Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FW 5
FW 5
Uploaded by
Michael LeroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FW 5
FW 5
Uploaded by
Michael LeroCopyright:
Available Formats
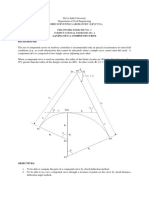
FIELD AREA OF A LOT BOUNDED BY A CURVE OFFSETS AT IRREGULAR
EXERCISE 05: INTERVAL
OBJECTIVE This field method is to determine areas of lots bounded by river, creek, or estero
and of those bounded by lake, pond, coastline, and the like.
INSTRUMENTS Steel tape
& ACCESORIES Chaining Pins
Range poles
Hubs or pegs
Triangle
PROCEDURE 1. Lay out your first baseline with point A at the first point of the curve under
study and point B at the curve’s end.
2. The curve is subdivided into more or less straight segments from curve points
which need attention down to the first baseline. Use swing offset method to
make sure the segment is perpendicular to the baseline.
3. Offsets are constructed from such points noting down (the distance of the
point on curve to the baseline, and (2) the distance of the baseline point to point
A.
OBSERVATION Distance Offset Difference Product
SHEET from Initial Positive Negative
Point
Dist 1
Dist 2 …
Total
Double area
Area
COMPUTATION 1. Difference is the difference between the two adjacent offsets.
Difference distance 0.00m (Initial Point A) = 0.00
Difference distance d1 = distance 0.00-d2
Difference distance d2 = d1-d3
Last offset = summation of last 2 offsets
2. Product = (distance from initial point) x (difference)
3. Total = summation of positive (negative) product
4. Double area = (positive product) - (negative product)
5. Area = double area / 2
QUESTIONS 1. Complete the table and determine the area of the curve:
AND Distance Offset Difference Product
PROBLEMS from Initial (m) Positive Negative
Point
0.00 0.00
10.00 8.40
18.00 12.70
30.00 8.80
40.00 6.50
54.00 0.00
You might also like
- Hse Assignment 2Document13 pagesHse Assignment 2Johan Aliff100% (3)
- A Court of Whispers And-1Document763 pagesA Court of Whispers And-1Saba AbrishamiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument11 pagesPDFwarlock123456zxcvb42% (24)
- Traverse Surveying: Group 2: Aguinaldo, Gilbert Javonillo, Aira Diosa Pena, July Anne Pisco, Vicente, JRDocument28 pagesTraverse Surveying: Group 2: Aguinaldo, Gilbert Javonillo, Aira Diosa Pena, July Anne Pisco, Vicente, JRMary Grace DangtayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 A Level Physics WB MSDocument4 pagesChapter - 15 A Level Physics WB MSmichelle winataNo ratings yet
- Diffraction GartingDocument8 pagesDiffraction GartingAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science PHYSICS PRACTICALSDocument10 pagesClass 10 Science PHYSICS PRACTICALSTanishaNo ratings yet
- Resolving Power - ManualDocument3 pagesResolving Power - ManualDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics 73.1 R&D Part 2Document4 pagesPhysics 73.1 R&D Part 2ggwp21No ratings yet
- 4th Lab ExperimentsDocument68 pages4th Lab ExperimentsAndro KhanNo ratings yet
- GE 105 Lecture 1Document23 pagesGE 105 Lecture 1HazelMaeJoseRico100% (1)
- 2003SP MicrowaveOpticsDocument34 pages2003SP MicrowaveOpticsOmar HraouiNo ratings yet
- 12PhysicsPractical 2022term2Document7 pages12PhysicsPractical 2022term2Dhruv GargNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 DivergenceDocument6 pagesExp 1 Divergenceitsmanish041No ratings yet
- PHYSICS LAB MAN Women SwwihddwkDocument10 pagesPHYSICS LAB MAN Women SwwihddwkndsknNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 ManualDocument16 pagesLaboratory 3 ManualAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Single Slit DiffractionDocument10 pagesSingle Slit DiffractionNCHE BORISNo ratings yet
- Exercise #3: Calibration For EDMI: 1. 1.1. Primary Objectives FulfilledDocument7 pagesExercise #3: Calibration For EDMI: 1. 1.1. Primary Objectives FulfilledDhanya SagarNo ratings yet
- Plane TableDocument31 pagesPlane TableSaileshNo ratings yet
- Metrology Laboratory: Experiment No. 1Document5 pagesMetrology Laboratory: Experiment No. 1Mitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Radial Stake Out 18Document6 pagesRadial Stake Out 18Mark B. BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Physics EmanualDocument38 pagesPhysics Emanualrobloxgamer01072005No ratings yet
- Experiment - 3: ∝ I The SI unit of resistance is Ohm (Ω)Document10 pagesExperiment - 3: ∝ I The SI unit of resistance is Ohm (Ω)Raghav Chaudhary 10-ANo ratings yet
- Light Intensity vs. Distance: EquipmentDocument7 pagesLight Intensity vs. Distance: Equipmentjohh smithNo ratings yet
- Geomatic Repoert No.2Document9 pagesGeomatic Repoert No.2Yusf ari jerjisNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 DivergenceDocument6 pagesExp 1 DivergenceSahil Bhatia100% (1)
- Summary Report On Principles of Superposition ExperimentDocument4 pagesSummary Report On Principles of Superposition ExperimentLaurie Claire MotolNo ratings yet
- Experiment (4) StasisDocument9 pagesExperiment (4) StasisBabong KobNo ratings yet
- PUSSYDocument5 pagesPUSSYDexter Merro GuinoNo ratings yet
- Sumande - Field Work No.9 - Determination of The Height of A Remote PointDocument14 pagesSumande - Field Work No.9 - Determination of The Height of A Remote PointCedrix SumandeNo ratings yet
- Johannes Final Laboratory #3 - Earthworks (Area and Volume)Document7 pagesJohannes Final Laboratory #3 - Earthworks (Area and Volume)BLESSA TORRESNo ratings yet
- NP2Document6 pagesNP2subhajana646No ratings yet
- PH 301 Engineering Optics: Lecture - 1Document43 pagesPH 301 Engineering Optics: Lecture - 1Mantavya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 03 - Edm CalibrationDocument2 pagesLab Report 03 - Edm CalibrationShivam ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Newtons Rings (Additional)Document6 pagesNewtons Rings (Additional)Dr. Deepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Class 12TH Practical ReadingsDocument14 pagesClass 12TH Practical ReadingsLakshya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Surveying Experiment 01Document4 pagesSurveying Experiment 01Danyar Mohammed TahirNo ratings yet
- QUIZ #1-A (Introduction, Distance, Correction and Leveling)Document3 pagesQUIZ #1-A (Introduction, Distance, Correction and Leveling)nonononowayNo ratings yet
- Course Name: SPC & Metrology Section Number: 2: Title: Angle MeasurementDocument6 pagesCourse Name: SPC & Metrology Section Number: 2: Title: Angle MeasurementrajeshNo ratings yet
- Final 2Document14 pagesFinal 2ccode904No ratings yet
- Angle of Minimum DeviationDocument5 pagesAngle of Minimum Deviationajithfan67% (3)
- Lab ManualsDocument9 pagesLab ManualsRaja KhanNo ratings yet
- Handout 3 Level - Horizontal Distances and AnglesDocument4 pagesHandout 3 Level - Horizontal Distances and AnglesTheresa DaherNo ratings yet
- Continuous Beam Lab 2019 PDFDocument6 pagesContinuous Beam Lab 2019 PDFDavid CharltonNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2:: 2.1 Free StationingDocument9 pagesExercise 2:: 2.1 Free Stationingswellchaser80No ratings yet
- Assessment Unit Test Graphing Scalars and Vectors With AnswersDocument12 pagesAssessment Unit Test Graphing Scalars and Vectors With AnswersTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- GE 105 Lecture 1 (LEAST SQUARES ADJUSTMENT) By: Broddett Bello AbatayoDocument49 pagesGE 105 Lecture 1 (LEAST SQUARES ADJUSTMENT) By: Broddett Bello AbatayoBroddett Bello Abatayo100% (1)
- Lat LongDocument4 pagesLat LongJesus Manuel Durand TorresNo ratings yet
- Traversing: Types, Purpose, Procedure, ErrorsDocument10 pagesTraversing: Types, Purpose, Procedure, ErrorsIrwan Pratama100% (1)
- Latitude, Longitude, and Great Circle Distances by Chip PearsonDocument4 pagesLatitude, Longitude, and Great Circle Distances by Chip PearsonSyed Subtain HussainNo ratings yet
- Compex 04 and Fieldex 02Document5 pagesCompex 04 and Fieldex 02Hwang YedangNo ratings yet
- Field Work No. 8 Determination of The Height of A Remote PointDocument9 pagesField Work No. 8 Determination of The Height of A Remote PointMikaella TambisNo ratings yet
- MAJ 3 - Handout 2Document12 pagesMAJ 3 - Handout 2Annalie LobianoNo ratings yet
- EdgeDetectionMain 2Document102 pagesEdgeDetectionMain 2ShreyaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistivity Test: Soil Engineering LabDocument10 pagesElectrical Resistivity Test: Soil Engineering LabAbhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- 09-Traverse SurveyingDocument26 pages09-Traverse SurveyingKristine DizonNo ratings yet
- 4th Year Lab ManualDocument99 pages4th Year Lab ManualMahesh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- E-M RatioDocument3 pagesE-M RatioviranjiforuNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual Experiments SECTION B EXPERIMENTS 2022-23Document9 pagesPhysics Lab Manual Experiments SECTION B EXPERIMENTS 2022-23Dhairya PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Moving Up The CurveDocument5 pagesMoving Up The CurveMark B. BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Newtons Ring Experiment1Document4 pagesNewtons Ring Experiment1Mahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- Asssessment - 2022 2 3Document2 pagesAsssessment - 2022 2 3Michael LeroNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Flowing Fluids and Pressure VariationDocument93 pagesCH 4 Flowing Fluids and Pressure VariationMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- 57 20 EFD Safety InstructionsDocument1 page57 20 EFD Safety InstructionsMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- Tlo1b2 Horiz Distance - TapingDocument3 pagesTlo1b2 Horiz Distance - TapingMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- CCNY LabManualDocument56 pagesCCNY LabManualMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- 5CE344 Water Resources Eng Lab ManualDocument67 pages5CE344 Water Resources Eng Lab ManualMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- 319 - CE8351 Surveying - NotesDocument167 pages319 - CE8351 Surveying - NotesMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- CE 134L Elementary Surveying Lab Lab InsDocument54 pagesCE 134L Elementary Surveying Lab Lab InsMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- Tlo1c Horiz Distance - Survey by TapingDocument9 pagesTlo1c Horiz Distance - Survey by TapingMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- Section I - General InformationDocument7 pagesSection I - General InformationMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- 047043841X 144Document10 pages047043841X 144Michael LeroNo ratings yet
- Panasonic Conduits PDFDocument1 pagePanasonic Conduits PDFMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- Leveling 1Document3 pagesLeveling 1Michael LeroNo ratings yet
- FW 6Document4 pagesFW 6Michael LeroNo ratings yet
- FW 8Document3 pagesFW 8Michael LeroNo ratings yet
- Tlo Determinacy of StructuresDocument10 pagesTlo Determinacy of StructuresMichael LeroNo ratings yet
- The Viking Portable Library World BibleDocument634 pagesThe Viking Portable Library World BibleJose Gonzalez AntomilNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Classification of Animals (Students Copy)Document4 pages1.2 Classification of Animals (Students Copy)Mohd Fauzan Che Hasim100% (1)
- Overpharma Globus SpineDocument20 pagesOverpharma Globus SpineruiduartNo ratings yet
- Educational Planning:: DefinitionDocument3 pagesEducational Planning:: DefinitionBasit AliNo ratings yet
- Lombardini 9LD Work Shop ManualDocument70 pagesLombardini 9LD Work Shop ManualWim Peeters67% (6)
- English Comprehension: B. He Would MakeDocument17 pagesEnglish Comprehension: B. He Would MakeAbhay BandilNo ratings yet
- Greene - Shear Tab CalcDocument6 pagesGreene - Shear Tab CalcNagender KumarNo ratings yet
- TOWARD A CONCEPT OF POSTMODERNISM. Ihab HassanDocument13 pagesTOWARD A CONCEPT OF POSTMODERNISM. Ihab HassanLucila Delgaudio (Lady Lemonade)No ratings yet
- DCS NS 430 Manual ENDocument86 pagesDCS NS 430 Manual ENOscar HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Health Management in The Oil and Gas IndustryDocument44 pagesHealth Management in The Oil and Gas IndustryClaudia TiradoNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentOana SvNo ratings yet
- Zero Coupon Bonds ($1 Maturity) Inputs Vasicek CIR Vasicek (A (B-R) DT + S DZ)Document20 pagesZero Coupon Bonds ($1 Maturity) Inputs Vasicek CIR Vasicek (A (B-R) DT + S DZ)david AbotsitseNo ratings yet
- PF 7000 2210Document3 pagesPF 7000 2210Javad KheyrollahikalvanaghNo ratings yet
- Additional Combined Science: Paper 2Document16 pagesAdditional Combined Science: Paper 2rodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Therapy Guide 2Document3 pagesInsulin Therapy Guide 2AimanRiddleNo ratings yet
- Control of HVDC Transmission System Based On MMC With Three-Level Flying Capacitor SubmoduleDocument22 pagesControl of HVDC Transmission System Based On MMC With Three-Level Flying Capacitor SubmoduleAnand Parakkat Parambil100% (1)
- Targeted SlimmingDocument8 pagesTargeted SlimmingHarsh Goyal67% (3)
- Hubbard and O'Brien (CH 2)Document24 pagesHubbard and O'Brien (CH 2)Sophia Alexandra CabuangNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Intensity (H)Document5 pagesMagnetic Field Intensity (H)M HASIN ISHMAM JEETNo ratings yet
- Eppe2023 Tuto 7QDocument4 pagesEppe2023 Tuto 7QMUHAMMAD AIMAN ZAKWAN BIN ROZANINo ratings yet
- Racecar Engineering June 2017Document101 pagesRacecar Engineering June 2017Big FloresNo ratings yet
- Tests FiDocument27 pagesTests FiIce AgeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Shell TheoryDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Shell TheorySurendraBhatta100% (1)
- Management FunctionsDocument18 pagesManagement FunctionsKennethNo ratings yet
- Rau's Ias - Study CircleDocument3 pagesRau's Ias - Study CircleArpit VermaNo ratings yet
- Silberman - Version For RepositoriesDocument9 pagesSilberman - Version For RepositoriesmohammedalssediNo ratings yet