Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stone Masnry Obj QSTN
Stone Masnry Obj QSTN
Uploaded by
RUPESH VIJAYAKUMAR0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views8 pagesThis document provides a quiz on building construction topics related to stone masonry and brick masonry. It contains 67 multiple choice questions covering various types of stone bonds and joints, tools used for stone and brick masonry, thickness of walls, bonds like English bond and Flemish bond, and load bearing capacity of masonry walls. The questions assess knowledge of concepts like ashlar masonry, coursed rubble masonry, headers, stretchers, quoins and more.
Original Description:
Stone masonary for psc
Original Title
stone masnry obj qstn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a quiz on building construction topics related to stone masonry and brick masonry. It contains 67 multiple choice questions covering various types of stone bonds and joints, tools used for stone and brick masonry, thickness of walls, bonds like English bond and Flemish bond, and load bearing capacity of masonry walls. The questions assess knowledge of concepts like ashlar masonry, coursed rubble masonry, headers, stretchers, quoins and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views8 pagesStone Masnry Obj QSTN
Stone Masnry Obj QSTN
Uploaded by
RUPESH VIJAYAKUMARThis document provides a quiz on building construction topics related to stone masonry and brick masonry. It contains 67 multiple choice questions covering various types of stone bonds and joints, tools used for stone and brick masonry, thickness of walls, bonds like English bond and Flemish bond, and load bearing capacity of masonry walls. The questions assess knowledge of concepts like ashlar masonry, coursed rubble masonry, headers, stretchers, quoins and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
OBJECTIVES QUESTIONS IN
BUILDING CONSTRUCTION
STONE MASONRY
&
BRICK MASONRY
By,
PSC WINNER
FREE Application for Civil Engineering
Complete Civil Engineering Application
3000+ Previous Year Questions
13+ Topic wise Categories
Questions from Last 15 Years PSC Exams.
You can Battle with Your Friends.
Click here to Download
Building Construction Page 1
Rubble masonry without
1. What is a dry rubble masonry ? mortar
2. What type of stone masonry is constructed using
square or rectangular blocks ? Ashlar masonry
3. The cheapest, roughest and poorest form of stone Un-coursed rubble
masonry is : masonry
4. The chips of stones used to fill up the stone masonry
is called : Spalls
5. In coursed rubble masonry sort-3 the thickness of
mortar joint is : 16mm
6. Which joint is not considered as a rusticated joint in
stone masonry ? Cramped joint
7. The type of masonry in which the stones are fine,
chisel, dressed and the thickness of joint does not
exceed 3mm is called : Ashlar fine masonry
8. ________ joints are usually jointed in ashlar masonry Flush
9. In ashlar fine masonry the joint thickness is does not
exceed : 3mm
10. Which type stone joint is suitable for heavy lateral
pressure : Table joint
11. In stone masonry, to make level surface ________ tool
is used : Drag
Building Construction Page 2
12. The course of stone placed immediately below the
cornice to improve the appearance of external face of
the wall is : Frieze
13. A covering of stone/concrete placed on the exposed
top of wall to prevent seepage of water is termed as : Coping
14. The masonry consists of accurately dressed stones
with extremely fine bed and end joints : Ashlar masonry
15. The course of stone masonry provided at the top of a
wall and usually ornamental in shape are known as : Cornice
16. Ornamental moulded course placed on top of wall is : Cornice
17. The stone masonry made at properly dressed stone
is known as : Ashlar masonry
The thickness of a stone
18. A stone masonry, the thickness of a course is plus the thickness of one
generally equal to : mortar joint
19. _______ masonry occupies an intermediate position Ashlar block in course
between the rubble masonry and the ashlar masonry masonry
20. The stone blocks of designed dimension placed
under the end of a beam to distribute the load over
grater area Template
The stones are either not
dressed or roughly
dressed and may be
21. In random rubble masonry : coursed or un-coursed
22. To construct a 10cm thick partition wall, preferred
bond will be : Stretcher bond
Building Construction Page 3
23. The portion of wall between facing and backing is
called ______ Hearting
24. The type of bond provided in brick masonry for
carrying heavy loads is : English bond
25. The slenderness ratio of masonry walls should not be
more than : 20
26. The type of bond in which every course contains
both headers and stretchers is called : Double Flemish bond
27. In a single day the maximum height of masonry to be
raised should not be more than 1.5m
28. The overlapping of brick / stones in masonry is
called : Bond
29. Vertical joints separating the bricks by mortar is : Perpend
30. The most important tool used for brick masonry is : Trowel
31. In _______ type of bond stretchers and headers are
arranged in alternate course. English bond
32. Tool used for checking verticality of masonry wall ? Plumb bob
33. The method of termination of the wall such a way
that the bricks left projecting in alternate courses for
the bonding future horizontal masonry construction Toothing
34. The bond in which the bricks are arranged at 45
degree in opposite direction from the centre line of
the wall thickness is : Herring bone bond
Building Construction Page 4
35. A header bond is usually used for : One brick wall
36. Two and half brick thickness of wall is roughly equal
to : 50 cm
To check the alignment of
37. In brick masonry the straight edge is used : work
38. The external corner or angles of walls are called : Quoins
39. Imaginary vertical line joining the arises is called : Perpends
40. Every header is centrally supported over the
stretcher below it in : Flemish bond
41. The amount of lap across the thickness of wall should
be minimum : 1/2 brick
42. Bond with alternate courses of stretchers and
headers : English bond
43. Two walls meet at 90° a _____ quoin is formed. Square
44. The formation of a whitish loose powder or crust on
the surface of brick walls is called : Efflorescence
45. Inclined surface of brick should be checked by : Wooden template
46. A junction means a connection between a main wall
and a : Partition wall
47. Brick should be saturated with water before making
wall so as to prevent absorption of moisture from : Mortar
48. The term 'lap' represents in brick masonry as : Horizontal distance
Building Construction Page 5
49. Horizontal course provided to strengthen a wall or
irregular small stone : Lacing course
50. Brick partition walls will have a thickness of : Half
51. Facing and backing of a wall constructed with
different classes of masonry is : Composite masonry
52. The safe permissible loads on ordinary brickwork in
c.m : 44 to 65
53. The brick laid with its breadth parallel to the face of
a wall is known as : Header bond
54. A piece of brick which is used to prevent vertical
joint in brick masonry : Closer
55. For construction of 100mm thick partition wall, it is
preferable to use Stretcher bond
56. In which type of bonding the bricks are laid headers
on the faces and it is mostly used for footings in
foundation ? Heading bond
57. The safe permissible load in brick masonry in mud is
___________ 140 kN/sq.m
58. English cross bond is otherwise known as ________ St. Andrews cross bond
59. The type of bond in which every course contains
both headers and stretchers, is called : Flemish bond
60. The bond in which a header course is introduced
after several stretcher course is : Facing bond
Building Construction Page 6
Front elevation is Flemish
bond and back elevation
61. In single Flemish bond is English bond
62. An example of raking bond is : Diagonal bond
63. Single Flemish bond cannot be used for a wall less
than ______ thick 300 mm
64. Line and pins is used : To maintain alignment
65. The arrangement of layers of stones or bricks by
which no continuous vertical joints are formed : Bond
66. Which is the strongest bond in brick work ? English bond
67. The external corner of a wall surface is technically
known as Quoin
Are you Finished Learning ?
Then
ATTEND MOCK TEST NOW
Building Construction Page 7
TO JOIN OUR TELEGRAM CHANNEL CLICK BELOW
Join Any of our Watsapp Group for More Info
Group 1 – Join Here
Group 2 – Join Here
Group 3 – Join Here
Group 4 – Join Here
Group 5 – Join Here
Building Construction Page 8
You might also like
- Introduction To Masonry StructuresDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Masonry StructuresShuvanjan Dahal93% (15)
- Brick Masonry Work: Tanvi PatelDocument42 pagesBrick Masonry Work: Tanvi PatelParthJainNo ratings yet
- Types of Bonds in Brick Masonry Wall ConstructionDocument28 pagesTypes of Bonds in Brick Masonry Wall Constructionzodiackiller1960sNo ratings yet
- MASONRYDocument12 pagesMASONRYEVANS KIPNGETICH100% (1)
- Introd Civil Engg Brick Masonry by SheelaDocument40 pagesIntrod Civil Engg Brick Masonry by Sheelafaizan shaikh100% (1)
- Brick MasonryDocument6 pagesBrick Masonryparkhe swaminiNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonryDocument22 pagesBrick MasonryS PraveenkumarNo ratings yet
- Unit II BMCPPTDocument53 pagesUnit II BMCPPTVijaykumar Nagnaik100% (1)
- Finals CE38Document12 pagesFinals CE38dridgely ric c. dyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4.4 WallDocument83 pagesChapter-4.4 WallHeni yitNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonaryDocument39 pagesBrick MasonaryKrishna 1No ratings yet
- 2 - Types - of - Stone - Brick - and - Block - Masonry (Compatibility Mode)Document63 pages2 - Types - of - Stone - Brick - and - Block - Masonry (Compatibility Mode)UmairNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonryDocument12 pagesBrick MasonrySanjaya PoudelNo ratings yet
- BrickDocument17 pagesBrickRosy Rose100% (1)
- MasonryDocument39 pagesMasonryAbdul Rahim100% (1)
- Building Constrction-Part I: Prof. Dr. Liaqat Ali QureshiDocument142 pagesBuilding Constrction-Part I: Prof. Dr. Liaqat Ali QureshiVivek Thakur Sujanian100% (1)
- Brick MasonryDocument17 pagesBrick MasonryHanish ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Brick Masonary 1Document34 pagesBrick Masonary 1Parth AnajwalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ADocument36 pagesUnit 4 AAr Shubham JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Masonry (Stone, Brick, Concrete Block) WorkDocument16 pagesMasonry (Stone, Brick, Concrete Block) WorkMelak EndayeNo ratings yet
- Types of Bonds in Brick Masonry Wall Construction and Their ApplicationsDocument6 pagesTypes of Bonds in Brick Masonry Wall Construction and Their ApplicationsSam ChongNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonryDocument37 pagesBrick MasonryWaris Ahmed Khan G100% (1)
- Brick MasonaryDocument49 pagesBrick MasonaryAryan SutharNo ratings yet
- BrickDocument36 pagesBrickMazharul Islam MahirNo ratings yet
- BCM Notes Unit No. IIDocument14 pagesBCM Notes Unit No. IIMahesh RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Masonry and Its Types: National Institute of Construction Management and ResearchDocument12 pagesMasonry and Its Types: National Institute of Construction Management and ResearchRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Masonry StructuresDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Masonry StructuresbaizubirajiNo ratings yet
- Brickmasonary 130402003136 Phpapp01Document36 pagesBrickmasonary 130402003136 Phpapp01Hamza SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonryDocument36 pagesBrick MasonryAbdullahNo ratings yet
- qqq123 PDFDocument36 pagesqqq123 PDFRAHUL KUMAR MEENANo ratings yet
- Interview Questions 2019Document99 pagesInterview Questions 2019Syed Jazib Ali shahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Bricklaying and MasonryDocument42 pagesChapter 3 Bricklaying and MasonryMin Htet Myint100% (1)
- Bricks: Dr. Attaullah ShahDocument27 pagesBricks: Dr. Attaullah ShahSonam DemaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Full NoteDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Full NoteSurajNo ratings yet
- Build Your Dream Home - 2023Document52 pagesBuild Your Dream Home - 2023Arjun Sharma VNo ratings yet
- Basics of Civil Engineering Cv0121 Unit 3 1Document139 pagesBasics of Civil Engineering Cv0121 Unit 3 1Hanish Manikanta100% (1)
- Brick BondDocument13 pagesBrick BondMZU Barch 2020No ratings yet
- Introduction To Masonry StructuresDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Masonry StructuresEdralyn LuadNo ratings yet
- ERA Unit 4 - ADocument41 pagesERA Unit 4 - AshivaniNo ratings yet
- Brick Masonry DefinitionDocument16 pagesBrick Masonry DefinitionEr Dinesh TambeNo ratings yet
- Secant Pile PDFDocument54 pagesSecant Pile PDFK H V V MADUSHANKA100% (1)
- Mansory 1Document5 pagesMansory 1John Isaac BanaagNo ratings yet
- BMC 2018Document54 pagesBMC 2018Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- List of ContentsDocument52 pagesList of ContentsAkílêšĥ DãvērãNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonryDocument17 pagesBrick MasonryHarshitha RoyalNo ratings yet
- Brick BondingDocument35 pagesBrick BondingSithi Raihana100% (1)
- Building Workshop Lecture 1Document29 pagesBuilding Workshop Lecture 1Robel YohannesNo ratings yet
- Brick BondDocument29 pagesBrick BondArchana AcchuNo ratings yet
- DSFFGDocument22 pagesDSFFGArjunRathodNo ratings yet
- 4-Masonry, Brick Block Rev3Document15 pages4-Masonry, Brick Block Rev3smithson JoeNo ratings yet
- CH-2 MasonryDocument24 pagesCH-2 MasonryEyoatem TeferiNo ratings yet
- Brickwork: Brickwork Is Masonry Produced by A Bricklayer, Using Bricks andDocument19 pagesBrickwork: Brickwork Is Masonry Produced by A Bricklayer, Using Bricks andmuraliNo ratings yet
- Cme Mod-III NotesDocument267 pagesCme Mod-III NotesPooja C PNo ratings yet
- 14 Masonry ConstructionMethodsDocument78 pages14 Masonry ConstructionMethodsMaverick LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Chap - 3 Elements of BuilldingDocument52 pagesChap - 3 Elements of BuilldingtekalignNo ratings yet
- Objectives in Building Material by PSC WinnerDocument24 pagesObjectives in Building Material by PSC WinnerPritha DasNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonaryDocument42 pagesBrick MasonarySaddam HossainNo ratings yet
- Masonry-Stone Masonry: of TogetherDocument12 pagesMasonry-Stone Masonry: of TogetherOm WalunjNo ratings yet
- The Modern Bricklayer - A Practical Work on Bricklaying in all its Branches - Volume III: With Special Selections on Tiling and Slating, Specifications Estimating, EtcFrom EverandThe Modern Bricklayer - A Practical Work on Bricklaying in all its Branches - Volume III: With Special Selections on Tiling and Slating, Specifications Estimating, EtcRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Poly Lecturer SyllabussDocument6 pagesPoly Lecturer SyllabussRUPESH VIJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Pro To AE 310dDocument5 pagesPro To AE 310dRUPESH VIJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Pro FGO To AE 8f12Document2 pagesPro FGO To AE 8f12RUPESH VIJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- AE Tran - Reposted - CancelledDocument7 pagesAE Tran - Reposted - CancelledRUPESH VIJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Tracer Provisional Answer KeyDocument1 pageTracer Provisional Answer KeyRUPESH VIJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Chpter 4 DesignDocument67 pagesChpter 4 DesignRUPESH VIJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
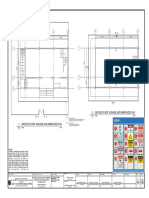
- 22fa0087 Plans Malinao Municipal-7 - 2Document25 pages22fa0087 Plans Malinao Municipal-7 - 2KrutteruHeroNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation DrawingDocument1 pagePile Foundation DrawingkiransimsNo ratings yet
- Take Off List For ProjectDocument4 pagesTake Off List For ProjectEvNo ratings yet
- Issued For Construction: ZAIT Engineering Solutions Pty LTDDocument1 pageIssued For Construction: ZAIT Engineering Solutions Pty LTDAhmedBoutlyNo ratings yet
- Temporary WorksDocument93 pagesTemporary WorksC BNo ratings yet
- AHM - FDEE - 20 Jan 2020Document18 pagesAHM - FDEE - 20 Jan 2020Salim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2 ConstructionDocument10 pagesPresentation 2 ConstructionGukan DoniNo ratings yet
- Method Statement - (WR) MSCL Pipe InstallationDocument7 pagesMethod Statement - (WR) MSCL Pipe InstallationFauziah ShaifulNo ratings yet
- Trial Trench A1 & A2 (No Services Found) Trial Trench A4 (No Services Found) Trial Trench A5 (No Services Found)Document9 pagesTrial Trench A1 & A2 (No Services Found) Trial Trench A4 (No Services Found) Trial Trench A5 (No Services Found)Yang ChanNo ratings yet
- FIG067 Dimensions, Area, and Design Data For Prestressed Concrete Girders AASHTO Types V and VI, Modified Bulb TeesDocument2 pagesFIG067 Dimensions, Area, and Design Data For Prestressed Concrete Girders AASHTO Types V and VI, Modified Bulb Teesmanny valgunaNo ratings yet
- Gregory P. TschebotarioffDocument2 pagesGregory P. TschebotariofffacedoneNo ratings yet
- BQ PmuDocument5 pagesBQ PmuAzamOthman100% (1)
- Ahmed Nasih: ProfileDocument18 pagesAhmed Nasih: ProfileRogueNo ratings yet
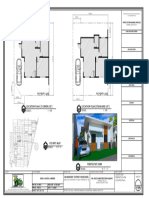
- Location Plan (Standard Lot) Location Plan (Corner Lot) : Office of The Building OfficialsDocument1 pageLocation Plan (Standard Lot) Location Plan (Corner Lot) : Office of The Building OfficialsMark Nico Meneses GallogoNo ratings yet
- LW247CJ-Cad CatalogDocument1 pageLW247CJ-Cad CatalogData 005No ratings yet
- MOS of Scaffolding SystemDocument9 pagesMOS of Scaffolding SystemAhmad Fauzi Bin OmarNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN SEMENTARA PDA PEMBANGUNAN JALUR KA BANDARA NYIA YOGYAKARTA INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT (PK 53r bp.22)Document5 pagesLAPORAN SEMENTARA PDA PEMBANGUNAN JALUR KA BANDARA NYIA YOGYAKARTA INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT (PK 53r bp.22)Amir UdinNo ratings yet
- Primary Report of Kottapuram Bridge RevDocument20 pagesPrimary Report of Kottapuram Bridge Rev123epcNo ratings yet
- Above Ceiling Closure Check ListDocument13 pagesAbove Ceiling Closure Check ListNabeel RumaniNo ratings yet
- Alsina Catalogue Alumecano EnglishDocument3 pagesAlsina Catalogue Alumecano Englishdep_vinNo ratings yet
- Grillage FoundationsDocument10 pagesGrillage FoundationsAbhish RajNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument2 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoKundan SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Typical TBM Work ScheduleDocument1 pageTypical TBM Work ScheduleMazhar BasaNo ratings yet
- Project Master ScheduleDocument1 pageProject Master ScheduleShandy StudioNo ratings yet
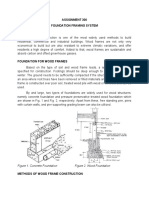
- Assignment 300 Foundation Framing System A. WoodDocument6 pagesAssignment 300 Foundation Framing System A. WoodSimone YuNo ratings yet
- VR 20220425 Geostructural Industrial PDFDocument6 pagesVR 20220425 Geostructural Industrial PDFJohnNo ratings yet
- Hospital PlumbingDocument1 pageHospital PlumbingGrace Orilla RavarraNo ratings yet
- Viswa Consult Pvt. LTD.: Bridge Load TestDocument8 pagesViswa Consult Pvt. LTD.: Bridge Load TestPradeep PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Construction Company in Petaling JayaDocument26 pagesConstruction Company in Petaling JayaPacific HRNo ratings yet
- Aditya Shekhar ResumeDocument2 pagesAditya Shekhar ResumeAnkit SoniNo ratings yet