Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concepts of Health and Wellness - PRIN1
Concepts of Health and Wellness - PRIN1
Uploaded by
Cejay Erl Magno0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesThe female reproductive system consists of internal organs and external genitalia. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones, while the uterine tubes transport eggs to the uterus where fetal development occurs. Oogenesis begins with oogonia in the ovaries that develop into primary oocytes, some of which become secondary oocytes if fertilized. Ovarian follicles contain developing eggs and secrete estrogens and other hormones. During the menstrual cycle, a mature follicle ruptures and releases an egg, then becomes the corpus luteum which secretes progesterone and estrogen.
Original Description:
Original Title
Concepts of Health and Wellness- PRIN1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe female reproductive system consists of internal organs and external genitalia. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones, while the uterine tubes transport eggs to the uterus where fetal development occurs. Oogenesis begins with oogonia in the ovaries that develop into primary oocytes, some of which become secondary oocytes if fertilized. Ovarian follicles contain developing eggs and secrete estrogens and other hormones. During the menstrual cycle, a mature follicle ruptures and releases an egg, then becomes the corpus luteum which secretes progesterone and estrogen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesConcepts of Health and Wellness - PRIN1
Concepts of Health and Wellness - PRIN1
Uploaded by
Cejay Erl MagnoThe female reproductive system consists of internal organs and external genitalia. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones, while the uterine tubes transport eggs to the uterus where fetal development occurs. Oogenesis begins with oogonia in the ovaries that develop into primary oocytes, some of which become secondary oocytes if fertilized. Ovarian follicles contain developing eggs and secrete estrogens and other hormones. During the menstrual cycle, a mature follicle ruptures and releases an egg, then becomes the corpus luteum which secretes progesterone and estrogen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Human Reproduction
Bachelor Of Science In Medical Laboratory Science
and possibly three small polar
bodies
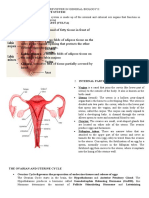
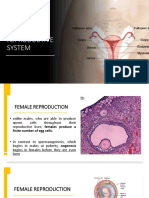
The Female Reproductive Organs
Female reproductive system
consists of the internal
reproductive organs and external
genitalia.
Ovaries
produce eggs
(oocytes) &
hormones
Uterine tubes
transport the
eggs
Uterus where
fetal development occurs
Vagina or birth canal
External genitalia constitute
the vulva
Mammary glands produce milk
Oogenesis
Egg forming cells (oocytes) go
through two divisions
1º = primary 2º = secondary
• Starts with a 2n=46 1ºoocyte Oogenesis – Oogonia to
that divides, resulting in two Oocytes
n=23 cells, but one is a large
2º oocytes and one is a small
1st polar body that may itself Germ cells from yolk sac
divide migrate to ovary and become
• Second division only occurs if potential egg cells called
2º oocytes is fertilized. oogonia
Results in one large n=23 In fetus, millions of oogonia
ovum (egg) and one small produced by mitosis but most
n=23 2nd polar body of them degenerate (atresia)
• Thus oogenesis results in one Some develop into immature
large fertilized egg (zygote) egg cells called primary
TRANSCRIBED BY : CG YRLE A. MAGNO 1
oocytes during fetal Stages of follicular development
development
200,000 to 2 millions present
at birth Primordial follicle
40,000 remain at puberty but Single layer of squamous cells
only 400 mature during a around the oocyte
woman’s reproductive life
Each month about 20 primary Primary follicle
oocytes become secondary Layers of cuboidal granulosa
oocytes but usually only one cells around the oocyte
survives to be ovulated from Granulosa cells secrete
Graafian follicle estrogens
Ovarian Follicles Secondary follicle
Antral cavity forms
Ovarian Follicles
Contain oocytes (egg Graafian follicle
cells) in various stages Follicle mature ready to ovulate
of development oocyte
Secrete estrogens that
function for: Ovulation
Growth and repair of Follicle ruptures releasing oocyte
uterine lining
Regulation of After ovulation, empty follicle
monthly female becomes a corpus luteum
cycle Corpus Luteum secretes:
Female sexual Progesterone –
characteristics completes the
Maintenance of preparation of uterine
bone and muscle lining
Mature (Graafian) Estrogens – work with
follicle releases an progesterone
oocyte each month Relaxin – relaxes
during ovulation uterine muscles and
pubic symphysis
Oocytes (egg cells) Inhibin – decreases
develop within follicles secretion of FSH and
LH
Corpus albicans is a white scar
tissue left after the corpus luteum
dies.
TRANSCRIBED BY : CG YRLE A. MAGNO 2
The Ovary – produces the egg
cell
Uterus
Uterine or Fallopian Tubes
- narrow, 4 inch tube that extends
from the ovary to uterus
Infundibulum is
open, funnel-
shaped portion
near the ovary
Fimbriae are
moving finger-like
processes
Ampulla is central
region of tube
Isthmus is Histology of the Uterus
narrowest portion
joins uterus Endometrium
- Simple columnar epithelium
- Stroma of connective tissue
and endometrial glands
Functional layer
Shed during menstruation
Basal layer
Replaces functional layer
each month
TRANSCRIBED BY : CG YRLE A. MAGNO 3
Myometrium Puberty begins with the first
3 layers of smooth menstrual bleeding
muscle (menarche)
Perimetrium Puberty begins when GnRH,
Visceral LH and FSH levels increase
peritoneum
MENOPAUSE
Vagina
Passageway for birth, Cessation of menstrual
menstrual flow and cycle
intercourse Ages 40-50
Organ of copulation
What is happening?
Term: - Menstrual cycle become
- hymen less regular
External genitalia - Ovulation is inconsistent
Major cause:
- Age related changes
- Number of follicles are
small
- Reduced amount of
estrogen
Climacteric- from irregular cycles
to complete cessation
Mammary Glands
PUBERTY IN FEMALES
TRANSCRIBED BY : CG YRLE A. MAGNO 4
You might also like
- A. Menstrual Cycle Here Are Important Events During The Menstrual CycleDocument2 pagesA. Menstrual Cycle Here Are Important Events During The Menstrual CycleRosiro33% (3)
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemRein Aldou Panao Enfermo100% (2)
- Soft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofDocument6 pagesSoft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofKhristin Joy GamponiaNo ratings yet
- Cervix Ca-Patho Initial DraftDocument17 pagesCervix Ca-Patho Initial Draftjam reparejoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Human ReproductionDocument8 pagesChapter-3 Human ReproductionbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Hands OutDocument15 pagesNCM 107 Hands OutErin SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Ch. 38 Human ReproductionDocument38 pagesCh. 38 Human ReproductionERIC ASAMAMLEH KLEMEHNo ratings yet
- Human Repro NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Repro NotesElvira Monica SayoNo ratings yet
- 11 The Female Reproductive System Lec11 PDFDocument40 pages11 The Female Reproductive System Lec11 PDFTee bagNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- Reproduction AnfismanDocument43 pagesReproduction AnfismanSyahirahNo ratings yet
- CLS224 Lecture 13 1 PDFDocument30 pagesCLS224 Lecture 13 1 PDFmike RNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: Dr. Emanuel Muro HkmuDocument41 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: Dr. Emanuel Muro HkmuMustafa DadahNo ratings yet
- NSVDDocument32 pagesNSVDChris Oliver Kevin Ledesma100% (3)
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument29 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemSamantha Joy TangcoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproduction11Document4 pagesFemale Reproduction11Cyber.HNo ratings yet
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre Kachigamba100% (1)
- Reproductive System ReviewerDocument4 pagesReproductive System ReviewerJewel Arcega PartoNo ratings yet
- N-315: Family Health Nursing: Course Coordinator & Instructor: Mrs. Deepa ThomasDocument41 pagesN-315: Family Health Nursing: Course Coordinator & Instructor: Mrs. Deepa ThomasDeepa ThomasNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi REPRO BETINADocument31 pagesFisiologi REPRO BETINADesy NataliaNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Document11 pagesCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive SystemDocument113 pagesQuarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive Systemsano.kthNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive SystemDocument51 pagesThe Female Reproductive SystemAbsar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument22 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionMmabatho Vilakazi100% (1)
- NOTESDocument5 pagesNOTESMacchi MagsNo ratings yet
- Notes Maternal Health NursingdsdsDocument21 pagesNotes Maternal Health NursingdsdsL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument69 pagesHuman Reproductionapi-202349222No ratings yet
- 10FRSDocument27 pages10FRSWakanda ForeverNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-The Reproductive System The Ovarian CycleDocument4 pagesUnit 1-The Reproductive System The Ovarian CycleJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System2Document27 pagesFemale Reproductive System2bobNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Document12 pagesUNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Menstruation FertilizationDocument2 pagesMenstruation FertilizationJamie Rose GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: Objectives: Identify On Diagrams The Male Reproductive System and State Their FunctionDocument42 pagesReproduction in Humans: Objectives: Identify On Diagrams The Male Reproductive System and State Their FunctionAnushka YadavNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: A Female's Internal Reproductive Organs Are The Vagina, Uterus, Fallopian Tubes, and OvariesDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive System: A Female's Internal Reproductive Organs Are The Vagina, Uterus, Fallopian Tubes, and OvariesMikka Ella BolanosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female ReproductiveDocument8 pagesAnatomy of Female ReproductiveYellowleafNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd QuarterDocument22 pagesScience 3rd QuarterBethel AquinoNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans Part 2Document37 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans Part 2Janae CampbellNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction.Document81 pagesHuman Reproduction.akulroy130507No ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle and Implantation)Document19 pagesMenstrual Cycle and Implantation)Ragdha MehdawiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesReproductive SystemamirehmoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System 2Document21 pagesFemale Reproductive System 2doreen03100% (1)
- Naim LBM 1-1Document38 pagesNaim LBM 1-1dimasNo ratings yet
- First Week of Human DevelopmentDocument81 pagesFirst Week of Human DevelopmentAsfoor gake10% (1)
- FEMALEDocument60 pagesFEMALETri JaraNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle QuestDocument37 pagesMenstrual Cycle Questsai deveraNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesOverview of The Female Reproductive SystemMonica J Ortiz PereiraNo ratings yet
- OgenisisDocument52 pagesOgenisisBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument28 pagesFemale Reproductive System1-LUMALANG Ashley Anne A.No ratings yet
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument29 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemRuben James A. PecsonNo ratings yet
- Embryology IDocument94 pagesEmbryology Imasemola koketsoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Human Reproduction - WatermarkDocument23 pagesChapter - 3 Human Reproduction - WatermarkDurgesh SainiNo ratings yet
- Female Cycles GAD 203Document20 pagesFemale Cycles GAD 203alhobabighnemNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument38 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemGregrodockerNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System For ClassDocument42 pagesReproductive System For Classshubham soniNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System 1Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System 1Rahil PatelNo ratings yet
- Ovum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Theories Prin LastDocument11 pagesTheories Prin LastCejay Erl MagnoNo ratings yet
- Lab MNGT 3Document6 pagesLab MNGT 3Cejay Erl MagnoNo ratings yet
- Lab MNGT 4Document5 pagesLab MNGT 4Cejay Erl MagnoNo ratings yet
- Lab MNGT 5Document9 pagesLab MNGT 5Cejay Erl MagnoNo ratings yet
- Readings 1Document5 pagesReadings 1Cejay Erl MagnoNo ratings yet
- Readings Source 2Document4 pagesReadings Source 2Cejay Erl MagnoNo ratings yet
- Soal-Soal PretesDocument8 pagesSoal-Soal Pretespoker011007No ratings yet
- Case Pre Ovarian CystDocument56 pagesCase Pre Ovarian Cystthesa1201No ratings yet
- Female Reproduction SystemDocument37 pagesFemale Reproduction SystemSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Role of Hormone in Female and Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesSCIENCE Role of Hormone in Female and Male Reproductive SystemJasmineNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Normal Spontaneous Vaginal D EliveryDocument20 pagesA Case Study On Normal Spontaneous Vaginal D EliveryNyj QuiñoNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of SexDocument322 pagesMaking Sense of SexChandrahasa Reddy ThatimakulaNo ratings yet
- TH THDocument12 pagesTH THchn pastranaNo ratings yet
- Science Grade-10-Pretest-EOSY-BreakDocument10 pagesScience Grade-10-Pretest-EOSY-BreakLeoh BaluyotNo ratings yet
- GRP II Gyne CaseDocument72 pagesGRP II Gyne CaseGreggy John Rivera CascayanNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 SLM4Document15 pagesScience10 Q3 SLM4Jomelyn Arzaga100% (2)
- Adnexal MassDocument28 pagesAdnexal MassJuan P. RuedaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Part 1 - SPC MLS1 - Histo LecDocument9 pagesFemale Reproductive System Part 1 - SPC MLS1 - Histo LecCesmaine SanchezNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document9 pagesModule 5CamilleCalmaLenonNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument55 pagesThe Reproductive System: Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsJeffrey Roy Adlawan LopezNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology Third Edition Peter M Doubilet Carol B Benson Beryl R BenacerrafDocument70 pagesAtlas of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology Third Edition Peter M Doubilet Carol B Benson Beryl R Benacerrafjessaeynmaei100% (6)
- Livestock Science: K. Asmad, P.R. Kenyon, S.J. Pain, K.C. Perera, T.J. Parkinson, N. Lopez-Villalobos, H.T. BlairDocument7 pagesLivestock Science: K. Asmad, P.R. Kenyon, S.J. Pain, K.C. Perera, T.J. Parkinson, N. Lopez-Villalobos, H.T. BlairsousamapNo ratings yet
- OG MD Part 1 Past Papers MCQ CategorisedDocument142 pagesOG MD Part 1 Past Papers MCQ CategorisedShyvonne PeirisNo ratings yet
- Consent For Laparoscopic Hysterectomy EnglishDocument4 pagesConsent For Laparoscopic Hysterectomy EnglishGaurav AroraNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)Document6 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technology (ART)Rabelais MedinaNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemRhod Vincent Jamolod TayongNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument89 pagesReproductive SystemIbrahim Mahmoud Ali100% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive SystemshaniaericaNo ratings yet
- Gest. HTN C. StudyDocument51 pagesGest. HTN C. StudyshangheartsyewNo ratings yet
- Midterm Understanding The Self ModuleDocument53 pagesMidterm Understanding The Self ModuleMarlon TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Basic Embryology Series PDFDocument252 pagesBasic Embryology Series PDFGrace Nduta0% (1)
- Self Fertility MassageDocument4 pagesSelf Fertility MassageDr. Smita MahajanNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJamesBatesypcmi100% (16)
- KGN Hospital Test Tube Baby LaturDocument35 pagesKGN Hospital Test Tube Baby LaturDr Aamir ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Protocol of UltrasoundDocument22 pagesProtocol of UltrasoundAzie Azizah AGNo ratings yet