Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FM Syllabus
FM Syllabus
Uploaded by
deepraj gawandCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HAS Manual Group 3Document53 pagesHAS Manual Group 3syakirah100% (4)
- Price Action Breakdown - Exclusive Price Action Trading Approach To Financial Markets (PDFDrive)Document85 pagesPrice Action Breakdown - Exclusive Price Action Trading Approach To Financial Markets (PDFDrive)KJV Global Trade100% (1)
- Be Comp Engg Sem-Viii r2019Document56 pagesBe Comp Engg Sem-Viii r2019Sahil KNo ratings yet
- Computer Engineering Syllabus Sem Viii Mumbai UniversityDocument44 pagesComputer Engineering Syllabus Sem Viii Mumbai UniversityDaivik ChaulkarNo ratings yet
- B E - Computer-EnggDocument27 pagesB E - Computer-EnggJai JindalNo ratings yet
- B.E CMPN - Sem VIIDocument85 pagesB.E CMPN - Sem VIIpavateNo ratings yet
- Sem 8 SyallbusDocument16 pagesSem 8 Syallbussushant kadamNo ratings yet
- Program Structure B.E. Information Technology, (Rev. 2016)Document60 pagesProgram Structure B.E. Information Technology, (Rev. 2016)Yash RajNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Engineering Syllabus Sem Viii Mumbai UniversityDocument60 pagesInformation Technology Engineering Syllabus Sem Viii Mumbai UniversityDaivik ChaulkarNo ratings yet
- 6.11 Information TechnologyDocument37 pages6.11 Information TechnologyMafia PathanNo ratings yet
- AI and DS-2 SyllabusDocument4 pagesAI and DS-2 SyllabusTanmay DoshiNo ratings yet
- B.E. Ecs Sem Viii SyllabusDocument66 pagesB.E. Ecs Sem Viii Syllabus8816 Gautam ManuelNo ratings yet
- University of MumbaiDocument32 pagesUniversity of MumbaiKenNo ratings yet
- MC SylbsDocument7 pagesMC SylbsUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University: WWW - Dbatu.ac - inDocument68 pagesDr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University: WWW - Dbatu.ac - inShubham NisalNo ratings yet
- Be CMPNDocument48 pagesBe CMPNAndy yelweNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. Production Engineering 2016-17Document29 pagesM.Tech. Production Engineering 2016-17R.C.PerumalNo ratings yet
- R2016 - BE EXTC Syllabus EvenDocument62 pagesR2016 - BE EXTC Syllabus EvenShailaja UdtewarNo ratings yet
- University of Mumbai: Electrical EngineeringDocument46 pagesUniversity of Mumbai: Electrical EngineeringAditya Kumar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 1.EM-IV SyllabusDocument4 pages1.EM-IV SyllabusSahil KNo ratings yet
- DSE SEM III Information Technology Engg Syllabus 2020-21Document35 pagesDSE SEM III Information Technology Engg Syllabus 2020-21Shaikh WasimaNo ratings yet
- CS 8th SEM AICTE121220115902Document17 pagesCS 8th SEM AICTE121220115902Abhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Program Structure B.E. Computer Engineering, (Rev. 2016) W.E.F. AY 2019-20Document1 pageProgram Structure B.E. Computer Engineering, (Rev. 2016) W.E.F. AY 2019-20TanmayNo ratings yet
- SEM 6 SyllabusDocument30 pagesSEM 6 SyllabusSaravanasundar NadarNo ratings yet
- Proposed Subject Scheme For B.Tech. (Computer Engineering)Document9 pagesProposed Subject Scheme For B.Tech. (Computer Engineering)api-26789938No ratings yet
- CSL Syllabus Sem-VIIDocument4 pagesCSL Syllabus Sem-VIISahil KNo ratings yet
- BTech 1ITSyllabusFinalYearVer1.1-1Document76 pagesBTech 1ITSyllabusFinalYearVer1.1-1Rajnikant NarwadeNo ratings yet
- Computer Engineering Syllabus - Sem VII & SEM VIII (Choice Based Credit and Grading System)Document56 pagesComputer Engineering Syllabus - Sem VII & SEM VIII (Choice Based Credit and Grading System)Saqlain BukhshNo ratings yet
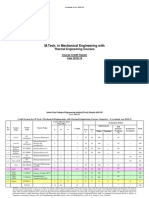
- M.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering WithDocument5 pagesM.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering WithvivekNo ratings yet
- Proposed Subject Scheme For B.Tech. (Information Technology)Document8 pagesProposed Subject Scheme For B.Tech. (Information Technology)api-26789938No ratings yet
- Rajasthan Technical University, Kota Teaching & Scheme of Examination For B.Tech. (Information Technology)Document4 pagesRajasthan Technical University, Kota Teaching & Scheme of Examination For B.Tech. (Information Technology)Giri RajNo ratings yet
- CSE Proposed Syllabus 2009-10Document27 pagesCSE Proposed Syllabus 2009-10accommodateNo ratings yet
- BamuDocument41 pagesBamujjkkNo ratings yet
- Be ExtcDocument126 pagesBe ExtcSushil Sirsat SVNITNo ratings yet
- Instru Sem ViDocument20 pagesInstru Sem ViSagar JathanNo ratings yet
- Secse 220915 215039Document41 pagesSecse 220915 215039jjkkNo ratings yet
- 4CBCSDocument37 pages4CBCSToshnav KhatkeNo ratings yet
- TE Automation and Robotics - (Sem V and VI) 2023.Document67 pagesTE Automation and Robotics - (Sem V and VI) 2023.Prathamesh KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 7th Semester MMUDocument15 pagesSyllabus 7th Semester MMUTushar JajodiaNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering With: Machine Design CoursesDocument5 pagesM.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering With: Machine Design CoursesvivekNo ratings yet
- CSE VIII Semester Scheme Syllabus 2Document21 pagesCSE VIII Semester Scheme Syllabus 2garima khasdeoNo ratings yet
- 6Document2 pages6KevinNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem Electrical ICDocument28 pages6th Sem Electrical ICPintu DaleiNo ratings yet
- Basic of ITDocument24 pagesBasic of ITUdit Kumar SarapNo ratings yet
- Csit Btech Iv Yr Vii Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Document25 pagesCsit Btech Iv Yr Vii Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Deepak DhakadNo ratings yet
- Mechsceheme 78Document2 pagesMechsceheme 78Anonymous SLKWYHBoNo ratings yet
- Corrected Final BE EXTC R2019 Syllabus 12-05-2022 8 PMDocument127 pagesCorrected Final BE EXTC R2019 Syllabus 12-05-2022 8 PMsoniathalavoorNo ratings yet
- B Tech (Computer) 0Document91 pagesB Tech (Computer) 0archanaNo ratings yet
- 7Document2 pages7KevinNo ratings yet
- Btech Syllabus For Gndec LudhianaDocument38 pagesBtech Syllabus For Gndec Ludhianaਅਰ ਜੋਤNo ratings yet
- Sem 7 - Ai & DSDocument57 pagesSem 7 - Ai & DSAKSHITI KACHHAWAHNo ratings yet
- Proposed Syllabus of Information Technology Fifth and Sixth Semester RTM Nagpur University, Nagpur ACADEMIC SESSION: 2014-2015Document28 pagesProposed Syllabus of Information Technology Fifth and Sixth Semester RTM Nagpur University, Nagpur ACADEMIC SESSION: 2014-2015hemantNo ratings yet
- Computer Engineering - Final Year Semester 78Document72 pagesComputer Engineering - Final Year Semester 78glitched matrixNo ratings yet
- Diploma 2nd Semester Course StructureDocument8 pagesDiploma 2nd Semester Course StructureMD AJMALNo ratings yet
- DR - Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, AurangabadDocument52 pagesDR - Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, AurangabadHokamgNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument40 pagesInformation TechnologyIshant Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Mtech ETC Syallbus 2014-15Document48 pagesMtech ETC Syallbus 2014-15sangam1234No ratings yet
- 6th MECH SandwitchDocument23 pages6th MECH SandwitchSubham BeheraNo ratings yet
- Scheme & Syllabus - B.E. (Computer Science and Engineering) PDFDocument150 pagesScheme & Syllabus - B.E. (Computer Science and Engineering) PDFLikith LikithNo ratings yet
- It Sem-Vi PDFDocument50 pagesIt Sem-Vi PDFEr Touhid AlamNo ratings yet
- Fourth Year Robotics & Automation: Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityDocument48 pagesFourth Year Robotics & Automation: Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityveereshaNo ratings yet
- Bhagwati Steel CentreDocument8 pagesBhagwati Steel CentreMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- BIR Collection and Payment Summary SampleDocument14 pagesBIR Collection and Payment Summary SampleNeeco1 FinanceNo ratings yet
- Project: Integration ManagementDocument71 pagesProject: Integration ManagementMustefa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Erd.2.f.008 Sworn AffidavitDocument2 pagesErd.2.f.008 Sworn Affidavitivee.upak032023No ratings yet
- MKT243 - Chapter 3 - Jba1142h - Muhamad Hafizi Bin AdnanDocument8 pagesMKT243 - Chapter 3 - Jba1142h - Muhamad Hafizi Bin AdnanMuhamad HafiziNo ratings yet
- Annual Report of IOCL 196Document1 pageAnnual Report of IOCL 196Nikunj ParmarNo ratings yet
- Market StructureDocument37 pagesMarket StructureJëssiçä R. ArëllanöNo ratings yet
- b1 Solving Set 3 May 2018 - OnlineDocument4 pagesb1 Solving Set 3 May 2018 - OnlineGadafi FuadNo ratings yet
- Instructional Guide For Accountancy: Class: Xi-XiiDocument108 pagesInstructional Guide For Accountancy: Class: Xi-XiiYonten PhuntshoNo ratings yet
- SBR-INT S24-J25 Syllabus and Study Guide - FinalDocument17 pagesSBR-INT S24-J25 Syllabus and Study Guide - FinalMyo NaingNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 8799 The Securities Regulation CodeDocument29 pagesRepublic Act No. 8799 The Securities Regulation CodeAstrid Gopo BrissonNo ratings yet
- Audit Firm Organizational ChartDocument4 pagesAudit Firm Organizational ChartMuhammad Tahir Lecturer at IBLNo ratings yet
- Firda Arfianti - LC53 - Equity Method, Two Consecutive YearsDocument5 pagesFirda Arfianti - LC53 - Equity Method, Two Consecutive YearsFirdaNo ratings yet
- Dual DegreeDocument12 pagesDual DegreeKaver SilverwingNo ratings yet
- EOI For Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan (GKRA)Document68 pagesEOI For Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan (GKRA)Dilip MishraNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument3 pagesAmazondesikudi9000No ratings yet
- Proxy Form / Borang ProksiDocument36 pagesProxy Form / Borang ProksiJonathan OngNo ratings yet
- Future of Power Generation Sector in BangladeshDocument28 pagesFuture of Power Generation Sector in BangladeshChishty Shai NomaniNo ratings yet
- Tally MCQ PDFDocument7 pagesTally MCQ PDFRAKESH MESHRAMNo ratings yet
- M0010 Risk Assessment ManualDocument51 pagesM0010 Risk Assessment ManualnivasmarineNo ratings yet
- GRP 1 Articles of IncorporationDocument4 pagesGRP 1 Articles of IncorporationQueenVictoriaAshleyPrietoNo ratings yet
- Thai Express: Our ObjectiveDocument7 pagesThai Express: Our ObjectivePETRE ARANGINo ratings yet
- MTP II AnswersDocument14 pagesMTP II AnswersEediko ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Solution - PAS - 1 - and - PAS - 2.pdf Filename - UTF-8''Quiz (Solution) % PDFDocument3 pagesQuiz - Solution - PAS - 1 - and - PAS - 2.pdf Filename - UTF-8''Quiz (Solution) % PDFSamuel BandibasNo ratings yet
- Acca f6 Taxation Vietnam 2012 Dec QuestionDocument13 pagesAcca f6 Taxation Vietnam 2012 Dec QuestionNguyễn GiangNo ratings yet
- Updated Resume - Kaushik SenguptaDocument3 pagesUpdated Resume - Kaushik SenguptaKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: KotlerDocument6 pagesChapter 13: Kotlerankita_shreeram100% (1)
- Bot 353 Long NotesDocument52 pagesBot 353 Long Notessushanttayde1No ratings yet
FM Syllabus
FM Syllabus
Uploaded by
deepraj gawandOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FM Syllabus
FM Syllabus
Uploaded by
deepraj gawandCopyright:
Available Formats
AC 5th May, 2018
Item No. 4.51
UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI
Revised syllabus (Rev- 2016) from Academic Year 2016 -17
Under
FACULTY OF TECHNOLOGY
Computer Engineering
Second Year with Effect from AY 2017-18
Third Year with Effect from AY 2018-19
Final Year with Effect from AY 2019-20
As per Choice Based Credit and Grading System
with effect from the AY 2016 17
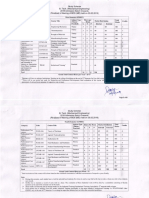
Program Structure B.E. Computer Engineering, (Rev. 2016) w.e.f. AY 2019-20
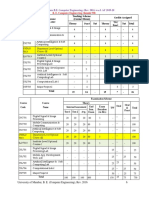
B. E. Computer Engineering (Semester-VIII)
Teaching Scheme
Credits Assigned
Course Course (Contact Hours)
Code Na m e TW/
Theory Pract Tut Theory Tut Total
Pract
Human Machine
CSC801 4 - - 4 - - 4
Interaction
CSC802 Distributed Computing 4 - - 4 - - 4
CSDLO Department Level Optional
4 - - 4 - - 4
801X Course -IV
Institute Level Optional
ILO801X 3 - - 3 - - 3
Course-II
Human Machine
CSL801 - 2 - - 1 1
Interaction Lab
Distributed Computing
CSL802 2 1 1
Lab
CSL803 Cloud Computing Lab - 4 - - 2 2
CSL804 Computational Lab-II - 2 - 1 1
CSP805 Major Project-II - 12 6 - 6
Total 15 22 - 15 11 - 26
Examination Scheme
Course Course Theory
Oral
Code Name Internal Assessment End Exam TW Oral & Total
Sem. Duratio Pract
Test 1 Test 2 Avg. Exam n ( in
Human Machine
CSC801 20 20 20 80 3 - - - 100
Interaction
CSC802 Distributed Computing 20 20 20 80 3 - - - 100
CSDLO Department Level Optional
801X Course -IV 20 20 20 80 3 - - - 100
Institute Level Optional
ILO801X 20 20 20 80 3 - - - 100
Course-II
Human Machine
CSC801 25 25 - 50
Interaction Lab
Distributed Computing
CSL802 - - - - - 25 25 50
Lab
Cloud Computing Lab
CSL803 - - - - - 50 -- 25 75
CSL804 Computational Lab-II
- - - - - 50 -- 25 75
CSP805 Major Project-II 50 -- 50 100
Total 80 80 80 320 -- 200 50 100 750
University of Mumbai, B. E. (Computer Engineering), Rev. 2016 7
Sem. Department Level Optional Course Institute Level Optional Course
(DLOC) (ILOC)
CSDLO5011: Multimedia System
V
CSDLO5012: Advance Operating System --------------------
CSDLO5013: Advance Algorithm
CSDLO6021: Machine Learning
CSDLO6022: Advance Database System
VI
CSDLO6023: Enterprise Resource Planning -------------------
CSDLO6024: Advance Computer Network
ILO7011. Product Lifecycle Management
ILO7012. Reliability Engineering
ILO7013. Management Information
CSDLO7031: Advance System Security & System
Digital Forensics ILO7014. Design of Experiments
VII
CSDLO7032: Big Data & Analytics ILO7015. Operation Research
ILO7016. Cyber Security and Laws
CSDLO7033: Robotics
ILO7017. Disaster Management &
Mitigation Measures
ILO7018. Energy Audit and Management
ILO7019. Development Engineering
ILO8021. Project Management
ILO8022. Finance Management
ILO8023. Entrepreneurship Development
DLO8011: High Performance Computing and Management
VIII DLO8012: Natural Language Processing ILO8024. Human Resource Management
DLO8013: Adhoc Wireless Network ILO8025. Professional Ethics and CSR
ILO8026. Research Methodology
ILO8027. IPR and Patenting
ILO8028. Digital Business Management
ILO8029. Environmental Management
University of Mumbai, B. E. (Computer Engineering), Rev. 2016 8
Course Code Course Name Credits
ILO 8022 Finance Management 03
Objectives:
1. Overview of Indian financial system, instruments and market
2. Basic concepts of value of money, returns and risks, corporate finance, working capital and its
management
3. Knowledge about sources of finance, capital structure, dividend policy
Outcomes:
1. Understand Indian finance system and corporate finance
2. Take investment, finance as well as dividend decisions
Module Detailed Contents Hrs
Overview of Indian Financial System: Characteristics, Components and Functions of
Financial System.
Financial Instruments: Meaning, Characteristics and Classification of Basic Financial
Instruments Equity Shares, Preference Shares, Bonds-Debentures, Certificates of
01 Deposit, and Treasury Bills. 06
Financial Markets: Meaning, Characteristics and Classification of Financial Markets
Capital Market, Money Market and Foreign Currency Market
Financial Institutions: Meaning, Characteristics and Classification of Financial
Institutions Commercial Banks, Investment-Merchant Banks and Stock Exchanges
Concepts of Returns and Risks: Measurement of Historical Returns and Expected
Returns of a Single Security and a Two-security Portfolio; Measurement of Historical
Risk and Expected Risk of a Single Security and a Two-security Portfolio. 06
02
Time Value of Money: Future Value of a Lump Sum, Ordinary Annuity, and Annuity
Due; Present Value of a Lump Sum, Ordinary Annuity, and Annuity Due; Continuous
Compounding and Continuous Discounting.
Overview of Corporate Finance: Objectives of Corporate Finance; Functions of
Corporate Finance Investment Decision, Financing Decision, and Dividend Decision.
Financial Ratio Analysis: Overview of Financial Statements Balance Sheet, Profit 09
03
and Loss Account, and Cash Flow Statement; Purpose of Financial Ratio Analysis;
Liquidity Ratios; Efficiency or Activity Ratios; Profitability Ratios; Capital Structure
Ratios; Stock Market Ratios; Limitations of Ratio Analysis.
Capital Budgeting: Meaning and Importance of Capital Budgeting; Inputs for Capital
Budgeting Decisions; Investment Appraisal Criterion Accounting Rate of Return,
Payback Period, Discounted Payback Period, Net Present Value(NPV), Profitability
Index, Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) 10
04
Working Capital Management: Concepts of Meaning Working Capital; Importance of
Working Capital Management; Factors Affecting a
Estimation of Working Capital Requirements; Management of Inventories;
Management of Receivables; and Management of Cash and Marketable Securities.
05 Sources of Finance: Long Term Sources Equity, Debt, and Hybrids; Mezzanine 05
University of Mumbai, B. E. (Computer Engineering), Rev. 2016 127
Finance; Sources of Short Term Finance Trade Credit, Bank Finance, Commercial
Paper; Project Finance.
Capital Structure:
Capital Structure Theories and Approaches Net Income Approach, Net Operating
Income Approach; Traditional Approach, and Modigliani-Miller Approach. Relation
between Capital Structure and Corporate Value; Concept of Optimal Capital Structure
Dividend Policy: Meaning and Importance of Dividend Policy; Factors Affecting an
06 03
-Miller Approach
Assessment:
Internal Assessment for 20 marks:
Consisting Two Compulsory Class Tests
First test based on approximately 40% of contents and second test based on remaining contents
(approximately 40% but excluding contents covered in Test I)
End Semester Examination:
Weightage of each module in end semester examination will be proportional to number of respective lecture
hours mentioned in the curriculum.
1. Question paper will comprise of total six questions, each carrying 20 marks
2. Question 1 will be compulsory and should cover maximum contents of the curriculum
3. Remaining questions will be mixed in nature (for example if Q.2 has part (a) from module 3 then
part (b) will be from any module other than module 3)
4. Only Four questions need to be solved.
REFERENCES:
1. Fundamentals of Financial Management, 13th Edition (2015) by Eugene F. Brigham and Joel F.
Houston; Publisher: Cengage Publications, New Delhi.
2. Analysis for Financial Management, 10th Edition (2013) by Robert C. Higgins; Publishers: McGraw
Hill Education, New Delhi.
3. Indian Financial System, 9th Edition (2015) by M. Y. Khan; Publisher: McGraw Hill Education, New
Delhi.
4. Financial Management, 11th Edition (2015) by I. M. Pandey; Publisher: S. Chand (G/L) & Company
Limited, New Delhi.
University of Mumbai, B. E. (Computer Engineering), Rev. 2016 128
You might also like
- HAS Manual Group 3Document53 pagesHAS Manual Group 3syakirah100% (4)
- Price Action Breakdown - Exclusive Price Action Trading Approach To Financial Markets (PDFDrive)Document85 pagesPrice Action Breakdown - Exclusive Price Action Trading Approach To Financial Markets (PDFDrive)KJV Global Trade100% (1)
- Be Comp Engg Sem-Viii r2019Document56 pagesBe Comp Engg Sem-Viii r2019Sahil KNo ratings yet
- Computer Engineering Syllabus Sem Viii Mumbai UniversityDocument44 pagesComputer Engineering Syllabus Sem Viii Mumbai UniversityDaivik ChaulkarNo ratings yet
- B E - Computer-EnggDocument27 pagesB E - Computer-EnggJai JindalNo ratings yet
- B.E CMPN - Sem VIIDocument85 pagesB.E CMPN - Sem VIIpavateNo ratings yet
- Sem 8 SyallbusDocument16 pagesSem 8 Syallbussushant kadamNo ratings yet
- Program Structure B.E. Information Technology, (Rev. 2016)Document60 pagesProgram Structure B.E. Information Technology, (Rev. 2016)Yash RajNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Engineering Syllabus Sem Viii Mumbai UniversityDocument60 pagesInformation Technology Engineering Syllabus Sem Viii Mumbai UniversityDaivik ChaulkarNo ratings yet
- 6.11 Information TechnologyDocument37 pages6.11 Information TechnologyMafia PathanNo ratings yet
- AI and DS-2 SyllabusDocument4 pagesAI and DS-2 SyllabusTanmay DoshiNo ratings yet
- B.E. Ecs Sem Viii SyllabusDocument66 pagesB.E. Ecs Sem Viii Syllabus8816 Gautam ManuelNo ratings yet
- University of MumbaiDocument32 pagesUniversity of MumbaiKenNo ratings yet
- MC SylbsDocument7 pagesMC SylbsUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University: WWW - Dbatu.ac - inDocument68 pagesDr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University: WWW - Dbatu.ac - inShubham NisalNo ratings yet
- Be CMPNDocument48 pagesBe CMPNAndy yelweNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. Production Engineering 2016-17Document29 pagesM.Tech. Production Engineering 2016-17R.C.PerumalNo ratings yet
- R2016 - BE EXTC Syllabus EvenDocument62 pagesR2016 - BE EXTC Syllabus EvenShailaja UdtewarNo ratings yet
- University of Mumbai: Electrical EngineeringDocument46 pagesUniversity of Mumbai: Electrical EngineeringAditya Kumar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 1.EM-IV SyllabusDocument4 pages1.EM-IV SyllabusSahil KNo ratings yet
- DSE SEM III Information Technology Engg Syllabus 2020-21Document35 pagesDSE SEM III Information Technology Engg Syllabus 2020-21Shaikh WasimaNo ratings yet
- CS 8th SEM AICTE121220115902Document17 pagesCS 8th SEM AICTE121220115902Abhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Program Structure B.E. Computer Engineering, (Rev. 2016) W.E.F. AY 2019-20Document1 pageProgram Structure B.E. Computer Engineering, (Rev. 2016) W.E.F. AY 2019-20TanmayNo ratings yet
- SEM 6 SyllabusDocument30 pagesSEM 6 SyllabusSaravanasundar NadarNo ratings yet
- Proposed Subject Scheme For B.Tech. (Computer Engineering)Document9 pagesProposed Subject Scheme For B.Tech. (Computer Engineering)api-26789938No ratings yet
- CSL Syllabus Sem-VIIDocument4 pagesCSL Syllabus Sem-VIISahil KNo ratings yet
- BTech 1ITSyllabusFinalYearVer1.1-1Document76 pagesBTech 1ITSyllabusFinalYearVer1.1-1Rajnikant NarwadeNo ratings yet
- Computer Engineering Syllabus - Sem VII & SEM VIII (Choice Based Credit and Grading System)Document56 pagesComputer Engineering Syllabus - Sem VII & SEM VIII (Choice Based Credit and Grading System)Saqlain BukhshNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering WithDocument5 pagesM.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering WithvivekNo ratings yet
- Proposed Subject Scheme For B.Tech. (Information Technology)Document8 pagesProposed Subject Scheme For B.Tech. (Information Technology)api-26789938No ratings yet
- Rajasthan Technical University, Kota Teaching & Scheme of Examination For B.Tech. (Information Technology)Document4 pagesRajasthan Technical University, Kota Teaching & Scheme of Examination For B.Tech. (Information Technology)Giri RajNo ratings yet
- CSE Proposed Syllabus 2009-10Document27 pagesCSE Proposed Syllabus 2009-10accommodateNo ratings yet
- BamuDocument41 pagesBamujjkkNo ratings yet
- Be ExtcDocument126 pagesBe ExtcSushil Sirsat SVNITNo ratings yet
- Instru Sem ViDocument20 pagesInstru Sem ViSagar JathanNo ratings yet
- Secse 220915 215039Document41 pagesSecse 220915 215039jjkkNo ratings yet
- 4CBCSDocument37 pages4CBCSToshnav KhatkeNo ratings yet
- TE Automation and Robotics - (Sem V and VI) 2023.Document67 pagesTE Automation and Robotics - (Sem V and VI) 2023.Prathamesh KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 7th Semester MMUDocument15 pagesSyllabus 7th Semester MMUTushar JajodiaNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering With: Machine Design CoursesDocument5 pagesM.Tech. in Mechanical Engineering With: Machine Design CoursesvivekNo ratings yet
- CSE VIII Semester Scheme Syllabus 2Document21 pagesCSE VIII Semester Scheme Syllabus 2garima khasdeoNo ratings yet
- 6Document2 pages6KevinNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem Electrical ICDocument28 pages6th Sem Electrical ICPintu DaleiNo ratings yet
- Basic of ITDocument24 pagesBasic of ITUdit Kumar SarapNo ratings yet
- Csit Btech Iv Yr Vii Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Document25 pagesCsit Btech Iv Yr Vii Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Deepak DhakadNo ratings yet
- Mechsceheme 78Document2 pagesMechsceheme 78Anonymous SLKWYHBoNo ratings yet
- Corrected Final BE EXTC R2019 Syllabus 12-05-2022 8 PMDocument127 pagesCorrected Final BE EXTC R2019 Syllabus 12-05-2022 8 PMsoniathalavoorNo ratings yet
- B Tech (Computer) 0Document91 pagesB Tech (Computer) 0archanaNo ratings yet
- 7Document2 pages7KevinNo ratings yet
- Btech Syllabus For Gndec LudhianaDocument38 pagesBtech Syllabus For Gndec Ludhianaਅਰ ਜੋਤNo ratings yet
- Sem 7 - Ai & DSDocument57 pagesSem 7 - Ai & DSAKSHITI KACHHAWAHNo ratings yet
- Proposed Syllabus of Information Technology Fifth and Sixth Semester RTM Nagpur University, Nagpur ACADEMIC SESSION: 2014-2015Document28 pagesProposed Syllabus of Information Technology Fifth and Sixth Semester RTM Nagpur University, Nagpur ACADEMIC SESSION: 2014-2015hemantNo ratings yet
- Computer Engineering - Final Year Semester 78Document72 pagesComputer Engineering - Final Year Semester 78glitched matrixNo ratings yet
- Diploma 2nd Semester Course StructureDocument8 pagesDiploma 2nd Semester Course StructureMD AJMALNo ratings yet
- DR - Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, AurangabadDocument52 pagesDR - Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, AurangabadHokamgNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument40 pagesInformation TechnologyIshant Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Mtech ETC Syallbus 2014-15Document48 pagesMtech ETC Syallbus 2014-15sangam1234No ratings yet
- 6th MECH SandwitchDocument23 pages6th MECH SandwitchSubham BeheraNo ratings yet
- Scheme & Syllabus - B.E. (Computer Science and Engineering) PDFDocument150 pagesScheme & Syllabus - B.E. (Computer Science and Engineering) PDFLikith LikithNo ratings yet
- It Sem-Vi PDFDocument50 pagesIt Sem-Vi PDFEr Touhid AlamNo ratings yet
- Fourth Year Robotics & Automation: Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityDocument48 pagesFourth Year Robotics & Automation: Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityveereshaNo ratings yet
- Bhagwati Steel CentreDocument8 pagesBhagwati Steel CentreMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- BIR Collection and Payment Summary SampleDocument14 pagesBIR Collection and Payment Summary SampleNeeco1 FinanceNo ratings yet
- Project: Integration ManagementDocument71 pagesProject: Integration ManagementMustefa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Erd.2.f.008 Sworn AffidavitDocument2 pagesErd.2.f.008 Sworn Affidavitivee.upak032023No ratings yet
- MKT243 - Chapter 3 - Jba1142h - Muhamad Hafizi Bin AdnanDocument8 pagesMKT243 - Chapter 3 - Jba1142h - Muhamad Hafizi Bin AdnanMuhamad HafiziNo ratings yet
- Annual Report of IOCL 196Document1 pageAnnual Report of IOCL 196Nikunj ParmarNo ratings yet
- Market StructureDocument37 pagesMarket StructureJëssiçä R. ArëllanöNo ratings yet
- b1 Solving Set 3 May 2018 - OnlineDocument4 pagesb1 Solving Set 3 May 2018 - OnlineGadafi FuadNo ratings yet
- Instructional Guide For Accountancy: Class: Xi-XiiDocument108 pagesInstructional Guide For Accountancy: Class: Xi-XiiYonten PhuntshoNo ratings yet
- SBR-INT S24-J25 Syllabus and Study Guide - FinalDocument17 pagesSBR-INT S24-J25 Syllabus and Study Guide - FinalMyo NaingNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 8799 The Securities Regulation CodeDocument29 pagesRepublic Act No. 8799 The Securities Regulation CodeAstrid Gopo BrissonNo ratings yet
- Audit Firm Organizational ChartDocument4 pagesAudit Firm Organizational ChartMuhammad Tahir Lecturer at IBLNo ratings yet
- Firda Arfianti - LC53 - Equity Method, Two Consecutive YearsDocument5 pagesFirda Arfianti - LC53 - Equity Method, Two Consecutive YearsFirdaNo ratings yet
- Dual DegreeDocument12 pagesDual DegreeKaver SilverwingNo ratings yet
- EOI For Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan (GKRA)Document68 pagesEOI For Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan (GKRA)Dilip MishraNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument3 pagesAmazondesikudi9000No ratings yet
- Proxy Form / Borang ProksiDocument36 pagesProxy Form / Borang ProksiJonathan OngNo ratings yet
- Future of Power Generation Sector in BangladeshDocument28 pagesFuture of Power Generation Sector in BangladeshChishty Shai NomaniNo ratings yet
- Tally MCQ PDFDocument7 pagesTally MCQ PDFRAKESH MESHRAMNo ratings yet
- M0010 Risk Assessment ManualDocument51 pagesM0010 Risk Assessment ManualnivasmarineNo ratings yet
- GRP 1 Articles of IncorporationDocument4 pagesGRP 1 Articles of IncorporationQueenVictoriaAshleyPrietoNo ratings yet
- Thai Express: Our ObjectiveDocument7 pagesThai Express: Our ObjectivePETRE ARANGINo ratings yet
- MTP II AnswersDocument14 pagesMTP II AnswersEediko ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Solution - PAS - 1 - and - PAS - 2.pdf Filename - UTF-8''Quiz (Solution) % PDFDocument3 pagesQuiz - Solution - PAS - 1 - and - PAS - 2.pdf Filename - UTF-8''Quiz (Solution) % PDFSamuel BandibasNo ratings yet
- Acca f6 Taxation Vietnam 2012 Dec QuestionDocument13 pagesAcca f6 Taxation Vietnam 2012 Dec QuestionNguyễn GiangNo ratings yet
- Updated Resume - Kaushik SenguptaDocument3 pagesUpdated Resume - Kaushik SenguptaKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: KotlerDocument6 pagesChapter 13: Kotlerankita_shreeram100% (1)
- Bot 353 Long NotesDocument52 pagesBot 353 Long Notessushanttayde1No ratings yet