Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
kath bernardo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesGlimepiride is an oral hypoglycemic drug used to treat type 2 diabetes. It works by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin and by increasing the sensitivity of cells to insulin. Common side effects include hypoglycemia, nausea, and skin reactions. Nurses monitor blood glucose levels, educate patients about signs of hypoglycemia, and ensure proper administration with meals to prevent low blood sugar. Drug interactions can increase or decrease its hypoglycemic effects, so blood glucose monitoring is important when taking other medications.
Original Description:
Original Title
DRUG-STUDY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGlimepiride is an oral hypoglycemic drug used to treat type 2 diabetes. It works by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin and by increasing the sensitivity of cells to insulin. Common side effects include hypoglycemia, nausea, and skin reactions. Nurses monitor blood glucose levels, educate patients about signs of hypoglycemia, and ensure proper administration with meals to prevent low blood sugar. Drug interactions can increase or decrease its hypoglycemic effects, so blood glucose monitoring is important when taking other medications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesDrug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
kath bernardoGlimepiride is an oral hypoglycemic drug used to treat type 2 diabetes. It works by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin and by increasing the sensitivity of cells to insulin. Common side effects include hypoglycemia, nausea, and skin reactions. Nurses monitor blood glucose levels, educate patients about signs of hypoglycemia, and ensure proper administration with meals to prevent low blood sugar. Drug interactions can increase or decrease its hypoglycemic effects, so blood glucose monitoring is important when taking other medications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
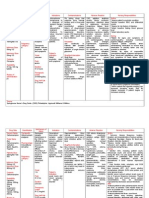
Generic Name Glimepiride
Picture
Brand Name Amaryl
Classification Oral Hypoglycemic Agent, Sulfonylureas
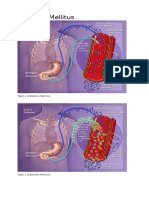
Mode of Action Stimulates the beta cells of the pancreas to increase release of
insulin. It also increases sensitivity of peripheral insulin
receptors, which increase insulin binding in the peripheral
tissues
Ordered Dosage
Adult [PO]
Initial: 1 mg daily
May increase in increments of 1 mg at intervals of 1-2
weeks according to response.
Maintenance: 4mg/day
Max: 6mg/day
Elderly
Initial: 1mg once daily
Indications Type 2 Diabetes mellitus
Contraindications Renal Impairment
Hepatic Impairment
Hypersensitivity
Type 1 diabetes or Insulin-dependent diabetes
Diabetic ketoacidosis (with or without coma)
Side Effects nausea,
upset stomach,
stomach pain,
vomiting,
diarrhea,
dizziness,
headache,
tiredness,
increased skin sensitivity to sunlight,
itching, or
skin rash.
Adverse Effects Significant:
o Hypoglycaemia, haemolytic anaemia (in G6PD
deficiency), hypersensitivity reaction (e.g.
anaphylaxis, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson
syndrome), weight gain.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
o Leukopenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia,
pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Endocrine disorders: Inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
secretion (SIADH).
Eye disorders: Visual disturbances.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Abdominal pain, diarrhoea,
nausea, vomiting, dysgeusia.
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Asthenia
Hepatobiliary disorders: Cholestasis, jaundice, hepatitis,
liver failure, hepatic porphyria.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Disulfiram-like
reactions, hyponatraemia.
Nervous system disorders: Headache, dizziness.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Photosensitivity,
alopecia.
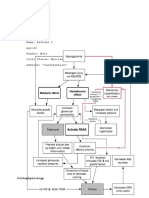
Drug Interactions Increased hypoglycaemic effect with:
NSAIDs (e.g. phenylbutazone),
insulin, oral antidiabetics (e.g. metformin),
salicylates, fluoxetine, anabolic steroids and androgens,
antibiotics (e.g. chloramphenicol, sulphonamides,
tetracyclines, quinolones, clarithromycin)
coumarin anticoagulants, disopyramide, fibrates, ACE
inhibitors, MAOIs, allopurinol, probenecid,
sulfinpyrazone, cyclophosphamide, fluconazole and
pentoxifylline.
Decreased hypoglycaemic effect with:
oestrogens, oral contraceptives
thiazide diuretics
glucocorticoids
phenothiazine derivatives (e.g. chlorpromazine)
sympathomimetics (e.g. epinephrine, albuterol,
terbutaline)
nicotinic acid (high doses) and nicotinic acid derivatives,
laxative (long term use),
phenytoin, diazoxide, glucagon, barbiturates, rifampicin
and isoniazid.
Signs of hypoglycaemia may be reduced or absent in
patients taking sympatholytic drugs (e.g. ß-blockers,
clonidine, guanethidine, reserpine).
May cause severe hypoglycaemia with miconazole.
Nursing Responsibilities 1. Instruct client to take the drug 15 to 30 minutes before
meals, do not take medication and skip meals
2. Monitor blood glucose levels daily
3. Teach client to maintain weight and dietary restrictions
along with medication.
4. Call the doctor for signs of hypoglycemia (fatigue,
hunger, cool moist skin, increase anxiety, dizziness, and
palpitations.)
5. Monitor urine or serum glucose levels frequently to
determine effectiveness of drug and dosage being used.
6. WARNING: Transfer to insulin therapy during periods of
high stress (eg, infections, surgery, trauma).
7. Use IV glucose if severe hypoglycemia occurs as a
result of overdose.
8. Arrange for consultation with dietitian to establish weight-
loss program and dietary control.
9. Arrange for thorough diabetic teaching program,
including disease, dietary control, exercise, signs and
symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia,
avoidance of infection, hygiene
10. Avoid alcohol while using this drug.
Reference Cunha, J.P. (2018). Amaryl side effects center. RxList.
Retrieved from www.rxlist.com/amaryl-side-effects-drug-
center on September 21, 2020
RNpedia. Glimepiride nursing considerations & management.
Retrieved from
www.rnpedia.com/nursing-notes/pharmacology-drug-
study-notes/glimepiride/ from September 21, 2020
MIMS Philippines. (2020). Glimepiride. Retrieved from
www.mimsonline.com.ph on September 21, 2020
You might also like
- ER Nurse ChecklistDocument3 pagesER Nurse Checklistdocpanchu100% (1)
- MeningitisDocument9 pagesMeningitisNader Smadi88% (8)
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 pagesDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- GlipizideDocument2 pagesGlipizideFeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Obat Antijamur Dan Antihistamin: Dr. Elly Usman, M.Si, AptDocument17 pagesObat Antijamur Dan Antihistamin: Dr. Elly Usman, M.Si, AptChindyNo ratings yet
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsVal Ian Palmes SumampongNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyDiana Laura LeiNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument2 pagesGliclazideReinell GoNo ratings yet
- 7-Lipid DisorderDocument6 pages7-Lipid DisorderApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On PtuDocument4 pagesDrug Study On PtuDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaria Charlene Orpilla0% (1)
- GlimepirideDocument3 pagesGlimepirideapi-3797941100% (1)
- HTTPDocument3 pagesHTTPChon 앙드레 BalanayNo ratings yet
- Ncp&drugstudDocument12 pagesNcp&drugstudSarah Mae Billano BermudezNo ratings yet
- DS Drug METFORMINDocument4 pagesDS Drug METFORMINAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- METFORMINDocument4 pagesMETFORMINkhesler BacallaNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Sheet1Document7 pagesPharma Sheet1Lyssa ShannenNo ratings yet
- Drug Name General Action Specific Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResDocument9 pagesDrug Name General Action Specific Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- ClonazepamDocument3 pagesClonazepamapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Doctor's Order Levodopa +carbidopa 250mg/25mg 1 Tab BIDDocument25 pagesDoctor's Order Levodopa +carbidopa 250mg/25mg 1 Tab BIDspain michaelisNo ratings yet
- Insulin and Oral HypoglycemicsDocument38 pagesInsulin and Oral HypoglycemicsEdwin GithogeNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Complete Albendazole Information From DrugsDocument4 pagesComplete Albendazole Information From DrugselephantynoseNo ratings yet
- Glimepiride Drug StudyDocument2 pagesGlimepiride Drug StudydyndzNo ratings yet
- Specific Drug Olanzapine (Classification IndicationDocument14 pagesSpecific Drug Olanzapine (Classification IndicationRIZZA JANE VELASCONo ratings yet
- Availability: Classifications: Central Nervous System Agent Nsaid (Cox-1) Analgesic Antipyretic Pregnancy Category: BDocument4 pagesAvailability: Classifications: Central Nervous System Agent Nsaid (Cox-1) Analgesic Antipyretic Pregnancy Category: BCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Additional Pharma CardsDocument21 pagesAdditional Pharma CardsBrilie Karl Viray100% (1)
- IbuprofenDocument3 pagesIbuprofenapi-3797941100% (1)
- Pharmacards CompilationDocument53 pagesPharmacards CompilationchristianfcualNo ratings yet
- NCMH Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNCMH Drug StudyHeartlee NapuranNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- EscitalopramDocument3 pagesEscitalopramhaslinda84No ratings yet
- CKD Case StudyDocument8 pagesCKD Case StudyEspiridionNo ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument3 pagesGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDocument11 pagesSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- 1.) Generic Name: Gabapentin Brand Name Classification Dosage Route and Frequency Mechanism of ActionDocument15 pages1.) Generic Name: Gabapentin Brand Name Classification Dosage Route and Frequency Mechanism of ActionTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyRaff GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Fullendocrine Nov 2014Document15 pagesFullendocrine Nov 2014roseNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Non-Steroidal Anti - Inflammatory DrugDocument27 pagesNon-Steroidal Anti - Inflammatory DrugMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Anti Diabetic DrugDocument3 pagesTutorial Anti Diabetic Drugnaveenvau1988No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Pharma Cards CHF DVTDocument14 pagesPharma Cards CHF DVTRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)Document2 pagesInsulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Product Name: New Zealand Data Sheet Apo-PrednisoneDocument13 pagesProduct Name: New Zealand Data Sheet Apo-PrednisonedomNo ratings yet
- Ma. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMa. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesTricia_De_Leon_6494No ratings yet
- Definitions OF DiagnosisDocument25 pagesDefinitions OF DiagnosisGlaire ZarateNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesHypoglycemiamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Classification: Recommended Dosage, Route, and FrequencyDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Classification: Recommended Dosage, Route, and FrequencyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- PHARMACARDS GonzagaDocument38 pagesPHARMACARDS GonzagaJay Marie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- LutsDocument35 pagesLutsJulian Eka Putra100% (1)
- Telomeres and EnduranceDocument6 pagesTelomeres and EnduranceDavid LaPointNo ratings yet
- BVMJ-Volume 42-Issue 1 - Page 80-85Document6 pagesBVMJ-Volume 42-Issue 1 - Page 80-85Maulana ArifNo ratings yet
- Acute. KetoacidosisdocxDocument12 pagesAcute. KetoacidosisdocxShara SampangNo ratings yet
- Week 5-CPHMDocument3 pagesWeek 5-CPHMAziz AyobNo ratings yet
- IATA Guidance On Managing Medical EventsDocument36 pagesIATA Guidance On Managing Medical EventsShinta Frennand100% (1)
- Harvard Scientists Have Proof Yoga, Meditation Work - Times of IndiaDocument2 pagesHarvard Scientists Have Proof Yoga, Meditation Work - Times of IndiataditNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument43 pagesBronchial AsthmaAmar BimavarapuNo ratings yet
- Puerperal PyrexiaDocument4 pagesPuerperal PyrexiaLulano MbasuNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Leading Research Perspectives 4Th Edition Elizabeth Rieger Full ChapterDocument67 pagesAbnormal Psychology Leading Research Perspectives 4Th Edition Elizabeth Rieger Full Chapternorma.fegley884100% (4)
- B Lood: Bleeding and Thrombosis in The Myeloproliferative DisordersDocument13 pagesB Lood: Bleeding and Thrombosis in The Myeloproliferative DisordersJicko Street HooligansNo ratings yet
- Diabetic ComaDocument15 pagesDiabetic ComaNader Smadi100% (1)
- Simopoulos Omega3 Review 2004Document15 pagesSimopoulos Omega3 Review 2004Voicu ValeriuNo ratings yet
- Essay 2Document4 pagesEssay 2api-341761696No ratings yet
- LGS InfographicDocument1 pageLGS InfographicCourtney CampNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease in Homoeopathy Part-1Document31 pagesChronic Kidney Disease in Homoeopathy Part-1Tarique ImamNo ratings yet
- Medical History Form 3 Years and OlderDocument3 pagesMedical History Form 3 Years and OlderJalisha SarmientoNo ratings yet
- English Analysing Themes and Ideas Presentation Beige Pink Lined StyleDocument14 pagesEnglish Analysing Themes and Ideas Presentation Beige Pink Lined StylejrdccuevasNo ratings yet
- Spirituality in NursingDocument14 pagesSpirituality in NursingJasmine JoveroNo ratings yet
- PhobiasDocument3 pagesPhobiasHaifi HunNo ratings yet
- Gateway B1 - Workbook Answer Key Gatewayonline - Marwel1Document1 pageGateway B1 - Workbook Answer Key Gatewayonline - Marwel1Đức Anh vũNo ratings yet
- Ajit Kulkarni - LachesisDocument8 pagesAjit Kulkarni - LachesisAntonio Andres BergesNo ratings yet
- Depression:-: Bipolar-I Disorder Bipolar-Ii Disorder Cyclothymic DisorderDocument1 pageDepression:-: Bipolar-I Disorder Bipolar-Ii Disorder Cyclothymic DisorderAli NawazNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Gangrene Cure by Carbon VegDocument5 pagesDiabetic Foot Gangrene Cure by Carbon Vegpratibha mishraNo ratings yet
- Classification of Drugs and Their EffectsDocument38 pagesClassification of Drugs and Their EffectsRPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- Anormalidades No Esqueleto de OvinosDocument10 pagesAnormalidades No Esqueleto de OvinosGildeniAguiarNo ratings yet
- Ashok Singh Topic 3Document9 pagesAshok Singh Topic 3Insta viralNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument3 pagesPediatricsTheju ReddyNo ratings yet