Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHEA-1201L-Pre-lab-Determination-of-water-hardness - Total Hardness of Water Using Ethylene DiammineTetraacetic Acid (EDTA) (A Titration Method)
CHEA-1201L-Pre-lab-Determination-of-water-hardness - Total Hardness of Water Using Ethylene DiammineTetraacetic Acid (EDTA) (A Titration Method)
Uploaded by
MarielleCaindecOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEA-1201L-Pre-lab-Determination-of-water-hardness - Total Hardness of Water Using Ethylene DiammineTetraacetic Acid (EDTA) (A Titration Method)
CHEA-1201L-Pre-lab-Determination-of-water-hardness - Total Hardness of Water Using Ethylene DiammineTetraacetic Acid (EDTA) (A Titration Method)
Uploaded by
MarielleCaindecCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEA 1201 L
PRE-LABORATORY
Total Hardness of Water Using Ethylene DiammineTetraacetic Acid (EDTA)
(A Titration Method)
1. Define water hardness. What methods can be used to remove water hardness?
Water hardness is the total calcium and magnesium ion concentration of a water solution. This is also
expressed as the concentration of calcium carbonate. Water hardness depends upon the amount of
chemical salts dissolved in the water. These salts, in the presence of heat or alkalinity, may react to
produce insoluble material which precipitates out of solution in the form of hard water scale. The
methods you can utilize in order to remove water hardness are ion exchange, chelation, lim softening,
and reverse osmosis.
2. In industrial settings, why is water hardness an important parameter for analyses?
Many industrial and domestic water users are concerned about the hardness of their water. When hard
water is heated, such as in a home water heater, solid deposits of calcium carbonate can form. This scale
can reduce the life of equipment, raise the costs of heating the water, lower the efficiency of electric
water heaters, and clog pipes.
3. Write the equation for the titration of Ca+2 with EDTA.
Zn2+ (aq) + EDTA4- (aq) → Ca(EDTA)2- (aq)
4. Write the equations for the endpoint color change of Eriochrome Black T (EBT) with Mg+2
EDTA4− + Mg2+ → [Mg-EDTA]2−
5. Report the water hardness as ppm CaCO3 of a 50 ml water sample that required 32. 50 ml of 0.01 M
EDTA to reach the end point of the titration
−3 0.01 mol EDTA
Moles of EDTA=32.50 x 10❑ Lx
L
−4
¿ 3.25 x 10❑
3.25 x 10−4 mol 100.0869 g
mass of CaCo 3=1 L x x
L mol
−2❑
¿ 3.25 x 10❑ g
3.25 x 10❑−2
= = 65 ppm
0.05
6. Answer briefly the following questions.
a. Why do we add a small amount of Mg 2+ to the solution in the preparation of the EDTA?
Adding a small amount of Mg 2+– EDTA to the titrant gives a sharper end point. Because Ca 2+ forms a
stronger complex with EDTA, it displaces Mg 2+, which then forms the red-colored Mg 2+– calmagite
complex.
b. What is the role of the ammonia buffer in the EDTA titration process.
The ammonia buffer is used to resist the change in pH. All of the reactions between metal ions and EDTA
are dependent on pH. Change in pH leads to an improper reaction between the metal ion and the EDTA.
c. Why do we see color transitions at the equivalence point?
We see color transitions at equivalence point because this indicates that the H + and OH- are in equal
concentrations. This also means that the endpoint is also going to take place, where the substance goes
from acidic to basic or vice versa.
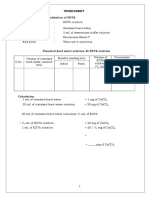
7. Complete the table below with the necessary information from Amrita. Then calculate corresponding
water hardness. Make sure to show all necessary sample solutions below. Which water sample has the
highest level of water hardness
Water Hardness
Volume
of Volume EDTA
Sample Buret Reading, mL EDTA
sample, used, mL
mL
Final Initial
Well water
Trial 1 15.0 mL 46.2 mL 50.0 mL 3.8 mL
Trial 2 15.0 mL 46.2 mL 50.0 mL 3.8 mL
Average, mg/L CaCO3 25 mg/L
Tap water
Trial 1 15.0 mL 47.7 mL 50.0 mL 2.3 mL
Trial 2 15.0 mL 47.7 mL 50.0 mL 2.3 mL
Average, mg/L CaCO3 12 mg/L
Sea water
Trial 1 15.0 mL 41.0 mL 50.0 mL 9.0 mL
Trial 2 15.0 mL 41.0 mL 50.0 mL 9.0 mL
Average, mg/L CaCO3 60 ppm
a.) Well Water
−3 0.01 mol EDTA
Moles of EDTA=3.8 x 10❑ Lx
L
−5
¿ 3.8 x 10❑
3.8 x 10−5 mol 100.0869 g
mass of CaCo 3=1 L x x
L mol
−3❑
¿ 3.80 x 10❑ g
−3❑
3.80 x 10❑
= = 25 ppm
0.015
b.) Tap Water
−3 0.01 mol EDTA
Moles of EDTA=2.3 x 10❑ Lx
L
−5
¿ 2.3 x 10❑
2.3 x 10−5 mol 100.0869 g
mass of CaCo 3=1 L x x
L mol
−3❑
¿ 2.30 x 10❑ g
2.30 x 10❑−3❑
= = 15 ppm
0.015
c.) Sea Water
0.01 mol EDTA
Moles of EDTA=9.0 x 10❑−3 Lx
L
¿ 9.0 x 10 ❑−5
0.90 x 10−4 mol 100.0869 g
mass of CaCo 3=1 L x x
L mol
−3❑
¿ 9.0 x 10 ❑ g
9.0 x 10❑−3❑
= = 60 ppm
0.015
The water sample that has the highest level of water hardness is seawater.
You might also like
- Pre-Laboratory#4 CHEM1103L CalorimetryDocument3 pagesPre-Laboratory#4 CHEM1103L CalorimetryMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water Student 2016Document8 pagesGravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water Student 2016Rishabh KotturgowdraNo ratings yet
- Vademecum For Vitamin FormulationsDocument144 pagesVademecum For Vitamin FormulationsSergio M Junior0% (1)
- Hema 1 August 2021Document84 pagesHema 1 August 2021Renz Gerard Amor100% (1)
- C1797-16e1 Standard Specification For Ground Calcium Carbonate and Aggregate Mineral Fillers For Use in Hydraulic Cement ConcreteDocument5 pagesC1797-16e1 Standard Specification For Ground Calcium Carbonate and Aggregate Mineral Fillers For Use in Hydraulic Cement ConcreteFahad RedaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Total Hardness of Water SamplesDocument15 pagesDetermination of Total Hardness of Water SamplesDavinci LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Water HardnessDocument14 pagesDetermination of Water HardnessCesarah CabungcalNo ratings yet
- Analytical Practical-#9Document7 pagesAnalytical Practical-#9Roselyn NormNo ratings yet
- ExperimentDocument6 pagesExperimentababnehbashar5No ratings yet
- 9.1 Water Tutorial Sheet-1 Solution PDFDocument4 pages9.1 Water Tutorial Sheet-1 Solution PDFDank CoderNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment: Short QuestionsDocument8 pagesWater and Its Treatment: Short QuestionsAthirath VeldandaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Hardness of WaterDocument13 pagesLab Report Hardness of WaterFelix YeboahNo ratings yet
- Complexometric Determination of Water Hardness Lab ReportDocument5 pagesComplexometric Determination of Water Hardness Lab ReportMichelle50% (2)
- Practical Book Analytical ChemistryDocument14 pagesPractical Book Analytical Chemistrysalman ahmedNo ratings yet
- Hardness of WaterDocument10 pagesHardness of WatersumanthNo ratings yet
- Hardness of Water: 1 Step: The Calcium Ion Coordinates With The Indicator (Eriochrome Black T)Document5 pagesHardness of Water: 1 Step: The Calcium Ion Coordinates With The Indicator (Eriochrome Black T)Niwled UyNo ratings yet
- Project Report - Hardness of Water r2 FinalDocument10 pagesProject Report - Hardness of Water r2 FinalS Balagopal SivaprakasamNo ratings yet
- Rohini 38460398726Document10 pagesRohini 38460398726Ranjana AroraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 Skt3033 A221Document16 pagesLab Report 1 Skt3033 A221izz isalahNo ratings yet
- Determination of Total Hardness of Water by EDTA Titration.Document3 pagesDetermination of Total Hardness of Water by EDTA Titration.Saharbano awanNo ratings yet
- DynamicDocument6 pagesDynamicansaamalshawabkeh246No ratings yet
- Hardness of WaterDocument11 pagesHardness of WaterVikrant Singh0% (1)
- Projecttitle:Determinationoftotalh Ard Nes Sof Wat ErDocument20 pagesProjecttitle:Determinationoftotalh Ard Nes Sof Wat ErToushif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Exp. 15 - Video: (Time: 21:39 Minutes)Document9 pagesExp. 15 - Video: (Time: 21:39 Minutes)Yogeesh B ENo ratings yet
- Complexation Titration: Determination of The Total Hardness of WaterDocument14 pagesComplexation Titration: Determination of The Total Hardness of WaterIntan SapuraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document11 pagesExperiment 4Frenzes PadabocNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 CHY1701 ETH VL2019201006023 Reference Material I 17-Jul-2019 Water NumericalsDocument9 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 CHY1701 ETH VL2019201006023 Reference Material I 17-Jul-2019 Water NumericalsAruldharshan SaravananNo ratings yet
- Calcium Analysis EDTA TitrationDocument6 pagesCalcium Analysis EDTA TitrationChun Wing Lai100% (2)
- Experiment 3Document12 pagesExperiment 3Randy KarisNo ratings yet
- Determination of Hardness and Calcium in The SampleDocument8 pagesDetermination of Hardness and Calcium in The SampleGobe Jam100% (1)
- Determining The Hardness of WaterDocument3 pagesDetermining The Hardness of Waterchrisbarnes051No ratings yet
- Chemistry 213: Experiment 7 Determining Water Hardness by EDTA TitrationDocument6 pagesChemistry 213: Experiment 7 Determining Water Hardness by EDTA TitrationAvinashNo ratings yet
- Module 2.2 Total Hardness of Water PrincipleDocument2 pagesModule 2.2 Total Hardness of Water Principlemarie parfanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Lab ManualDocument25 pagesEngineering Chemistry Lab ManualmsdineshpaiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Experiment No. 4Document3 pagesLab Manual For Experiment No. 4Bhukya SwamyNo ratings yet
- GROUP2 Act 6 - Water Hardness Determination - WorksheetDocument5 pagesGROUP2 Act 6 - Water Hardness Determination - WorksheetNitrogenNo ratings yet
- EDTA Titration CalculationsDocument2 pagesEDTA Titration CalculationsMuhammed IslahuddinNo ratings yet
- Titration I - Standardization of EDTA: WorksheetDocument52 pagesTitration I - Standardization of EDTA: WorksheetSIVARAMAN MNo ratings yet
- Water 09Document4 pagesWater 09Prashant ZadeNo ratings yet
- Lampiran PerhitunganDocument4 pagesLampiran Perhitunganellyana firdausNo ratings yet
- Calcium Analysis by EDTA.22Document3 pagesCalcium Analysis by EDTA.22alexlugalia7No ratings yet
- Problems On EDTADocument4 pagesProblems On EDTAAniket Kundu100% (1)
- Unit-2 B-Determination of Hardness of Water & UNIT-3 - Hard Water and IndustriesDocument4 pagesUnit-2 B-Determination of Hardness of Water & UNIT-3 - Hard Water and Industriesvandv printsNo ratings yet
- Water TechnologyDocument15 pagesWater TechnologyRamkiNo ratings yet
- 4d Application of Complexometric TitrationDocument16 pages4d Application of Complexometric TitrationnajwaNo ratings yet
- EDTA ExperimentDocument5 pagesEDTA ExperimentMahmoud MahmoudmNo ratings yet
- FR AnachemDocument5 pagesFR AnachemYüri ÄnnNo ratings yet
- CE 365 F2017 Wk4 Hardness LabDocument10 pagesCE 365 F2017 Wk4 Hardness LabHayden Chappelear-RobbinsNo ratings yet
- Water Technology: Schematic of The Components of The Social Cost of Water PollutionDocument48 pagesWater Technology: Schematic of The Components of The Social Cost of Water PollutiondanishNo ratings yet
- Ebtindicatorand Theory: ObiectoDocument5 pagesEbtindicatorand Theory: ObiectoMohammed HaziqNo ratings yet
- Hardness of WaterDocument9 pagesHardness of WaterMaame Efua NeizerNo ratings yet
- Chm421-Experiment 5 - Distillation and Hardness of WaterDocument11 pagesChm421-Experiment 5 - Distillation and Hardness of Waternipale hiNo ratings yet
- TopicsDocument67 pagesTopicsNithin ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Session: 3 Engineering ChemistryDocument17 pagesSession: 3 Engineering ChemistryDUE DATENo ratings yet
- Chemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposeDocument4 pagesChemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposekuochsochinNo ratings yet
- Water PPT (Fe 22-23)Document46 pagesWater PPT (Fe 22-23)Aaditya MalaniNo ratings yet
- WH Softening 1Document47 pagesWH Softening 1Abdallah AlRawashdehNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationDocument14 pagesRedox Titrationnorsiah100% (2)
- Group 01 HardnessDocument7 pagesGroup 01 HardnessHaniya SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Analysis of Hard Water - F2010 PDFDocument7 pagesLab 7 - Analysis of Hard Water - F2010 PDFEsha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Hard Eness WaterDocument4 pagesHard Eness WaterLaura OliverosNo ratings yet
- Reportsheet#6 - Properties and Purification of Water - Chem1103lDocument7 pagesReportsheet#6 - Properties and Purification of Water - Chem1103lMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Reportsheet#8 - Determination of Air Pollutants (Nox) in Cigarette Smoke - Chem1103lDocument4 pagesReportsheet#8 - Determination of Air Pollutants (Nox) in Cigarette Smoke - Chem1103lMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Reportsheet#5 - Determination of Heat of Combustion Using A Bomb Calorimeter - Chem1103lDocument6 pagesReportsheet#5 - Determination of Heat of Combustion Using A Bomb Calorimeter - Chem1103lMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Reportsheet#7 - Determination of Dissolved Oxygen Content and Chloride in Water - Chem1103lDocument8 pagesReportsheet#7 - Determination of Dissolved Oxygen Content and Chloride in Water - Chem1103lMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Reportsheet#2 Chemicalactivityandcorrosionofmetals Chem1103l Group26Document7 pagesReportsheet#2 Chemicalactivityandcorrosionofmetals Chem1103l Group26MarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Reportsheet#4 Calorimetry Chem1103lDocument6 pagesReportsheet#4 Calorimetry Chem1103lMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Pre-Laboratory#5 - CHEM1103 - DETERMINATION OF HEAT OF COMBUSTION USING A BOMB CALORIMETERDocument3 pagesPre-Laboratory#5 - CHEM1103 - DETERMINATION OF HEAT OF COMBUSTION USING A BOMB CALORIMETERMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Report#3 Testingthetensilestrengthofmetalsusingtheuniversaltestingmachine Chem1103l Group26Document8 pagesReport#3 Testingthetensilestrengthofmetalsusingtheuniversaltestingmachine Chem1103l Group26MarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- CHEA 1201L - PreLab For Gravimetric Analysis - Gravimetric Analysis of SulfurDocument5 pagesCHEA 1201L - PreLab For Gravimetric Analysis - Gravimetric Analysis of SulfurMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Pre-Laboratory#3 - CHEM1103L - Testing The Tensile Strength of Metals Using The Universal TestingDocument1 pagePre-Laboratory#3 - CHEM1103L - Testing The Tensile Strength of Metals Using The Universal TestingMarielleCaindecNo ratings yet
- Hi-Tech Projects (E-Copy) Jan15Document17 pagesHi-Tech Projects (E-Copy) Jan15Chetan Mukhija100% (1)
- Experiment 2Document6 pagesExperiment 2Rohann James Abrogueña ReañoNo ratings yet
- ConsumerChemistry9 q3 Mod1 ChemicalsFoundinCosmetics v3Document32 pagesConsumerChemistry9 q3 Mod1 ChemicalsFoundinCosmetics v3Kristine Ibarreta-Jazul67% (3)
- SOP For Analysis of WaterDocument5 pagesSOP For Analysis of WatermrugeshjNo ratings yet
- Complex Reaction BP 2023Document28 pagesComplex Reaction BP 2023fojirof555No ratings yet
- 2.5.11. Complexometric Titrations 20511eDocument1 page2.5.11. Complexometric Titrations 20511ePhuc DVNo ratings yet
- Blood TubesDocument4 pagesBlood Tubesgail_eunice12No ratings yet
- John Carlo Dela Cruz - CHEM - Q3 - W2Document6 pagesJohn Carlo Dela Cruz - CHEM - Q3 - W2johncarlodc99No ratings yet
- Decontamination PreDocument31 pagesDecontamination Presch203No ratings yet
- 3101 - Complexometric TitrationDocument21 pages3101 - Complexometric Titrationraisul razaNo ratings yet
- 25 Water Treatment Training Boiler Water TreatmentDocument94 pages25 Water Treatment Training Boiler Water TreatmentMohamad Eshra100% (1)
- Basf Home Care and I&i 2020 Guide To Sustainable IngredientsDocument20 pagesBasf Home Care and I&i 2020 Guide To Sustainable IngredientsLaban KantorNo ratings yet
- Aust Endodontic J - 2021 - Eskander - Effect of Phytic Acid and Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid On Penetration Depth ofDocument6 pagesAust Endodontic J - 2021 - Eskander - Effect of Phytic Acid and Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid On Penetration Depth ofMahmoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Hematology Lec Specimen CollectionDocument3 pagesHematology Lec Specimen CollectionKathleen Cobrador EribalNo ratings yet
- D1411-09 Standard Test Methods For Water-Soluble Chlorides Present As Admixtures in Graded Aggregate Road MixesDocument5 pagesD1411-09 Standard Test Methods For Water-Soluble Chlorides Present As Admixtures in Graded Aggregate Road MixesFederico MontesverdesNo ratings yet
- Alternativfe Chelator GLDA To EDTA Dis Sol Vine GL ArticleDocument4 pagesAlternativfe Chelator GLDA To EDTA Dis Sol Vine GL ArticlewarwickNo ratings yet
- Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Polluted Soils and WaterDocument11 pagesPhytoremediation of Heavy Metal Polluted Soils and Waterdaimon_p100% (1)
- Introduction To HematologyDocument67 pagesIntroduction To HematologyMera MendozaNo ratings yet
- Nasi Pecel PDFDocument10 pagesNasi Pecel PDFkhansarafidaNo ratings yet
- Cu-Ca-Fe EDTA MSDSDocument2 pagesCu-Ca-Fe EDTA MSDSasmaamNo ratings yet
- Endo-Eze AET Illustrated Technique Guide PDFDocument18 pagesEndo-Eze AET Illustrated Technique Guide PDFZmeu CristinaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Water HardnessDocument5 pagesDetermination of Water HardnessLi Kim100% (1)
- Root Canal Irrigants & Chemical Aids in EndodonticsDocument28 pagesRoot Canal Irrigants & Chemical Aids in EndodonticsCristina Ene100% (1)
- Pharm AnalysisDocument6 pagesPharm AnalysisMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Practical Windows and Inhibitors For Grade 2 Titanium Use in Alkaline Peroxide Bleach SolutionsDocument9 pagesPractical Windows and Inhibitors For Grade 2 Titanium Use in Alkaline Peroxide Bleach SolutionsGeetha ThiruvengadamNo ratings yet
- ColaTerge LFD CDocument1 pageColaTerge LFD CmndmattNo ratings yet
- Methods of Sampling and Test (Physical and Chemical) For Water and WastewaterDocument10 pagesMethods of Sampling and Test (Physical and Chemical) For Water and Wastewaterlabn6446No ratings yet