Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Permeability
Cell Permeability
Uploaded by
Rav Evan VigillaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Permeability
Cell Permeability
Uploaded by
Rav Evan VigillaCopyright:
Available Formats
CELL PERMEABILITY Application
____________________________________________________________
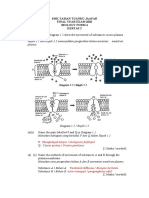
Definition of terms Case 1: Bryan, 15 y.o. male is performing an experiment about red blood
cell tonicity. He was instructed by his preceptor to put 2% NaCl in the RBC
Osmosis: movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable suspension. What do you think will happen in the RBCs, will it crenate or
membrane hemolyse? Why?
Osmotic pressure (OP): pressure exerted by impermeable solutes, the
Case 2: Hannah, 11 y.o. presents with cough, fever, and palpitation. Upon
higher the solute conc. the higher OP
physical examination she seems dehydrated, with sunken eyes. The
attending physician ordered D5W. What tonicity of IV fluid did the doctor
Tonicity: measure of the solution’s ability to change the volume of cells by
give to maintain her intravascular volume? Isotonic, Hypotonic,
altering their water content
Hypertonic? And what would be the expected blood picture of RBCs?
____________________________________________________________
ISOTONIC SOLUTION -Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMT,
-SAME salt concentration as the normal cells of ASCPi
the body and the blood
-EQUAL osmotic pressure
0.9% NaCl (PNSS)
Ringers Lactate
D5W
PNSS – normal physiologic saline solution
HYPOTONIC SOLUTION
-LOWER osmotic pressure than that of a body
fluid
-Water movement INto a cell
-Leads to swOllen, bOrsting (hemOlysis)
Pure water
0.45% NaCl
HYPERTONIC SOLUTION
-HIGHER osmotic pressure than that of a body
fluid
-Water movement OUT of the cell
-Leads to shRink, cRenation
You might also like
- Fluids & Electrolytes: A. 2 Body CompartmentsDocument5 pagesFluids & Electrolytes: A. 2 Body CompartmentsJULIUS ART VINCENT A. PADINITNo ratings yet
- Fluids & ElectrolytesDocument15 pagesFluids & Electrolytesarvinnnn100% (2)
- Osmotic Fragility of Red Blood CellsDocument3 pagesOsmotic Fragility of Red Blood Cellschaudhry umar farooqNo ratings yet
- Maptek I-Site Studio Geotechnical ModuleDocument4 pagesMaptek I-Site Studio Geotechnical ModulekennycasillaNo ratings yet
- Cell Tonicity LABDocument4 pagesCell Tonicity LABa jNo ratings yet
- Blood Case 4Document12 pagesBlood Case 4إنعام الحفيانNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes-EnhanceDocument165 pagesFluids & Electrolytes-EnhanceJes CmtNo ratings yet
- Philippine Integrated Nurse Licensure ExaminationDocument96 pagesPhilippine Integrated Nurse Licensure Examinationmhiersalyn mirulNo ratings yet
- Surmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1Document18 pagesSurmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1Kim RamosNo ratings yet
- 03a Cell TonicityDocument4 pages03a Cell TonicityMary Jewel0% (1)
- 312 MidDocument60 pages312 MidVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Surmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1Document20 pagesSurmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1leone shikukuNo ratings yet
- ExamView - Chapter - 05Document6 pagesExamView - Chapter - 05Stella WangNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesBlood TransfusionDocument6 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesBlood TransfusionMaria Erica Jan MirandaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesCoy EnNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1Wiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- DiajdjdjddhDocument5 pagesDiajdjdjddhNowami Rb LagataNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument179 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesduypalaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid SelectionDocument12 pagesIntravenous Fluid SelectionTracy100% (4)
- Fluid, Electrolytes, Acid-Base and Shock ObjectivesDocument18 pagesFluid, Electrolytes, Acid-Base and Shock ObjectivesmajedNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes Lesson Outline For BBDocument14 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Lesson Outline For BBdlneisha61100% (1)
- Assisting in Ivf InsertionDocument76 pagesAssisting in Ivf Insertionrechelle mae legaspiNo ratings yet
- Syock & ManagementDocument34 pagesSyock & ManagementIndra Anwari RukmanNo ratings yet
- Am Am - IVDocument7 pagesAm Am - IVamietootNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes-2Document82 pagesFluids and Electrolytes-2Jem Loterte100% (1)
- 418 Septic Shock Sirs and ModsDocument51 pages418 Septic Shock Sirs and ModsApril Ann HortilanoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Resuscitation - The Evidence PDFDocument54 pagesFluid Resuscitation - The Evidence PDFrsia fatimahNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes HandoutDocument16 pagesFluids & Electrolytes Handoutapi-3722454100% (3)
- Assessment of Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument15 pagesAssessment of Fluid and ElectrolyteDip Ayan MNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Presenter: Dr. Siyum Mathewos (Omfs-Ri) Modulator: Dr. Dereje (Omfs, Consultant)Document87 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Balance: Presenter: Dr. Siyum Mathewos (Omfs-Ri) Modulator: Dr. Dereje (Omfs, Consultant)Siyum MathewosNo ratings yet
- Raglands Adrenal Test PDFDocument5 pagesRaglands Adrenal Test PDFwxcvbnnbvcxwNo ratings yet
- IV FluidDocument49 pagesIV Fluidibrahimadnan040No ratings yet
- Dialysis Disequilibrium SyndromeDocument7 pagesDialysis Disequilibrium Syndromesatyagraha84No ratings yet
- Capitulo 6 Dinamica Humor AcuosoDocument10 pagesCapitulo 6 Dinamica Humor AcuosoLuisa Mayta PitmanNo ratings yet
- 5766 Serous FluidsDocument21 pages5766 Serous FluidsAdeniyi AkisekuNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument79 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesReignallienn Inocencio MartinNo ratings yet
- Iv TherapyDocument3 pagesIv TherapyNashleyah AnayatinNo ratings yet
- Determination of HemolysisDocument3 pagesDetermination of Hemolysislindsay becudoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dss PKB - RsDocument39 pagesFluid Dss PKB - RsancillaagraynNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes, Balance and DisturbancesDocument157 pagesFluid and Electrolytes, Balance and DisturbancesDani PhilipNo ratings yet
- Fluids & ElectrolytesDocument43 pagesFluids & Electrolytesapi-3722454100% (7)
- Laboratory: Reference: Labtest PDFDocument6 pagesLaboratory: Reference: Labtest PDFChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document396 pagesWeek 3Danica Mae BianitoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument28 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing: Fluids and ElectrolytesDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Intro To Fluid and Electrolytes 2022Document42 pagesIntro To Fluid and Electrolytes 2022David Dwane Art SilorioNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock RosalDocument27 pagesHypovolemic Shock RosalBEA RADANo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument19 pagesPHARMACOLOGYKiela Therese LabroNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Selection PDFDocument12 pagesIntravenous Fluid Selection PDFVASGJGNo ratings yet
- Derupe-IV FluidsDocument5 pagesDerupe-IV FluidsEllamae DerupeNo ratings yet
- Mehu107 - U1 - T09 - Crystalloids, Colloids, Blood Products and Blood SubstitutesDocument8 pagesMehu107 - U1 - T09 - Crystalloids, Colloids, Blood Products and Blood SubstitutesDANIEL ESTEBAN RODRIGUEZ TEJADANo ratings yet
- Mod 3C Nursing Care Plan - Macanas, Evangeline Anne A. BSN 2BDocument4 pagesMod 3C Nursing Care Plan - Macanas, Evangeline Anne A. BSN 2BEvangeline Anne MacanasNo ratings yet
- Sodium and Potassium DisordersDocument7 pagesSodium and Potassium DisordersShia LevyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Diarrhea and DehydrationDocument12 pagesPediatric Diarrhea and Dehydrationgbunyara100No ratings yet
- Emergency Fluid TherapyDocument7 pagesEmergency Fluid TherapyAnaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorders and Critically Ill Patients: From Pathophysiology to TreatmentFrom EverandMetabolic Disorders and Critically Ill Patients: From Pathophysiology to TreatmentCarole IchaiNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceFrom EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Spectrum of Amniotic Fluid Embolism: Is Intralipid the solution ?From EverandThe Spectrum of Amniotic Fluid Embolism: Is Intralipid the solution ?No ratings yet
- Conn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandConn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 10 - H&e Staining MethodsDocument8 pages10 - H&e Staining MethodsRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Works of Juan LunaDocument10 pagesWorks of Juan LunaRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- The 19TH Century World of Jose RizalDocument3 pagesThe 19TH Century World of Jose RizalRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Dawn of Filipino NationalismDocument4 pagesDawn of Filipino NationalismRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Sources, Criticism of History, and VoyageDocument4 pagesMeaning, Sources, Criticism of History, and VoyageRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Laro NG LahiDocument5 pagesLaro NG LahiRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EpidemiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To EpidemiologyRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Disease Frequency and MorbidityDocument5 pagesMeasures of Disease Frequency and MorbidityRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiologic Surveillance and Epidemic Outbreak InvestigationDocument15 pagesEpidemiologic Surveillance and Epidemic Outbreak InvestigationRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- P4.1 Primary Healthcare and Philippines Healthcare Delivery SystemDocument4 pagesP4.1 Primary Healthcare and Philippines Healthcare Delivery SystemRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Tissues and MembranesDocument2 pagesTissues and MembranesRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- MICROSDocument3 pagesMICROSRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Physiochemical PropertiesDocument2 pagesCell and Physiochemical PropertiesRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Gsmintelligentalarmsystem Installation and User ManualDocument8 pagesGsmintelligentalarmsystem Installation and User ManualPierfrancesco FravoliniNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery Types and Indications: Mousa Ibrahim MousaDocument42 pagesOrthognathic Surgery Types and Indications: Mousa Ibrahim MousahashimalarwliaNo ratings yet
- Disinfects: Topical Anesthetic Foam SoapDocument1 pageDisinfects: Topical Anesthetic Foam SoapAnnValenciaNo ratings yet
- NDRRMC UPDATE Re SitreDocument31 pagesNDRRMC UPDATE Re SitreQuiapo ChurchNo ratings yet
- Selective Red Cell Variables in Chippiparai Hound Breeds of Tamil Nadu - A Pilot Study in 30 DogsDocument6 pagesSelective Red Cell Variables in Chippiparai Hound Breeds of Tamil Nadu - A Pilot Study in 30 DogsIndian Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences RNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement For One Hundred Years of SolitudeDocument6 pagesThesis Statement For One Hundred Years of Solitudegxirgjwff100% (2)
- BE IV Sem Hall Tickets Dec 2020-Pages-80-211Document132 pagesBE IV Sem Hall Tickets Dec 2020-Pages-80-211Sai Kiran ParimiNo ratings yet
- Goal 4-Differentiated Lesson For Math-International TravelDocument5 pagesGoal 4-Differentiated Lesson For Math-International Travelapi-331573270No ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document5 pagesLab Report 1jvelezdanielaNo ratings yet
- Product NewsDocument112 pagesProduct Newsnunes999No ratings yet
- Gyprock Red Book Book 3 Commercial Installation GuideDocument230 pagesGyprock Red Book Book 3 Commercial Installation GuideAznie ZyNo ratings yet
- Math 241 Section 2.1 (3-2-2021)Document20 pagesMath 241 Section 2.1 (3-2-2021)H ANo ratings yet
- Ce 373 2Document4 pagesCe 373 2Neil OheneNo ratings yet
- Advanced 250 V Three-Phase BLDC Controller With Embedded STM32 MCUDocument32 pagesAdvanced 250 V Three-Phase BLDC Controller With Embedded STM32 MCUOne SpringNo ratings yet
- KS3 Africa 5ghanafactsheetDocument3 pagesKS3 Africa 5ghanafactsheetSandy SaddlerNo ratings yet
- Class 4 GK WorksheetDocument21 pagesClass 4 GK WorksheetJayesh Shukla0% (1)
- MODULE-VIII Processing Seledted Food ItemDocument8 pagesMODULE-VIII Processing Seledted Food ItemKyla Gaile MendozaNo ratings yet
- STS1 1Document42 pagesSTS1 1Peter Paul Rebucan PerudaNo ratings yet
- 7-Day Metabolism Repair Rapid Fat LossDocument27 pages7-Day Metabolism Repair Rapid Fat LossLennart Bjurstrom100% (1)
- Druids: A Basic Fantasy RPG SupplementDocument10 pagesDruids: A Basic Fantasy RPG SupplementR_J_ValdebenitoNo ratings yet
- FY 2024-2028 National Aviation Research PlanDocument88 pagesFY 2024-2028 National Aviation Research PlanPoojaa ShirsatNo ratings yet
- Halliday - Lexicology and Corpus LinguisticsDocument191 pagesHalliday - Lexicology and Corpus LinguisticsIonela Voicu89% (9)
- LabVentMgmt RPDocument100 pagesLabVentMgmt RPGanesh.MahendraNo ratings yet
- Bio Kertas 2 - SkemaDocument11 pagesBio Kertas 2 - SkemaHaslinda SheikhNo ratings yet
- Module 11Document64 pagesModule 11Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Subject Name: Biology 9Document22 pagesSubject Name: Biology 9Naveed Ahmed ButtNo ratings yet
- Sistem Thinking Dan Analisa Pengambilan KeputusanDocument47 pagesSistem Thinking Dan Analisa Pengambilan KeputusanyudiferiandiNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 5992761Document22 pagesGrundfosliterature 5992761BENJAMIN NIAMYNo ratings yet
- 100 Korean Proverbs With Meanings For TOPIK 2Document19 pages100 Korean Proverbs With Meanings For TOPIK 2Rumah Sakit Bhakti NugrahaNo ratings yet