Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsElement Notation
Element Notation
Uploaded by
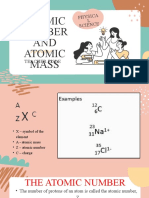
Angeli MercedThe document provides an approach to solving problems involving elemental notation. It explains that given the atomic number Z, one looks up the corresponding element and finds its atomic mass A from the periodic table. The number of neutrons n is then calculated as Z - A. This same process is followed whether given Z, the number of protons p, the number of electrons e, or the atomic mass A. Key notations are defined, including that Z=p for neutral atoms and n=A-Z.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- HW1problemsDocument2 pagesHW1problems666-66574No ratings yet
- Atomic Number, MassDocument19 pagesAtomic Number, MassEisle Keith Rivera TapiaNo ratings yet
- Radiogenic IsotopesDocument47 pagesRadiogenic IsotopesRicky DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Phasor: a sinusoidal function whose amplitude (A), frequency (ω), and phase (θ) are time-invariantDocument96 pagesPhasor: a sinusoidal function whose amplitude (A), frequency (ω), and phase (θ) are time-invariantMeghna PatnaikNo ratings yet
- CHM 138 Chap 4Document81 pagesCHM 138 Chap 4SyifasyhrahNo ratings yet
- Siegel Modular Forms Mod PDocument15 pagesSiegel Modular Forms Mod Prammurty2.hri2022No ratings yet
- The Subatomic ParticlesDocument5 pagesThe Subatomic ParticlescedrickjamesarestaNo ratings yet
- Formulas SheetDocument3 pagesFormulas SheetJuan jose Sánchez VelascoNo ratings yet
- Qualifier 2018Document12 pagesQualifier 2018Karishtain NewtonNo ratings yet
- Integral Sets and Cayley Graphs of Finite Groups: Roger C. Alperin Brian L. PetersonDocument12 pagesIntegral Sets and Cayley Graphs of Finite Groups: Roger C. Alperin Brian L. PetersonMonu KadyanNo ratings yet
- Matrices Over ZDocument3 pagesMatrices Over Zalok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13: Simple Linear Regression in Matrix FormatDocument9 pagesLecture 13: Simple Linear Regression in Matrix FormatSNo ratings yet
- Z-Transforms and Their Applications For Solving Difference EquationsDocument3 pagesZ-Transforms and Their Applications For Solving Difference EquationsAbhîñåv ChëbrølūNo ratings yet
- MATH 600, 2nd Examination: Rings and Modules Solutions and Grading KeyDocument3 pagesMATH 600, 2nd Examination: Rings and Modules Solutions and Grading KeyyameroNo ratings yet
- Rational Z-TransformDocument11 pagesRational Z-TransformJohn Assad100% (1)
- 3 in 1: A simple way to prove that e, ln (r) and π are irrationalDocument4 pages3 in 1: A simple way to prove that e, ln (r) and π are irrationalLyôn HockleinNo ratings yet
- l5 Atomic Number Mass Number Isotopes 3Document11 pagesl5 Atomic Number Mass Number Isotopes 3devendra singhNo ratings yet
- Bohr Diagrams and IonsDocument2 pagesBohr Diagrams and Ionsapi-310503032No ratings yet
- 2.2 (B) Proton and Nucleon NumberDocument11 pages2.2 (B) Proton and Nucleon NumberwannwaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass and Atomic NumberDocument18 pagesAtomic Mass and Atomic NumberTherese GBNo ratings yet
- 01 BendingStressesinBeamDocument13 pages01 BendingStressesinBeamisithkesara23No ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument11 pagesAtomic Modelamirrsohail8No ratings yet
- MatriksDocument6 pagesMatriksaldaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structure 1Document29 pagesDiscrete Structure 1malikabdullah0120No ratings yet
- Bending StressesDocument13 pagesBending StressesIsuru Udayanga NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- Bending Stresses in Beams - Part1Document8 pagesBending Stresses in Beams - Part1Isuru Udayanga NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument119 pagesLecture 2 Atoms Molecules and IonsDon Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles and Their PropertiesDocument6 pagesSubatomic Particles and Their PropertiesSahar HakimiNo ratings yet
- CA - Lesson - 3 - How+Atoms+Differ 1Document17 pagesCA - Lesson - 3 - How+Atoms+Differ 1arodaina511No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Enumeration (Lecture Notes) (David G. Wagner) (Z-Library)Document23 pagesBasic Principles of Enumeration (Lecture Notes) (David G. Wagner) (Z-Library)ishimweinesolgaNo ratings yet
- Chemi Chapter 3Document4 pagesChemi Chapter 3俊恒No ratings yet
- Phys 221 ExercisesDocument4 pagesPhys 221 ExercisesKristine Rodriguez-CarnicerNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory: Report BigprojectDocument10 pagesCircuit Theory: Report BigprojectVũ Hoàng LongNo ratings yet
- 1st Day Reviewer 2Document16 pages1st Day Reviewer 2Aiona MenorNo ratings yet
- LN3 Properties Eigenvalues&EigenvectorsDocument7 pagesLN3 Properties Eigenvalues&EigenvectorsNikhilesh PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Pe 588Document25 pagesPe 588sakyalolNo ratings yet
- Nazarov Podkorytov Ball InequalityDocument22 pagesNazarov Podkorytov Ball InequalityAlvaro CorvalanNo ratings yet
- Calculus II: Advanced Level Pure MathematicsDocument18 pagesCalculus II: Advanced Level Pure MathematicsmtbayleyNo ratings yet
- 17-U-382 Assignment 2Document6 pages17-U-382 Assignment 2Kayonde VanessaNo ratings yet
- Lu DecompositionDocument4 pagesLu DecompositionNguyen Tan MinhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Atomic StructureDocument27 pagesLesson 6 Atomic StructureTeacher JoanNo ratings yet
- Set Theory 31 34Document14 pagesSet Theory 31 34arunvks2000No ratings yet
- Homework 7 The Stern-Gerlach Experiment: μ - ⃗ B z ∂ ∂ z μ - ⃗ B) =μ ∂ B ∂ z, B z μ μ z SDocument3 pagesHomework 7 The Stern-Gerlach Experiment: μ - ⃗ B z ∂ ∂ z μ - ⃗ B) =μ ∂ B ∂ z, B z μ μ z SFurkan AkalNo ratings yet
- Lienard's Generalization of Larmour's FormulaDocument5 pagesLienard's Generalization of Larmour's FormulaJoão Vitor GamaNo ratings yet
- Generation of Integer Sequences 4-6-19Document21 pagesGeneration of Integer Sequences 4-6-19E Frank CorneliusNo ratings yet
- Polar CoordinatesDocument18 pagesPolar CoordinatesSayemin NaheenNo ratings yet
- Notes On Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument10 pagesNotes On Sub Atomic ParticlesBon PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Part BDocument16 pagesUnit 3 Part Blopohi2934No ratings yet
- Day 33Document8 pagesDay 33g.sathyanarayanan252008No ratings yet
- A BH V BH: Mathematics Triangle CylinderDocument11 pagesA BH V BH: Mathematics Triangle Cylinderart16marasiganNo ratings yet
- DSP Lecture Notes 1-2Document78 pagesDSP Lecture Notes 1-2Ashok BattulaNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis Handout 2 Results On Power SeriesDocument4 pagesComplex Analysis Handout 2 Results On Power SeriesVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Homework 8: Ha Pham November 20, 2008Document5 pagesHomework 8: Ha Pham November 20, 2008Mainak SamantaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-BLUEDocument18 pagesUnit 4-BLUE陳力熊No ratings yet
- FPS NNTDMDocument14 pagesFPS NNTDMPentti HaukkanenNo ratings yet
- BstractDocument18 pagesBstractTudor MicuNo ratings yet
- Plyas Random Walk Theorem 2014Document7 pagesPlyas Random Walk Theorem 2014Martin PanicioNo ratings yet
- MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems: Introduction To Describing FunctionsDocument31 pagesMCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems: Introduction To Describing FunctionsAbdesselem BoulkrouneNo ratings yet
- Centroids PDFDocument34 pagesCentroids PDFAndrea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Discrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81From EverandDiscrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81No ratings yet
- Molarity of IonsDocument2 pagesMolarity of IonsAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemDocument2 pagesBasic ChemAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Unit CircleDocument4 pagesUnit CircleAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Social MediaDocument2 pagesSocial MediaAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Composition of FunctionsDocument8 pagesComposition of FunctionsAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- HCL and NaOH Reaction LimitingDocument3 pagesHCL and NaOH Reaction LimitingAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Exponential FunctionDocument1 pageDerivative of Exponential FunctionAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Cooking in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesEthnic Cooking in The PhilippinesAngeli Merced100% (1)
- Combined Gas LawDocument2 pagesCombined Gas LawAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisorderAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- MosquitoDocument3 pagesMosquitoAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Physics SolnDocument1 pagePhysics SolnAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument2 pagesPolymersAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Young's ModulusDocument1 pageYoung's ModulusAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Homo HeteroDocument1 pageHomo HeteroAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Weight by Volume 2Document3 pagesWeight by Volume 2Angeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Rate of Change in VolumeDocument1 pageRate of Change in VolumeAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- GSM CalculatorDocument1 pageGSM CalculatorAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas EquationDocument1 pageIdeal Gas EquationAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Wein's Displacement LawDocument1 pageWein's Displacement LawAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 - 11 - Q1 - M5Document15 pagesChemistry 1 - 11 - Q1 - M5Elisa PauloNo ratings yet
- ICB Ex20 21Document8 pagesICB Ex20 21romaNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometers Lecture 2Document6 pagesSpectrophotometers Lecture 2Sabah MajzoubNo ratings yet
- Module Three Lesson One Guided NotesDocument5 pagesModule Three Lesson One Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- IGCSE UNIT - 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS NotesDocument12 pagesIGCSE UNIT - 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS Notesvishrudh lakshminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Element Builder Gizmo LabDocument5 pagesElement Builder Gizmo Labsarah watsonNo ratings yet
- Atomic MathDocument2 pagesAtomic MathchabriesNo ratings yet
- Isotopes & Mass Spectrum: Doodle NotesDocument4 pagesIsotopes & Mass Spectrum: Doodle NotesLama DebanyNo ratings yet
- What Is An Atom Like?Document3 pagesWhat Is An Atom Like?류성의No ratings yet
- SSD - Dynamics of Bolch Electrons - 20221011revDocument38 pagesSSD - Dynamics of Bolch Electrons - 20221011revfmnoori4No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 13Document3 pagesAtomic Structure 13ericadarmandNo ratings yet
- Act 3 Part 1 Symbols of Elements and Formulas of Inorganic Compounds - WordDocument6 pagesAct 3 Part 1 Symbols of Elements and Formulas of Inorganic Compounds - WordMaria Angela GeongoNo ratings yet
- Slater's Rules ANSWERSDocument8 pagesSlater's Rules ANSWERSPintu SinghNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 - AMDocument5 pagesWorksheet 3 - AMHydeki RyugaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Superconductor (Final)Document36 pagesUnit-4 Superconductor (Final)ShivaranjanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Quantum Numbers Worksheet 2020Document2 pages01 - Quantum Numbers Worksheet 2020elaria hanyNo ratings yet
- Photoelectron Spectroscopy & Xps Ups: Addis Ababa University Department of Chemistry PHD ProgramDocument37 pagesPhotoelectron Spectroscopy & Xps Ups: Addis Ababa University Department of Chemistry PHD ProgramGuru P MNo ratings yet
- Bruker OpticsDocument9 pagesBruker Opticsahmed samyNo ratings yet
- Annual Plan 7th (1 H. 36 W)Document10 pagesAnnual Plan 7th (1 H. 36 W)Казына НаршаеваNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q3 Adm Module For PrintingDocument36 pagesG8 Science Q3 Adm Module For PrintingJenn ElardeNo ratings yet
- TMS1122 Lec 5 3 9 2020Document28 pagesTMS1122 Lec 5 3 9 2020sanjunaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument10 pagesAtoms and MoleculesUtsav Kumar MathurNo ratings yet
- Career Point - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesCareer Point - Chemical BondingKeshav BandilNo ratings yet
- Transuranium Element - WikipediaDocument6 pagesTransuranium Element - WikipediaRatna Dewi SyarifahNo ratings yet
- Lewis Symbol ActivityDocument6 pagesLewis Symbol ActivityJessa EspirituNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Exam Review KEYDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Exam Review KEYERVIN DANCANo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChemical BondingAjay WaliaNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Structure & Bonding QDocument115 pagesCHM1 Structure & Bonding QGoutham SivagnanamNo ratings yet
- 002 Ionic BondingDocument23 pages002 Ionic BondingDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Physics 1Document24 pagesCell Physics 1Ahmad Al-ThunebatNo ratings yet
Element Notation
Element Notation
Uploaded by
Angeli Merced0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe document provides an approach to solving problems involving elemental notation. It explains that given the atomic number Z, one looks up the corresponding element and finds its atomic mass A from the periodic table. The number of neutrons n is then calculated as Z - A. This same process is followed whether given Z, the number of protons p, the number of electrons e, or the atomic mass A. Key notations are defined, including that Z=p for neutral atoms and n=A-Z.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an approach to solving problems involving elemental notation. It explains that given the atomic number Z, one looks up the corresponding element and finds its atomic mass A from the periodic table. The number of neutrons n is then calculated as Z - A. This same process is followed whether given Z, the number of protons p, the number of electrons e, or the atomic mass A. Key notations are defined, including that Z=p for neutral atoms and n=A-Z.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageElement Notation
Element Notation
Uploaded by
Angeli MercedThe document provides an approach to solving problems involving elemental notation. It explains that given the atomic number Z, one looks up the corresponding element and finds its atomic mass A from the periodic table. The number of neutrons n is then calculated as Z - A. This same process is followed whether given Z, the number of protons p, the number of electrons e, or the atomic mass A. Key notations are defined, including that Z=p for neutral atoms and n=A-Z.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
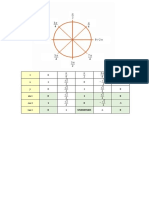
Element
Z A p e n Approach to Solving Problem
Notation
Since the given is Z, look for the element whose atomic
24
¿12 Mg 12 24 12 12 12 number is 12. Then Z=p=e=12. Get also the value of A
(atomic mass) from the Periodic Table. Then, n = Z-A.
Since the given is p=35, this is equal to Z. Then, look for
80 the element whose atomic number is 35. Then Z=p=e.
¿35 Br 35 80 35 35 45 Get also the value of A (atomic mass) from the Periodic
Table. Then, n = Z-A.
Since the given is e=80, this is equal to Z. Then, look for
201
¿80 Hg 80 201 80 80 121 the element whose atomic number is 80. Then Z=p=e.
The atomic mass is also given,then, n = Z-A.
Since the given is Z, look for the element whose atomic
137
¿56 Ba 56 137 56 56 81 number is 56. Then Z=p=e. Get also the value of A
(atomic mass) from the Periodic Table. Then, n = Z-A.
Since the given is e=24, this is equal to Z. Then, look for
52 the element whose atomic number is 24. Then Z=p=e.
¿24 Cr 24 52 24 24 28 Get also the value of A (atomic mass) from the Periodic
Table. Then, n = Z-A.
Z is Atomic Number of an element that is also equal to the number of protons (p)
A is the Average Atomic Mass of the element
p is the number of protons (Equal to Z)
e is the number of electrons that is also equal to the number of protons and atomic number (e=p=Z)
for a neutral element.
N is the number of neutrons that is equal to atomic mass less atomic number
Notation Meaning Notes
From the Periodic Table of Elements:
Atomic
Z Atomic Number Number (Z)
Element
Symbol
A Average Atomic Mass Atomic Mass Element
(A)
Equal to the Atomic Number
p number of protons
p=Z
Equal to the number of protons (or Z since p=Z) less the
e number of electrons charge of the atom
e = p - charge = Z - charge
Equal to atomic mass less atomic number
n number of neutrons
n=A-Z
You might also like
- HW1problemsDocument2 pagesHW1problems666-66574No ratings yet
- Atomic Number, MassDocument19 pagesAtomic Number, MassEisle Keith Rivera TapiaNo ratings yet
- Radiogenic IsotopesDocument47 pagesRadiogenic IsotopesRicky DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Phasor: a sinusoidal function whose amplitude (A), frequency (ω), and phase (θ) are time-invariantDocument96 pagesPhasor: a sinusoidal function whose amplitude (A), frequency (ω), and phase (θ) are time-invariantMeghna PatnaikNo ratings yet
- CHM 138 Chap 4Document81 pagesCHM 138 Chap 4SyifasyhrahNo ratings yet
- Siegel Modular Forms Mod PDocument15 pagesSiegel Modular Forms Mod Prammurty2.hri2022No ratings yet
- The Subatomic ParticlesDocument5 pagesThe Subatomic ParticlescedrickjamesarestaNo ratings yet
- Formulas SheetDocument3 pagesFormulas SheetJuan jose Sánchez VelascoNo ratings yet
- Qualifier 2018Document12 pagesQualifier 2018Karishtain NewtonNo ratings yet
- Integral Sets and Cayley Graphs of Finite Groups: Roger C. Alperin Brian L. PetersonDocument12 pagesIntegral Sets and Cayley Graphs of Finite Groups: Roger C. Alperin Brian L. PetersonMonu KadyanNo ratings yet
- Matrices Over ZDocument3 pagesMatrices Over Zalok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13: Simple Linear Regression in Matrix FormatDocument9 pagesLecture 13: Simple Linear Regression in Matrix FormatSNo ratings yet
- Z-Transforms and Their Applications For Solving Difference EquationsDocument3 pagesZ-Transforms and Their Applications For Solving Difference EquationsAbhîñåv ChëbrølūNo ratings yet
- MATH 600, 2nd Examination: Rings and Modules Solutions and Grading KeyDocument3 pagesMATH 600, 2nd Examination: Rings and Modules Solutions and Grading KeyyameroNo ratings yet
- Rational Z-TransformDocument11 pagesRational Z-TransformJohn Assad100% (1)
- 3 in 1: A simple way to prove that e, ln (r) and π are irrationalDocument4 pages3 in 1: A simple way to prove that e, ln (r) and π are irrationalLyôn HockleinNo ratings yet
- l5 Atomic Number Mass Number Isotopes 3Document11 pagesl5 Atomic Number Mass Number Isotopes 3devendra singhNo ratings yet
- Bohr Diagrams and IonsDocument2 pagesBohr Diagrams and Ionsapi-310503032No ratings yet
- 2.2 (B) Proton and Nucleon NumberDocument11 pages2.2 (B) Proton and Nucleon NumberwannwaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass and Atomic NumberDocument18 pagesAtomic Mass and Atomic NumberTherese GBNo ratings yet
- 01 BendingStressesinBeamDocument13 pages01 BendingStressesinBeamisithkesara23No ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument11 pagesAtomic Modelamirrsohail8No ratings yet
- MatriksDocument6 pagesMatriksaldaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structure 1Document29 pagesDiscrete Structure 1malikabdullah0120No ratings yet
- Bending StressesDocument13 pagesBending StressesIsuru Udayanga NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- Bending Stresses in Beams - Part1Document8 pagesBending Stresses in Beams - Part1Isuru Udayanga NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument119 pagesLecture 2 Atoms Molecules and IonsDon Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles and Their PropertiesDocument6 pagesSubatomic Particles and Their PropertiesSahar HakimiNo ratings yet
- CA - Lesson - 3 - How+Atoms+Differ 1Document17 pagesCA - Lesson - 3 - How+Atoms+Differ 1arodaina511No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Enumeration (Lecture Notes) (David G. Wagner) (Z-Library)Document23 pagesBasic Principles of Enumeration (Lecture Notes) (David G. Wagner) (Z-Library)ishimweinesolgaNo ratings yet
- Chemi Chapter 3Document4 pagesChemi Chapter 3俊恒No ratings yet
- Phys 221 ExercisesDocument4 pagesPhys 221 ExercisesKristine Rodriguez-CarnicerNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory: Report BigprojectDocument10 pagesCircuit Theory: Report BigprojectVũ Hoàng LongNo ratings yet
- 1st Day Reviewer 2Document16 pages1st Day Reviewer 2Aiona MenorNo ratings yet
- LN3 Properties Eigenvalues&EigenvectorsDocument7 pagesLN3 Properties Eigenvalues&EigenvectorsNikhilesh PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Pe 588Document25 pagesPe 588sakyalolNo ratings yet
- Nazarov Podkorytov Ball InequalityDocument22 pagesNazarov Podkorytov Ball InequalityAlvaro CorvalanNo ratings yet
- Calculus II: Advanced Level Pure MathematicsDocument18 pagesCalculus II: Advanced Level Pure MathematicsmtbayleyNo ratings yet
- 17-U-382 Assignment 2Document6 pages17-U-382 Assignment 2Kayonde VanessaNo ratings yet
- Lu DecompositionDocument4 pagesLu DecompositionNguyen Tan MinhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Atomic StructureDocument27 pagesLesson 6 Atomic StructureTeacher JoanNo ratings yet
- Set Theory 31 34Document14 pagesSet Theory 31 34arunvks2000No ratings yet
- Homework 7 The Stern-Gerlach Experiment: μ - ⃗ B z ∂ ∂ z μ - ⃗ B) =μ ∂ B ∂ z, B z μ μ z SDocument3 pagesHomework 7 The Stern-Gerlach Experiment: μ - ⃗ B z ∂ ∂ z μ - ⃗ B) =μ ∂ B ∂ z, B z μ μ z SFurkan AkalNo ratings yet
- Lienard's Generalization of Larmour's FormulaDocument5 pagesLienard's Generalization of Larmour's FormulaJoão Vitor GamaNo ratings yet
- Generation of Integer Sequences 4-6-19Document21 pagesGeneration of Integer Sequences 4-6-19E Frank CorneliusNo ratings yet
- Polar CoordinatesDocument18 pagesPolar CoordinatesSayemin NaheenNo ratings yet
- Notes On Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument10 pagesNotes On Sub Atomic ParticlesBon PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Part BDocument16 pagesUnit 3 Part Blopohi2934No ratings yet
- Day 33Document8 pagesDay 33g.sathyanarayanan252008No ratings yet
- A BH V BH: Mathematics Triangle CylinderDocument11 pagesA BH V BH: Mathematics Triangle Cylinderart16marasiganNo ratings yet
- DSP Lecture Notes 1-2Document78 pagesDSP Lecture Notes 1-2Ashok BattulaNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis Handout 2 Results On Power SeriesDocument4 pagesComplex Analysis Handout 2 Results On Power SeriesVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Homework 8: Ha Pham November 20, 2008Document5 pagesHomework 8: Ha Pham November 20, 2008Mainak SamantaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-BLUEDocument18 pagesUnit 4-BLUE陳力熊No ratings yet
- FPS NNTDMDocument14 pagesFPS NNTDMPentti HaukkanenNo ratings yet
- BstractDocument18 pagesBstractTudor MicuNo ratings yet
- Plyas Random Walk Theorem 2014Document7 pagesPlyas Random Walk Theorem 2014Martin PanicioNo ratings yet
- MCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems: Introduction To Describing FunctionsDocument31 pagesMCE693/793: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems: Introduction To Describing FunctionsAbdesselem BoulkrouneNo ratings yet
- Centroids PDFDocument34 pagesCentroids PDFAndrea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Discrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81From EverandDiscrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81No ratings yet
- Molarity of IonsDocument2 pagesMolarity of IonsAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemDocument2 pagesBasic ChemAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Unit CircleDocument4 pagesUnit CircleAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Social MediaDocument2 pagesSocial MediaAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Composition of FunctionsDocument8 pagesComposition of FunctionsAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- HCL and NaOH Reaction LimitingDocument3 pagesHCL and NaOH Reaction LimitingAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Exponential FunctionDocument1 pageDerivative of Exponential FunctionAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Cooking in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesEthnic Cooking in The PhilippinesAngeli Merced100% (1)
- Combined Gas LawDocument2 pagesCombined Gas LawAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisorderAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- MosquitoDocument3 pagesMosquitoAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Physics SolnDocument1 pagePhysics SolnAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument2 pagesPolymersAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Young's ModulusDocument1 pageYoung's ModulusAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Homo HeteroDocument1 pageHomo HeteroAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Weight by Volume 2Document3 pagesWeight by Volume 2Angeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Rate of Change in VolumeDocument1 pageRate of Change in VolumeAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- GSM CalculatorDocument1 pageGSM CalculatorAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas EquationDocument1 pageIdeal Gas EquationAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Wein's Displacement LawDocument1 pageWein's Displacement LawAngeli MercedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 - 11 - Q1 - M5Document15 pagesChemistry 1 - 11 - Q1 - M5Elisa PauloNo ratings yet
- ICB Ex20 21Document8 pagesICB Ex20 21romaNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometers Lecture 2Document6 pagesSpectrophotometers Lecture 2Sabah MajzoubNo ratings yet
- Module Three Lesson One Guided NotesDocument5 pagesModule Three Lesson One Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- IGCSE UNIT - 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS NotesDocument12 pagesIGCSE UNIT - 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS Notesvishrudh lakshminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Element Builder Gizmo LabDocument5 pagesElement Builder Gizmo Labsarah watsonNo ratings yet
- Atomic MathDocument2 pagesAtomic MathchabriesNo ratings yet
- Isotopes & Mass Spectrum: Doodle NotesDocument4 pagesIsotopes & Mass Spectrum: Doodle NotesLama DebanyNo ratings yet
- What Is An Atom Like?Document3 pagesWhat Is An Atom Like?류성의No ratings yet
- SSD - Dynamics of Bolch Electrons - 20221011revDocument38 pagesSSD - Dynamics of Bolch Electrons - 20221011revfmnoori4No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 13Document3 pagesAtomic Structure 13ericadarmandNo ratings yet
- Act 3 Part 1 Symbols of Elements and Formulas of Inorganic Compounds - WordDocument6 pagesAct 3 Part 1 Symbols of Elements and Formulas of Inorganic Compounds - WordMaria Angela GeongoNo ratings yet
- Slater's Rules ANSWERSDocument8 pagesSlater's Rules ANSWERSPintu SinghNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 - AMDocument5 pagesWorksheet 3 - AMHydeki RyugaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Superconductor (Final)Document36 pagesUnit-4 Superconductor (Final)ShivaranjanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Quantum Numbers Worksheet 2020Document2 pages01 - Quantum Numbers Worksheet 2020elaria hanyNo ratings yet
- Photoelectron Spectroscopy & Xps Ups: Addis Ababa University Department of Chemistry PHD ProgramDocument37 pagesPhotoelectron Spectroscopy & Xps Ups: Addis Ababa University Department of Chemistry PHD ProgramGuru P MNo ratings yet
- Bruker OpticsDocument9 pagesBruker Opticsahmed samyNo ratings yet
- Annual Plan 7th (1 H. 36 W)Document10 pagesAnnual Plan 7th (1 H. 36 W)Казына НаршаеваNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q3 Adm Module For PrintingDocument36 pagesG8 Science Q3 Adm Module For PrintingJenn ElardeNo ratings yet
- TMS1122 Lec 5 3 9 2020Document28 pagesTMS1122 Lec 5 3 9 2020sanjunaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument10 pagesAtoms and MoleculesUtsav Kumar MathurNo ratings yet
- Career Point - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesCareer Point - Chemical BondingKeshav BandilNo ratings yet
- Transuranium Element - WikipediaDocument6 pagesTransuranium Element - WikipediaRatna Dewi SyarifahNo ratings yet
- Lewis Symbol ActivityDocument6 pagesLewis Symbol ActivityJessa EspirituNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Exam Review KEYDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Exam Review KEYERVIN DANCANo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChemical BondingAjay WaliaNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Structure & Bonding QDocument115 pagesCHM1 Structure & Bonding QGoutham SivagnanamNo ratings yet
- 002 Ionic BondingDocument23 pages002 Ionic BondingDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Physics 1Document24 pagesCell Physics 1Ahmad Al-ThunebatNo ratings yet