Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Material Science
Material Science
Uploaded by
AnneCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Propeller Design CalculationDocument8 pagesPropeller Design CalculationDave Carter100% (7)
- 004 - Efficient Foam ProductionDocument122 pages004 - Efficient Foam ProductionNo Promises71% (7)
- Practice Problem Machine DesignDocument10 pagesPractice Problem Machine DesignVishak Regu100% (2)
- Cmos Process FlowDocument29 pagesCmos Process FlowPushparaj Karu100% (1)
- ASTM F606-02 - Propiedades Mecanicas TornillosDocument14 pagesASTM F606-02 - Propiedades Mecanicas TornillosedwinsazzzNo ratings yet
- Conductoare Neizolate Din Al: Po (KW) PSCC (KW)Document5 pagesConductoare Neizolate Din Al: Po (KW) PSCC (KW)Ciprian ApalaghițeiNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Iodin NumberDocument268 pagesPerhitungan Iodin NumberrusydianaabdNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument16 pagesHeat ExchangersiosuarizNo ratings yet
- Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger: Parallel FlowDocument24 pagesConcentric Tube Heat Exchanger: Parallel FlowFalcon KingdomNo ratings yet
- DBP RitDocument9 pagesDBP RitTuyú Amaro Aldo MauricioNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic AccelorometerDocument58 pagesElectrostatic AccelorometerShah HussainNo ratings yet
- Termo Lampiran 4Document16 pagesTermo Lampiran 4Anyberta Dwi ListyantiNo ratings yet
- No P/Kpa X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Ɣ1 Ɣ2 LN (Ɣ1) LN (Ɣ2) Ge/Rt Ge/Rtx1X2Document1 pageNo P/Kpa X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Ɣ1 Ɣ2 LN (Ɣ1) LN (Ɣ2) Ge/Rt Ge/Rtx1X2Gladys ElvinaNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan EsterDocument6 pagesPerhitungan EsteralfinNo ratings yet
- KSL - Theo Vs KSL - Expt: N (RPS)Document1 pageKSL - Theo Vs KSL - Expt: N (RPS)Krishnakant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHX SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHX Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- Beryl (Radial Thru-Hole) RG SeriesDocument2 pagesBeryl (Radial Thru-Hole) RG Seriesester853No ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHY SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHY Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- 2023 TPM351ppyDocument7 pages2023 TPM351ppyJenyver LappyNo ratings yet
- PorticosDocument87 pagesPorticosJorge Aurelio Menacho YanacNo ratings yet
- Exercises On ELECTRICAL MACHINESDocument29 pagesExercises On ELECTRICAL MACHINESDavide100% (1)
- LOU2 Labo 6 para Mi Bello Marco Que Hara Bien Los AnexosDocument5 pagesLOU2 Labo 6 para Mi Bello Marco Que Hara Bien Los AnexosJuan Jose LlamoccaNo ratings yet
- LOU2 Labo 6Document5 pagesLOU2 Labo 6Juan Jose LlamoccaNo ratings yet
- From Equation C 1/vmax 2.225 Vmax 0.449 M Km/vmax 3.039 KM M Vmax 1.366Document7 pagesFrom Equation C 1/vmax 2.225 Vmax 0.449 M Km/vmax 3.039 KM M Vmax 1.366Umar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Tk01 Revised Assignment3Document131 pagesTk01 Revised Assignment3FauzulNo ratings yet
- Complete Process Flow Diagram: Ethene + Oxygen To Ethylene Oxide ReactionDocument1 pageComplete Process Flow Diagram: Ethene + Oxygen To Ethylene Oxide ReactiondoraNo ratings yet
- PHY 2042 Experiment #7Document3 pagesPHY 2042 Experiment #7Kelsey WNo ratings yet
- Estimates Differences T-T90 2010Document3 pagesEstimates Differences T-T90 2010Alexander MartinezNo ratings yet
- Grafik 6.3 Dan 6.5Document2 pagesGrafik 6.3 Dan 6.5FRANS WILLIAM S SNo ratings yet
- Regeri Linear PaperDocument2 pagesRegeri Linear PaperAsmull Nur KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Datos de Los Planos ResistentesDocument1 pageDatos de Los Planos ResistentesHans Sebastian Contreras RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CTM/CFPM FN 4/CfpmDocument2 pagesCTM/CFPM FN 4/CfpmKuo1018No ratings yet
- Iteration Process For RCC Analysis (Linear Analyzes Rotating Crack Method)Document6 pagesIteration Process For RCC Analysis (Linear Analyzes Rotating Crack Method)shams sultaniNo ratings yet
- Project BEM 92303Document12 pagesProject BEM 92303Jair BoulosNo ratings yet
- Tugas2 - Dwi Nur FebrinaDocument4 pagesTugas2 - Dwi Nur Febrinadwinurfebrina14No ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHR SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHR Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledLucas Hernández Karla BereniceNo ratings yet
- 阻力與推進HWDocument3 pages阻力與推進HWKuo1018No ratings yet
- RegresilinierotkDocument4 pagesRegresilinierotkRanti RahayuNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor PDFDocument29 pagesBatch Reactor PDFSaranya KannanNo ratings yet
- The Conductance of Strong and Weak ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesThe Conductance of Strong and Weak Electrolytessexycassie100% (6)
- sm1 061Document3 pagessm1 061Paulo Henrique D. FavarettoNo ratings yet
- Experiment #2: Parallel Plate Capacitors and Dielectric ConstantsDocument2 pagesExperiment #2: Parallel Plate Capacitors and Dielectric ConstantsMari KuljanishviliNo ratings yet
- Calculation Of Shrinkage Loss Material Properties: Res. Auto Sh. Strain (1-β) XεDocument3 pagesCalculation Of Shrinkage Loss Material Properties: Res. Auto Sh. Strain (1-β) XεVarun VermaNo ratings yet
- Freak G N Fproduk G N F GDocument8 pagesFreak G N Fproduk G N F GRifah Rizkiyah HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHG SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHG Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHQ SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHQ Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document9 pagesExperiment 7MahmoudSehweilNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document9 pagesTutorial 6yılmaz çepniNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Eadie (1942) Measured The Initial Reaction Rate of Hydrolysis of Acetylcholme (Substrate) byDocument6 pages2.5 Eadie (1942) Measured The Initial Reaction Rate of Hydrolysis of Acetylcholme (Substrate) byRoxan Bueno MoraNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Modul 4 Turbin Pelton-1Document3 pagesPerhitungan Modul 4 Turbin Pelton-1wahid argaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2 REHAN (New)Document6 pagesTugas 2 REHAN (New)시우민SeohyunNo ratings yet
- Volumen (V) Vs Conductividad (K)Document3 pagesVolumen (V) Vs Conductividad (K)Stevens LucasNo ratings yet
- Acon (Radial Thru-Hole) DKL SerieDocument2 pagesAcon (Radial Thru-Hole) DKL Seriexyz99No ratings yet
- Resistencias SMD WIN-1524917Document4 pagesResistencias SMD WIN-1524917Ignacio Barriga NuñezNo ratings yet
- SR Passives T910Document1 pageSR Passives T910Gato KurroNo ratings yet
- Penentuan Uji Kelarutan KTI ParacetamolDocument6 pagesPenentuan Uji Kelarutan KTI ParacetamolMinul1412No ratings yet
- Beryl (Radial Thru-Hole) RT SeriesDocument2 pagesBeryl (Radial Thru-Hole) RT Seriesester853No ratings yet
- Capa Panasonic Low EsrDocument5 pagesCapa Panasonic Low EsrClovis APOVONo ratings yet
- H2C204 Vs 1/tDocument2 pagesH2C204 Vs 1/tAdindaRezaOctaviaNo ratings yet
- P3D Sol1Document6 pagesP3D Sol1alvaro juro pomaNo ratings yet
- Room Temperature, K Substance N Density Literature Values Mpa.S Pa.S G/CM.SDocument11 pagesRoom Temperature, K Substance N Density Literature Values Mpa.S Pa.S G/CM.SJames Aaron SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Rizki UbaidillahDocument27 pagesCurriculum Vitae Rizki Ubaidillahfachri pesatNo ratings yet
- Plastic Moment Capacity - RevisedDocument19 pagesPlastic Moment Capacity - RevisedVishal NalwarNo ratings yet
- Using of Cavitation Disperser For Porous Ceramic and Concrete Material PreparationDocument4 pagesUsing of Cavitation Disperser For Porous Ceramic and Concrete Material PreparationmjunaidNo ratings yet
- 178-2019 - BS en IsoDocument32 pages178-2019 - BS en IsoVan Thu DangNo ratings yet
- Report WritingDocument24 pagesReport WritingVasudevanNo ratings yet
- The Slow Strain Rate Stress CorrosionDocument31 pagesThe Slow Strain Rate Stress CorrosionBehnam HosseinzaeiNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Three Phase Induction MotorDocument8 pagesThesis On Three Phase Induction Motorafknlbbnf100% (2)
- Jee 31dec2023 QP MorDocument10 pagesJee 31dec2023 QP MorphychemgodNo ratings yet
- Fluids ManualDocument10 pagesFluids ManualAngela Dimaano SaladaNo ratings yet
- A Cautionary Note On The Use of The Evans Method For Magnetic MeasurementsDocument1 pageA Cautionary Note On The Use of The Evans Method For Magnetic MeasurementskawtherahmedNo ratings yet
- Estimating The Probability of Mining Induced Seismic Events Using Mine Scale Inelastic Numerical MethodsDocument11 pagesEstimating The Probability of Mining Induced Seismic Events Using Mine Scale Inelastic Numerical MethodsJuan Andres Jarufe RavenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document24 pagesLecture 05ijaz fazilNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Unit 1,2Document7 pagesImportant Questions Unit 1,2rajeswariNo ratings yet
- Applications of Conductive Polymers As SensitizersDocument7 pagesApplications of Conductive Polymers As SensitizersCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Analytical Methods For Estimation of Metals: Shah Jignesh, Khanvilkar Vineeta, Shirode Abhay and Kadam VilasraoDocument18 pagesAnalytical Methods For Estimation of Metals: Shah Jignesh, Khanvilkar Vineeta, Shirode Abhay and Kadam VilasraoGRd JNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Bend Test of Reinforcing Steel BarsDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 - Bend Test of Reinforcing Steel BarsJaya Mae Mañago0% (1)
- Basic Electronics Objective Type QuestionsDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics Objective Type QuestionsParames WaranNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument16 pagesAnalysispatilayush1894No ratings yet
- 1.2379 en PDFDocument2 pages1.2379 en PDFVasileSpireaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Buoyancy PDFDocument25 pages5 - Buoyancy PDFFrenz VillasisNo ratings yet
- ZHF XPXN 0DC08 Omi 001-1Document110 pagesZHF XPXN 0DC08 Omi 001-1Online 4-lifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 560982adad40bDocument5 pagesChapter 3 560982adad40bJimson MasculinoNo ratings yet
- 2SD357Document2 pages2SD357bambuga07No ratings yet
- Bathnagar Et Al 2016Document13 pagesBathnagar Et Al 2016Marcelo CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Chemfix 11 Water ProofingDocument2 pagesChemfix 11 Water ProofingSheikh BeryalNo ratings yet
- Ultra-low-Cycle Fatigue Failure of Metal Structures Under Strong EarthquakesDocument231 pagesUltra-low-Cycle Fatigue Failure of Metal Structures Under Strong EarthquakesYarielNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science11 - Q1 - MODULE-5 EDITED - 08082020Document23 pagesPhysical-Science11 - Q1 - MODULE-5 EDITED - 08082020Sergio AgnerNo ratings yet
Material Science
Material Science
Uploaded by
AnneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Material Science
Material Science
Uploaded by
AnneCopyright:
Available Formats
17.
7 solution
i)Normalizing: Heating at least 55°C above the upper critical temperature, and above
Acm for compositions greater than the eutectoid. After sufficient time has been allowed
for the alloy to completely transform to austenite which is a treatment terminated by
cooling in air. Finally, the microstructural product of this treatment is fine pearlite
ii)Full annealing: Heat to about 50°C until the alloy comes to equilibrium, and both
furnace cooled and steel cool to room temperature at the same rate. Finally, the
microstructural product of this anneal is coarse pearlite that is relatively soft and
ductile.
iii)Quenching: Heat to a temperature within the austenite phase region and allow the
specimen to austenitize, then quench to room temperature in oil or water. Finally, the
microstructural product of this anneal is martensite.
iv)Tempering: Heat a quenched specimen to a temperature in a jet of air or, in some
case, in oil bath until the time to the desired hardness. Finally, the microstructural
product of this anneal is martensite. Finally, the microstructural product of this
treatment is tempered martensite.
17.10 solution
a)For 0.2wt % C , heat to about 990°C since the A3 temperature is 830°C
b)For 0.5wt % C , heat to about 820°C since the A3 temperature is 765°C
c)For 1.15wt % C , heat to about 775°C since the A3 temperature is 725°C
17.23 solution
The softening point of a glass is that temperature at which the viscosity is
4 ×106 (Pa . s), these temperature for the 96% silica, borosilicate, and soda-lime
glasses are 1550°C, 840°C, 700°C, correspondingly.
17.24 solution
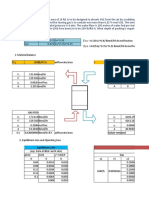
1/T viscosity T
0.002 31.084 500
0.001818 27.63 550
0.00167 25.33 600
0.00143 20.72 700
0.00125 16.11 800
0.00111 12.66 900
lnµ versus 1/T
35
30
25
20
lnµ
15
10
5
0
0.001 0.0012 0.0014 0.0016 0.0018 0.002 0.0022
1/T
8.3145 J
Qvis =slope × R=( ) slope
mol . K
Qvis =
∆T
= (
mol . K ∆T )
R ( ∆ lnμ ) 8.3145 J ( ∆ lnμ )
Therefore,
Qvis =
( mol . K )
8.3145 J
( 31.084−12.66 )
=
172 KJ
0.002−0.00111 mol
You might also like
- Propeller Design CalculationDocument8 pagesPropeller Design CalculationDave Carter100% (7)
- 004 - Efficient Foam ProductionDocument122 pages004 - Efficient Foam ProductionNo Promises71% (7)
- Practice Problem Machine DesignDocument10 pagesPractice Problem Machine DesignVishak Regu100% (2)
- Cmos Process FlowDocument29 pagesCmos Process FlowPushparaj Karu100% (1)
- ASTM F606-02 - Propiedades Mecanicas TornillosDocument14 pagesASTM F606-02 - Propiedades Mecanicas TornillosedwinsazzzNo ratings yet
- Conductoare Neizolate Din Al: Po (KW) PSCC (KW)Document5 pagesConductoare Neizolate Din Al: Po (KW) PSCC (KW)Ciprian ApalaghițeiNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Iodin NumberDocument268 pagesPerhitungan Iodin NumberrusydianaabdNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument16 pagesHeat ExchangersiosuarizNo ratings yet
- Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger: Parallel FlowDocument24 pagesConcentric Tube Heat Exchanger: Parallel FlowFalcon KingdomNo ratings yet
- DBP RitDocument9 pagesDBP RitTuyú Amaro Aldo MauricioNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic AccelorometerDocument58 pagesElectrostatic AccelorometerShah HussainNo ratings yet
- Termo Lampiran 4Document16 pagesTermo Lampiran 4Anyberta Dwi ListyantiNo ratings yet
- No P/Kpa X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Ɣ1 Ɣ2 LN (Ɣ1) LN (Ɣ2) Ge/Rt Ge/Rtx1X2Document1 pageNo P/Kpa X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Ɣ1 Ɣ2 LN (Ɣ1) LN (Ɣ2) Ge/Rt Ge/Rtx1X2Gladys ElvinaNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan EsterDocument6 pagesPerhitungan EsteralfinNo ratings yet
- KSL - Theo Vs KSL - Expt: N (RPS)Document1 pageKSL - Theo Vs KSL - Expt: N (RPS)Krishnakant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHX SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHX Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- Beryl (Radial Thru-Hole) RG SeriesDocument2 pagesBeryl (Radial Thru-Hole) RG Seriesester853No ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHY SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHY Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- 2023 TPM351ppyDocument7 pages2023 TPM351ppyJenyver LappyNo ratings yet
- PorticosDocument87 pagesPorticosJorge Aurelio Menacho YanacNo ratings yet
- Exercises On ELECTRICAL MACHINESDocument29 pagesExercises On ELECTRICAL MACHINESDavide100% (1)
- LOU2 Labo 6 para Mi Bello Marco Que Hara Bien Los AnexosDocument5 pagesLOU2 Labo 6 para Mi Bello Marco Que Hara Bien Los AnexosJuan Jose LlamoccaNo ratings yet
- LOU2 Labo 6Document5 pagesLOU2 Labo 6Juan Jose LlamoccaNo ratings yet
- From Equation C 1/vmax 2.225 Vmax 0.449 M Km/vmax 3.039 KM M Vmax 1.366Document7 pagesFrom Equation C 1/vmax 2.225 Vmax 0.449 M Km/vmax 3.039 KM M Vmax 1.366Umar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Tk01 Revised Assignment3Document131 pagesTk01 Revised Assignment3FauzulNo ratings yet
- Complete Process Flow Diagram: Ethene + Oxygen To Ethylene Oxide ReactionDocument1 pageComplete Process Flow Diagram: Ethene + Oxygen To Ethylene Oxide ReactiondoraNo ratings yet
- PHY 2042 Experiment #7Document3 pagesPHY 2042 Experiment #7Kelsey WNo ratings yet
- Estimates Differences T-T90 2010Document3 pagesEstimates Differences T-T90 2010Alexander MartinezNo ratings yet
- Grafik 6.3 Dan 6.5Document2 pagesGrafik 6.3 Dan 6.5FRANS WILLIAM S SNo ratings yet
- Regeri Linear PaperDocument2 pagesRegeri Linear PaperAsmull Nur KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Datos de Los Planos ResistentesDocument1 pageDatos de Los Planos ResistentesHans Sebastian Contreras RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CTM/CFPM FN 4/CfpmDocument2 pagesCTM/CFPM FN 4/CfpmKuo1018No ratings yet
- Iteration Process For RCC Analysis (Linear Analyzes Rotating Crack Method)Document6 pagesIteration Process For RCC Analysis (Linear Analyzes Rotating Crack Method)shams sultaniNo ratings yet
- Project BEM 92303Document12 pagesProject BEM 92303Jair BoulosNo ratings yet
- Tugas2 - Dwi Nur FebrinaDocument4 pagesTugas2 - Dwi Nur Febrinadwinurfebrina14No ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHR SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHR Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledLucas Hernández Karla BereniceNo ratings yet
- 阻力與推進HWDocument3 pages阻力與推進HWKuo1018No ratings yet
- RegresilinierotkDocument4 pagesRegresilinierotkRanti RahayuNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor PDFDocument29 pagesBatch Reactor PDFSaranya KannanNo ratings yet
- The Conductance of Strong and Weak ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesThe Conductance of Strong and Weak Electrolytessexycassie100% (6)
- sm1 061Document3 pagessm1 061Paulo Henrique D. FavarettoNo ratings yet
- Experiment #2: Parallel Plate Capacitors and Dielectric ConstantsDocument2 pagesExperiment #2: Parallel Plate Capacitors and Dielectric ConstantsMari KuljanishviliNo ratings yet
- Calculation Of Shrinkage Loss Material Properties: Res. Auto Sh. Strain (1-β) XεDocument3 pagesCalculation Of Shrinkage Loss Material Properties: Res. Auto Sh. Strain (1-β) XεVarun VermaNo ratings yet
- Freak G N Fproduk G N F GDocument8 pagesFreak G N Fproduk G N F GRifah Rizkiyah HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHG SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHG Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- Decon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHQ SeriesDocument2 pagesDecon (Radial Thru-Hole) SHQ Serieszuigh899gNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document9 pagesExperiment 7MahmoudSehweilNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document9 pagesTutorial 6yılmaz çepniNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Eadie (1942) Measured The Initial Reaction Rate of Hydrolysis of Acetylcholme (Substrate) byDocument6 pages2.5 Eadie (1942) Measured The Initial Reaction Rate of Hydrolysis of Acetylcholme (Substrate) byRoxan Bueno MoraNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Modul 4 Turbin Pelton-1Document3 pagesPerhitungan Modul 4 Turbin Pelton-1wahid argaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2 REHAN (New)Document6 pagesTugas 2 REHAN (New)시우민SeohyunNo ratings yet
- Volumen (V) Vs Conductividad (K)Document3 pagesVolumen (V) Vs Conductividad (K)Stevens LucasNo ratings yet
- Acon (Radial Thru-Hole) DKL SerieDocument2 pagesAcon (Radial Thru-Hole) DKL Seriexyz99No ratings yet
- Resistencias SMD WIN-1524917Document4 pagesResistencias SMD WIN-1524917Ignacio Barriga NuñezNo ratings yet
- SR Passives T910Document1 pageSR Passives T910Gato KurroNo ratings yet
- Penentuan Uji Kelarutan KTI ParacetamolDocument6 pagesPenentuan Uji Kelarutan KTI ParacetamolMinul1412No ratings yet
- Beryl (Radial Thru-Hole) RT SeriesDocument2 pagesBeryl (Radial Thru-Hole) RT Seriesester853No ratings yet
- Capa Panasonic Low EsrDocument5 pagesCapa Panasonic Low EsrClovis APOVONo ratings yet
- H2C204 Vs 1/tDocument2 pagesH2C204 Vs 1/tAdindaRezaOctaviaNo ratings yet
- P3D Sol1Document6 pagesP3D Sol1alvaro juro pomaNo ratings yet
- Room Temperature, K Substance N Density Literature Values Mpa.S Pa.S G/CM.SDocument11 pagesRoom Temperature, K Substance N Density Literature Values Mpa.S Pa.S G/CM.SJames Aaron SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Rizki UbaidillahDocument27 pagesCurriculum Vitae Rizki Ubaidillahfachri pesatNo ratings yet
- Plastic Moment Capacity - RevisedDocument19 pagesPlastic Moment Capacity - RevisedVishal NalwarNo ratings yet
- Using of Cavitation Disperser For Porous Ceramic and Concrete Material PreparationDocument4 pagesUsing of Cavitation Disperser For Porous Ceramic and Concrete Material PreparationmjunaidNo ratings yet
- 178-2019 - BS en IsoDocument32 pages178-2019 - BS en IsoVan Thu DangNo ratings yet
- Report WritingDocument24 pagesReport WritingVasudevanNo ratings yet
- The Slow Strain Rate Stress CorrosionDocument31 pagesThe Slow Strain Rate Stress CorrosionBehnam HosseinzaeiNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Three Phase Induction MotorDocument8 pagesThesis On Three Phase Induction Motorafknlbbnf100% (2)
- Jee 31dec2023 QP MorDocument10 pagesJee 31dec2023 QP MorphychemgodNo ratings yet
- Fluids ManualDocument10 pagesFluids ManualAngela Dimaano SaladaNo ratings yet
- A Cautionary Note On The Use of The Evans Method For Magnetic MeasurementsDocument1 pageA Cautionary Note On The Use of The Evans Method For Magnetic MeasurementskawtherahmedNo ratings yet
- Estimating The Probability of Mining Induced Seismic Events Using Mine Scale Inelastic Numerical MethodsDocument11 pagesEstimating The Probability of Mining Induced Seismic Events Using Mine Scale Inelastic Numerical MethodsJuan Andres Jarufe RavenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document24 pagesLecture 05ijaz fazilNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Unit 1,2Document7 pagesImportant Questions Unit 1,2rajeswariNo ratings yet
- Applications of Conductive Polymers As SensitizersDocument7 pagesApplications of Conductive Polymers As SensitizersCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Analytical Methods For Estimation of Metals: Shah Jignesh, Khanvilkar Vineeta, Shirode Abhay and Kadam VilasraoDocument18 pagesAnalytical Methods For Estimation of Metals: Shah Jignesh, Khanvilkar Vineeta, Shirode Abhay and Kadam VilasraoGRd JNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Bend Test of Reinforcing Steel BarsDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 - Bend Test of Reinforcing Steel BarsJaya Mae Mañago0% (1)
- Basic Electronics Objective Type QuestionsDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics Objective Type QuestionsParames WaranNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument16 pagesAnalysispatilayush1894No ratings yet
- 1.2379 en PDFDocument2 pages1.2379 en PDFVasileSpireaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Buoyancy PDFDocument25 pages5 - Buoyancy PDFFrenz VillasisNo ratings yet
- ZHF XPXN 0DC08 Omi 001-1Document110 pagesZHF XPXN 0DC08 Omi 001-1Online 4-lifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 560982adad40bDocument5 pagesChapter 3 560982adad40bJimson MasculinoNo ratings yet
- 2SD357Document2 pages2SD357bambuga07No ratings yet
- Bathnagar Et Al 2016Document13 pagesBathnagar Et Al 2016Marcelo CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Chemfix 11 Water ProofingDocument2 pagesChemfix 11 Water ProofingSheikh BeryalNo ratings yet
- Ultra-low-Cycle Fatigue Failure of Metal Structures Under Strong EarthquakesDocument231 pagesUltra-low-Cycle Fatigue Failure of Metal Structures Under Strong EarthquakesYarielNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science11 - Q1 - MODULE-5 EDITED - 08082020Document23 pagesPhysical-Science11 - Q1 - MODULE-5 EDITED - 08082020Sergio AgnerNo ratings yet