Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further Differentiation
Exs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further Differentiation
Uploaded by
ASYA HIZLIOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further Differentiation
Exs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further Differentiation
Uploaded by
ASYA HIZLICopyright:
Available Formats
IB Mathematics SL & HL exercise set 6-1-60v1
Further Differentiation – techniques & applications
content: basic & further differentiation rules – including chain rule, product rule & quotient rule; equation of
tangent or normal to a curve; finding and justifying maxima, minima & inflexion points; optimization
8 questions ♦ answers given on last page
■ No calculator on 1 – 5 ■
dy
1. For each function in (a) to (f), find .
dx
ln x
(a) y= (b) y = e cos x
x
1 x2 + 1
(c) y = ln (d) y =
x x2 −1
x 2 + ax
(e) y = ln (1 + tan 2 x ) (f) y = , a, b [a and b are real constants]
x+b
2. Given f ( x ) = 4 + 2sin 3x , find the equation of the (a) tangent to the curve and the (b) normal to
π
the curve at the point where x = .
3
x2 − 3
3. Find the exact coordinates of all maximum and minimum points on the graph of y = .
ex
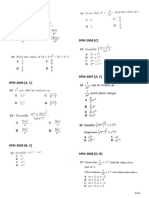
4. An isosceles triangle lies in the x-y coordinate plane
with its vertices at ( −1, 0 ) , (1, 0 ) and ( 0, c ) .
A rectangle (shaded in diagram) is inscribed in the
triangle such that one of its side is on the x-axis. Find
the exact dimensions of the rectangle with the largest
possible area.
5. Find the exact coordinates of the two points on the graph of y = 9 − x 2 that are closest to ( 0, 4 ) .
© InThinking – IB Maths HL & SL 1
IB Mathematics SL & HL exercise set 6-1-60v1
Further Differentiation – techniques & applications
■ calculator allowed on 6 – 8 ■
6. Find the coordinates of all points of inflexion on the graph of the equation in question # 3.
7. A container is to be made in the shape of a cylinder with a hemisphere
attached on top. The total volume of the container will be 120 cm3 .
(a) Given that the radius of the base is r cm, show that the total surface
5πr 2 240
area, S, of the container is given by the function S ( r ) = + .
3 r
(b) Hence, find the value of the radius, r, that will produce a container
with minimum surface area.
4 3
sphere: surface area = 4πr 2 ; volume = πr
3
a
8. Consider the function g ( x ) = . Given that g ( 0 ) = 3 , g ( 0 ) = − 3 and the graph of g
x + bx + c
2
has a horizontal tangent at x = 1 , find the values of a, b and c.
© InThinking – IB Maths HL & SL 2
IB Mathematics SL & HL exercise set 6-1-60v1
Further Differentiation – techniques & applications
Answers
dy 1 − ln x
= − sin x ( ecos x )
dy
1. (a) = (b)
dx x2 dx
dy 1 dy x3 − 3x
(c) =− (d) =
dx x dx
( x2 − 1)
3
dy dy x 2 + 2bx + ab
(e) = 2 tan x (f) =
( x + b)
2
dx dx
1 π
2. (a) y = − 6 x + 2π + 4 (b) y = x− +4
6 18
12
3. minimum point at ( −1, − 2e ) ; maximum point at 3, 3 .
e
c
4. dimensions of rectangle: 1 unit by units
2
3 2 9 3 2 9
5. , and − ,
2 2 2 2
6. inflexion points at ( − 0.236, − 3.73) and ( 4.24, 0.216 ) [approximate to 3 significant figures]
7. (b) r 2.84 cm
8. a = − 6, b = −2, c = − 2
© InThinking – IB Maths HL & SL 3
You might also like
- Project 02 - Business DecisionsDocument27 pagesProject 02 - Business Decisionsapi-458902916No ratings yet
- Pragati Full Test 6 Question Paper PDFDocument23 pagesPragati Full Test 6 Question Paper PDFAkash A73% (15)
- FE Civil Exam - UpdatedDocument163 pagesFE Civil Exam - UpdatedPierre DuniganNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 11 SolutionsDocument3 pagesRD Sharma Class 11 SolutionsRD Sharma Solutions33% (30)
- Btech Construction Management Assignments Ist YearDocument55 pagesBtech Construction Management Assignments Ist YearbasheerkkNo ratings yet
- 25 Pure Maths Resourceful Mock 2016-2Document4 pages25 Pure Maths Resourceful Mock 2016-2BWENGYE NICHOLASNo ratings yet
- Olan MTC Seminar Paper One Questions PDFDocument5 pagesOlan MTC Seminar Paper One Questions PDFJeremiah NakibingeNo ratings yet
- Math Tutorial SheetDocument3 pagesMath Tutorial SheetKondwani BandaNo ratings yet
- P3 3rd Revision Material PDFDocument18 pagesP3 3rd Revision Material PDFrachitNo ratings yet
- Orddiffsoln 1996Document6 pagesOrddiffsoln 1996Graham MooreNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Sathyabhama University B.EB. Tech - 1st Semester Engineering Mathematics-I Sample Paper 3Document4 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Sathyabhama University B.EB. Tech - 1st Semester Engineering Mathematics-I Sample Paper 3mashaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1B Semester Test 1 (V2) MemoDocument8 pagesMathematics 1B Semester Test 1 (V2) MemoLwando MankwaliNo ratings yet
- Edexcel C3 PaperADocument3 pagesEdexcel C3 PaperAwinstonNo ratings yet
- Eng Maths III (Civil A)Document2 pagesEng Maths III (Civil A)Madan PanditNo ratings yet
- University of Ghana (All Rights Reserved)Document3 pagesUniversity of Ghana (All Rights Reserved)Mynel Kojo DenkyiNo ratings yet
- e 5792Document7 pagese 5792sevag002816No ratings yet
- Class 12 Question Paper 3Document3 pagesClass 12 Question Paper 3Sohail150788No ratings yet
- Slow AdvanceminorDocument2 pagesSlow Advanceminorarnrc79No ratings yet
- MAT 221 TEST 2 Revision QuestionsDocument2 pagesMAT 221 TEST 2 Revision QuestionsemmanuelmbuseNo ratings yet
- Add Math Idterm Exam Beaconouse P 1Document8 pagesAdd Math Idterm Exam Beaconouse P 1furiouslighning1929No ratings yet
- 06a. Practice Set 2Document6 pages06a. Practice Set 2aNo ratings yet
- Areas (67 Bits)Document26 pagesAreas (67 Bits)AbhiNo ratings yet
- End of Term One Examinations Senior Five Pure Mathematics: 3 HoursDocument4 pagesEnd of Term One Examinations Senior Five Pure Mathematics: 3 HoursPeter KanNo ratings yet
- Integration Final ReviewDocument3 pagesIntegration Final ReviewRajesh KNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics IDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics INikash SubediNo ratings yet
- Test 4 - SMKJT - Ques&AnsDocument10 pagesTest 4 - SMKJT - Ques&AnsLIM YEE WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- 102100683529Document3 pages102100683529nishmalmuhammad58No ratings yet
- Calculus Test12 Sol 20191015Document7 pagesCalculus Test12 Sol 20191015Mạc Hải LongNo ratings yet
- Grade-11 Mathematics, Model Set CDocument4 pagesGrade-11 Mathematics, Model Set Carjab acharyaNo ratings yet
- 2021 PypDocument15 pages2021 PypFelicya SugiriNo ratings yet
- C - Mathematics-XIIMat - 071Document4 pagesC - Mathematics-XIIMat - 071www.storytime1No ratings yet
- B3 2-R3Document27 pagesB3 2-R3api-3782519No ratings yet
- Assignment of Class 11 ScienceDocument8 pagesAssignment of Class 11 Scienceshankarharu12No ratings yet
- Sin Sin 1 Cos +: X XDX X X DX XDocument2 pagesSin Sin 1 Cos +: X XDX X X DX XAlok RajNo ratings yet
- MSCBSE0005Document28 pagesMSCBSE0005milapdhruvcomputerworkNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A Level Mathematics Pure Mathematics Year 1 by Smith, Harry (2017) .PDF 4Document3 pagesEdexcel A Level Mathematics Pure Mathematics Year 1 by Smith, Harry (2017) .PDF 4luxingzhang727No ratings yet
- Transformations of GraphsDocument11 pagesTransformations of GraphsMartin DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Calc2 Exam2 2018Document2 pagesCalc2 Exam2 2018Oumayma El KadiNo ratings yet
- IPE QuestionsDocument7 pagesIPE QuestionsPRASADNo ratings yet
- APP2Document3 pagesAPP2Dayana JimenezNo ratings yet
- Cal1 TD2 (2023 24)Document2 pagesCal1 TD2 (2023 24)Da VyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 TestDocument6 pagesChapter 3 TestJose SegalesNo ratings yet
- S.6 MTC 1Document4 pagesS.6 MTC 1wankyaabubaker2020No ratings yet
- JEESankalp Practice Paper-01Document16 pagesJEESankalp Practice Paper-01jayeshsadafule383No ratings yet
- C-16 C-102 Sbtet-Mar2018Document3 pagesC-16 C-102 Sbtet-Mar2018DrGudimella Vrk SagarNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam QuestionDocument4 pagesSample Exam QuestionUmmi ThohirahNo ratings yet
- Final: Problems and AnswersDocument3 pagesFinal: Problems and AnswersDoris riverosNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 01-11-2021fDocument6 pagesPractice Paper 01-11-2021frakshitk023No ratings yet
- N.B: Answer Six Questions, Taking Three From Each SectionDocument2 pagesN.B: Answer Six Questions, Taking Three From Each SectionRakib HasanNo ratings yet
- 1993 AP CalcDocument30 pages1993 AP CalcHenry JurneyNo ratings yet
- 2024 Tutorial 1 Graphing Techniques I Level 0 (Solutions)Document5 pages2024 Tutorial 1 Graphing Techniques I Level 0 (Solutions)afreenazraa2007No ratings yet
- C3 Paper A ShortDocument4 pagesC3 Paper A ShortxAfgunNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2008 Paper 1 Solutions by FIITJEEDocument23 pagesIIT JEE 2008 Paper 1 Solutions by FIITJEEAbhinav100% (43)
- 2016-2-Joh-Dbl Batu Pahat-QDocument2 pages2016-2-Joh-Dbl Batu Pahat-QNur B TapriNo ratings yet
- B0-R4_Jan2023Document2 pagesB0-R4_Jan2023Ram LalNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Additional MathematicsDocument16 pagesCambridge O Level: Additional Mathematicsweedking1985No ratings yet
- Graphs & Functions: Higher MathsDocument17 pagesGraphs & Functions: Higher MathsOmaru NimagaNo ratings yet
- Cal1 Final Sample PDFDocument3 pagesCal1 Final Sample PDFAnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- KCET 2020 Previous Year Question Paper For Maths - Free PDF DownloadDocument21 pagesKCET 2020 Previous Year Question Paper For Maths - Free PDF Downloaditsmerana326No ratings yet
- L'hospitalDocument5 pagesL'hospitalAvinash RayNo ratings yet
- ADSPDocument2 pagesADSPRajaa KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- 05a. Quadratics - Completing The SquareDocument1 page05a. Quadratics - Completing The Squarejingcong liuNo ratings yet
- F3 C1 Indices SPMDocument5 pagesF3 C1 Indices SPMMei Shuen CheamNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian InterpolationDocument10 pagesLagrangian InterpolationEnos Lolang100% (2)
- Tangent PlanesDocument16 pagesTangent PlanesFerdinand Sebastian Barnabas100% (1)
- Solution of Sturm-Liouville Problems: Dr. T. PhaneendraDocument9 pagesSolution of Sturm-Liouville Problems: Dr. T. PhaneendraParth VijayNo ratings yet
- The Laplace Transform of A Periodic FunctionDocument4 pagesThe Laplace Transform of A Periodic FunctionWisdom Academy029No ratings yet
- Fibonacci Classroom Worksheet SolutionsDocument2 pagesFibonacci Classroom Worksheet Solutionsf10691122No ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2Document41 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2Drew StrauchNo ratings yet
- Demo 50 Quantitative Aptitude For Competitive Exams OswaalDocument50 pagesDemo 50 Quantitative Aptitude For Competitive Exams Oswaaltablettharun345No ratings yet
- mth108 MCQ For PracticeDocument8 pagesmth108 MCQ For PracticeCoder CoderNo ratings yet
- Graph Coloring & Hamiltonian CyclesDocument8 pagesGraph Coloring & Hamiltonian Cyclesaman100% (1)
- Darling Dambakku Darling DambakkuDocument5 pagesDarling Dambakku Darling DambakkuanjanareadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Seborg Et Al.)Document20 pagesChapter 3 (Seborg Et Al.)Jamel CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 Linear Algebra by Shailendra Kumar End GAME of MathematicsDocument32 pagesQuiz 4 Linear Algebra by Shailendra Kumar End GAME of MathematicsAbhijit NathNo ratings yet
- Topic 16 - Infinite Series and Its Convergence (Non-Negative Series) ContinuedDocument11 pagesTopic 16 - Infinite Series and Its Convergence (Non-Negative Series) ContinuedMoksh YadavNo ratings yet
- Elementary Linear Algebra With Applications 9th Edition by Kolman Hill ISBN Solution ManualDocument14 pagesElementary Linear Algebra With Applications 9th Edition by Kolman Hill ISBN Solution Manuallaurie100% (22)
- Dwnload Full Linear Algebra and Its Applications 5th Edition Lay Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Linear Algebra and Its Applications 5th Edition Lay Solutions Manual PDFmoldwarp.collumgn81100% (10)
- m3 Vtu NotesDocument25 pagesm3 Vtu NotesSandesh S Gowda80% (5)
- Exponential EquationDocument31 pagesExponential EquationRowel GrateNo ratings yet
- Speed MathematicsDocument188 pagesSpeed MathematicsKrishna Prasad KNo ratings yet
- 3 3Document28 pages3 3Jonalyn Bautista-Canlas100% (1)
- Some Properties of The Lozinskii Logarithmic Norm: Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument10 pagesSome Properties of The Lozinskii Logarithmic Norm: Ordinary Differential EquationsCavia PorcellusNo ratings yet
- Class 12 TH Unacademy NotesDocument54 pagesClass 12 TH Unacademy NotesArpita JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Probability Chapter Test For SSC StudentsDocument2 pagesProbability Chapter Test For SSC StudentsAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNo ratings yet
- Recurrence Relation 2Document13 pagesRecurrence Relation 2satya.ibsNo ratings yet