Professional Documents
Culture Documents
APATAN
APATAN
Uploaded by
JOHN CARLO APATAN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views27 pagesOrthopedic nursing focuses on musculoskeletal disorders like fractures and bone injuries. Traction is the application of pulling forces to parts of the body to treat fractures and spinal issues. There are different types of casts and traction used for specific purposes - skeletal traction is directly attached to bone while cervical traction uses a neck brace during procedures. Nursing management of casts and traction includes monitoring circulation, teaching exercises, and caring for the cast as it sets and hardens.
Original Description:
f
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOrthopedic nursing focuses on musculoskeletal disorders like fractures and bone injuries. Traction is the application of pulling forces to parts of the body to treat fractures and spinal issues. There are different types of casts and traction used for specific purposes - skeletal traction is directly attached to bone while cervical traction uses a neck brace during procedures. Nursing management of casts and traction includes monitoring circulation, teaching exercises, and caring for the cast as it sets and hardens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views27 pagesAPATAN
APATAN
Uploaded by
JOHN CARLO APATANOrthopedic nursing focuses on musculoskeletal disorders like fractures and bone injuries. Traction is the application of pulling forces to parts of the body to treat fractures and spinal issues. There are different types of casts and traction used for specific purposes - skeletal traction is directly attached to bone while cervical traction uses a neck brace during procedures. Nursing management of casts and traction includes monitoring circulation, teaching exercises, and caring for the cast as it sets and hardens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 27
ORTHOPEDIC NURSING
CAST & TRACTIONS
OBJECTIVES
To define Orthopedic Nursing
To identify the different types of cast
and traction
To determine the uses of types of cast
and traction
To distinguish each type of cast and
traction and specific purpose of it.
ORTHOPEDIC
NURSING.
Orthopedic nursing is a specialty that
focuses on musculoskeletal diseases and
disorders. These orthopedic issues include
conditions like arthritis, bone fractures,
broken bones, joint replacements, genetic
malformations, arthritis, and osteoporosis.
TRACTION
Traction is the application of a pulling force to a
part of the body. refers to the set of mechanisms
for straightening broken bones or relieving
pressure on the spine.
TYPE OF CAST AND
TRACTION
ADJSKIN TRACTION: SKIN
TRACTION :ECTIVE
is maintained by direct application of a pulling force
on the client’s skin . It is generally used as a
temporary measure.
SKELETAL
TRACTION
is attached directly to bone , providing a strong
steady, continuous pull, and can be used for
prolonged periods
CERVICAL
TRACTION
During cervical traction, a metal brace is placed around your neck. The brace is
then attached to a body harness or weights, which are used to help correct the
affected area. Cervical traction is performed using a general anesthetic, so you’ll
be asleep throughout the entire procedure.
MODERN
TECHNIQUE
BUCK'S TRACTION
Buck's skin traction is widely used in the lower limb
for femoral fractures, lower backache, acetabular and
hip fractures. Skin traction rarely reduces a fracture,
but reduces pain and maintains length in fractures.
The skin is prepared and shaved -it must be dry.
Friar's balsam may be used to improve adhesion.
DUNLOP'S
TRACTION
is placed along the axis of the forearm as well
as at right angles to the humerus by means of a
broad sling placed around the upper arm. Bed
blocks are required on the lateral side (fracture
side up) of the bed.
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Alteration in Peripheral Tissue Perfusion:
Circulatory Care: tissue perfusion is enhanced by client exercises within
the limitations of the traction.
Circulatory Care: tissue perfusion is enhanced by client exercises within
the limitations of the traction.
Exercises, regular deep breathing and coughing, adequate fluids, and
elastic stocking work together to prevent deep venous thrombosis.
Teaching the client about anti-coagulant is essential.
CAST
A protective shell of fiberglass, plastic, or
plaster, and bandage that is molded to
protect broken or fractured limb
For example: cases of cells that form in the
tubules of the kidneys are sometimes
detected in urine samples.
CAST
A protective shell of fiberglass, plastic, or
plaster, and bandage that is molded to
protect broken or fractured limb
For example: cases of cells that form in the
tubules of the kidneys are sometimes
detected in urine samples.
PLASTER CAST
These are wrapped around the
injured body part over a stockinette
and cotton padding. As they dry,
the strips harden. The cast takes 24
to 48 hours to harden fully.
SYNTHETIC CAST
This is made from fiberglass or plastic
strips. These are wrapped around the
injury over a stockinette and cotton
padding. Synthetic casts can be
different colors. A synthetic cast is
lighter than plaster. It dries in a few
minutes, but may take a few hours to
harden fully. Synthetic stockinettes
and padding are also available. These
can get wet for bathing or swimming.
CAST BRACE
This is made of hard plastic.
Soft pads inside the brace
push against (compress) the
injury. The brace is held in
place with Velcro strips and
can be removed. A cast
brace may be used right
after the injury occurs. Or, it
may be used toward the end
of healing, after another cast
has been removed.
SPLINT (ALSO CALLED A HALF
CAST)
Splints, also known as half-casts,
provide less support than casts,
but are faster and easier to use.
They also can be tightened or
loosened easily if the swelling in
the arm or leg increases or
decreases. Ready-made or off-the-
shelf splints are available in many
different sizes and shapes
Care required while the plaster cast dries once applied heat is
given off for ~ 15 minutes & may be uncomfortable while the
plaster sets, the cast will remain soft & touching may lead to
indentations which may then create pressure spots until dry
handle the cast with palms of hands only - not fingers do not
rest cast on hard surfaces or sharp edges
FIXATION
Fixation in orthopedics is the
process by which an injury is
rendered immobile. This may be
accomplished by internal fixation,
using intramedullary rod, Kirsches
wire or dynamic compression plate;
or by external fixation, using a
spanning external fixator, Taylor
Spatial Frame or Ilizarov apparatus.
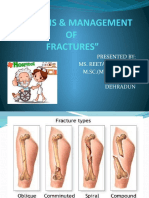
FRACTURES
Fixation in orthopedics is the process by
which an injury is rendered immobile.
This may be accomplished by internal
fixation, using intramedullary rod,
Kirsches wire or dynamic compression
plate; or by external fixation, using a
spanning external fixator, Taylor
Spatial Frame or Ilizarov apparatus.
INTERNAL FIXATION
Internal fixation
surgical procedure that
stabilizes and joins the
ends of fractured
(broken) bones by
mechanical devices
such as metal plates,
pins, rods, wires or
screws
EXTERNALFIXATION
An external fixation device
may be used to keep
fractured bones stabilized
and in alignment. The
device can be adjusted
externally to ensure the
bones remain in an optimal
position during the healing
process. This device is
commonly used in children
and when the skin over the
fracture has been
damaged.Feb
THANK YOU
FOR Do you have any questions?
LISTENING!
REFERENCES
HTTPS://WWW.GOOGLE.COM/SEARCH?
Q=EXTERNALFIXATION+IN+ORTHOPEDICS&SOURCE=LMNS&BIH=638&BIW=13
66&HL=EN&SA=X&VED=2AHUKEWIXZPINPIV3AHVQZOSBHFPUDD0Q_AUOAH
OECAEQAA
HTTPS://WWW.MOUNTNITTANY.ORG/WELLNESS-ARTICLE/CAST-CARE-
TYPES-OF-CASTS-AND-CAST-AIDS
You might also like
- Below Knee ProsthesisDocument30 pagesBelow Knee ProsthesisArun KumarNo ratings yet
- NP1 CHN 2018 PDFDocument86 pagesNP1 CHN 2018 PDFJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Cast and TractionsDocument6 pagesCast and Tractionsmiss RN100% (12)
- Operating Room InstrumentsDocument59 pagesOperating Room InstrumentsMayolianne Dumay100% (1)
- Different Types of Bone FracturesDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of Bone FracturesShe Aquino100% (1)
- Orthopedic NursingDocument9 pagesOrthopedic Nursingsilimaanghang100% (3)
- Occlusal Splint (Autosaved)Document69 pagesOcclusal Splint (Autosaved)Hatem Ibrahim Ahmed AburiaNo ratings yet
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument15 pagesNCP Self Care DeficitSkye M. PetersNo ratings yet
- For Health ProfessionalsDocument9 pagesFor Health ProfessionalsKiko Matsing JavierNo ratings yet
- Casts and TractionDocument37 pagesCasts and TractionShiiza Dusong Tombucon-AsisNo ratings yet
- Activity22 (Traction)Document5 pagesActivity22 (Traction)Gabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- LilianDocument5 pagesLilianLilian Laureto SabinesNo ratings yet
- What Is Traction?Document5 pagesWhat Is Traction?Tweenie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Ortho AssignmentDocument18 pagesOrtho AssignmentSean Derick Cariño MercadoNo ratings yet
- Fractures: A. Pusey-Murray (MRS) RN, Cert Psych Nursing & Nursing Admin, BSC (Hons), MPH, Dip. Ed. PHD (C)Document68 pagesFractures: A. Pusey-Murray (MRS) RN, Cert Psych Nursing & Nursing Admin, BSC (Hons), MPH, Dip. Ed. PHD (C)okacia100% (1)
- Casting & Splinting Techniques 2107Document8 pagesCasting & Splinting Techniques 2107khelianderrick81No ratings yet
- Plaster of ParisDocument14 pagesPlaster of ParisAjah Agnes EzinneNo ratings yet
- Is The Use of A Pulling Force To Treat Muscle and Skeleton DisordersDocument42 pagesIs The Use of A Pulling Force To Treat Muscle and Skeleton DisordersShane Arianne Faye BaldoveNo ratings yet
- Basic Techniques For Splinting of Musculoskeletal Injuries UpToDateDocument13 pagesBasic Techniques For Splinting of Musculoskeletal Injuries UpToDateNina JácomeNo ratings yet
- Prosthesis: Uganeswary VenugopalDocument14 pagesProsthesis: Uganeswary VenugopalUganeswary VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Caring Patient With CastDocument61 pagesCaring Patient With CastMary MisolaNo ratings yet
- ProsthesisDocument14 pagesProsthesisUganeswary Venugopal100% (1)
- Orthopedic Fixation DevicesDocument9 pagesOrthopedic Fixation DevicesJoel Santos100% (1)
- Reflection CastsDocument1 pageReflection CastsTrisha Marie JimenezNo ratings yet
- Muskuskeletal SystemDocument65 pagesMuskuskeletal SystemMary Danielle SaludarioNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Surgery - Farid Mahmud AditaDocument4 pagesOrthopedic Surgery - Farid Mahmud AditaMaria Widyaneni TrinastutiNo ratings yet
- Amputation and ProsthesisDocument5 pagesAmputation and Prosthesisaishp2897No ratings yet
- SplintingDocument31 pagesSplinting4LetterLie31No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 External Fixation IDocument19 pagesLecture 5 External Fixation IAnkit LakshyaNo ratings yet
- Occlusal Appliance TherapyDocument32 pagesOcclusal Appliance TherapyZakria Al-HadadNo ratings yet
- Occlusal SplintsDocument26 pagesOcclusal SplintsCha Xue Chin0% (1)
- Care of Patients With TractionDocument25 pagesCare of Patients With Tractionmftaganas100% (1)
- BandageDocument23 pagesBandageMARIA FENo ratings yet
- Cast Care: Printable Version Download PDF Cite This Page Tweet ThisDocument4 pagesCast Care: Printable Version Download PDF Cite This Page Tweet ThisMaricar Demegillo OlescoNo ratings yet
- Applying Splint - CheklistDocument3 pagesApplying Splint - CheklistAh AlshaibaniNo ratings yet
- Or and DR Instruments PDFDocument59 pagesOr and DR Instruments PDFMayolianne Dumay100% (1)
- DIRECTIONS: Explain The Following. 1. Discuss Briefly The Importance of The Different Bandaging TechniquesDocument4 pagesDIRECTIONS: Explain The Following. 1. Discuss Briefly The Importance of The Different Bandaging TechniquesJohn Joshua ReyesNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in The Treatment of FracturesDocument29 pagesRecent Advances in The Treatment of Fracturesmanjunatha100% (1)
- Immobilization ExtricationDocument75 pagesImmobilization ExtricationJohn Britto100% (3)
- 8orthopedic and ENT Surgeries (4 Files Merged)Document225 pages8orthopedic and ENT Surgeries (4 Files Merged)Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedics and Orthopaedic Nursing RNDocument70 pagesOrthopaedics and Orthopaedic Nursing RNFaith LwabilaNo ratings yet
- Cast and Cast CareDocument3 pagesCast and Cast CareErrol B. Tiozon100% (1)
- Instrumentation and Techniques in Equine Fracture Fixation: Joerg Auer, OMV, MS and Jeffrey P Watkins, DVM, MSDocument20 pagesInstrumentation and Techniques in Equine Fracture Fixation: Joerg Auer, OMV, MS and Jeffrey P Watkins, DVM, MSSergio Nieves MoranNo ratings yet
- Fracture FinalDocument56 pagesFracture FinalnobelaugustineNo ratings yet
- Levels of Care Promotive: DEXA Scan - The Most Accurate Screening Test For Low Bone Strength Is A DualDocument2 pagesLevels of Care Promotive: DEXA Scan - The Most Accurate Screening Test For Low Bone Strength Is A DualLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Fracture (Cast Care)Document6 pagesFracture (Cast Care)Vane UcatNo ratings yet
- Fractures and Low Back Pain: Dr. Lubna DwerijDocument49 pagesFractures and Low Back Pain: Dr. Lubna DwerijNoor MajaliNo ratings yet
- Maps 2114 Unit 3.2 Pop, Dressings & Bandages ChandraDocument27 pagesMaps 2114 Unit 3.2 Pop, Dressings & Bandages ChandraALicoco BotNo ratings yet
- Abdominal BandagingDocument34 pagesAbdominal BandagingStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniNo ratings yet
- Abdominal OrgansDocument28 pagesAbdominal OrgansRS BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- FrakturDocument188 pagesFrakturSiti RaihanatiNo ratings yet
- Fracture 190706114534Document61 pagesFracture 190706114534Precious BlessingNo ratings yet
- Traction & Application of p0pDocument19 pagesTraction & Application of p0pSham NazrinNo ratings yet
- Reduction and CastsDocument12 pagesReduction and CastsTrisha Marie JimenezNo ratings yet
- Transfemoral Prosthesis - Suspension, Sockect DesignDocument36 pagesTransfemoral Prosthesis - Suspension, Sockect DesignMayank Bindu RawatNo ratings yet
- Fractures: Mary Grace B. Gutierrez Resti Mariano Ma. Cindy O. BautistaDocument50 pagesFractures: Mary Grace B. Gutierrez Resti Mariano Ma. Cindy O. BautistaJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Internal Fixation ToolsDocument22 pagesInternal Fixation ToolsChandan Kumar ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Appendix Basic First Aid Basic Support 2Document28 pagesAppendix Basic First Aid Basic Support 2Loraine PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Koch AO Manual Chapter 2 2005Document45 pagesKoch AO Manual Chapter 2 2005Juan Guillermo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Forearm SplintingDocument6 pagesForearm SplintingArabelle GONo ratings yet
- Patterns & Management FractureDocument31 pagesPatterns & Management FractureReet KhureshaNo ratings yet
- Dept. of Orthopaedics, KMC MangaloreDocument8 pagesDept. of Orthopaedics, KMC MangalorechinmayghaisasNo ratings yet
- How to Apply StarkTape Kinesiology Tape. Best Kinesiology Taping TechniquesFrom EverandHow to Apply StarkTape Kinesiology Tape. Best Kinesiology Taping TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reduction, Relocation and Splinting in Emergency Room (RASER)From EverandReduction, Relocation and Splinting in Emergency Room (RASER)No ratings yet
- Olivarez CollegeDocument2 pagesOlivarez CollegeJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Normal ValuesDocument8 pagesNormal ValuesJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Apatan, John Carlo S. RNDocument143 pagesApatan, John Carlo S. RNJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program of ImmunizationDocument9 pagesExpanded Program of ImmunizationJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Asthma Vs COPD PDFDocument10 pagesAsthma Vs COPD PDFJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Img 20230409 0001Document1 pageImg 20230409 0001JOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Lilly Wiggill Copy of Disorders Packet PDFDocument9 pagesLilly Wiggill Copy of Disorders Packet PDFJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- COPD Chronic Bronchitis EmphysemaDocument3 pagesCOPD Chronic Bronchitis EmphysemaJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Where The Dream and The Dreamer Become ONEDocument5 pagesWhere The Dream and The Dreamer Become ONEJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- PB2 NP2Document26 pagesPB2 NP2JOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever Human: ImmunodeficiencyDocument9 pagesTyphoid Fever Human: ImmunodeficiencyJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Radio Phenomenal Script BroadcastingDocument4 pagesRadio Phenomenal Script BroadcastingJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- SIH C: Prepared By: John Carlo S. Apatan SNDocument8 pagesSIH C: Prepared By: John Carlo S. Apatan SNJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- 259Document1 page259JOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Smoking EffectsDocument1 pageSmoking EffectsJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The FootDocument1 pageAnatomy of The FootJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Apatan, John Carlo SenaderoDocument1 pageApatan, John Carlo SenaderoJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communicationarm AnimalsDocument8 pagesTherapeutic Communicationarm AnimalsJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Cva Group 1 NCM 116Document24 pagesCase Scenario Cva Group 1 NCM 116JOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- John Carlo Apatan - Checklist On Discontinuing An IV InfusionDocument2 pagesJohn Carlo Apatan - Checklist On Discontinuing An IV InfusionJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 21 ConvertDocument6 pagesPDF Document 21 ConvertJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- JOHN CARLO APATAN - Checklist On Tracheostomy CareDocument3 pagesJOHN CARLO APATAN - Checklist On Tracheostomy CareJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- JOHN CARLO APATAN - Mental Health Status AssessmentDocument5 pagesJOHN CARLO APATAN - Mental Health Status AssessmentJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Cast, PDFDocument26 pagesCast, PDFDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- 316 RLE - Cast CareDocument4 pages316 RLE - Cast CareSophia LalagunaNo ratings yet
- Assisting With Cast ApplicationDocument6 pagesAssisting With Cast ApplicationPrince TulauanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Musculoskeletal 1Document163 pagesNursing Musculoskeletal 1Ilhan RascalNo ratings yet
- Surgery - Care of Casts and TractionsDocument7 pagesSurgery - Care of Casts and TractionsMaria Eleni ÖNo ratings yet
- Cast ImmobilisationDocument15 pagesCast Immobilisationnurul_abdullah_34No ratings yet
- Complications of Hip Spica 10-12-11Document15 pagesComplications of Hip Spica 10-12-11faruq34No ratings yet
- Assistive Devices For Walking, Casts, and Traction CareDocument7 pagesAssistive Devices For Walking, Casts, and Traction Careアンナドミニク100% (1)
- Bandha Vidhi FinalDocument64 pagesBandha Vidhi FinalShorab Khan82% (11)
- FIX - Splinting and CastingDocument34 pagesFIX - Splinting and CastingWildan Hilmi AnsoriNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 - Musculoskeletal (MODULE 3)Document16 pagesNCM 116 - Musculoskeletal (MODULE 3)Meryville Jacildo100% (2)
- 4-Conservative Treatment FX, CastingDocument53 pages4-Conservative Treatment FX, CastingMuhammad TaqwaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal-System NLE ReviewDocument124 pagesMusculoskeletal-System NLE ReviewRitamaria0% (1)
- Management of Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument69 pagesManagement of Musculoskeletal DisordersJSeasharkNo ratings yet
- Nle Tips For OrthopedicDocument2 pagesNle Tips For OrthopedicCharie OcampoNo ratings yet
- 51 - Plaster Application - FinalDocument11 pages51 - Plaster Application - FinalFaVNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic EmergenciesDocument37 pagesOrthopedic EmergenciesRajiv NegandhiNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Nursing Orthopedic Gadget-A Piece of Special Device Designed To Correct Deformoities or To PreserveDocument5 pagesOrthopedic Nursing Orthopedic Gadget-A Piece of Special Device Designed To Correct Deformoities or To PreserveSophia Kaye AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention (Risk For Trauma) RationaleDocument5 pagesNursing Intervention (Risk For Trauma) RationaleJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Complication PopDocument16 pagesComplication PopkristinNo ratings yet
- Cast CareDocument4 pagesCast CarernrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Casts and TractionDocument37 pagesCasts and TractionShiiza Dusong Tombucon-AsisNo ratings yet
- Care of Your Plaster CastDocument2 pagesCare of Your Plaster CastNick GraysonNo ratings yet
- CastDocument16 pagesCastSheena Flores Abuga-a100% (1)
- CastDocument12 pagesCastJohn AlanoNo ratings yet
- Splints and Tractions in OrthopaedicsDocument56 pagesSplints and Tractions in OrthopaedicsNinaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument6 pagesCongenital Hip DislocationserpeptumdanaeNo ratings yet