Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsComparison of Transcription, Translation and Replication
Comparison of Transcription, Translation and Replication
Uploaded by
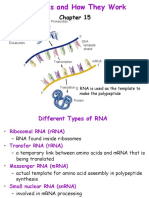
Drashty DesaiThe document compares and contrasts replication, transcription, and translation between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Replication begins at a single origin in prokaryotes and multiple origins in eukaryotes. Transcription uses one RNA polymerase in prokaryotes and three in eukaryotes. Translation involves a 30S ribosomal subunit in prokaryotes and a 50S subunit in eukaryotes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Microbiology An Introduction 13th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument24 pagesMicrobiology An Introduction 13th Edition Tortora Test Bankeugenephedrayy2bfk98% (43)
- Ebook Guyton Hall Physiology Review Guyton Physiology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Guyton Hall Physiology Review Guyton Physiology PDF Full Chapter PDFrichard.tamayo139100% (32)
- Buckingham - Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical ApplicationsDocument479 pagesBuckingham - Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applicationsfakefacebook75891% (11)
- Biotechnology A Problem ApproachDocument223 pagesBiotechnology A Problem ApproachPathifnder Publication94% (49)
- BIOL 182: Biology II Assignment 3 - Cell Division, Genetics and Molecular BiologyDocument7 pagesBIOL 182: Biology II Assignment 3 - Cell Division, Genetics and Molecular BiologyMayaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline General Biology II: Course Code (S) and Mesrs Objectives Science (200.B0), Registered in 101-LCU-05Document12 pagesCourse Outline General Biology II: Course Code (S) and Mesrs Objectives Science (200.B0), Registered in 101-LCU-05Nicole GuNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionDocument46 pages3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionyazicigaamzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Protein SynthesisDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Protein SynthesisT MokshithaNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument100 pagesTranscriptionSreshttNo ratings yet
- RNA Synthesis and SplicingDocument64 pagesRNA Synthesis and SplicingLaurine PigossoNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 5Document38 pages11 Chapter 5toobashafiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationDocument14 pagesChapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationAdonias NiyurukundoNo ratings yet
- Dna L12 NotesDocument6 pagesDna L12 NotesellieNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: Unit 3Document64 pagesMolecular Biology: Unit 3John Rajan ThavamNo ratings yet
- Transcripcion EucariotaDocument21 pagesTranscripcion EucariotaAntoniaNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Presented by Quratulain (19-Arid-1403) Asadullah (19-Arid-1379)Document32 pagesRegulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Presented by Quratulain (19-Arid-1403) Asadullah (19-Arid-1379)Beauty LiciousNo ratings yet
- Usanee Anukool (PH.D.) Clinical Microbiology Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University 2 July 2009Document60 pagesUsanee Anukool (PH.D.) Clinical Microbiology Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University 2 July 2009Suruk UdomsomNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Ofelia Solano Saludar: Department of Natural Sciences University of St. La Salle Bacolod CityDocument55 pagesMrs. Ofelia Solano Saludar: Department of Natural Sciences University of St. La Salle Bacolod CitymskikiNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument75 pagesTranscriptionspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- RNA TranscriptionDocument7 pagesRNA Transcriptionshereefadoma96No ratings yet
- LECTURE 12 TranslationDocument17 pagesLECTURE 12 TranslationAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- 5 11transcription-2013Document30 pages5 11transcription-2013jernsssNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 BIO 1510Document34 pagesChapter 15 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression - Group 1 (Roll No 1 - 23)Document34 pagesGene Expression - Group 1 (Roll No 1 - 23)Kaung Wai Yan HeinNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument38 pagesTranscription and RNA ProcessingRishi Kumar100% (1)
- Transcription in EukaryotesDocument49 pagesTranscription in EukaryotesmrlabdesigneNo ratings yet
- MB Chapter 5 TranscriptionDocument32 pagesMB Chapter 5 TranscriptionMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document6 pagesLecture 3tiaria.wilson24No ratings yet
- Transcription in Prokaryotes: Single RNA PolymeraseDocument29 pagesTranscription in Prokaryotes: Single RNA PolymeraseShubhamNo ratings yet
- Bala Sir Transcrption PDFDocument9 pagesBala Sir Transcrption PDFAnjali Ak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument35 pagesTranscription and TranslationMing mingNo ratings yet
- Transcription, Translation, Genetic Code Mutations (Part 2) - Compressed PDFDocument131 pagesTranscription, Translation, Genetic Code Mutations (Part 2) - Compressed PDFMuhammad Haris AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression - Protein SynthesisDocument39 pagesGene Expression - Protein SynthesisTawonga ManjiniNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: RNA Synthesis and ProcessingDocument54 pagesBiochemistry: RNA Synthesis and ProcessingAqsa YaminNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument9 pagesTranscription and TranslationlinhNo ratings yet
- Rna Biosynthesis (Transicription)Document33 pagesRna Biosynthesis (Transicription)Alaa AlmajedNo ratings yet
- S2. Transcription Translation Gene RegulationDocument87 pagesS2. Transcription Translation Gene RegulationDeriq Maorenz CruzNo ratings yet
- Transcription NotesDocument2 pagesTranscription Notesmartinc08No ratings yet
- Transkripsi Dan Translasi SMA Permata Insani IslamicDocument58 pagesTranskripsi Dan Translasi SMA Permata Insani IslamicMaria Angelina Genere KobanNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument61 pagesTranscriptiondeepak mauryaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument34 pagesTranscriptiondrhydrogenNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Faculty of Medicine, Sriwijaya UniversityDocument51 pagesCentral Dogma: Faculty of Medicine, Sriwijaya UniversityIlsya PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Transcriptiontranslation 170210171328Document34 pagesTranscriptiontranslation 170210171328Farah B. BtoushNo ratings yet
- BY150 Session 2 DR Brissett 2022 - TaggedDocument45 pagesBY150 Session 2 DR Brissett 2022 - TaggedL FelicityNo ratings yet
- De La Proteina La GenaDocument67 pagesDe La Proteina La GenaiuventasNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument31 pagesTranscriptionDeeptanshu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Transcription in Prokaryotes: Dindin H. Mursyidin Laboratory of Molecular Biology Lambung Mangkurat UniversityDocument39 pagesTranscription in Prokaryotes: Dindin H. Mursyidin Laboratory of Molecular Biology Lambung Mangkurat UniversityNadia Nur FitriaNo ratings yet
- Transcription: Dr. Anirudra Gurung, Department of Botany, St. Joseph's College, DarjeelingDocument9 pagesTranscription: Dr. Anirudra Gurung, Department of Botany, St. Joseph's College, DarjeelingRahul JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument58 pagesTranscription and Translationkevin_ramos007No ratings yet
- Transcription in ProkaryotesDocument16 pagesTranscription in ProkaryotesAditya Kanwal100% (2)
- Biomol R2 Kurniahtunnisa 0402517015 RefleksiDocument15 pagesBiomol R2 Kurniahtunnisa 0402517015 RefleksiKurniah TunnisaNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument51 pagesTranslationAleena MustafaNo ratings yet
- RNA - Polymerase 1 ClassDocument21 pagesRNA - Polymerase 1 ClassSeemaNo ratings yet
- Transcription (Semister I MIC)Document117 pagesTranscription (Semister I MIC)Challagandla AnilNo ratings yet
- Rna and Amino AcidDocument14 pagesRna and Amino AcidIndestructible queenNo ratings yet
- RNA Metabolism: Durriya Naeem KhanDocument26 pagesRNA Metabolism: Durriya Naeem KhanMniaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RegulationDocument40 pagesTranscription and RegulationRUDRANSH PUJARINo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Transcription: DR Vaishali Dhat Professor, Department of Biochemistry DR DypmcDocument25 pagesTranscription: DR Vaishali Dhat Professor, Department of Biochemistry DR Dypmcnishkarsh chauhanNo ratings yet
- Transcription NotesDocument16 pagesTranscription NotesArathi PillaiNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression 1Document28 pagesGene Expression 1ha88ial88No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument60 pagesProtein Synthesislucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- RNA Synthesis, Processing SBT 211Document59 pagesRNA Synthesis, Processing SBT 211TADIWANASHE TINONETSANANo ratings yet
- L1 TranscriptionDocument13 pagesL1 TranscriptionvarasamaliaNo ratings yet
- IGA 10e SM Chapter 07Document10 pagesIGA 10e SM Chapter 07duabgelorNo ratings yet
- Mukesh's Biology Project TranscriptionDocument33 pagesMukesh's Biology Project TranscriptionM.S.Mukesh Kumar X-ANo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Central DogmaDocument8 pagesModule 1 - Central DogmaAnanya SinghNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument31 pagesTranscriptionDeeptanshu PrakashNo ratings yet
- CH Test BDocument4 pagesCH Test BTahfeel -- GamingNo ratings yet
- Designer DNA ChallengeDocument11 pagesDesigner DNA ChallengeTimothy TwomeyNo ratings yet
- Biology: Study MaterialDocument202 pagesBiology: Study MaterialSandeep100% (1)
- University of Rajshahi MSC SyllabusDocument16 pagesUniversity of Rajshahi MSC SyllabusProf. Dr. M. KhalequzzamanNo ratings yet
- Your World Biotechnology and You Vol 13-1 R20070820WDocument16 pagesYour World Biotechnology and You Vol 13-1 R20070820WAdelin AnastasiuNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology Exam Essay (Free Response) Questions: Unit 1 Biochemistry, Water, EnzymesDocument37 pagesAp Biology Exam Essay (Free Response) Questions: Unit 1 Biochemistry, Water, EnzymesBeatrice MallariNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BiotechnologyDocument43 pagesSyllabus Biotechnologyabdul basitNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Eligibility Test (BET) For DBT-JRF Award (2009-10)Document18 pagesBiotechnology Eligibility Test (BET) For DBT-JRF Award (2009-10)Nandakumar HaorongbamNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Control of Gene ExpressionDocument82 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Control of Gene ExpressionJing Li100% (1)
- Covid Vaccines - Complete Report - Graphene, Nanotechnology and TranshumanismDocument11 pagesCovid Vaccines - Complete Report - Graphene, Nanotechnology and TranshumanismLilith100% (2)
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- Directorate of Learning Systems Directorate of Learning SystemsDocument50 pagesDirectorate of Learning Systems Directorate of Learning SystemsMatin Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio 308 Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesBio 308 Lecture NotesPeter Sin-KeoNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology 2020 Practice Exam and Notes 3 MCQ AnswersDocument32 pagesAp Biology 2020 Practice Exam and Notes 3 MCQ AnswersEric ChiangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Guided Notes-1Document7 pagesChapter 12 Guided Notes-1MasonNo ratings yet
- 化學生物學handout Ch. 1Document45 pages化學生物學handout Ch. 1Krisan Mallion LuisNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy 4th Edition BaumanDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy 4th Edition BaumanAmandaReynoldsagfcy100% (32)
- Molecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 5: Dna Replication, Repair, and RecombinationDocument25 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 5: Dna Replication, Repair, and RecombinationIsmael Torres-PizarroNo ratings yet
- Long Test As Level Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesLong Test As Level Nucleic AcidPrisky Jofan SimbarNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
Comparison of Transcription, Translation and Replication
Comparison of Transcription, Translation and Replication
Uploaded by
Drashty Desai0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe document compares and contrasts replication, transcription, and translation between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Replication begins at a single origin in prokaryotes and multiple origins in eukaryotes. Transcription uses one RNA polymerase in prokaryotes and three in eukaryotes. Translation involves a 30S ribosomal subunit in prokaryotes and a 50S subunit in eukaryotes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document compares and contrasts replication, transcription, and translation between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Replication begins at a single origin in prokaryotes and multiple origins in eukaryotes. Transcription uses one RNA polymerase in prokaryotes and three in eukaryotes. Translation involves a 30S ribosomal subunit in prokaryotes and a 50S subunit in eukaryotes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageComparison of Transcription, Translation and Replication
Comparison of Transcription, Translation and Replication
Uploaded by
Drashty DesaiThe document compares and contrasts replication, transcription, and translation between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Replication begins at a single origin in prokaryotes and multiple origins in eukaryotes. Transcription uses one RNA polymerase in prokaryotes and three in eukaryotes. Translation involves a 30S ribosomal subunit in prokaryotes and a 50S subunit in eukaryotes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Replication Transcription Translation
Prokaryote Eukaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote
Synthesis begins at the origin Synthesis: begins at many RNA Molecules: RNA Molecules: 30S ribosomal subunit with 50S ribosomal subunit binds
of replication (ORI) replication origins mRNA: encodes the amino acid mRNA: encodes the amino acid initiation factors and GTP bind forming 70S initiation complex
OriC (origin of replication for sequence of a polypeptide sequence of a polypeptide to mRNA and fMet initiator during which time the initiation
E. Coli) is 245 base pairs and tRNA: brings amino acids to the tRNA: brings amino acids to the tRNA to form 30S initiation factors are released and GTP
consists of 4 9-mer and 3 13- ribosome during translation ribosome during translation complex hydrolyzed
mer sequences rRNA: combines with ribosomal rRNA: combines with ribosomal the 30S ribosome binds to the small ribosomal subunit binds
DNAa: binds to the 13-mers proteins to from the ribosome proteins to from the ribosome Shine-Dalgarno sequence to the methylated cap at the
DNAc: (helicase inhibitor) snRNA: combines with certain snRNA: combines with certain (typically 5'-AGGAGG-3') 5' end of the mRNA, it then
delivers DNAb (helicase) to the proteins and is involved in RNA proteins and is involved in RNA migrates to the initiation site-
template processing processing usually the first AUG that it
encounters
Helicase: clamps around each Helicase: clamps around each Only one single RNA Three RNA Polymerases: amino acids added one by one amino acids added one by one
single strand of DNA and single strand of DNA and Polymerase RNA Polymerase I: 5.8S, 18S, by the preceding amino acid at by the preceding amino acid at
unwinds the DNA unwinds the DNA and 28S rRNA genes the C-terminus the C-terminus
DNA Primase: polymerase DNA Primase: polymerase RNA Polymerase II: all protein translation proceeds along the translation proceeds along the
which is required for DNA which is required for DNA coding genes (mRNA) and mRNA in the 5' to 3' direction mRNA in the 5' to 3' direction
polymerase to begin elongation polymerase to begin elongation some snRNAs
DNA Polymerase I: removes DNA polymerase: responsible RNA Polymerase III: tRNA each addition involves each addition involves
and replaces RNA primer for elongation of leading and genes and some snRNAs elongation factors elongation factors
5'to 3; exonculcease activity lagging strands Promotor: located upstream at Promotor: consists of a EF-Tu and GTP usher the EF-Tu and GTP usher the
(RNA primer Removal) -35 and -10 bp from collection of conserved short appropriate tRNA into the A site appropriate tRNA into the A site
5'to 3' polymerase activity transcription start site sequence elements near the of the ribosome of the ribosome
(replace primer with DNA) -35 consensus sequence transcription start site peptidyl transferase: peptide peptidyl transferase: peptide
3' to 5' exonuclease activity 5'-TTGACA-3' GC Box: GGGCGG; -70 to -200 bond formation between the bond formation between the
(proofreading) -10 consensus sequence TATA Box: TATAA; -20 to -35 two adjacent amino two adjacent amino
Polymerase II: involved in 5'-TATAAT-3' (Pribnow box) CAAT Box: CCAAT; -80 peptide bond formation causes peptide bond formation causes
repairing damaged DNA RNA polymerase and a sigma Transcription Factors: the initiating tRNA in the P-site the initiating tRNA in the P-site
3'to 5' exonuclease activity factor bind to the -35 and -10 TATA box binding protein: to release its amino acid and it to release its amino acid and it
DNA Polymerase III: multi- regions, this adhered weakly to subunit of TFIID binds TATA box dissociates dissociates
subunit protein for elongation the bacterial DNA and slides of promotor the ribosome continues to the ribosome continues to
of DNA daughter strand along until it reaches the TFIID: causes distortion of move along to the next codon move along to the next codon
main polymerase in bacteria promotor where it binds tightly DNA double helix allowing for and it requires elongation and it requires elongation
5' to 3' (responsible for and opens up the double helix recruitment of other factors and GTP factors and GTP
elongation of leading and to expose DNA transcription factors
lagging strand) DNA is unwound and TFIIB: involved in Rna
3' to 5' exonuclease activity transcription begins polymerase interactions (start
site recognition)
DNA Ligase: ligates Okasaki DNA Ligase: ligates Okasaki TFIIH: contains DNA helicase peptidyl transferase: catalyzes peptidyl transferase: catalyzes
fragments fragments to unwind DNA and activates the formation of a peptide the formation of a peptide
Single stranded binding Single stranded binding RNA polymerase by bond between the first two bond between the first two
proteins: bind to single proteins: bind to single phosphorylation amino acids (fMet and Ser) of amino acids (fMet and Ser) of
stranded DNA in the replication stranded DNA in the replication TFIIE: involved in positioning a polypeptide chain on the a polypeptide chain on the
fork and prevent reannealing fork and prevent reannealing RNA polymerase ribosome ribosome
Clamp protein: holds DNA Clamp protein: holds DNA RNA polymerase II and TFIID
onto template onto template and other transcription factors
Termination: occurs when a Termination: occurs when a
from the basal transcription
Topoisomerase: swivel DNA Topoisomerase: swivel DNA stop codon (UAG, UAA and stop codon (UAG, UAA and
machinery
allowing for free rotation of allowing for free rotation of Topoisomerase- relaxes Topoisomerase- relaxes UGA) reaches the A site of a UGA) reaches the A site of a
DNA around backbones DNA around backbones negative supercoils negative supercoils ribosome. The A site accepts a ribosome. The A site accepts a
Gyrase- introduces -ve Gyrase- introduces -ve protein called a release factor. protein called a release factor.
Telomerase: synthesizes DNA
supercoils supercoils Prokaryotes possess 3 release Eukaryotes contain a single
using an RNA template to seal
intrinsic termination found in intrinsic termination found in factors: RF1 (recognizes UAA releasing factor: -eRF
the gaps left at the 5' end of
RNA transcript RNA transcript and UAG), RF2 (recognizes
the new DNA resulting from
extrinsic termination such as extrinsic termination such as UAA and UGA) and RF3 which
RNA primer removal
rho proteins in prokaryotes rho proteins in prokaryotes stimulates termination
You might also like
- Microbiology An Introduction 13th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument24 pagesMicrobiology An Introduction 13th Edition Tortora Test Bankeugenephedrayy2bfk98% (43)
- Ebook Guyton Hall Physiology Review Guyton Physiology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Guyton Hall Physiology Review Guyton Physiology PDF Full Chapter PDFrichard.tamayo139100% (32)
- Buckingham - Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical ApplicationsDocument479 pagesBuckingham - Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applicationsfakefacebook75891% (11)
- Biotechnology A Problem ApproachDocument223 pagesBiotechnology A Problem ApproachPathifnder Publication94% (49)
- BIOL 182: Biology II Assignment 3 - Cell Division, Genetics and Molecular BiologyDocument7 pagesBIOL 182: Biology II Assignment 3 - Cell Division, Genetics and Molecular BiologyMayaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline General Biology II: Course Code (S) and Mesrs Objectives Science (200.B0), Registered in 101-LCU-05Document12 pagesCourse Outline General Biology II: Course Code (S) and Mesrs Objectives Science (200.B0), Registered in 101-LCU-05Nicole GuNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionDocument46 pages3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionyazicigaamzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Protein SynthesisDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Protein SynthesisT MokshithaNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument100 pagesTranscriptionSreshttNo ratings yet
- RNA Synthesis and SplicingDocument64 pagesRNA Synthesis and SplicingLaurine PigossoNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 5Document38 pages11 Chapter 5toobashafiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationDocument14 pagesChapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationAdonias NiyurukundoNo ratings yet
- Dna L12 NotesDocument6 pagesDna L12 NotesellieNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: Unit 3Document64 pagesMolecular Biology: Unit 3John Rajan ThavamNo ratings yet
- Transcripcion EucariotaDocument21 pagesTranscripcion EucariotaAntoniaNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Presented by Quratulain (19-Arid-1403) Asadullah (19-Arid-1379)Document32 pagesRegulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Presented by Quratulain (19-Arid-1403) Asadullah (19-Arid-1379)Beauty LiciousNo ratings yet
- Usanee Anukool (PH.D.) Clinical Microbiology Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University 2 July 2009Document60 pagesUsanee Anukool (PH.D.) Clinical Microbiology Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University 2 July 2009Suruk UdomsomNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Ofelia Solano Saludar: Department of Natural Sciences University of St. La Salle Bacolod CityDocument55 pagesMrs. Ofelia Solano Saludar: Department of Natural Sciences University of St. La Salle Bacolod CitymskikiNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument75 pagesTranscriptionspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- RNA TranscriptionDocument7 pagesRNA Transcriptionshereefadoma96No ratings yet
- LECTURE 12 TranslationDocument17 pagesLECTURE 12 TranslationAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- 5 11transcription-2013Document30 pages5 11transcription-2013jernsssNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 BIO 1510Document34 pagesChapter 15 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression - Group 1 (Roll No 1 - 23)Document34 pagesGene Expression - Group 1 (Roll No 1 - 23)Kaung Wai Yan HeinNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument38 pagesTranscription and RNA ProcessingRishi Kumar100% (1)
- Transcription in EukaryotesDocument49 pagesTranscription in EukaryotesmrlabdesigneNo ratings yet
- MB Chapter 5 TranscriptionDocument32 pagesMB Chapter 5 TranscriptionMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document6 pagesLecture 3tiaria.wilson24No ratings yet
- Transcription in Prokaryotes: Single RNA PolymeraseDocument29 pagesTranscription in Prokaryotes: Single RNA PolymeraseShubhamNo ratings yet
- Bala Sir Transcrption PDFDocument9 pagesBala Sir Transcrption PDFAnjali Ak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument35 pagesTranscription and TranslationMing mingNo ratings yet
- Transcription, Translation, Genetic Code Mutations (Part 2) - Compressed PDFDocument131 pagesTranscription, Translation, Genetic Code Mutations (Part 2) - Compressed PDFMuhammad Haris AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression - Protein SynthesisDocument39 pagesGene Expression - Protein SynthesisTawonga ManjiniNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: RNA Synthesis and ProcessingDocument54 pagesBiochemistry: RNA Synthesis and ProcessingAqsa YaminNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument9 pagesTranscription and TranslationlinhNo ratings yet
- Rna Biosynthesis (Transicription)Document33 pagesRna Biosynthesis (Transicription)Alaa AlmajedNo ratings yet
- S2. Transcription Translation Gene RegulationDocument87 pagesS2. Transcription Translation Gene RegulationDeriq Maorenz CruzNo ratings yet
- Transcription NotesDocument2 pagesTranscription Notesmartinc08No ratings yet
- Transkripsi Dan Translasi SMA Permata Insani IslamicDocument58 pagesTranskripsi Dan Translasi SMA Permata Insani IslamicMaria Angelina Genere KobanNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument61 pagesTranscriptiondeepak mauryaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument34 pagesTranscriptiondrhydrogenNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Faculty of Medicine, Sriwijaya UniversityDocument51 pagesCentral Dogma: Faculty of Medicine, Sriwijaya UniversityIlsya PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Transcriptiontranslation 170210171328Document34 pagesTranscriptiontranslation 170210171328Farah B. BtoushNo ratings yet
- BY150 Session 2 DR Brissett 2022 - TaggedDocument45 pagesBY150 Session 2 DR Brissett 2022 - TaggedL FelicityNo ratings yet
- De La Proteina La GenaDocument67 pagesDe La Proteina La GenaiuventasNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument31 pagesTranscriptionDeeptanshu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Transcription in Prokaryotes: Dindin H. Mursyidin Laboratory of Molecular Biology Lambung Mangkurat UniversityDocument39 pagesTranscription in Prokaryotes: Dindin H. Mursyidin Laboratory of Molecular Biology Lambung Mangkurat UniversityNadia Nur FitriaNo ratings yet
- Transcription: Dr. Anirudra Gurung, Department of Botany, St. Joseph's College, DarjeelingDocument9 pagesTranscription: Dr. Anirudra Gurung, Department of Botany, St. Joseph's College, DarjeelingRahul JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument58 pagesTranscription and Translationkevin_ramos007No ratings yet
- Transcription in ProkaryotesDocument16 pagesTranscription in ProkaryotesAditya Kanwal100% (2)
- Biomol R2 Kurniahtunnisa 0402517015 RefleksiDocument15 pagesBiomol R2 Kurniahtunnisa 0402517015 RefleksiKurniah TunnisaNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument51 pagesTranslationAleena MustafaNo ratings yet
- RNA - Polymerase 1 ClassDocument21 pagesRNA - Polymerase 1 ClassSeemaNo ratings yet
- Transcription (Semister I MIC)Document117 pagesTranscription (Semister I MIC)Challagandla AnilNo ratings yet
- Rna and Amino AcidDocument14 pagesRna and Amino AcidIndestructible queenNo ratings yet
- RNA Metabolism: Durriya Naeem KhanDocument26 pagesRNA Metabolism: Durriya Naeem KhanMniaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RegulationDocument40 pagesTranscription and RegulationRUDRANSH PUJARINo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Transcription: DR Vaishali Dhat Professor, Department of Biochemistry DR DypmcDocument25 pagesTranscription: DR Vaishali Dhat Professor, Department of Biochemistry DR Dypmcnishkarsh chauhanNo ratings yet
- Transcription NotesDocument16 pagesTranscription NotesArathi PillaiNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression 1Document28 pagesGene Expression 1ha88ial88No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument60 pagesProtein Synthesislucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- RNA Synthesis, Processing SBT 211Document59 pagesRNA Synthesis, Processing SBT 211TADIWANASHE TINONETSANANo ratings yet
- L1 TranscriptionDocument13 pagesL1 TranscriptionvarasamaliaNo ratings yet
- IGA 10e SM Chapter 07Document10 pagesIGA 10e SM Chapter 07duabgelorNo ratings yet
- Mukesh's Biology Project TranscriptionDocument33 pagesMukesh's Biology Project TranscriptionM.S.Mukesh Kumar X-ANo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Central DogmaDocument8 pagesModule 1 - Central DogmaAnanya SinghNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument31 pagesTranscriptionDeeptanshu PrakashNo ratings yet
- CH Test BDocument4 pagesCH Test BTahfeel -- GamingNo ratings yet
- Designer DNA ChallengeDocument11 pagesDesigner DNA ChallengeTimothy TwomeyNo ratings yet
- Biology: Study MaterialDocument202 pagesBiology: Study MaterialSandeep100% (1)
- University of Rajshahi MSC SyllabusDocument16 pagesUniversity of Rajshahi MSC SyllabusProf. Dr. M. KhalequzzamanNo ratings yet
- Your World Biotechnology and You Vol 13-1 R20070820WDocument16 pagesYour World Biotechnology and You Vol 13-1 R20070820WAdelin AnastasiuNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology Exam Essay (Free Response) Questions: Unit 1 Biochemistry, Water, EnzymesDocument37 pagesAp Biology Exam Essay (Free Response) Questions: Unit 1 Biochemistry, Water, EnzymesBeatrice MallariNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BiotechnologyDocument43 pagesSyllabus Biotechnologyabdul basitNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Eligibility Test (BET) For DBT-JRF Award (2009-10)Document18 pagesBiotechnology Eligibility Test (BET) For DBT-JRF Award (2009-10)Nandakumar HaorongbamNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Control of Gene ExpressionDocument82 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Control of Gene ExpressionJing Li100% (1)
- Covid Vaccines - Complete Report - Graphene, Nanotechnology and TranshumanismDocument11 pagesCovid Vaccines - Complete Report - Graphene, Nanotechnology and TranshumanismLilith100% (2)
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- Directorate of Learning Systems Directorate of Learning SystemsDocument50 pagesDirectorate of Learning Systems Directorate of Learning SystemsMatin Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio 308 Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesBio 308 Lecture NotesPeter Sin-KeoNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology 2020 Practice Exam and Notes 3 MCQ AnswersDocument32 pagesAp Biology 2020 Practice Exam and Notes 3 MCQ AnswersEric ChiangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Guided Notes-1Document7 pagesChapter 12 Guided Notes-1MasonNo ratings yet
- 化學生物學handout Ch. 1Document45 pages化學生物學handout Ch. 1Krisan Mallion LuisNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy 4th Edition BaumanDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy 4th Edition BaumanAmandaReynoldsagfcy100% (32)
- Molecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 5: Dna Replication, Repair, and RecombinationDocument25 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 5: Dna Replication, Repair, and RecombinationIsmael Torres-PizarroNo ratings yet
- Long Test As Level Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesLong Test As Level Nucleic AcidPrisky Jofan SimbarNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet