Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Romeo and Juliet KO AQA 2018
Romeo and Juliet KO AQA 2018
Uploaded by
Dinanga0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesThis document provides an overview of William Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet to help with revision for an AQA GCSE English Literature exam. It summarizes the plot in five acts, identifies the main characters of Romeo, Juliet, Friar Lawrence, and others. It outlines several major themes of the play, including conflict, love, fate, and tragedy. It also lists assessment objectives and suggests ways to stretch analysis, such as considering different performances, contexts, and critical perspectives of the famous story of the star-crossed lovers.
Original Description:
Original Title
Romeo_and_Juliet_KO_AQA_2018
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of William Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet to help with revision for an AQA GCSE English Literature exam. It summarizes the plot in five acts, identifies the main characters of Romeo, Juliet, Friar Lawrence, and others. It outlines several major themes of the play, including conflict, love, fate, and tragedy. It also lists assessment objectives and suggests ways to stretch analysis, such as considering different performances, contexts, and critical perspectives of the famous story of the star-crossed lovers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesRomeo and Juliet KO AQA 2018
Romeo and Juliet KO AQA 2018
Uploaded by
DinangaThis document provides an overview of William Shakespeare's play Romeo and Juliet to help with revision for an AQA GCSE English Literature exam. It summarizes the plot in five acts, identifies the main characters of Romeo, Juliet, Friar Lawrence, and others. It outlines several major themes of the play, including conflict, love, fate, and tragedy. It also lists assessment objectives and suggests ways to stretch analysis, such as considering different performances, contexts, and critical perspectives of the famous story of the star-crossed lovers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare AQA GCSE English Literature Paper 1 (1hr 45mins) Section A: 50 minute response
Section A: 50 minute response – Extract to whole
Plot: Significant characters: Themes in the play:
Prologue: Refers to an ill-fated couple with its use of the word Romeo A young Montague. Not interested in violence, only love. Themes are important ideas which run through the play. You will
“star-crossed”. It does not merely set the scene of Romeo and He’s passionate and sensitive yet also impulsive. He can come across them many times. They connect together the story,
Juliet, it also tells the audience exactly what is going to happen. be immature but his idealism and passion make him an the characters and the different acts and sections in the play.
Act One: In Italy, two noble families (the Montagues and Capulets) empathetic character.
are feuding yet again. Romeo is in love with Rosaline, who rejects Juliet A young Capulet. Naïve and sheltered at the beginning, CONFLICT: A key driving force in the play violence & hate
his love. As a result, he is depressed. To cure Romeo of his develops into a strong character. She is courageous and and it occurs between a range of death,
lovesickness, Benvolio persuades him to attend a masked ball at determined, passionate, loyal, brave and tragic. characters: between warring households; secrecy
the Capulets, where he might see prettier girls and therefore forget within families; within friendship groups; family
about Rosaline. Romeo meets Juliet and they instantly fall in love Friar Friend to both Romeo and Juliet. Father figure and jolly
Lawrence man. Kind, civic-minded, a proponent of moderation. and between members of the youth vs age
with one another. Tybalt hears Romeo’s voice at the ball and is communities. This conflict results in individual vs
furious that a Montague has dared to attend. Also expert with potions and herbs.
violence. Violence opens the play and also society/religion
Act Two: Romeo stands beneath Juliet’s balcony. He sees Juliet concludes it with the deaths of the two order vs chaos
leaning over the railing, hears her calling out his name and wishes Nurse Like a mother to Juliet / confidante. Often says
inappropriate things. Her view of love is earthy and lovers. Note that the motif of light vs dark appearance vs
that he wasn’t a Montague. He reveals his presence and they is also linked to many of these themes. reality
resolve, after a passionate exchange, to be married secretly. sexual, whereas Juliet is idealistic and intense.
Act Three: Romeo returns from his recent marriage to Juliet and Lord Patriarch. Juliet’s father. Prudent and caring but can fly LOVE: The love Romeo and Juliet share is conflict
encounters Tybalt, who challenges Romeo to a duel. Unbeknownst Capulet into rage if respect is lacking. Loves Juliet but social status beautiful, passionate, exhilarating, courtly love
to all present, Tybalt is now Romeo’s kinsman by marriage so means he commands respect and obedience from all. transformative and they are willing to give marriage
Romeo refuses. Mercutio is livid with Romeo’s refusal and fights Mercutio Romeo’s close friend. Witty, bawdy, cynical and a hot- everything for it. But it is also chaotic and sex
with Tybalt who underhandedly kills Mercutio. Furious by the headed character. Kinsman to the Prince, loyal, proud destructive, bringing death to friends, youth
death of his friend, Romeo kills Tybalt and takes shelter in the and loved by his peers. family and to themselves. It is worth fate
Friar’s cell. The Prince exiles Romeo for his part in the fray. Benvolio Romeo’s cousin. Tries to keep the peace and keep noting that the motif of light vs dark is
Act Four: In despair, Juliet seeks Friar Lawrence’s advice. He gives Romeo’s mind off of Rosaline. Makes genuine effort to also linked to many of these themes.
her a sleeping potion, which for a time will cause her to appear diffuse the violence and offers a listening ear to Romeo.
dead. Thus, on the day of her supposed marriage to Paris, she will Prince Leader of Verona, concerned with keeping order between FATE: No matter how much they love each love
be carried to the family vault. By the time she awakens, Romeo will the warring families. Holds political power and is other or what plans they make, their authority
be summoned to the vault and take her away to Mantua. frustrated by social unrest and defiance of the struggles against fate only help fulfil it. But conflict
Act Five: The Friar’s letter fails to reach Romeo. When he hears of Montagues and Capulets. defeating or escaping fate is not the point. death and grief
Juliet’s death, Romeo procures a deadly poison from an apothecary Tybalt Juliet’s cousin. Obsessed by family honour; quick to draw No one escapes fate. It is Romeo and masculinity
and secretly returns to Verona to say his last farewell to his his sword. A proud man who cannot lose face. Hates Juliet's determination to struggle against religion
deceased wife and die by her side. When Juliet awakens from her Montagues. Vain, aggressive and violent. fate in order to be together, whether in family
deep sleep, she realises Romeo’s error and kills herself with his life or death that shows the fiery passion tragedy
dagger. The Capulets and Montague decide to reconcile as a result of their love and which makes that love
of the deaths of their children. eternal.
Assessment Objectives: Minor characters: Stretch yourself:
AO1 (40%) - Make an informed personal response using a critical Lady Capulet Whilst analysing an extract, quickly refer out to other parts of the play.
style. Use textual references, including quotations, to support and Peter Watch different performances of key scenes to provide you with ‘ammunition’ when
illustrate interpretations. Gregory discussing form.
AO2 (40%) - Analyse the language, form and structure used by a Lord Montague Listen to an audio version – abridged and unabridged.
writer to create meanings and effects, using relevant subject Balthasar Consider different critical perspectives.
terminology where appropriate. Sampson Appreciate audiences then and now (values, ideas, etc).
AO3 (20%) - Show understanding of the relationships between Abram Learn about Aristotelian tragedy.
texts & the contexts in which they were written. Lady Montague According to Aristotle, "the structure of the best tragedy should not be simple but complex
AO4 (4 marks) - Use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures and one that represents incidents arousing fear and pity—for that is peculiar to this form of
for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate spelling and Revise these characters by linking art. Revise: fatal flaw, hamartia, catharsis, tragic hero, protagonist, antagonist, comic relief,
punctuation them to the main characters. external and internal conflict and poetic justice.
Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare AQA GCSE English Literature Paper 1 (1hr 45mins) Section A: 50 minute response – Extract to whole
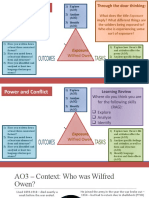
Shakespeare’s Literary techniques / Methods (AO2) Themes Understanding AO2 Context AO3
Foreshadowing Alliteration Love Language: the writer’s choice of Duelling and the concept of honour: Maintaining the honour of your
Asides Blank verse Fate words and their effect. family name was hugely important at the time. If you were challenged
Stage directions Iambic pentameter Authority to a duel and you refused, you would be deemed a coward, thus
Timing Imagery Conflict Structure: how the plot is damaging your honour and the status of your family. Most Elizabethan
Stichomythia Oxymoron Death and Grief ordered and put together. The gentlemen carried swords in public and many did fight in the streets.
Pathetic fallacy Personification Parent/Child relationship organisation of the narrative, Courtly Love & cures for lovesickness: common in medieval literature
Exits Poetic verse Youth and Age how it begins develops and where a knight was consumed with passion for an unattainable
noblewoman; Romeo fits this perfectly. Elizabethan doctors saw
Entrances Prose Women ends.
unrequited love or desire as a disease, a type of melancholy sometimes
Dramatic Irony Pun Hypocrisy and Prejudice
called lovesickness. They tried various cures and sometimes sent
Soliloquy Sonnet Power and Ambition Form: the text type that the patients to church to confess to a priest. They believed that if
Rhyming couplets Masculinity writer uses and what it shows lovesickness was left untreated, it could lead to madness.
Metaphor about the writer's intentions, Role of women in a patriarchal society: Elizabethan England was a
Simile characters or key themes. society controlled by men. Women were seen as the weaker sex and
Hyperbole were expected to be meek and mild, and most importantly, obedient to
Plot summary: their fathers and later their husbands.
Prologue Introduction to the tragedy 3.2 Juliet forgives Romeo. Arranged marriages: Marriages amongst the wealthy were arranged by
1.1 Montagues and Capulets fight. 3.3 Friar Lawrence advises Romeo. parents in order to match or improve social standing. However, in
Romeo is love-sick. practice, parents did try to choose someone their child liked and was
1.2 Romeo reluctantly agrees to go to the Capulet party. 3.4 Capulet promises Juliet to Paris. happy to marry. Secret marriages such as that between the young
1.3 Her mother urges Juliet to marry Count Paris. 3.5 Romeo and Juliet sleep together. Romeo and Juliet would have been both illegal and shocking.
Juliet refuses to marry Paris. The Italian setting of the play: The play is set in Italy, which was known
1.4 Mercutio urges Romeo not to give in to the misery of love. 4.1 Friar Lawrence’s potion plan for Juliet. for its warring states. It is also a Catholic country; religion was extremely
1.5 Romeo and Juliet fall in love at the party. 4.2 Juliet ‘gives in’ to her parents. important and marriage vows were seen as sacred – once made, they
2.1 Romeo escapes his friends. 4.3 Juliet takes the potion. could not be broken.
2.2 Romeo and Juliet exchange love vows on her balcony. 4.4 Preparations for the wedding. Social context: Patriarchal society, women and their role in society.
2.3 Friar Lawrence agrees to marry Romeo and Juliet. 4.5 Juliet found ‘dead’. Historical context: Reigning monarch was Elizabeth I.
2.4 Romeo arranges to marry Juliet. 5.1 Romeo hears of Juliet’s ‘death’. Cultural context: Includes religion, beliefs and superstitions.
2.5 Nurse reports back to Juliet. 5.2 Friar Lawrence hears that his message didn’t get through. Shakespeare’s theatre, the conventions and experience of being at The
2.6 The secret wedding. 5.3 Romeo and Juliet kill themselves. Globe
3.1 Mercutio and Tybalt killed in street fight. Romeo banished.
Important quotations:
- “O, she doth teach the torches to burn bright!” - “I will make a desperate tender / Of my child’s love. I think she will be - “How now wife, / have you delivered to her our decree?”
- “I have no joy in this contract tonight / It is too sudden, too rash, too ill- ruled / In all aspects by me.” - “Talk not to me, for I’ll not speak a word. / Do as thou wilt, for I have
advised” ‘ - “Methinks I see you now you look so low / As one dead in the bottom of done with thee.”
- “Come death and welcome, Juliet wills it so.” a tomb.” “The fearful passage of their death-mark’d love.”
- “Art thou gone so, love lord, ay husband, friend?” - “Thou desperate pilot, now at once run on / The dashing rocks thy sea- - “Here’s much to do with hate, but more with love / Why then, O
- “Banishment? Be merciful, say Death” sick weary bark.” brawling love, O loving hate.”
- “Let two more summers wither in their pride / Ere we may think her - “More light and light, more dark and dark our woes.” - “Behold this night / Earth-treading stars that make dark heaven light.”
ripe to be a bride.” - “And you be mine, I’ll give you to my friend; / And you be not, hang, - “He that hath the steerage of my course / Direct my sail
- “For this alliance may so happy prove / To turn your households’ beg, starve, die in the streets.” - “This intrusion shall / Now seeming sweet, convert to bitt’rest gall.”
rancour to pure love.” - “Come weep with me, past hope, past cure, past help.” - “Juliet is the sun. Arise, fair sun, and kill the envious moon.”
- “The love–devouring Death do what he dare, / It is enough I may but - “I will do it without fear or doubt, / To live an unstained wife to my - “Within the infant rind of this weak flower / Poison hath residence, and
call her mine.” sweet love.” medicine power.”
- “Away to heaven, respective lenity, / And fire-eyed fury be my conduct - “My dismal scene I needs must act alone.” - “Thou detestable maw, thou womb of death, / Gorged with the dearest
now.” - “O mischief, thou art swift / To enter in the thoughts of desperate morsel of the earth.”
- “O woe! O woeful, woeful day! / Most lamentable day, most woeful men.” - “A greater power than we can contradict / Hath thwarted our intents.”
day.” - “See what a scourge is laid upon your hate, / That heaven finds a - “A plague on both your houses!”
- “Your looks are pale and wild, and do import / Some misadventure.” means to kill your joys with love.” - “O I am Fortune’s Fool!”
You might also like
- 1.06 Macbeth Character DevelopmentDocument2 pages1.06 Macbeth Character DevelopmentJakeFromStateFarmNo ratings yet
- Section B - Unseen PoemDocument3 pagesSection B - Unseen Poemsanjoeyap00No ratings yet
- Watermark TkambnotesDocument10 pagesWatermark Tkambnotesapi-324122235100% (1)
- Touchstone 1 Unit 1 QuizDocument2 pagesTouchstone 1 Unit 1 Quizlilianepc80% (5)
- EE Film Disney PrincessDocument20 pagesEE Film Disney PrincessElzNo ratings yet
- Rounding Upper and Lower BoundsDocument1 pageRounding Upper and Lower BoundsDinangaNo ratings yet
- Practice Language Reading ExamsDocument28 pagesPractice Language Reading ExamsEseel AlsammarraieNo ratings yet
- Analysis of - and Women Must WeepDocument1 pageAnalysis of - and Women Must WeepAshish JosephNo ratings yet
- Musalsal Hadith Text in EnglishDocument51 pagesMusalsal Hadith Text in EnglishLA SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Blood Brothers Revision Eduqas AqaDocument10 pagesBlood Brothers Revision Eduqas Aqaapi-325988444No ratings yet
- Masculinity in Romeo and JulietDocument3 pagesMasculinity in Romeo and Julietmattb140100% (2)
- Sam Shohet English Language A Paper 1Document6 pagesSam Shohet English Language A Paper 1Sam ShohetNo ratings yet
- De Jong 1991 Narrative in Drama The Art of The Euripidean Messenger SpeechDocument112 pagesDe Jong 1991 Narrative in Drama The Art of The Euripidean Messenger SpeechEzequiel Rivas100% (2)
- Love Relationships Course BookletDocument120 pagesLove Relationships Course BookletonlyknowshowtoplayminecraftNo ratings yet
- Jan 2020 1B PDFDocument32 pagesJan 2020 1B PDFzaifa shaNo ratings yet
- The Lemon OrchardDocument3 pagesThe Lemon OrchardVidya Prab50% (2)
- Base Details AnalysisDocument5 pagesBase Details AnalysisSashiNo ratings yet
- Alone SummaryDocument33 pagesAlone SummaryRohayanti Binti YaakopNo ratings yet
- General Paper - Paper 1 Notes (First Edition 2021)Document33 pagesGeneral Paper - Paper 1 Notes (First Edition 2021)sasha g liddleNo ratings yet
- Of Mice and Men (4ET1 Esssay Questions)Document2 pagesOf Mice and Men (4ET1 Esssay Questions)M M100% (1)
- Anthology Part 1 Non FictionDocument24 pagesAnthology Part 1 Non FictionpaulNo ratings yet
- Year 10 IGCSE Songs of OurselvesDocument31 pagesYear 10 IGCSE Songs of OurselvesManal ImranNo ratings yet
- Year 11 - A Christmas Carol HT1Document3 pagesYear 11 - A Christmas Carol HT1Fiona Tobi LawalNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet - NotesDocument11 pagesRomeo and Juliet - NotesSkye G-s0% (1)
- Preparing For The Edexcel A Level English Language and PDFDocument4 pagesPreparing For The Edexcel A Level English Language and PDFMaría M Malak100% (1)
- Bridge To Wiseman's Cove Spelling ListDocument2 pagesBridge To Wiseman's Cove Spelling Listkizzytoy45No ratings yet
- Anthology-Poetry-Guide-OGAT-v1 (2) WJEC Eduqas GCSE EnglishDocument38 pagesAnthology-Poetry-Guide-OGAT-v1 (2) WJEC Eduqas GCSE EnglishMaryamNo ratings yet
- Romeo & Juliet NotesDocument19 pagesRomeo & Juliet NotesJessica DeveryNo ratings yet
- Omam EssaysDocument37 pagesOmam EssaysSam ShohetNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet Scene SummariesDocument2 pagesRomeo and Juliet Scene Summariesapi-493629348No ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet BookletDocument32 pagesRomeo and Juliet BookletWilliamNo ratings yet
- Year 10 CharacterisationDocument3 pagesYear 10 Characterisationbina ebinger-sack100% (1)
- Year 9 English Drama Text Response Text: Play Script Adaptation of Bram Stoker's Dracula Genre: Gothic/HorrorDocument5 pagesYear 9 English Drama Text Response Text: Play Script Adaptation of Bram Stoker's Dracula Genre: Gothic/HorrorMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- 1123 s18 Ms 22 PDFDocument14 pages1123 s18 Ms 22 PDFSyed AsharNo ratings yet
- Merchant of Venice Workbook Answers: Act I Scene 1Document11 pagesMerchant of Venice Workbook Answers: Act I Scene 1Arshad MohammedNo ratings yet
- An-Inspector-Calls-Revision-Guide 2Document53 pagesAn-Inspector-Calls-Revision-Guide 2Liane RegnardNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet Knowledge OrganiserDocument1 pageRomeo and Juliet Knowledge OrganiserMariate VengesayiNo ratings yet
- English Notes Year 9Document2 pagesEnglish Notes Year 9SonicyBabaNo ratings yet
- The Things They Carried Ib Summer AssignmentDocument9 pagesThe Things They Carried Ib Summer Assignmentapi-462884787No ratings yet
- English 9 Summer Week 3Document18 pagesEnglish 9 Summer Week 3Felix Ray DumaganNo ratings yet
- The Stranger LitChartDocument33 pagesThe Stranger LitChartqdgvrgjx42No ratings yet
- ADV Paper 1Document13 pagesADV Paper 12qncki2bwbckaNo ratings yet
- How Does Steinbeck Present The Theme of Death inDocument2 pagesHow Does Steinbeck Present The Theme of Death inChan Long Hin Derek100% (1)
- Grade 12 SSIP Sessions 6-7 English FAL (LN) Booklet 2013Document39 pagesGrade 12 SSIP Sessions 6-7 English FAL (LN) Booklet 2013Anita LestariNo ratings yet
- A Christmas CarolDocument25 pagesA Christmas Carolenglish4simonsacademyNo ratings yet
- Quotation Bank MacbethDocument2 pagesQuotation Bank MacbethduhgyusdfuiosNo ratings yet
- Exposure - PI ReadyDocument36 pagesExposure - PI ReadyCharles Jasper100% (1)
- Great Expectations - Charles DickensDocument299 pagesGreat Expectations - Charles Dickensjeanmarc100% (7)
- Romeo & Juliet CharactersDocument10 pagesRomeo & Juliet CharactersNik NurisyaNo ratings yet
- Examiner Report Jan 2019 4EB1Document12 pagesExaminer Report Jan 2019 4EB1JerryNo ratings yet
- Book Questions 4 GMTDocument9 pagesBook Questions 4 GMTKiki CorleoneNo ratings yet
- English Novel Study ExamDocument6 pagesEnglish Novel Study Examapi-388178708No ratings yet
- Gcse Media Revision PackDocument17 pagesGcse Media Revision Packapi-227569827No ratings yet
- Lord of The Flies WorkbookDocument14 pagesLord of The Flies WorkbookHongNhung Pham MA.100% (1)
- The Theme of LoveDocument3 pagesThe Theme of LoveEmir AvdispahićNo ratings yet
- Essay of Mice and MenDocument2 pagesEssay of Mice and MenLizzeth ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Ingris IO Transcript and ExtractDocument3 pagesIngris IO Transcript and Extractpulkit mohataNo ratings yet
- 2017 Updated Gcse Eduqas Student Friendly - Y9-11 - in ProgressDocument19 pages2017 Updated Gcse Eduqas Student Friendly - Y9-11 - in Progressapi-200352820No ratings yet
- Merchant of VeniceDocument12 pagesMerchant of VeniceBingkat MacarimbangNo ratings yet
- York Notes Gcse Workbook The Merchant of VeniceDocument25 pagesYork Notes Gcse Workbook The Merchant of VeniceShanthi LingeshNo ratings yet
- Heaney, The Barn IOC - Points & AnalysisDocument2 pagesHeaney, The Barn IOC - Points & AnalysisNicholas50% (8)
- COMPARISON Prayer Before Birth and War PhotographerDocument1 pageCOMPARISON Prayer Before Birth and War PhotographerDinangaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Jun 2CDocument15 pages2021 Jun 2CDinangaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Jun 1CDocument21 pages2021 Jun 1CDinangaNo ratings yet
- Fongrsy Salt-PreparationDocument1 pageFongrsy Salt-PreparationDinangaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Jan 2CDocument16 pages2021 Jan 2CDinangaNo ratings yet
- 4MA1 1HR Rms 20220303Document20 pages4MA1 1HR Rms 20220303DinangaNo ratings yet
- 4MA1 1HR Que 20220111Document32 pages4MA1 1HR Que 20220111Dinanga100% (1)
- IGCSE Files&documents Telegram ChannelDocument176 pagesIGCSE Files&documents Telegram ChannelDinangaNo ratings yet
- 4MA1 1H Que 20220111Document28 pages4MA1 1H Que 20220111DinangaNo ratings yet
- Rubycitalan - Chem MT 1 6Document3 pagesRubycitalan - Chem MT 1 6DinangaNo ratings yet
- 4HB1 01 Rms 20220303Document10 pages4HB1 01 Rms 20220303DinangaNo ratings yet
- 4HB1 01 Que 20220108Document24 pages4HB1 01 Que 20220108DinangaNo ratings yet
- 4HB1 02 Rms 20220303Document10 pages4HB1 02 Rms 20220303DinangaNo ratings yet
- Fongrsy - Acids Bases and AlkalisDocument2 pagesFongrsy - Acids Bases and AlkalisDinangaNo ratings yet
- Kiserbj241 - Grade 8 ScienceDocument3 pagesKiserbj241 - Grade 8 ScienceDinangaNo ratings yet
- 4HB1 02 Que 20220114Document24 pages4HB1 02 Que 20220114DinangaNo ratings yet
- An Inspector CallsDocument68 pagesAn Inspector CallsDinangaNo ratings yet
- International Gcse English Language A Young Dyslexic Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesInternational Gcse English Language A Young Dyslexic Lesson PlanDinangaNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) : Pearson Edexcel International GCSEDocument24 pagesInformation and Communication Technology (ICT) : Pearson Edexcel International GCSEDinangaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Algebra1Document2 pagesUnit 1 - Algebra1DinangaNo ratings yet
- Still I Rise Lesson Planv2Document3 pagesStill I Rise Lesson Planv2DinangaNo ratings yet
- Still I Rise WorksheetDocument2 pagesStill I Rise WorksheetDinangaNo ratings yet
- Out Out Scasi Essay FinalDocument3 pagesOut Out Scasi Essay FinalDinangaNo ratings yet
- Caa9b7b6 1Document3 pagesCaa9b7b6 1DinangaNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument6 pagesElectricityDinangaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and InheritanceDocument5 pagesReproduction and InheritanceDinangaNo ratings yet
- Inverse PercentagesDocument1 pageInverse PercentagesDinangaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Living OrganismsDocument28 pagesStructure of Living OrganismsDinangaNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Variety of Living OrganismsDocument1 pageThe Nature and Variety of Living OrganismsDinangaNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal in London: He Chose The English City To Be His New Home For 3 ReasonsDocument9 pagesJose Rizal in London: He Chose The English City To Be His New Home For 3 ReasonsKharen DomilNo ratings yet
- RT I Translation StudiesDocument2 pagesRT I Translation StudiesRahma Yulia SyahfitriNo ratings yet
- The Gods and Goddesses of Greek Mythology Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesThe Gods and Goddesses of Greek Mythology Quiz AnswersRejanaNo ratings yet
- Symbolist Movement Its Origins and Its ConsequencesDocument29 pagesSymbolist Movement Its Origins and Its ConsequencesAllan LourençoNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test English 1Document4 pagesThird Periodical Test English 1Kleng Delos Santos BernardoNo ratings yet
- Blood Brothers Character RevisionDocument8 pagesBlood Brothers Character RevisionTara HanleyNo ratings yet
- Group7 Activity3Document4 pagesGroup7 Activity3Pearl Alexandra FabitoNo ratings yet
- On Destroying BooksDocument1 pageOn Destroying Bookssubhani495No ratings yet
- A Paragraph Is A Group of Related Sentences That Support One Main IdeaDocument12 pagesA Paragraph Is A Group of Related Sentences That Support One Main IdeaJustine Joi GuiabNo ratings yet
- Harry Potter and Future's Past Chapter 2 Married - , A Harry Potter Fanfic - FanFictionDocument7 pagesHarry Potter and Future's Past Chapter 2 Married - , A Harry Potter Fanfic - FanFictionHammaad ZargarNo ratings yet
- BhasaDocument3 pagesBhasasivakamipaleriNo ratings yet
- Sources and Studies in The Literature of Jewish Mysticism Edited Daniel AbramsDocument759 pagesSources and Studies in The Literature of Jewish Mysticism Edited Daniel AbramsFulvidor Galté Oñate100% (1)
- Peter, Paul, John, Thomas and Philip With Their Companions in Late Antiquity, ISBN 978-90-429-4553-1Document20 pagesPeter, Paul, John, Thomas and Philip With Their Companions in Late Antiquity, ISBN 978-90-429-4553-1Anonymous i5pNjipxj5No ratings yet
- Humanitas in First Century AD Seneca andDocument33 pagesHumanitas in First Century AD Seneca andCarlosChaconNo ratings yet
- Chips CH 1 PDFDocument11 pagesChips CH 1 PDFJawad KhalidNo ratings yet
- Wjec English Literature A Level Coursework Word CountDocument4 pagesWjec English Literature A Level Coursework Word Countwisaj0jat0l3100% (1)
- Book Review Kura-Kura BerjanggutDocument3 pagesBook Review Kura-Kura BerjanggutRidwan SaidNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument5 pagesFigures of SpeechSheila Mae LiraNo ratings yet
- Canterville Ghost Character SketchesDocument5 pagesCanterville Ghost Character SketchesAswajith K Babu17% (6)
- A Show of The Nine WorthiesDocument7 pagesA Show of The Nine WorthiesStefanoDiCaprioNo ratings yet
- Finals Exam Phil LitDocument3 pagesFinals Exam Phil LitDarlene De PazNo ratings yet
- Love or Lust - Romeo and Juliet (Part 2) #3Document5 pagesLove or Lust - Romeo and Juliet (Part 2) #3krmce pNo ratings yet
- Women's FictionDocument2 pagesWomen's FictionvasiNo ratings yet
- Beren and Lúthien by J.R.R. TolkienDocument7 pagesBeren and Lúthien by J.R.R. TolkienJoseph SuezoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Introduction To Literary Theory - Literature - MIT OpenCourseWareDocument1 pageSyllabus - Introduction To Literary Theory - Literature - MIT OpenCourseWaregervacionoriel27.jobsNo ratings yet
- FinalTime Table MA Def Eco Eng Hin His Mar Phi Pol Psy San Soc Urd Yog Sem-I II III IV Exam January 2022Document23 pagesFinalTime Table MA Def Eco Eng Hin His Mar Phi Pol Psy San Soc Urd Yog Sem-I II III IV Exam January 2022Yogesh MahajanNo ratings yet