Professional Documents
Culture Documents
24
24
Uploaded by
ATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLON0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pages24
24
Uploaded by
ATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
NCM 106 - PHARMACOLOGY
CASE STUDY: CLIENT WITH A PSEUDOMONAL INFECTION
DIRECTION: Read and analyze the case. Answer the accompanying questions.
FSH, 46 years old, has a wound infection. The culture report stated that the
infection was due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FSH’s temperature was 104 ℉
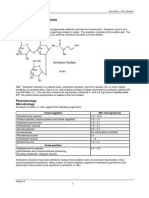
(40 °C). Amikacin sulfate (Amikin) is to be administered intravenously in 100
mL of Dextrose 5% in Water over 45 minutes every 8 hours. Dosage is 15
mg/kg/day in three divided doses. FSH weighs 165 lb.
1. What is the drug classification of Amikacin? How many
milligrams of Amikacin should FSH receive every 8 hours?
Amikasin sulfate is classified as an antibiotic. Amikacin
sulfate belongs to the aminoglycoside antibiotics class of
drugs. It works by killing bacteria or preventing their
growth and is used to treat serious bacterial infections in
many different parts of the body.
The client should receive 374 milligrams every 8 hours.
2. What type of intravenous infusion should be used? What
would be the IV flow rate?
22 or 23 gauge and 1-1.5inches long needle should be
used.
3. Why should a wound culture be taken before determining the
antibacterial agent?
Acquiring samples prior to the administration of antibiotics
allows healthcare providers to identify the pathogenic
microorganisms that caused the infection. This also helps to
improve patient treatment by determining which antibiotic
would be most effective in treating the infection and healing
the wound. The infection was caused by Pseudomonas
aeruginosa, according to the culture results. The physician
then directed that the recommended antibiotic, Amikacin
sulfate, be administered by IV infusion.
4. What should a hearing assessment include?
Because of the increased risk of ototoxicity, the nurse should
assess FSH's hearing before and after therapy. Especially if the
patient will be getting the medicine for more than two weeks to
identify hearing damage. This is because drug-induced damage
to these auditory and balance system components can result in
hearing loss, tinnitus, and disequilibrium or dizziness.
5. FSH’s urine output in the last 8 hours was 125 mL. Explain the
possible cause for the amount of urine output. What nursing
action should be taken?
When the antibiotic Amikacin is used, there are certain side
effects. There is an increase in urine excretion of casts,
nephrotoxicity, and azotemia in GU or genitourinary. Because
of the increased risk of nephrotoxicity, the nurse should treat
dehydration before starting medication and monitor renal
function, including urine output, specific gravity, urinalysis,
BUN and creatinine levels, and CrCl. Nephrotoxicity is defined
as a fast decline in kidney function caused by the toxic effects
of medicines.
6. What laboratory tests indicate renal function?
Urinalysis, BUN and creatinine levels, urine output, specific
gravity, and CrCl are all laboratory tests that reflect renal
function.
7. The physician requests peak and trough serum amikacin levels.
When should the peak serum level and trough serum level be
drawn?
Collect blood 30 minutes to 1 hour after the IV infusion stops
for peak levels; draw blood soon before the following dosage
for trough levels. 1 hour after the IM injection, take a blood
level.
REFERENCES:
Lippincott, W., & Wilkins (2022). Nursing 2022 drug
handbook. 42nd edition. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer
Al-Naimi, M. S., Rasheed, H. A., Hussien, N. R., Al-Kuraishy, H.
M., & Al-Gareeb, A. I. (2019). Nephrotoxicity: Role and
significance of renal biomarkers in the early detection of acute
renal injury. Journal of advanced pharmaceutical technology &
research, 10(3), 95–99.
https://doi.org/10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_336_18
NCM 106 - PHARMACOLOGY
You might also like
- Pharmacology Hesi Exam Study Guide 2015Document96 pagesPharmacology Hesi Exam Study Guide 2015sak genius100% (31)
- Hesi Exit Exam ReviewDocument35 pagesHesi Exit Exam ReviewIndia91% (92)
- Status Epilepticus Case Study Kristopher Kirby.Document4 pagesStatus Epilepticus Case Study Kristopher Kirby.KrisNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Seizures: Postgraduate Dept of PediatricsDocument42 pagesNeonatal Seizures: Postgraduate Dept of PediatricsG VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Deenanath Mangeshkar Hospital, Pune: Case StudyDocument22 pagesDeenanath Mangeshkar Hospital, Pune: Case Studysanika shinde100% (4)
- 100 Questions That Appear On Every NBMEDocument4 pages100 Questions That Appear On Every NBMEMonica FloresNo ratings yet
- CANCER ReportDocument135 pagesCANCER ReportEnzo TimbolNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 - RodriguezDocument3 pagesCase Study 2 - RodriguezRAZELLE JOY CATIAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Pharma W15Document4 pagesPharma W15Eh paano kung HindiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan and Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan and Drug StudyPaul Anthony Marcos JaenaNo ratings yet
- Standing OrdersDocument27 pagesStanding OrdersDolly Sharma100% (2)
- Case Study 1: Nicole: 1. Discuss The Significance of Nicole's Laboratory FindingsDocument12 pagesCase Study 1: Nicole: 1. Discuss The Significance of Nicole's Laboratory FindingsClint NavarroNo ratings yet
- Ciloxan Ear Drops Solution REG SPC PF20-0134 September 2020 CleanDocument7 pagesCiloxan Ear Drops Solution REG SPC PF20-0134 September 2020 CleanTanitNo ratings yet
- I. Readings Bronchopneumonia Bronchopneumonia Is An Illness of Lung Which Is Caused by Different Organism LikeDocument9 pagesI. Readings Bronchopneumonia Bronchopneumonia Is An Illness of Lung Which Is Caused by Different Organism Likeellis_NWU_09No ratings yet
- I. Readings Bronchopneumonia Bronchopneumonia Is An Illness of Lung Which Is Caused by Different Organism LikeDocument9 pagesI. Readings Bronchopneumonia Bronchopneumonia Is An Illness of Lung Which Is Caused by Different Organism Likeellis_NWU_09No ratings yet
- Pharm Exam1Document17 pagesPharm Exam1Jill Putman Beistline75% (4)
- Position Paper: Ipecac SyrupDocument12 pagesPosition Paper: Ipecac SyrupCaio César BianchiNo ratings yet
- Ati Pharmacology Proctored ExamDocument4 pagesAti Pharmacology Proctored Examkinyuaboris990No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Practice Test For NclexDocument10 pagesPharmacology Practice Test For NclexKira99% (96)
- Urine CltureDocument15 pagesUrine CltureCris FischerNo ratings yet
- Elsiver NCLEX Critical CareDocument112 pagesElsiver NCLEX Critical CareHasan A AsFour100% (1)
- Patients With Multiple DisordersDocument7 pagesPatients With Multiple DisordersKathleen Joy PingenNo ratings yet
- OBSTETRICS DrugsDocument6 pagesOBSTETRICS DrugsDan Agyemang NketiahNo ratings yet
- DBL Amikacin Injection DescriptionDocument9 pagesDBL Amikacin Injection Descriptionnela sharonNo ratings yet
- OB Hem Uterotonic Medications For Prevention and Treatment of PPHDocument7 pagesOB Hem Uterotonic Medications For Prevention and Treatment of PPHpwytymbm56No ratings yet
- Amikacin SulfateDocument4 pagesAmikacin SulfateCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Suspected Anaphylactic Shock Associated With Rocuronium in An Infant: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesSuspected Anaphylactic Shock Associated With Rocuronium in An Infant: A Case Reportjeffrey aptaNo ratings yet
- Anaphylactic ReactionDocument12 pagesAnaphylactic Reactionelite100sprinter100% (1)
- Oxytocics: Adverse EffectsDocument3 pagesOxytocics: Adverse EffectsMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Bspha C1 Las 3Document41 pagesBspha C1 Las 3Muhammad Haroon RazaNo ratings yet
- "Magic Bullets": The AntibodiesDocument40 pages"Magic Bullets": The AntibodiesSherief AKNo ratings yet
- A. How Would You Respond To This Patient?Document2 pagesA. How Would You Respond To This Patient?KimNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery Case PresentationDocument29 pagesLabor and Delivery Case PresentationJoshua ABNo ratings yet
- Cefazolin (Ancef ®) : D5W, NsDocument9 pagesCefazolin (Ancef ®) : D5W, Nsbabe5606No ratings yet
- Antineoplastic DrugsDocument38 pagesAntineoplastic DrugsTrixia CamporedondoNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Therapy in Clinical PracticeDocument8 pagesIntravenous Therapy in Clinical PracticeTyron Rigor Silos100% (1)
- Immunology & Oncology Review 2Document99 pagesImmunology & Oncology Review 2Melchor Felipe SalvosaNo ratings yet
- SCENARIO: at 8:30am, Mrs. Cercan Come in at The Unit With Her Husband. They Are Bringing The ReferralDocument3 pagesSCENARIO: at 8:30am, Mrs. Cercan Come in at The Unit With Her Husband. They Are Bringing The ReferralDinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- Reduction in The Desired Effect Blood-Brain Barrier Drug ToxicityDocument15 pagesReduction in The Desired Effect Blood-Brain Barrier Drug ToxicityRose OcampoNo ratings yet
- Standing OrdersDocument18 pagesStanding OrdersVijith.V.kumar78% (9)
- Committee Opinion: Onabotulinumtoxina and The BladderDocument4 pagesCommittee Opinion: Onabotulinumtoxina and The Bladderw yNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Garlic Supplements On The Pharmacokinetics of SaquinavirDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Garlic Supplements On The Pharmacokinetics of SaquinavirHolga JahitNo ratings yet
- FNP 3Document25 pagesFNP 3Jhexy Rhay BayagenNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Panel UTI - Saniel Abu MarianoDocument66 pagesDay 2 Panel UTI - Saniel Abu MarianoRye CalderonNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Review 2015Document8 pagesAnaphylaxis Review 2015Anonymous ZUaUz1wwNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYLAXISDocument21 pagesANAPHYLAXISMicah TuringanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NCLEX QuestionsDocument128 pagesPharmacology NCLEX QuestionsChristine Williams100% (2)
- Drug - Guide - Scavenger - Hunt - Docx 16th EditionDocument5 pagesDrug - Guide - Scavenger - Hunt - Docx 16th EditionYousaf FarookNo ratings yet
- Ac002600 PDFDocument4 pagesAc002600 PDFShintya ShintyaNo ratings yet
- 50 Item Pharmacology ExamDocument17 pages50 Item Pharmacology ExamZaphanta Rhea P. BangaoetNo ratings yet
- 12-Uterotonic and Tocolytic Drugs (R Dyer) PDFDocument6 pages12-Uterotonic and Tocolytic Drugs (R Dyer) PDFJTNo ratings yet
- Pharma ExamDocument7 pagesPharma ExamGeno Adrian T PampangaNo ratings yet
- Procedural AnesthesiaDocument40 pagesProcedural AnesthesiaJovian LutfiNo ratings yet
- Sepsis in PregnancyDocument21 pagesSepsis in PregnancynimiNo ratings yet
- Ac IphinDocument5 pagesAc IphinAdittya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics drugsDocument5 pagesObstetrics drugsMallika NelaturiNo ratings yet
- Drug InfoDocument11 pagesDrug InfoArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Guide To Clinical Audit Antibiotic Use in Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesGuide To Clinical Audit Antibiotic Use in Urinary Tract Infectionihtisham1No ratings yet
- Antibiotics in NeurosurgeryDocument12 pagesAntibiotics in Neurosurgerylouglee9174100% (1)
- Pharm - NSG Science - Ppt.prevised2Document86 pagesPharm - NSG Science - Ppt.prevised2RAINBOW40No ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guideline On Neonatal Sepsis: Summarized by Dr. Catherine Chua October 2012Document3 pagesClinical Practice Guideline On Neonatal Sepsis: Summarized by Dr. Catherine Chua October 2012Joey CuayoNo ratings yet
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!From EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Intravenous Therapy Administration: a practical guideFrom EverandIntravenous Therapy Administration: a practical guideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 25Document3 pages25ATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- Name: Athena Dianne B. Aguillon Block: NG Date of Submission: August 27, 2022Document3 pagesName: Athena Dianne B. Aguillon Block: NG Date of Submission: August 27, 2022ATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- A Study of Blood Transfusion in Pediatric Patients at A Teaching Hospital, Aden, YemenDocument3 pagesA Study of Blood Transfusion in Pediatric Patients at A Teaching Hospital, Aden, YemenATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- 22Document6 pages22ATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3ATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- Name: Athena Dianne B. Aguillon Block: 2-NgDocument3 pagesName: Athena Dianne B. Aguillon Block: 2-NgATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of Peer-Supported Interventions For Health Promotion and Disease PreventionDocument2 pagesA Systematic Review of Peer-Supported Interventions For Health Promotion and Disease PreventionATHENA DIANNE BARON AGUILLONNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Ott Speaks (Interview Part 1)Document10 pagesJonathan Ott Speaks (Interview Part 1)Jimy RobayoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document9 pagesDrug Study 2Justin PasaronNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Repletion Guideline PMGDocument4 pagesElectrolyte Repletion Guideline PMGHany ElbarougyNo ratings yet
- Colds and Flu-An Overview of Their ManagementDocument6 pagesColds and Flu-An Overview of Their ManagementMFerdyYahyaRamadhanNo ratings yet
- Lista de Precios 2019: Alvarez Martinez HaydeeDocument2 pagesLista de Precios 2019: Alvarez Martinez HaydeeedgarNo ratings yet
- A Sas Procedure For Outlier Detection inDocument5 pagesA Sas Procedure For Outlier Detection inYi XinNo ratings yet
- Australasian Anaesthesia 2015Document107 pagesAustralasian Anaesthesia 2015Sean SmythNo ratings yet
- C Ovid 19 Treatment GuidelinesDocument274 pagesC Ovid 19 Treatment Guidelinesrenugadevi_dNo ratings yet
- Of Complex Formation With Proteins Is Called As Protein Binding of DrugsDocument16 pagesOf Complex Formation With Proteins Is Called As Protein Binding of DrugsDeepak duaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ResistanceDocument8 pagesAntibiotics ResistanceboredtarteelNo ratings yet
- JURIS Objective QuestionDocument6 pagesJURIS Objective QuestionDeependra PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Pharmacotherapy Clinic GuidelinesDocument41 pagesDiabetes Pharmacotherapy Clinic GuidelinesAbo-ahmed ElmasryNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MontelukastDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userNo ratings yet
- GDC Prime Information Brochure 2026Document39 pagesGDC Prime Information Brochure 2026Swathi GNo ratings yet
- CH04 PMCTC ALARM - Prof. DR - Dr. Noroyono Wibowo, SpOG (K)Document41 pagesCH04 PMCTC ALARM - Prof. DR - Dr. Noroyono Wibowo, SpOG (K)Putri MahacakriNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsDocument1 pageAcute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsSreya SanilNo ratings yet
- AKTU Admit CardDocument3 pagesAKTU Admit CardmaheshpanditNo ratings yet
- Oral Dosage Forms That Should Not Be Crushed: Active Ingredient(s) Dosage Form(s) Reasons/Comments3Document8 pagesOral Dosage Forms That Should Not Be Crushed: Active Ingredient(s) Dosage Form(s) Reasons/Comments3Salsabila TazkiyahNo ratings yet
- Lawsonia Inermis L. - A Commercially Important Primaeval Dying and Medicinal Plant With Diverse Pharmacological Activity A ReviewDocument18 pagesLawsonia Inermis L. - A Commercially Important Primaeval Dying and Medicinal Plant With Diverse Pharmacological Activity A ReviewTuấn Nguyen AnhNo ratings yet
- Open Systems Pharmacology SuiteDocument597 pagesOpen Systems Pharmacology Suitedivyenshah3No ratings yet
- PubMed Cheat Sheet ExternalDocument2 pagesPubMed Cheat Sheet ExternalEduardo LimaNo ratings yet
- Dapoxetine Dosing InformationDocument25 pagesDapoxetine Dosing InformationA.R.AthreyaNo ratings yet
- Annual 2016: For The Year Ended December 31, 2016Document66 pagesAnnual 2016: For The Year Ended December 31, 2016Acc RameNo ratings yet
- Smoking Weed Before Doing HomeworkDocument5 pagesSmoking Weed Before Doing Homeworkafmsovtck100% (1)
- Childhood Bipolar Disorder: A Clinical VignetteDocument4 pagesChildhood Bipolar Disorder: A Clinical VignetteWiwik SundariNo ratings yet
- Usmle Step 2 Secrets 5Th Edition Theodore Oconnell Ebook Full ChapterDocument51 pagesUsmle Step 2 Secrets 5Th Edition Theodore Oconnell Ebook Full Chapterjohn.sanmiguel190100% (7)