Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sustainable Construction - 5
Sustainable Construction - 5
Uploaded by
visanu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThe document discusses sustainable design and construction procedures for a project. It outlines that project managers should discuss opportunities to design out waste and minimize resource use with architects. It also states that an Environmental Management Plan (EMP) and Site Waste Management Plan (SWMP) must be produced. The SWMP should include details of decisions that impact waste management at various stages, including material selection, construction methods, and post-completion review.
Original Description:
Original Title
221732359-Sustainable-Construction_5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses sustainable design and construction procedures for a project. It outlines that project managers should discuss opportunities to design out waste and minimize resource use with architects. It also states that an Environmental Management Plan (EMP) and Site Waste Management Plan (SWMP) must be produced. The SWMP should include details of decisions that impact waste management at various stages, including material selection, construction methods, and post-completion review.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageSustainable Construction - 5
Sustainable Construction - 5
Uploaded by
visanuThe document discusses sustainable design and construction procedures for a project. It outlines that project managers should discuss opportunities to design out waste and minimize resource use with architects. It also states that an Environmental Management Plan (EMP) and Site Waste Management Plan (SWMP) must be produced. The SWMP should include details of decisions that impact waste management at various stages, including material selection, construction methods, and post-completion review.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
7.
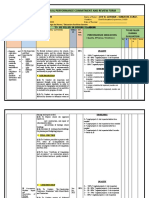
3 Design and procurement
Project Manager’s should discuss with architects/developers what
opportunities exist to design out waste and minimise use of natural resources.
Energy management is a priority and a summary of the University’s
requirements are in Appendix H. The EMP must be produced. The SWMP
should include details of decisions that impact on waste management,
including those on:
1. Materials use:
Design specifications
Materials used
Method of construction
Logistics (site layout/storage/delivery)
2. Approach to material resource efficiency:
Design & Site design & Construction Post-completion
conception tendering phases (principal contractor
(client in conjunction (client in (principal and, for lessons
conjunction with conjunction with contractor, in learnt, all parties)
designers &
planners)
designers, planners
and, once
conjunction with all
contractors on site)
• Reconcile final
waste data with
• Consider waste appointed, the
principal contractor)
• Regular tool box SWMP
efficient materials
• Draft SWMP
talks • Calculate
& methods of
construction identifying waste
• Adequate resource savings
types
ordering, delivery,
and storage of
• Apply lessons
• Record design materials
learnt for future
projects
stage
considerations
• Update SWMP as
waste is processed
• Build waste or removed
management
targets into tender
specifications
7.4 Pre-construction
The SWMP must identify and record the amount of waste produced from
Decant and Demolition activities and include estimates of the amount of waste
to be managed.
7.5 Construction
The Principal Contractor is responsible for managing risk on the site and
updating the EMP and SWMP. These documents will form part of site audits.
7.6 Post construction/occupation
The Project Team should review the project and this should include:
Completion of EMP and SWMP;
6 Sustainable Construction
Vers 1.0 17.10.08
When printed this document is UNCONTROLLED
You might also like
- Renault LoganDocument25 pagesRenault LoganMukul AttriNo ratings yet
- Trial Agreement 1-2022Document4 pagesTrial Agreement 1-2022api-589951233No ratings yet
- Rtcmd-Esu Oct 4 2016 PDFDocument9 pagesRtcmd-Esu Oct 4 2016 PDFVic ValdezNo ratings yet
- L7 - Production Management and Work PlanningDocument45 pagesL7 - Production Management and Work PlanningtyuNo ratings yet
- Builders PlantDocument29 pagesBuilders PlantJulaida KaliwonNo ratings yet
- Material Logistics Plan: Step Title Supporting Section in The Further Information and Checklist' DocumentDocument20 pagesMaterial Logistics Plan: Step Title Supporting Section in The Further Information and Checklist' DocumentchristopherNo ratings yet
- 1 - Manajemen ProyekDocument38 pages1 - Manajemen Proyekstudio electNo ratings yet
- CV SampleDocument4 pagesCV SampleCG Nepali BabuNo ratings yet
- Design of Underground Structures PDFDocument49 pagesDesign of Underground Structures PDFHaftom GebreegziabiherNo ratings yet
- ResumeH SHAHULHAMEEDDocument5 pagesResumeH SHAHULHAMEEDalbaraaabgmNo ratings yet
- MANCOM PRESENTATION Sept.27,2021-PLANNINGDocument13 pagesMANCOM PRESENTATION Sept.27,2021-PLANNINGDennisNo ratings yet
- Unit 22, Group 2 Project ProposalDocument10 pagesUnit 22, Group 2 Project ProposalXiao QiangNo ratings yet
- Stage - Plan Through DeployDocument18 pagesStage - Plan Through DeployDebayan RayNo ratings yet
- Complete Prof Prac ReviewerDocument13 pagesComplete Prof Prac ReviewerDaphne Ann Athena DacibarNo ratings yet
- Alaa CVDocument3 pagesAlaa CVmralghamdiali89No ratings yet
- Job Planning and ControlDocument27 pagesJob Planning and ControlIfeoluwa DareNo ratings yet
- Sec03 - Duties and ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pagesSec03 - Duties and ResponsibilitiesYusufNo ratings yet
- JobsDocument6 pagesJobsFaquruddinNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 Site Supervision and Safety Management in Construction NotesDocument16 pagesTOPIC 3 Site Supervision and Safety Management in Construction NotesF2043 AMMAR AZ-ZHAFRI BIN ABDUL HALIMNo ratings yet
- 0 Construction DocumentsDocument11 pages0 Construction DocumentsJibwa100% (7)
- Basic Knowledge in Construction ManagementDocument32 pagesBasic Knowledge in Construction ManagementKhaing SuNo ratings yet
- The Building Team: DR Alice LunguDocument18 pagesThe Building Team: DR Alice LunguAlice S LunguNo ratings yet
- Job Description of Structural Design Engineer - CivilDocument4 pagesJob Description of Structural Design Engineer - CivilJimit PayNo ratings yet
- Duties & Service (259)Document13 pagesDuties & Service (259)Nor Nadhirah NadzreyNo ratings yet
- CS09 - Software ArchitectureDocument31 pagesCS09 - Software ArchitectureKunal RatnaparkhiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Ni Sir Mej Kulang Ata Ako NG SS SorryDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Ni Sir Mej Kulang Ata Ako NG SS SorryNeil Patrick PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Planning of Farm StructuresDocument9 pagesPlanning of Farm StructuresCt Kamariah Md SaatNo ratings yet
- Course Abstract - DEDocument11 pagesCourse Abstract - DEAnurag VaghelaNo ratings yet
- Challenge in Implementing Mega Scale and Complex ProjectsDocument30 pagesChallenge in Implementing Mega Scale and Complex ProjectsRashmita SahuNo ratings yet
- Cut & Bend RebarsDocument16 pagesCut & Bend RebarsParam SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Steps of A ProjectDocument30 pagesSteps of A ProjectNihar MandalNo ratings yet
- Construction Project Management-Organisation Structure-Ahmedabad-CEPT UNIVERSITYDocument13 pagesConstruction Project Management-Organisation Structure-Ahmedabad-CEPT UNIVERSITYRahul Sompura92% (25)
- HV/MV Onshore/offshore Substation Manager: Reporting To RoleDocument1 pageHV/MV Onshore/offshore Substation Manager: Reporting To RoleWilliam CoreyNo ratings yet
- Presentacion Construccion FundamentalsDocument76 pagesPresentacion Construccion FundamentalsRicardo GuadianaNo ratings yet
- Construction: ProcessDocument6 pagesConstruction: Processslamet suryantoNo ratings yet
- IU BIM Execution Plan TemplateDocument12 pagesIU BIM Execution Plan TemplateAyman KandeelNo ratings yet
- Exam Guide: Programming, Planning & PracticeDocument13 pagesExam Guide: Programming, Planning & PracticeCamille CiokonNo ratings yet
- Effective Work PackageDocument10 pagesEffective Work PackageMikhail HannaNo ratings yet
- Part 1construction Methods and Project ManagementDocument82 pagesPart 1construction Methods and Project ManagementHonorio Joshua P.No ratings yet
- Hany Elmohmady - Senior Site Civil Engineer CVDocument2 pagesHany Elmohmady - Senior Site Civil Engineer CVHany El-mohmadyNo ratings yet
- ResumeAsamehHaider PDFDocument3 pagesResumeAsamehHaider PDFJenniferNo ratings yet
- PPP Exam GuideDocument15 pagesPPP Exam GuideESwar KarthikNo ratings yet
- CVL412 - ProjManagProcess WEEK 2 RLairdDocument49 pagesCVL412 - ProjManagProcess WEEK 2 RLairdIlyaas OsmanNo ratings yet
- K-3b. Nitin Ramkrushna Nandanwar - WW EngineerDocument8 pagesK-3b. Nitin Ramkrushna Nandanwar - WW EngineerharendraNo ratings yet
- DFS Awareness JTCDocument33 pagesDFS Awareness JTClim kang haiNo ratings yet
- Construction Process: by Syed Burhanuddin Hilmi Syed MohamadDocument61 pagesConstruction Process: by Syed Burhanuddin Hilmi Syed MohamadIzzati HamidNo ratings yet
- ABS MODU Jan 2018 Part 3Document5 pagesABS MODU Jan 2018 Part 3Hisham TariqNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Job Description Directory (To-Be) : Reliance Industries LimitedDocument6 pages6.6 Job Description Directory (To-Be) : Reliance Industries Limitedsatyamech1_395565923No ratings yet
- RC Building Design ProjectDocument21 pagesRC Building Design ProjectMuhd MuqhreyNo ratings yet
- ARCH804 - Workshop 3Document31 pagesARCH804 - Workshop 3Allen GaoNo ratings yet
- Quality Management in Const PDFDocument42 pagesQuality Management in Const PDFBernard OctavianusNo ratings yet
- Offsite PM Handout RIBA Plan of Work Stages OverviewDocument2 pagesOffsite PM Handout RIBA Plan of Work Stages OverviewMohamed ElkashifNo ratings yet
- Outline: Engr. Nico E. FunaDocument7 pagesOutline: Engr. Nico E. FunaSofia GarciaNo ratings yet
- DED Session 6 - Cost EstimateDocument54 pagesDED Session 6 - Cost EstimateNiño Gerard AdigueNo ratings yet
- General Objectives of Phase: Schematic DesignDocument6 pagesGeneral Objectives of Phase: Schematic DesignRashad AbdelhyNo ratings yet
- Practice Notes FOR Quantity Surveyors: Pre-Contract Estimates and Cost PlansDocument7 pagesPractice Notes FOR Quantity Surveyors: Pre-Contract Estimates and Cost PlansShahrirNo ratings yet
- Chapter4.1 - Project Management ProcessDocument21 pagesChapter4.1 - Project Management ProcessRafiqah AbdillahNo ratings yet
- 4D Modeling VDC CertificateDocument24 pages4D Modeling VDC Certificatem_925No ratings yet
- Water Recycling - London - Kern - LorisDocument13 pagesWater Recycling - London - Kern - LorisYu ChenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - CM - 2072Document39 pagesChapter 2 - CM - 2072Subash PoudelNo ratings yet
- Design Construction Manual2002 - 10Document1 pageDesign Construction Manual2002 - 10visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 2Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 2visanuNo ratings yet
- Design Construction Manual2002 - 6Document1 pageDesign Construction Manual2002 - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 6Document1 pageBentonite 6visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 7Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 7visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 1Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 8Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 8visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 4Document1 pageBentonite 4visanuNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Basics - 6Document1 pageCommunication Skills Basics - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 3Document1 pageBentonite 3visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 15Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 15visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 1Document1 pageBentonite 1visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 4visanuNo ratings yet
- Bentonite 2Document1 pageBentonite 2visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 6Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 6visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 1visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 2visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 5Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 5visanuNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3Document1 pageANALYSIS & DESIGN - Chen, Duan, Bridge Engineering Handbook, (CRC 1999) - 3visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 13Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 13visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 14Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 14visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 10Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 10visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 11Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 11visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 12Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 12visanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering - 9Document1 pageBasic Civil Engineering - 9visanu100% (1)
- Public Etendering in The European Union. Trust in Evolution.Document28 pagesPublic Etendering in The European Union. Trust in Evolution.Nicky SantoroNo ratings yet
- Fashion Merchandising: Sourcing: AbstractDocument12 pagesFashion Merchandising: Sourcing: AbstractNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- 9 HagerServiceDocument10 pages9 HagerServiceNedim HadžiaganovićNo ratings yet
- MNC Involving in Agricultural Production in Developing CountriesDocument32 pagesMNC Involving in Agricultural Production in Developing CountriesHoang Daoo0% (1)
- Iraq Pharmaceuticals Market OpportunitiesDocument4 pagesIraq Pharmaceuticals Market Opportunitiesneerleo50% (2)
- Purchasing: Meaning Aand Definition of PurchasingDocument6 pagesPurchasing: Meaning Aand Definition of PurchasingShahl kvNo ratings yet
- IML601 (Chap 10)Document20 pagesIML601 (Chap 10)SITINUR SAAIDAH MOHAMADNo ratings yet
- Role of Project Leadership and Communication in KenyaDocument13 pagesRole of Project Leadership and Communication in KenyaBruce Uluma Sr.No ratings yet
- Successful Buyer-Supplier Relationships: The Role of NegotiationsDocument17 pagesSuccessful Buyer-Supplier Relationships: The Role of NegotiationsSasha KingNo ratings yet
- Mekelle University College of Business and EconomicsDocument50 pagesMekelle University College of Business and Economicsayele eshete100% (1)
- CPSM BrochureDocument13 pagesCPSM BrochureRAHUL SINGH100% (1)
- TOR-Transfer of Requirement Q&ADocument7 pagesTOR-Transfer of Requirement Q&Ar kNo ratings yet
- Brochure PGD SCMDocument7 pagesBrochure PGD SCMMatthew MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- Procurement Engineer Resume Samples - Velvet JobsDocument37 pagesProcurement Engineer Resume Samples - Velvet JobsNitin VermaNo ratings yet
- 5 Mic FilterDocument6 pages5 Mic FilterGunwant VarmaNo ratings yet
- Ind AS 115Document36 pagesInd AS 115yashNo ratings yet
- Purchasing and Supply Management 14th Edition Johnson Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesPurchasing and Supply Management 14th Edition Johnson Solutions Manualtroyshahqarcdmwijt100% (13)
- 4 Nature of Industrial BuyingDocument21 pages4 Nature of Industrial BuyingSachin Hundekar100% (1)
- Problems and Prospects of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME's) in IndiaDocument22 pagesProblems and Prospects of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME's) in IndiaAmol LahaneNo ratings yet
- PhilGEPS RA 9184 (Latest)Document82 pagesPhilGEPS RA 9184 (Latest)ejanelagat100% (2)
- Procurement Law Primer v1-9Document213 pagesProcurement Law Primer v1-9john thos. brownNo ratings yet
- Technical Bid InstructionsDocument29 pagesTechnical Bid InstructionsAmydchic100% (1)
- PROCUREMENTDocument100 pagesPROCUREMENTtinsae mulatu92% (12)
- Ipcrf 2023Document8 pagesIpcrf 2023MARY JERICA OCUPENo ratings yet
- Pas 7000-2014Document72 pagesPas 7000-2014Jose LopezNo ratings yet
- Min Quotation CurrentDocument5 pagesMin Quotation CurrentbarakaNo ratings yet
- Site Administration and ControlDocument43 pagesSite Administration and Controlशर्मा अविनाशNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment 1111Document30 pagesAcknowledgment 1111Alfan KotadiaNo ratings yet