANCAJAS School: Malingin National High School
Position/Designation: TEACHER 3 Division: Division of Cebu Province
Contact Number: 09236789698 Email address:
Bibliograhy:
1. Starr C., Evers C.,Starr L. (2016) Earth and Life Sciences (pp. 4-6). Sampaloc Manila Philippines: Rex Bookstore.
2. Olivar, J.T II., Morales-Ramos, A.C., (2016). Exploring Life Through science. Earth and Life Science (pp. 8-10). Quezon Avenue,
Quezon City:Phoenix Publishing House.
You might also like
- Iplan TemplateDocument9 pagesIplan TemplateeyadcampNo ratings yet
- Chapter V: Curriculum Evaluation: A. Purposes of EvaluationDocument11 pagesChapter V: Curriculum Evaluation: A. Purposes of Evaluationvea verzonNo ratings yet
- Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesCurriculum GuideBowina Kho100% (1)
- Earth & Life Science DLP 15Document3 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 15Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- List of Behavioral Verbs - Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesList of Behavioral Verbs - Lesson PlanncplmrsNo ratings yet
- DLP ELS 1Q Origin of The UniverseDocument6 pagesDLP ELS 1Q Origin of The Universekathleen b. cabacabaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- S11-12 ES-Id-20Document5 pagesS11-12 ES-Id-20Hannisch Anne SakuraNo ratings yet
- DLP 2Document5 pagesDLP 2Raquel DomingoNo ratings yet
- DLP Earth and Life Science 1st QuarterDocument6 pagesDLP Earth and Life Science 1st Quarterkathleen b. cabacaba67% (3)
- Curriculum Guide: 1. Objectives The Learners Should Be Able To: Nowledge EmemberingDocument3 pagesCurriculum Guide: 1. Objectives The Learners Should Be Able To: Nowledge EmemberingAngielo LabajoNo ratings yet
- Blanco DLP FormatDocument5 pagesBlanco DLP FormatEdmundSeronBlanco100% (1)
- Earth & Life Science DLP 11Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 11Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- DLP Format Blank SheetDocument25 pagesDLP Format Blank SheetRhea Rose PelaezNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 13Document5 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 13Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan 02Document5 pagesIplan 02Jay Ed NamzugNo ratings yet
- DLP 3Document6 pagesDLP 3Baby YanyanNo ratings yet
- 2.4 How World Religions BeganDocument5 pages2.4 How World Religions BeganRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Ipan) Tool - V.05Document11 pagesInstructional Plan (Ipan) Tool - V.05Jesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Kojiki Creation TheoryDocument32 pagesUnderstanding The Kojiki Creation TheoryShyrra AndersonNo ratings yet
- 21st Century-LC-Q124Document5 pages21st Century-LC-Q124Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLP PE6 - 1.1 The Learner Describes The Philippines Physical Activity Pyramid.Document15 pagesDLP PE6 - 1.1 The Learner Describes The Philippines Physical Activity Pyramid.Farah Torreta75% (4)
- SIPP Tool - v.05 IPlan 2019Document12 pagesSIPP Tool - v.05 IPlan 2019Jesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- DLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarDocument4 pagesDLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarHayee TyNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Curriculum GuideDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Curriculum GuideJade ViloriaNo ratings yet
- DLP WRB 10 2Document5 pagesDLP WRB 10 2ironickNo ratings yet
- I PlanDocument12 pagesI PlanJovie Ababon BellitaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningHelen LaurelNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- DLP DemoDocument7 pagesDLP Demoves100% (2)
- DLP ELS 1Q Origin of The UniverseDocument7 pagesDLP ELS 1Q Origin of The Universekathleen b. cabacabaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAnngela Arevalo BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Iplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 1Document4 pagesIplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 1Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLP 2Document5 pagesDLP 2Baby YanyanNo ratings yet
- C1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Document4 pagesC1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Jonathan Gabriel Nario Jr.No ratings yet
- iPLAN COOKERY TENDocument5 pagesiPLAN COOKERY TENVhernaAveltPiezasNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionDocument5 pages3.3 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionDocument5 pages3.2 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- SIPP-Tool v.05Document9 pagesSIPP-Tool v.05Rose Mae TecsonNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAhbby LaureaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningEdgar Jr. SenarloNo ratings yet
- DLP Per DevDocument8 pagesDLP Per DevJeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- Final Dlp222Document8 pagesFinal Dlp222Pauline Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Blank Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesBlank Detailed Lesson PlanJames Arnold PanilagaoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Curriculum GuideDocument5 pagesInstructional Planning: Curriculum GuideAnngela Arevalo BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Iplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 3Document4 pagesIplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 3Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLP Ucsp 30Document5 pagesDLP Ucsp 30Jeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- PE 9 Week 1 Group 1 DLPDocument16 pagesPE 9 Week 1 Group 1 DLPJoyce SollestaNo ratings yet
- DLP TemplateDocument4 pagesDLP TemplateAcilla Mae BongoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideDocument20 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideJerwin MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Iplan English Q1W1Document5 pagesIplan English Q1W1jesannilpenas1985No ratings yet
- 21st Century Q2 LC24Document4 pages21st Century Q2 LC24Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning (Iplan)Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning (Iplan)Nathalie Yvonne AliserNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJoel MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Michael KitNo ratings yet
- DLP DemoDocument7 pagesDLP Demoartjill printingNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatJulia Maria LoviteNo ratings yet
- Final Curriculum Implementation Matrix Cim World ReligionDocument5 pagesFinal Curriculum Implementation Matrix Cim World ReligionBaby YanyanNo ratings yet
- Iplan English Q1W1Document5 pagesIplan English Q1W1jesannilpenas1985No ratings yet
- Ip Etech 10TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 10TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 9TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 9TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 8TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 8TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 7TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 7TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 2ND WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 2ND WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 4TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 4TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 13Document5 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 13Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 1ST WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 1ST WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 3RD WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 3RD WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Ip Etech 5TH WeekDocument2 pagesIp Etech 5TH WeekBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 11Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 11Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 14Document4 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 14Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 15Document3 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 15Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) in Earth & Life Science: S11/12ES-Ia-e-4Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) in Earth & Life Science: S11/12ES-Ia-e-4Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan - 38 - People Media (Lec)Document2 pagesIplan - 38 - People Media (Lec)Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 12Document4 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 12Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan 37 Debate2Document2 pagesIplan 37 Debate2Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Explain That The Earth Consists of Four Subsystems, Across Whose Boundaries Matter and Energy Flow. CodeDocument3 pagesExplain That The Earth Consists of Four Subsystems, Across Whose Boundaries Matter and Energy Flow. CodeBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan - 35 - Uses of Social MediaDocument2 pagesIplan - 35 - Uses of Social MediaBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesCurriculum GuideBowina Kho100% (1)
- Lesson 5 SlideDocument11 pagesLesson 5 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Iplan 36 Debate1Document2 pagesIplan 36 Debate1Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 SlideDocument25 pagesLesson 2 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 SlideDocument24 pagesLesson 4 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 SlideDocument16 pagesLesson 3 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 SlideDocument23 pagesLesson 1 SlideBowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Educ 106 Q2L1Document3 pagesEduc 106 Q2L1Keith Ernest AbalosNo ratings yet
- BestColleges College Planning ChecklistDocument2 pagesBestColleges College Planning ChecklistSiangNo ratings yet
- Syllabus COMM 230-Fall 2021Document6 pagesSyllabus COMM 230-Fall 2021RUDR MATNo ratings yet
- NTA JEE Main Test 2Document74 pagesNTA JEE Main Test 2Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World Course Guide 1st Sem 2020-2021Document10 pagesContemporary World Course Guide 1st Sem 2020-2021Chelsea Duazo EncinaresNo ratings yet
- Philosophy College Vision: Course Syllabus in Catering ManagementDocument7 pagesPhilosophy College Vision: Course Syllabus in Catering ManagementCristy Lansangan Mejia100% (1)
- Faculty Peer Online Classroom Observations: PhilosophyDocument9 pagesFaculty Peer Online Classroom Observations: PhilosophyAmparo Christine Recon-PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Holy Angel University School of Education Angeles City: 2platrigoDocument12 pagesHoly Angel University School of Education Angeles City: 2platrigoJoshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Utsav Shrestha AcademicWritingDocument14 pagesUtsav Shrestha AcademicWritingBulls GhimireNo ratings yet
- Advt No. I - 28 - 1 To 7 - Rectt - 2023-24 - Corrected 4.11.23Document11 pagesAdvt No. I - 28 - 1 To 7 - Rectt - 2023-24 - Corrected 4.11.23animeshprasad30No ratings yet
- Fermator Premium Landing Door Lock CE Certificate PDFDocument8 pagesFermator Premium Landing Door Lock CE Certificate PDFHabibulla BavajiNo ratings yet
- Zou and Zhang 2017Document16 pagesZou and Zhang 2017Erda BakarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2023: Introduction To Development StudiesDocument16 pagesTutorial Letter 101/3/2023: Introduction To Development StudiesMatlhodi Pholoso MashapaNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection (BAHRM322) : Dr. Adoree A. RamosDocument9 pagesRecruitment and Selection (BAHRM322) : Dr. Adoree A. RamosAdoree RamosNo ratings yet
- General Science, Quantitative Reasoning & Analysis and Research Aptitude. These Can Be Further Divided Into Below TopicsDocument2 pagesGeneral Science, Quantitative Reasoning & Analysis and Research Aptitude. These Can Be Further Divided Into Below TopicsXam HemaNo ratings yet
- CalenderDocument1 pageCalenderEman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mdms in Nepal - Mdms in Nepal Apply - Mdms in Study - Study Mdms in NepalDocument6 pagesMdms in Nepal - Mdms in Nepal Apply - Mdms in Study - Study Mdms in NepalOfficial Global Dream EducationNo ratings yet
- New York State - NclexDocument5 pagesNew York State - NclexBia KriaNo ratings yet
- Mantiquil Masaligan High School: Senen Priscillo P. Paulin, Ceso VDocument3 pagesMantiquil Masaligan High School: Senen Priscillo P. Paulin, Ceso VMars TubatoNo ratings yet
- SBU Commercial Law Review (6 FEBRUARY 2024)Document16 pagesSBU Commercial Law Review (6 FEBRUARY 2024)Susanna Martha B. IbeNo ratings yet
- ANSWER SHEET PRC LogoDocument2 pagesANSWER SHEET PRC LogoRii Rii100% (1)
- Assessment of The English Remedial Programme at ADocument17 pagesAssessment of The English Remedial Programme at Aishaqzai evisaNo ratings yet
- Resume Format PDF For TeachersDocument6 pagesResume Format PDF For Teachersfskt032h100% (1)
- Edu 533 Sas#17Document8 pagesEdu 533 Sas#17Lalaine Villamar DizonNo ratings yet
- Annabelle EDUC 204 Evaluating The Result of School Administration and SupervisionDocument26 pagesAnnabelle EDUC 204 Evaluating The Result of School Administration and SupervisionCristhel MacajetoNo ratings yet
- English Literature: Grade 12Document68 pagesEnglish Literature: Grade 12Kirran Khumar GollaNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis GuidelinesDocument31 pagesItem Analysis GuidelinesLuna Ledezma100% (1)
- Intersummer 2021 Course Offerings: Arts, Humanities, Soc ScienceDocument15 pagesIntersummer 2021 Course Offerings: Arts, Humanities, Soc ScienceRamkumar HaridossNo ratings yet
- FASH2002 Sustainable Fashion Semester 1 2022 Bentley Perth Campus INTDocument12 pagesFASH2002 Sustainable Fashion Semester 1 2022 Bentley Perth Campus INTArchVFXNo ratings yet