Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Step-Down Converter Controller: Dirk Gehrke, Texas Instruments
Step-Down Converter Controller: Dirk Gehrke, Texas Instruments
Uploaded by
José ManuelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Step-Down Converter Controller: Dirk Gehrke, Texas Instruments
Step-Down Converter Controller: Dirk Gehrke, Texas Instruments
Uploaded by
José ManuelCopyright:
Available Formats
Step-Down Converter
Controller
Dirk Gehrke, Texas Instruments
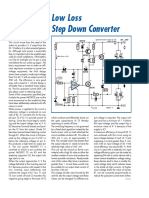
+3V3...+6V R1
33m Ω
The TPS6420x controller is designed to
S
operate from one to three series-con- G T1
nected cells or from a 3.3 V or 5 V sup- IC1 4
Si2323
ply obtained from a USB port. At its out- 5
I SENSE
6
D L1 +3V3
VIN SW
put it can produce 3.3 V at 2 A, suitable 5µH 24m Ω
2A9
for powering a microcontroller-based sys- TPS64202 R2 R3
C3
DBV
619k
tem. With a suitable choice of external 1
EN FB
3
4p7
components (inductor, P-channel MOS- Optional
2
FET and Schottky diode) the device can C1 C4
be operated over a wide range of possi- R4
47µ
X7R 10µ D1 C2 6V3
ble output voltages and currents. A fur- 100m Ω
365k
10V
ther advantage is its extremely low qui- MBRM120
escent current consumption in power-
down mode (100 nA typical) and in 050267 - 11
no-load operation (20 mA). Also, if the
input voltage is less than or equal to the
desired output voltage, the device can reached, the MOSFET is switched off and no adverse effect on the efficiency of the
connect the output directly to the input. remains in the off state until the output converter. It can be damped using the
Using just a few external components the voltage once again falls below the nom- (optional) RC series network.
TPS6420x can cover an output voltage inal value. At very low output currents the At higher output currents the switch-down
range from 1.2 V up to the input voltage controller therefore operates in ‘discon- converter operates in continuous conduc-
at up to 3 A, as long as a suitable P- tinuous mode’ (DCM). Each switching tion mode (CCM). In this mode the induc-
channel MOSFET and Schottky diode are cycle begins with the current at zero. It tor current never falls to zero. The output
used. The device is an asynchronous rises to the threshold or maximum value, voltage is directly proportional to the
step-down converter which, unlike the and then falls again back to zero. At the switching mark-space ratio in this mode.
more widely-used PFM (pulse-frequency moment of switch-off the Schottky diode If the Si2323 P-channel MOSFET from
modulation) and PWM (pulse width mod- causes the residual energy in the induc- Vishay-Siliconix is not available, the
ulation) types, involves a constant on-time tor to appear as a quickly-decaying oscil- IRLML6401 (12 V type) or IRLML6402
and/or constant off-time. Conventional lation at the resonant frequency of the (20 V type) from IRF can be used instead.
controllers operate in PWM mode at output filter. This low-energy oscillation in Both these types have a higher on resist-
medium to high loads, switching to PFM discontinuous mode is normal and has ance, but do offer a lower gate capaci-
at lower loads in order to minimise
switching losses. The controller described
here also adjusts its switching frequency TPS On time Off time Applications
in accordance with the load to achieve
a similar effect to the PFM/PWM con- Ideal for high efficiency over the
trollers. 64200 1.6 µs 600 ns
entire range of output loads
The circuit diagram shows a classical
step-down converter with an input volt- Reduced on-time for higher fre-
age range from 3.3 V to 6 V and an out- 1.6/0.8/0.4/ quency operation than TPS64200,
64201 600 ns
put voltage of 3.3 V at a current of up to 0.2 µs with switching frequency outside
audio range
2 A. The optional 33 mΩ shunt resistor
provides for current limiting. The
Ideal for high switching frequency
TPS64202 offers a minimum on-time
applications where the mark-space
selectable between 1.6 ms, 0.8 ms, ratio approaches 1, such as con-
0.4 ms and 0.2 ms and a fixed off-time 64202 0.6/0.8/0.4 µs 300 ns
verting 3.8 V to 3.3 V; the mini-
of 300 ns. A MOSFET in the supply volt- mum off time determines the
age path is switched on by the controller switching frequency
for as long as is necessary for the output
voltage to reach its nominal value, or Ideal for circuits with a low mark-
until the maximum permissible current, as space ratio where high switching
frequency is required, such as con-
determined by the shunt resistor, is 64203 0.6 µs 600 ns
verting 5 V to 1.5 V; the minimum
reached. If the current does exceed this on time determines the switching
limit the MOSFET is switched off for frequency
300 ns. If the nominal output voltage is
elektor electronics - 7-8/2006
tance. An alternative for the Schottky The voltage drop at 1 A is somewhat Literature at http://www.ti.com:
diode suggested is the MBRM140 (avail- higher: 0.6 V instead of 0.45 V. The SOT23 Step-Down Controller, document
able from Digi-Key and Farnell), although devices are manufactured by IRF and reference number SLVS485
this is in an SMB package rather than the ON Semiconductor. TPS6402 Evaluation Module (3.3 V, 2 A),
Powermite package of the MBRM120. (050267-1) document reference number SLVU093
7-8/2006 - elektor electronics 3
You might also like
- GRS 890 900 GR 801 900Document28 pagesGRS 890 900 GR 801 900Osmar Franco Pires100% (24)
- Mahindra Rexton RX7 REPAIR MANUAL MAN 00216 Part 6 of 7 Rev 1Document197 pagesMahindra Rexton RX7 REPAIR MANUAL MAN 00216 Part 6 of 7 Rev 1Claudio Flores100% (3)
- Samsung FJM Service ManualDocument182 pagesSamsung FJM Service Manualcgsorin50% (2)
- Ak56 Service ManualDocument50 pagesAk56 Service Manualnita_alecsandru100% (1)
- UCN5810 DatasheetDocument7 pagesUCN5810 DatasheetkarimNo ratings yet
- Slvs 485Document30 pagesSlvs 485Similinga MnyongeNo ratings yet
- tps64202 IC PDFDocument30 pagestps64202 IC PDFBobby JavierNo ratings yet
- Tps 51116Document29 pagesTps 51116Ioan HtcNo ratings yet
- Datasheet LTC3728L & LTC3728LX PDFDocument32 pagesDatasheet LTC3728L & LTC3728LX PDFSelmar CavalcantiNo ratings yet
- Off-Line Current Mode PWM Control Circuit With Very Low Start Up CurrentDocument7 pagesOff-Line Current Mode PWM Control Circuit With Very Low Start Up CurrentSero StivNo ratings yet
- 0 - 44 DB RF AttenuatorDocument2 pages0 - 44 DB RF AttenuatorOndrej LomjanskiNo ratings yet
- UC2842B/3B/4B/5B UC3842B/3B/4B/5B: High Performance Current Mode PWM ControllerDocument15 pagesUC2842B/3B/4B/5B UC3842B/3B/4B/5B: High Performance Current Mode PWM Controllernita_alecsandruNo ratings yet
- TPS51123 DatasheetDocument38 pagesTPS51123 DatasheetEduard Vega AyalaNo ratings yet
- Tps 51123Document37 pagesTps 51123Krista TranNo ratings yet
- Datasheet of RCA Power Transistor 40389Document5 pagesDatasheet of RCA Power Transistor 40389Rafael GarciaNo ratings yet
- A 3946KLB-A3946KLP - Drive de PotênciaDocument13 pagesA 3946KLB-A3946KLP - Drive de PotênciaTiago LeonhardtNo ratings yet
- Sensorless BLDC Controller A4960: Description Features and BenefitsDocument34 pagesSensorless BLDC Controller A4960: Description Features and BenefitsadilNo ratings yet
- On Usb, For Bipolar Trannies and Fets: Transistor Curve TraDocument8 pagesOn Usb, For Bipolar Trannies and Fets: Transistor Curve TraHecOsNo ratings yet
- DocumentationDocument3 pagesDocumentationapi-3854737No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - 5011203309-SE09Document1 pageMicrosoft Word - 5011203309-SE09JORGE RODNo ratings yet
- Páginas Extraídas de Manual - MX2Document8 pagesPáginas Extraídas de Manual - MX2Anonymous 97JlpvN4No ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument19 pagesData SheetRobertoBarbosaNo ratings yet
- FAN7392 High-Current, High-And Low-Side, Gate-Drive IC: Features DescriptionDocument18 pagesFAN7392 High-Current, High-And Low-Side, Gate-Drive IC: Features DescriptionRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- LTC 3124Document28 pagesLTC 3124m3rishorNo ratings yet
- 3 V Headphone Amplifier: Ton GiesbertsDocument1 page3 V Headphone Amplifier: Ton GiesbertsTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- Sgmicro-Sgm6132yps8g-Tr C87095Document14 pagesSgmicro-Sgm6132yps8g-Tr C87095ghozi mtNo ratings yet
- LTC1628-SYNC High Efficiency, 2-Phase Synchronous Step-Down Switching RegulatorDocument32 pagesLTC1628-SYNC High Efficiency, 2-Phase Synchronous Step-Down Switching Regulatorملاك حمزهNo ratings yet
- LTC1628/LTC1628-PG High Efficiency, 2-Phase Synchronous Step-Down Switching RegulatorsDocument32 pagesLTC1628/LTC1628-PG High Efficiency, 2-Phase Synchronous Step-Down Switching RegulatorsCarlos Henrique RibasNo ratings yet
- Circuit Note: 12-Bit, 4-20ma Loop-Powered Thermocouple Measurement System Using ARM Cortex-M3Document7 pagesCircuit Note: 12-Bit, 4-20ma Loop-Powered Thermocouple Measurement System Using ARM Cortex-M3Srinivasa MuralidharaNo ratings yet
- 2.5A Switch Step Down Switching Regulator: DescriptionDocument10 pages2.5A Switch Step Down Switching Regulator: DescriptionVictor CuaicalNo ratings yet
- RS232 转USB 方案DIY资料,已做成功Document2 pagesRS232 转USB 方案DIY资料,已做成功李宏观No ratings yet
- EM5106 ExcellianceMOSDocument10 pagesEM5106 ExcellianceMOSSib Repair CenterNo ratings yet
- 3728lxff PDFDocument38 pages3728lxff PDFMaria Aleici JerezNo ratings yet
- AT89C2051-based Countdown TimerDocument3 pagesAT89C2051-based Countdown TimerKumawat ArunNo ratings yet
- A8293 DatasheetDocument20 pagesA8293 DatasheetcarlosgnNo ratings yet
- Datasheet CXA2503ARDocument72 pagesDatasheet CXA2503ARJose BenavidesNo ratings yet
- 14-Bit and 16-Bit A-to-D and D-to-A ConvertersDocument32 pages14-Bit and 16-Bit A-to-D and D-to-A ConvertersRobert L.No ratings yet
- Switch Amplifier-Galvanic Barrier Make Pepper Fusch in AgitatorsDocument6 pagesSwitch Amplifier-Galvanic Barrier Make Pepper Fusch in AgitatorsSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Detector 700 Amplifier For Parabolic Mic AmplifierDocument20 pagesDetector 700 Amplifier For Parabolic Mic AmplifierjimdigrizNo ratings yet
- Abb Ag: OperationDocument4 pagesAbb Ag: OperationCosmic Garash 2No ratings yet
- A4960 A Automotive DatasheetDocument34 pagesA4960 A Automotive DatasheetCanerNo ratings yet
- Sim Card CircuitDocument8 pagesSim Card Circuitmirfanbilal75% (4)
- LTC6401-8 - Data SheetsDocument16 pagesLTC6401-8 - Data Sheetsl2000316No ratings yet
- RT9080N Datasheet ModDocument14 pagesRT9080N Datasheet ModDavid MAILLOTNo ratings yet
- Variable Power Supply: Ideal For The Small WorkshopDocument5 pagesVariable Power Supply: Ideal For The Small WorkshopJorge Manuel Marques VitorinoNo ratings yet
- Uma 1021Document16 pagesUma 1021So Was RedNo ratings yet
- RMS-to-DC Conversion Just Got EasyDocument2 pagesRMS-to-DC Conversion Just Got Easyzeropoint_romeoNo ratings yet
- LMX2322Document14 pagesLMX2322Igo_MichelNo ratings yet
- Sboa 290 CSHXGHDCXCFXDDCGDocument6 pagesSboa 290 CSHXGHDCXCFXDDCGKarthik SuryaNo ratings yet
- Tsop 752 WDocument13 pagesTsop 752 WMatias RendonNo ratings yet
- T2117 Zero-Voltage Switch With Adjustable Ramp PDFDocument16 pagesT2117 Zero-Voltage Switch With Adjustable Ramp PDFnenadNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Brushless Motor Adapter: Semiconductor Technical DataDocument8 pagesClosed Loop Brushless Motor Adapter: Semiconductor Technical DataVictor HemzNo ratings yet
- Motion Coordinator Motion Coordinator: Quick Connection GuideDocument8 pagesMotion Coordinator Motion Coordinator: Quick Connection Guidespotlight studiosNo ratings yet
- Ucc28c40, Ucc28c41, Ucc28c42, Ucc28c43, Ucc28c44, Ucc28c45 Ucc38c40, Ucc38c41, Ucc38c42, Ucc38c43, Ucc38c44, Ucc38c45Document32 pagesUcc28c40, Ucc28c41, Ucc28c42, Ucc28c43, Ucc28c44, Ucc28c45 Ucc38c40, Ucc38c41, Ucc38c42, Ucc38c43, Ucc38c44, Ucc38c45curz0% (1)
- K115V2 - Low Voltage Stereo Amplifier: Specifications: TestingDocument3 pagesK115V2 - Low Voltage Stereo Amplifier: Specifications: Testingyulanvp100% (1)
- TSOP22.., TSOP24.., TSOP48.., TSOP44..: Vishay SemiconductorsDocument7 pagesTSOP22.., TSOP24.., TSOP48.., TSOP44..: Vishay SemiconductorsOZAN GOKCENNo ratings yet
- Controlador CAN MC33389Document49 pagesControlador CAN MC33389Jorge Martinez PerezNo ratings yet
- PM174 Powermeter: Quick Start GuideDocument11 pagesPM174 Powermeter: Quick Start Guideusamakhan205No ratings yet
- tps54239 ReguladorDocument24 pagestps54239 ReguladorAntonioPierreNo ratings yet
- MAX16840 LED Driver With Integrated MOSFET For MR16 and Other 12V AC Input LampsDocument12 pagesMAX16840 LED Driver With Integrated MOSFET For MR16 and Other 12V AC Input Lampszuffflor_925748656No ratings yet
- HCF4538B: Dual Monostable MultivibratorDocument10 pagesHCF4538B: Dual Monostable MultivibratorHector Rafael MirandaNo ratings yet
- LWNMNP : General Description FeaturesDocument16 pagesLWNMNP : General Description FeaturesArturo ArmuellesNo ratings yet
- Bimos Ii 8-Bit Serial-Input, Latched Drivers: Absolute Maximum Ratings at 25 C Free-Air TemperatureDocument7 pagesBimos Ii 8-Bit Serial-Input, Latched Drivers: Absolute Maximum Ratings at 25 C Free-Air TemperatureAlexNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document19 pagesWeek 2José ManuelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C++Document21 pagesIntroduction To C++José ManuelNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document26 pagesWeek 4José ManuelNo ratings yet
- Arduino and HC-12 Long Range Wireless Communication Module - HowToMechatronicsDocument25 pagesArduino and HC-12 Long Range Wireless Communication Module - HowToMechatronicsJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- RC Servo Tester/Exerciser: Ray KingDocument2 pagesRC Servo Tester/Exerciser: Ray KingJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document17 pagesWeek 1José ManuelNo ratings yet
- Geiger Counter: Malte FischerDocument1 pageGeiger Counter: Malte FischerJosé Manuel100% (1)
- Week 3Document17 pagesWeek 3José ManuelNo ratings yet
- 1 UkDocument2 pages1 UkJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- 2 UkDocument2 pages2 UkJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Headphone Amp: Jeff MacaulayDocument2 pagesHybrid Headphone Amp: Jeff MacaulayJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Controller: Gert BaarsDocument2 pagesStepper Motor Controller: Gert BaarsJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- Low Loss Step Down Converter: Michel FrankeDocument1 pageLow Loss Step Down Converter: Michel FrankeJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- Microchip Analog EbookDocument31 pagesMicrochip Analog EbookJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- Universal LCD Module: Ullrich KreiensenDocument3 pagesUniversal LCD Module: Ullrich KreiensenJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- Increased Range For DVM: 2 V 910k 100k 20 V 1M 10k 200 V 1M 1k 2000 V 1M 100 200 Ma 0 1k 2 Ma 0 100 20 Ma 0 10 200 Ma 0 1Document1 pageIncreased Range For DVM: 2 V 910k 100k 20 V 1M 10k 200 V 1M 1k 2000 V 1M 100 200 Ma 0 1k 2 Ma 0 100 20 Ma 0 10 200 Ma 0 1José ManuelNo ratings yet
- 3D Printed Robot Arm - 16 Steps (With Pictures)Document25 pages3D Printed Robot Arm - 16 Steps (With Pictures)José ManuelNo ratings yet
- Amptitudes - MicrochipDocument5 pagesAmptitudes - MicrochipJosé ManuelNo ratings yet
- Training AvrDocument64 pagesTraining AvrCamilo Andres Cardozo FajardoNo ratings yet
- Problem:: Digital System Synthesis Instructor: Dr. Mahdi AbbasiDocument3 pagesProblem:: Digital System Synthesis Instructor: Dr. Mahdi Abbasijhk7888No ratings yet
- Transformer Protection and Transformer FaultDocument3 pagesTransformer Protection and Transformer FaultThirumalNo ratings yet
- Agarwal Formula PD PDFDocument100 pagesAgarwal Formula PD PDFsrajalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Hydro-Unit Technical Data Premium LineDocument64 pagesHydro-Unit Technical Data Premium Linemmihai_popa20060% (1)
- Process Control Lab ManualDocument338 pagesProcess Control Lab ManualMichael Edwards75% (4)
- Computerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For NanofluidsDocument59 pagesComputerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For Nanofluidssa_kulkarni3065No ratings yet
- ящики PDFDocument406 pagesящики PDFVadimNo ratings yet
- MAS-1 Charging, Starting and Ignition Systems PDFDocument25 pagesMAS-1 Charging, Starting and Ignition Systems PDFmanojNo ratings yet
- Designing NFC AntennaDocument20 pagesDesigning NFC Antennas6666hussia6No ratings yet
- Service Manual Konica Minolta Bizhub C300-350 Series Color Digital MFDDocument122 pagesService Manual Konica Minolta Bizhub C300-350 Series Color Digital MFDbhripulNo ratings yet
- Ford Ranger BrochureDocument23 pagesFord Ranger BrochureStefanos TzortzisNo ratings yet
- vd4 ABB VCB ManualDocument72 pagesvd4 ABB VCB ManualSayak Roy ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Ebook Arduino LeonardoDocument109 pagesEbook Arduino LeonardoToni JunihartonoNo ratings yet
- Toshiba 8GB NAND TC58NVG3S0FTAI0 PDFDocument73 pagesToshiba 8GB NAND TC58NVG3S0FTAI0 PDFMilan MilenovicNo ratings yet
- Manual SerDia2010 enDocument235 pagesManual SerDia2010 eneduargon.94No ratings yet
- Instrumentation - Unit 5Document125 pagesInstrumentation - Unit 5Rinki KeswaniNo ratings yet
- RCF Art310a Base Amp Art Series Se515666 2005Document3 pagesRCF Art310a Base Amp Art Series Se515666 2005tlw72100% (1)
- HV Solutions CatalogDocument48 pagesHV Solutions CatalogDeninson PizarroNo ratings yet
- Power Factor CodeDocument9 pagesPower Factor CodeKen AndradeNo ratings yet
- Datasheet E1400ZZ0001Document5 pagesDatasheet E1400ZZ0001yatinun thanathunnithipNo ratings yet
- OmniStar Enhanced DFB Laser AM-OMNIDocument5 pagesOmniStar Enhanced DFB Laser AM-OMNICarmen SparksNo ratings yet
- Spanish PavanDocument5 pagesSpanish Pavanlisten4758100% (1)
- Arc Flash & Shock Hazard AnalysisDocument10 pagesArc Flash & Shock Hazard Analysisnarasimhamurthy414No ratings yet
- 2n7000 TransistorDocument11 pages2n7000 TransistoramirnasrabadiNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Itacr E311 Multiprog Exercises and Solutions Festo PLC Double Side PR - PDFDocument113 pagesToaz - Info Itacr E311 Multiprog Exercises and Solutions Festo PLC Double Side PR - PDFAbuhanif SaikNo ratings yet