Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structures Worksheet
Cell Structures Worksheet
Uploaded by
Charlene BarcelonaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structures Worksheet
Cell Structures Worksheet
Uploaded by
Charlene BarcelonaCopyright:
Available Formats
Note-Taking Worksheet
Cells
Section 1 Cell Structure
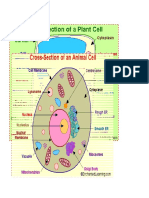
A. Common cell structures—outer covering called cell membrane and internal gelatin-like
cytoplasm
1. Comparing cells—size and shape relate to function
2. Two cell types
a. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound internal structures.
b. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound internal structures.
B. Cell organization
1. Composed of cellulose, a cell wall grows, gives shape to, and protects the cells of
plant, algae, fungi, and most bacteria.
2. Cell membrane —protective layer around all cells
a. For cells with cell walls, the cell membrane is inside the cell wal
l b. A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste products out of the cell.
3. Cytoplasm—gelatin-like substance inside cell membrane
a. Cytoskeleton —scaffolding-like structure in cytoplasm which helps cell keep its shape
b. In the cytoplasm, eukaryotic cells have organelles which help with cell life processes.
4. Nucleus—contains instructions for everything cell does; includes DNA
5. Energy-processing organelles—help cells do their work
a. Green organelles in plant cells contain chloroplast make food.
b. Organelles which release energy from food are called mitochondria. 6. Manufacturing
organelles
a. Ribosomes make proteins for cell activities.
b. Some ribosomes attach to the rough part of the endoplasmic reticulum, a series of
smooth or rough membranes that move materials around in a cell.
7. Transporting and storing organelles
a. Golgi bodies move substances out of a cell or to other parts of a cell.
b. Vacuoles –membrane-bound temporary storage spaces
8. Recycling organelles– lysosomes break down food molecules and cell wastes. C. From
cell to organism
9. Tissues–group of similar cells working together on one job
10. Different types of tissues working together make up an organ
11. A group of organs working together on a particular function form a(n) organ system
D. Answer the following process questions about the cell structures and functions.
12. Why do cells have organelles?
Cells have organelles mainly because it keeps the cells alive.Organelles provide a
purpose within cells to assist with cellular activity. Nearly all eukaryotic cells have core
organelles. They perform important functions that are required for cells to survive,
including as gathering energy, producing new proteins, getting rid of waste, and
etc.The nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and numerous other organelles
are examples of core organelles.
13. How does the shape of organelles help perform its function?
The organelles shape is vital to help perform it functions because it has a different functions to our body.The
cytoskeleton is the one responsible for the shape of these cells.The cytoskeleton is a crucial, complex, and
dynamic component of the cell. It assists during endocytosis (the uptake of external materials by a cell) and
moves parts of the cell during processes of development and motility. It also anchors organelles in place.
14. How does the structure of the cell relate to its function?
A cell's structure and function are related to one another. The shape and size of a cell, help determine its
specific function in our body.The structure of the cell is crucial because cells provide structure and support
to the body of an organism.
15. How can analyzing the relationships of cell organelles help us to understand living things?
Analyzing the relationships of cell organelles help us to understand living things because simply we are
made of it.We study and explore cells because they are the foundation of our life. We are all made up of
cells, and it is vital that we learn and have the knowledge of the function of all of the organelles found in
cells in order to fully understand how cells work.Thus, it aids in our understanding of how organisms work,
on how we function.
You might also like
- Cell Structure and Function Semi Detailed LPDocument8 pagesCell Structure and Function Semi Detailed LPCJ Perito75% (4)
- Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesPlant and Animal CellRonald AzoresNo ratings yet
- Bio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesDocument18 pagesBio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesMuhammad Mahi Nurul IslamNo ratings yet
- Miller & Levine Biology Chapter 7 SummaryDocument6 pagesMiller & Levine Biology Chapter 7 Summarybob0% (1)
- Rockdust Research Compiled by Steve DiverDocument13 pagesRockdust Research Compiled by Steve Diver1324asdfNo ratings yet
- Training The ABC's of Perfumery by Stephen V. Dowthwaite, PerfumersWorldDocument28 pagesTraining The ABC's of Perfumery by Stephen V. Dowthwaite, PerfumersWorldSteve86% (7)
- Bpes2 SemDocument95 pagesBpes2 Semnishthabanga1525No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsNo ratings yet
- Cell of BiologyDocument2 pagesCell of Biologymdy380001No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function - Q A-2020-21 Gr-8Document3 pagesCell Structure and Function - Q A-2020-21 Gr-8umasankar sivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Gen Zoology ReviewerDocument19 pagesGen Zoology ReviewerDarey ApostolNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument19 pagesSummaryAntenehMarelignNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesMUTWIRINo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument43 pagesUntitled Presentationtagudjameslervy.cte.cpcNo ratings yet
- Edible Plant CellDocument4 pagesEdible Plant CellgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- CELLS For Class8Document15 pagesCELLS For Class8cbseiscNo ratings yet
- Inte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Document11 pagesInte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science BDocument5 pagesReviewer in Science BAshliah Aira MarohomNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955Document9 pagesSubmitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955mahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- Key Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellDocument14 pagesKey Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Cell and Its FunctionDocument24 pagesParts of The Cell and Its FunctionErnest De Mesa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocument19 pagesCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (2)
- Looking Inside Cells - Gr7Document3 pagesLooking Inside Cells - Gr7Jung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Composition of Cells Name: John Patrick Quines Year and Section: BSN 2-A 1. Discuss The Functions of The Parts of The CellDocument1 pageActivity 1: Composition of Cells Name: John Patrick Quines Year and Section: BSN 2-A 1. Discuss The Functions of The Parts of The CellJohn Patrick Leal QuinesNo ratings yet
- Membrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesMembrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemFarah Jaye Verde CayayanNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Draw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellDocument3 pagesDraw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellPratik SagarNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesCellular Structures and FunctionsakosidanielaNo ratings yet
- GsciDocument9 pagesGscimahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and Functions PDFDocument3 pagesCell - Structure and Functions PDFmaya__scribd100% (1)
- Sample AssignmentDocument4 pagesSample Assignmentmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- Diagram of Plant CellDocument4 pagesDiagram of Plant CellekongNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument23 pagesPlant and Animal CellAnnisa Aulia100% (1)
- Rebosura - Lec Asst 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument4 pagesRebosura - Lec Asst 1 - Cell OrganizationBSN Mary Ellaine RebosuraNo ratings yet
- Acad Fall08 ThecellDocument13 pagesAcad Fall08 Thecellhassanmusahassan81No ratings yet
- Задания (строение)Document12 pagesЗадания (строение)D1chuNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell PROJECTDocument6 pagesPlant Cell PROJECTYoussef AmrNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument26 pagesCellsNairita LetipoNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument23 pagesCell Biology BasicsAbume DougyNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells - De, Nition, Diagram, Structure & FunctionDocument2 pagesPlant Cells - De, Nition, Diagram, Structure & FunctionJoseph OloruntobaNo ratings yet
- Notes For Biology Form OneDocument8 pagesNotes For Biology Form Onelopem clarysonNo ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- PRESENTATIONDocument35 pagesPRESENTATIONAtulNo ratings yet
- L041 - Laboratory Exercise No. 1B - Dautil JastineDocument2 pagesL041 - Laboratory Exercise No. 1B - Dautil JastineJastine Managbanag DautilNo ratings yet
- 1.1cell ConceptDocument10 pages1.1cell ConceptMokariya SanjayNo ratings yet
- Animal CellsDocument29 pagesAnimal Cellschinatu4No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CellsDocument19 pagesChapter 3 CellsEuniece AnicocheNo ratings yet
- Parts & Function of CellsDocument25 pagesParts & Function of CellsHariet ObieNo ratings yet
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- Cell Lesson NotesDocument8 pagesCell Lesson NotesNikshita KNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science Notesdeepti jainNo ratings yet
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 - CellDocument9 pagesTOPIC 2 - CellAl Johan Atienza100% (1)
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Document7 pagesCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- General Biology Modules 1 3Document36 pagesGeneral Biology Modules 1 3Glen MillarNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Early Poems, Federico Garcia LorcaDocument47 pagesEarly Poems, Federico Garcia LorcaAndrea RaicevicNo ratings yet
- TeluguDocument10 pagesTeluguBrintha RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Investigative ResearchDocument27 pagesInvestigative ResearchJodi SorianoNo ratings yet
- Squash GrahamDocument15 pagesSquash GrahamGlenn Angelo69% (26)
- Malika Air-Conditioning CoDocument3 pagesMalika Air-Conditioning CoDeepanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Layout and OperationDocument77 pagesThermal Power Plant Layout and OperationAlex100% (1)
- Giloy or Guduchi PDFDocument529 pagesGiloy or Guduchi PDFBhavana GangurdeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Studies of Medicinal Plant Citrullus Colocynthis: A ReviewDocument9 pagesPharmacological Studies of Medicinal Plant Citrullus Colocynthis: A ReviewVinayNo ratings yet
- Adl Et Al-2019-Journal of Eukaryotic MicrobiologyDocument116 pagesAdl Et Al-2019-Journal of Eukaryotic MicrobiologyGonzalo CantúNo ratings yet
- Palitaw Recipe in PhilippinesDocument11 pagesPalitaw Recipe in PhilippinesVanessa May AquinoNo ratings yet
- GROUPI Tagupa Yonson PS CellCycleDocument4 pagesGROUPI Tagupa Yonson PS CellCycleJohn Lloyd SalinasNo ratings yet
- 5-6. LM in Eng 5 Q4 Week 5-6Document24 pages5-6. LM in Eng 5 Q4 Week 5-6Benedict PoeNo ratings yet
- LumberDocument4 pagesLumberMarielSevillaNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Notes Class 10Document8 pagesWater Resources Notes Class 10Seshavalli G50% (2)
- Hakamada Et Al., 2020 - Influence of Stand Density On Growth and Water Use Efficiency in Eucalyptus ClonesDocument8 pagesHakamada Et Al., 2020 - Influence of Stand Density On Growth and Water Use Efficiency in Eucalyptus ClonesIvankaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Classification Flip BookDocument1 pageLevels of Classification Flip Booksmileyhappychan3286No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Natural Compounds 2007, 43, 317-318 PDFDocument3 pagesChemistry of Natural Compounds 2007, 43, 317-318 PDFCasca RMNo ratings yet
- Indian SpicesDocument11 pagesIndian SpicesSunil Kumar100% (2)
- Solution Assignment2Document1 pageSolution Assignment2Daman RajNo ratings yet
- Verbenaceae Botany ProjectDocument13 pagesVerbenaceae Botany ProjectAamir HusainNo ratings yet
- Nutrient-Rich Food List: Marty KendallDocument3 pagesNutrient-Rich Food List: Marty KendallMohammed A. RahimNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument14 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationYasser ZubaidiNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument327 pagesAgricultureRaghu100% (7)
- SMP Ujian Semester Kelas 9Document11 pagesSMP Ujian Semester Kelas 9KHOIRURROZIQIN0% (1)
- DEC OSS Business IntroductionDocument28 pagesDEC OSS Business Introductionamr kouranyNo ratings yet
- 28 Waxes Used in Cosmetics PDFDocument1 page28 Waxes Used in Cosmetics PDFMahmud Murtofa Salekin100% (1)
- Furniture: Blanket ChestsDocument113 pagesFurniture: Blanket ChestsThe 18th Century Material Culture Resource Center100% (5)
- Reda Hps g3 PsDocument1 pageReda Hps g3 PszopitaNo ratings yet