Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Sub - Solving Series Parallel Circuit Using Voltage and Current Divider Rule
Chapter 2 Sub - Solving Series Parallel Circuit Using Voltage and Current Divider Rule
Uploaded by
MOHAMAD FADZLI BIN HANIFF 14668Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Sub - Solving Series Parallel Circuit Using Voltage and Current Divider Rule
Chapter 2 Sub - Solving Series Parallel Circuit Using Voltage and Current Divider Rule
Uploaded by
MOHAMAD FADZLI BIN HANIFF 14668Copyright:
Available Formats
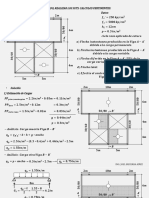
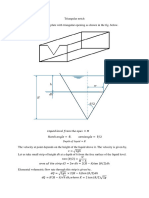
SOLVING SERIES PARALELL CIRCUIT USING VOLTAGE & CURRENT DIVIDER RULE
𝑹𝑻 = 𝟓𝒌𝜴 + 𝟑𝒌𝜴 + 𝟐𝒌𝜴 = 𝟏𝟎𝒌𝜴
You can calculate the source current 𝑰𝑺 flowing from 𝑽𝟐 using Ohm’s Law:
𝑽𝟐 𝟏𝟎𝑽
𝑰𝑺 = = = 𝟏𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝑻 𝟏𝟎𝒌𝜴
Since 𝑽𝟐 , 𝑹𝟏 , 𝑹𝟐 and 𝑹𝟑 //(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 ) are connected in series:
𝑰𝑺 = 𝑰𝑹𝟏 = 𝑰𝑹𝟐 = 𝑰𝑹𝟑//(𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔) = 𝟏𝑨
You can calculate the voltage across 𝑹𝟏 ,
𝑹𝟐 and 𝑹𝟑 //(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 ) by using
𝑹
𝑰𝑺 voltage divider rule:𝑽𝑿 = 𝑽𝑺 ( 𝑿 )
𝑹 𝑻
Voltage at 𝑹𝟑 //(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 ):
𝑽𝑹𝟑//(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔)
𝑹𝟑 //(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 )
= 𝑽𝟐 ( )
𝑹𝑻
𝟐𝒌𝜴
= 𝟏𝟎𝑽 ( ) = 𝟐𝑽
𝟏𝟎𝒌𝜴
Since 𝑹𝟑 is parallel with (𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 ):
𝑽𝑹𝟑//(𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔) = 𝑽𝑹𝟑 = 𝑽𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔 = 𝟐𝑽
𝑰𝑹𝟑//(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔)
You can calculate the current flowing
through 𝑹𝟑 and 𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 using Ohm’s
+
Law:
𝑽𝑹 𝟑 𝟐𝑽
𝑽𝑹𝟑//(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔) 𝑰𝑹𝟑 = = = 𝟏/𝟑𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝟑 𝟔𝒌𝜴
𝑽𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔 𝟐𝑽
- 𝑰𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 = = = 𝟐/𝟑𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 𝟑𝒌𝜴
𝑹
OR using current divider rule: 𝑰𝑿 = 𝑰𝑺 ( 𝑻 )
𝑹 𝑿
𝑹𝟑 //(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 𝟐𝒌𝜴
𝑰𝑹𝟑 = 𝑰𝑹𝟑 //(𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔) ( ) = 𝟏𝑨 ( ) = 𝟏/𝟑𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝟑 𝟔𝒌𝜴
𝑹𝟑 //(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 𝟐𝒌𝜴
𝑰𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔 = 𝑰𝑹𝟑//(𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔) ( ) = 𝟏𝑨 ( ) = 𝟐/𝟑𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 𝟑𝒌𝜴
𝑰(𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔) You can calculate the voltage across 𝑹𝟒 and
𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 by using voltage divider rule.
To find the voltage at 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 use voltage
divider:
𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔
𝑽𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔 = 𝑽𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔 ( )
+ 𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔
𝑽𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔 𝟏𝒌𝜴
𝑽𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔 = 𝟐𝑽 ( ) = 𝟐/𝟑𝑽
𝟑𝒌𝜴
-
𝑰𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔
Since 𝑹𝟓 is parallel with 𝑹𝟔 :
+
𝑽𝑹𝟓 = 𝑽𝑹𝟔 = 𝟐/𝟑𝑽
𝑽𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔
Since 𝑹𝟒 and 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 are connected in
- series:
𝑰𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 = 𝑰𝑹𝟒 = 𝑰𝑹𝟓//𝑹𝟔 = 𝟐/𝟑𝒎𝑨
You can calculate the current flowing through 𝑹𝟓 and 𝑹𝟔 using Ohm’s Law:
𝑽𝑹 𝟓 𝟐/𝟑𝑽
𝑰𝑹𝟓 = = = 𝟏/𝟑𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝟓 𝟐𝒌𝜴
𝑽𝑹 𝟐/𝟑𝑽
𝑰𝑹𝟔 = 𝟔= = 𝟏/𝟑𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝟔 𝟐𝒌𝜴
Or using divider rule:
𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 𝟏𝒌𝜴
𝑰𝑹𝟓 = 𝑰𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 ( ) = 𝟐/𝟑𝒎𝑨 ( ) = 𝟏/𝟑𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝟓 𝟐𝒌𝜴
𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 𝟏𝒌𝜴
𝑰𝑹𝟔 = 𝑰𝑹𝟒+ 𝑹𝟓 //𝑹𝟔 ( ) = 𝟐/𝟑𝒎𝑨 ( ) = 𝟏/𝟑𝒎𝑨
𝑹𝟔 𝟐𝒌𝜴
You might also like
- Heat Exchangers Condensers Feedwater Heaters: Formulas: FormulasDocument1 pageHeat Exchangers Condensers Feedwater Heaters: Formulas: Formulasjj cruzNo ratings yet
- Steps in Combined Rectangular FootingDocument1 pageSteps in Combined Rectangular FootingDae NyghtNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic CalculationsDocument6 pagesThermodynamic CalculationsAbella, Yahoney B.No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Propeller TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 3 Propeller TheorytvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- AER602 SummaryDocument2 pagesAER602 Summarymuhammad.shibl.imamNo ratings yet
- Week04 DynamicsDocument20 pagesWeek04 Dynamicsfireengineer.cstNo ratings yet
- Che 222 Tutorial 1Document13 pagesChe 222 Tutorial 1naverfallNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Grupo 2030560Document16 pagesTask 3 Grupo 2030560german.toro3885No ratings yet
- CINEMÁTICA DEL CUERPO RÍGIDO U2 HibDocument47 pagesCINEMÁTICA DEL CUERPO RÍGIDO U2 HibAyrton OchoaNo ratings yet
- H°A°2 - Ejercicio 4 (Control Por Deformación y Fisuración)Document16 pagesH°A°2 - Ejercicio 4 (Control Por Deformación y Fisuración)Shiro NishizawaNo ratings yet
- Armand File WAG DELETEDocument3 pagesArmand File WAG DELETERay Armand GappiNo ratings yet
- H°P° - Ejercicio 1 (Diseño de Vigas Pretensadas)Document8 pagesH°P° - Ejercicio 1 (Diseño de Vigas Pretensadas)Ronald Alcides Mirones ColqueNo ratings yet
- Formulario de FísicaDocument2 pagesFormulario de FísicaMayen Hernandez OsvaldoNo ratings yet
- OBRA DE CAPTACIÓN GRUPO A - ContinuacionDocument7 pagesOBRA DE CAPTACIÓN GRUPO A - ContinuacionJonathan Sanchez MoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document14 pagesLecture 8Joesph SamiNo ratings yet
- Applied - Electricity - Assignment (Davinci's - Tutorial - Classes)Document10 pagesApplied - Electricity - Assignment (Davinci's - Tutorial - Classes)easesaymichael02No ratings yet
- Progress Report - Maria IndiraDocument12 pagesProgress Report - Maria Indirasafira andrianiNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicseden l. abadNo ratings yet
- Lec2 NotesDocument26 pagesLec2 Notesameya1981No ratings yet
- Practical ReactionDocument8 pagesPractical ReactionToMemNo ratings yet
- CircuitDocument51 pagesCircuitmohammed quthahNo ratings yet
- Formulario Obras Civiles NOMBRE: Pablo Suquillo: Valores Ru F'C Ru (kg/cm2) (kg/cm2)Document1 pageFormulario Obras Civiles NOMBRE: Pablo Suquillo: Valores Ru F'C Ru (kg/cm2) (kg/cm2)suquillopNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Presentation 4 AnnuitiesDocument38 pagesEngineering Economy Presentation 4 AnnuitiesQwertyuiop QwertyuiopNo ratings yet
- HE Lecture 13Document8 pagesHE Lecture 13presidentisc nit-rourkelaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential v2Document6 pagesElectric Potential v2jglaurencio0410qcNo ratings yet
- Code PED FormulaDocument24 pagesCode PED FormulaAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- ME 202. Statics of Rigid Bodies. 05. Distributed LoadDocument14 pagesME 202. Statics of Rigid Bodies. 05. Distributed LoadJerime JimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Step 4Document17 pagesUnit 3 - Step 4orlando cartagena100% (1)
- Formula Sheet For ICT - 3Document2 pagesFormula Sheet For ICT - 3kazeemsodikisola1991No ratings yet
- Electric Field Due To Unifiromly Chared Plane SheetDocument2 pagesElectric Field Due To Unifiromly Chared Plane Sheetprinceprem369xNo ratings yet
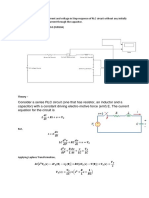
- Aim-To Simulate Analysis Current and Voltage in Step Response of RLC Circuit Without Any InitiallyDocument4 pagesAim-To Simulate Analysis Current and Voltage in Step Response of RLC Circuit Without Any Initiallysaksham mahajanNo ratings yet
- SPRINGSDocument11 pagesSPRINGSAnne Dominique QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Problem Session-2Document32 pagesProblem Session-2İkigül Aşçıevladı KirlitaşNo ratings yet
- Chap2 Thermodynamics 5 2Document29 pagesChap2 Thermodynamics 5 2vfg4tyj9gtNo ratings yet
- MT 21006 TP Unit 4 Lec 4 30 Oct 2023Document10 pagesMT 21006 TP Unit 4 Lec 4 30 Oct 2023Aditya GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Bayes RuleDocument4 pagesBayes RuleAlejandro Santos IIINo ratings yet
- Bayes RuleDocument4 pagesBayes RuleAlejandro Santos IIINo ratings yet
- Bayes RuleDocument4 pagesBayes RuleAlejandro Santos IIINo ratings yet
- RE1 Assignment 1 For Dr. Hosseini by John Kevin de CastroDocument7 pagesRE1 Assignment 1 For Dr. Hosseini by John Kevin de CastroHans SamNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of Op-AmpDocument5 pagesDynamic Analysis of Op-AmpSayemNo ratings yet
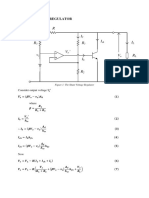
- Shunt Voltage RegulatorDocument4 pagesShunt Voltage RegulatorSamuel mutindaNo ratings yet
- MT 21006 TP Unit 4 Lec 3 26 Oct 2023Document14 pagesMT 21006 TP Unit 4 Lec 3 26 Oct 2023Aditya GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Procon Project EDITED 1Document4 pagesProcon Project EDITED 1Erwin CabangalNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits - Exercises - MemoDocument23 pagesMagnetic Circuits - Exercises - MemoTshepang SemenyaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Losses and EfficiencyDocument13 pagesTransformer Losses and Efficiencydaetersomine548No ratings yet
- Stochastic Assigment - PDF 2Document11 pagesStochastic Assigment - PDF 2Eyasu Kanbato OtoroNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 13 For Paper SavingDocument8 pagesLECTURE 13 For Paper Savingعبد المهيمن احمد قصيNo ratings yet
- Chapter 33 - Electromagnetic WavesDocument43 pagesChapter 33 - Electromagnetic WavesDiễn Trần PhướcNo ratings yet
- Heat and Combustion TASKDocument15 pagesHeat and Combustion TASKchijoeNo ratings yet
- 18 Integration TechniquesDocument18 pages18 Integration Techniquesأيوب عبد الأمير هزبر /تقنية غازNo ratings yet
- Exp.12 Okkk 1 PDFDocument7 pagesExp.12 Okkk 1 PDFعمر صفاء حسينNo ratings yet
- Power TransmissionDocument6 pagesPower TransmissionAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Caida LibreDocument12 pagesCaida Librefredy chozo tunoqueNo ratings yet
- Reporte 1 Axel Lopez Mec.Document8 pagesReporte 1 Axel Lopez Mec.AXEL LÓPEZ RIVERANo ratings yet
- Triangular NotchDocument2 pagesTriangular NotchRochakNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Inductance of Magnetically Coupled Parallel Two InductorsDocument4 pagesEquivalent Inductance of Magnetically Coupled Parallel Two InductorsOzan AbutNo ratings yet
- Ch 6 - waves (PHY 001) Solution of Probems.pdf · إصدار ١Document5 pagesCh 6 - waves (PHY 001) Solution of Probems.pdf · إصدار ١make handNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document65 pagesWeek 8sunil kumar sahNo ratings yet
- Voice Data Video CrosswalkDocument11 pagesVoice Data Video CrosswalkJulio SibrianNo ratings yet
- Separator (Grs-10eb 100eb) Manual (Rev4)Document16 pagesSeparator (Grs-10eb 100eb) Manual (Rev4)voinea ionut75% (4)
- Platerite 8600Sl: Thermal Plate RecorderDocument6 pagesPlaterite 8600Sl: Thermal Plate RecorderYuwis AlqarniNo ratings yet
- Grundfos CM-PM1Document16 pagesGrundfos CM-PM1b LiewNo ratings yet
- MQS Interconnection: For The Automotive IndustryDocument324 pagesMQS Interconnection: For The Automotive IndustryYan ChenNo ratings yet
- Ques AnswerDocument8 pagesQues AnswerRafeek makramNo ratings yet
- MIMO OFDM Using USRPDocument9 pagesMIMO OFDM Using USRPjsingh19No ratings yet
- ETAP ERRor MessageDocument2 pagesETAP ERRor Messageabhijit_wceNo ratings yet
- KENWOOD TS 870S Mods1 SchematicDocument6 pagesKENWOOD TS 870S Mods1 SchematicLuis CarlosNo ratings yet
- Soft SwitchDocument187 pagesSoft SwitchJong Hee LeeNo ratings yet
- EMBER LED - vSHINE LED FAÇADE LIGHTDocument7 pagesEMBER LED - vSHINE LED FAÇADE LIGHTjrobins1228No ratings yet
- Infiniti TSS450 Subwoofer and Satelite Speakers SystemDocument12 pagesInfiniti TSS450 Subwoofer and Satelite Speakers SystemtommylawNo ratings yet
- 4208u 3-09 Rev A PDFDocument4 pages4208u 3-09 Rev A PDFgarrigan12No ratings yet
- Mce Product Specs All SectionsDocument186 pagesMce Product Specs All SectionsSunilkumar100% (1)
- Rizal PlayDocument22 pagesRizal PlayRijan Earl Rosaciña100% (1)
- Premium 32-Bit 2ch DAC: The AK4490 Integrates A Newly Developed Switched Capacitor Filter "OSR Doubler"Document68 pagesPremium 32-Bit 2ch DAC: The AK4490 Integrates A Newly Developed Switched Capacitor Filter "OSR Doubler"bentNo ratings yet
- Bit Comparator Using Different Logic Style of Full AdderDocument3 pagesBit Comparator Using Different Logic Style of Full Adderfabio-delima8012No ratings yet
- SDB CVDocument3 pagesSDB CVashwini32No ratings yet
- Dah HCM78X9-435-460WDocument2 pagesDah HCM78X9-435-460WMarcio AbreuNo ratings yet
- Z92JDocument63 pagesZ92JJose Luis Coderque SalasNo ratings yet
- Deep Freezer DW 86L388Document4 pagesDeep Freezer DW 86L388dharm_ajayNo ratings yet
- ZAPI AC-0 Manual Carretillas EPDocument62 pagesZAPI AC-0 Manual Carretillas EPRicardo Gamez Ortega50% (2)
- Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College VLSI DESIGNDocument38 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Engineering College VLSI DESIGNjitendra kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Sailor RT4822Document31 pagesSailor RT4822Сергей Бородин0% (1)
- Datastage Parellel Jobs PDFDocument719 pagesDatastage Parellel Jobs PDFNivedhaSekarNo ratings yet
- Ecdis Things You Should Know YesDocument52 pagesEcdis Things You Should Know YesNiclas67% (3)
- Advantages of Bundled Conductors in Transmission LinesDocument5 pagesAdvantages of Bundled Conductors in Transmission Linesf3ziii100% (1)
- Training Manual BD-C6900Document144 pagesTraining Manual BD-C6900Leonardo Javier Obermeyer100% (2)
- Testing of DC MachinesDocument15 pagesTesting of DC MachinesMadhu TallapanenimadhuNo ratings yet
- 48V DC - DC Converter - Mild Hybrid DC - DC Converter - EatonDocument3 pages48V DC - DC Converter - Mild Hybrid DC - DC Converter - EatonShubham KaklijNo ratings yet