Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hand Outs - 05242022 - Subject Verb Agreement 1
Hand Outs - 05242022 - Subject Verb Agreement 1
Uploaded by
Skye Maia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views3 pages1. The document reviews rules for subject-verb agreement in sentences. It discusses how the subject and verb must match in number and how this creates a unified relationship between the two.
2. Key verb types that are discussed include helping verbs like "to be" and "to do" as well as sensory verbs.
3. Twenty rules for subject-verb agreement are then outlined, covering situations like singular vs plural subjects, compound subjects, intervening words, collective nouns, indefinite pronouns, and others.
Original Description:
it's use to write a better sentence
Original Title
Hand-outs-_05242022_Subject-verb-agreement-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document reviews rules for subject-verb agreement in sentences. It discusses how the subject and verb must match in number and how this creates a unified relationship between the two.
2. Key verb types that are discussed include helping verbs like "to be" and "to do" as well as sensory verbs.
3. Twenty rules for subject-verb agreement are then outlined, covering situations like singular vs plural subjects, compound subjects, intervening words, collective nouns, indefinite pronouns, and others.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views3 pagesHand Outs - 05242022 - Subject Verb Agreement 1
Hand Outs - 05242022 - Subject Verb Agreement 1
Uploaded by
Skye Maia1. The document reviews rules for subject-verb agreement in sentences. It discusses how the subject and verb must match in number and how this creates a unified relationship between the two.
2. Key verb types that are discussed include helping verbs like "to be" and "to do" as well as sensory verbs.
3. Twenty rules for subject-verb agreement are then outlined, covering situations like singular vs plural subjects, compound subjects, intervening words, collective nouns, indefinite pronouns, and others.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
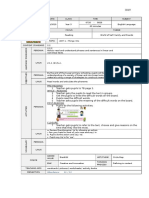
REVIEW SUBJECT AND VERB AGREEMENT
Subject-Verb Agreement Review
Like socks, the subject and predicate of a sentence have to match
and agree. (Tressler and Shelmadine,1951) The subject (a noun or a
pronoun) tells us the focus of the sentence while the verb makes a
statement about it. With correct subject-verb agreement, the relationship between these two
important sentence parts is unified thus making the idea of the sentence easier to understand.
Essential to mastering the rules governing subject-verb agreement are the following Verb
Basics.
Helping Verbs
to be- am, is, are, was, were
to do - do, does, did to have – has, have, had
Sensory Words Verbs - look, feel, taste etc.
Know the Rules!
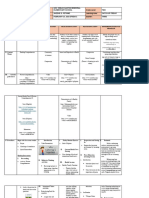
1. If the subject is singular, the verb must be singular.
Example:
She writes every day.
2. If the subject is plural, the verb must be plural.
Example:
They write every day.
3. When the subject of the sentence is composed of two or more nouns or pronouns
connected by and, use a plural verb.
Example:
The doctoral student and the committee members write every day.
4. When there is one subject and more than one verb, the verbs throughout the
sentence must agree with the subject.
Example:
Interviews are one way to collect data and allow researchers to gain in-depth
understanding of participants.
5. Intervening words like together with, in addition to, along with, as well as, including
and similar constructions following the subject do not affect the number of the subject.
Examples:
The student, as well as the committee members, is excited.
Strategies that the teacher uses to encourage classroom participation include using
small groups and clarifying expectations.
6. When two or more singular nouns or pronouns are connected by "or" or "nor," use a
singular verb.
Example:
The chairperson or the CEO approves the proposal before proceeding.
7. When a compound subject contains both a singular and a plural noun or pronoun
joined by "or" or "nor," the verb should agree with the part of the subject that is closest
to the verb. This is also called the rule of proximity.
Examples:
The student or the committee members write every day.
The committee members or the student writes every day.
8. The words and phrases "each," "each one," "either," "neither," "everyone,"
"everybody," "anyone," "anybody," "nobody," "somebody," "someone," and "no one"
are singular and require a singular verb.
Examples:
Each of the participants was willing to be recorded.
Neither alternative hypotheses was accepted. I will offer a 5000php gift card to
everybody who participates in the study.
No one was available to meet with me at the preferred time.
9. Non-count nouns take a singular verb.
Examples:
Education is the key to success.
Diabetes affects many people around the world.
The information obtained from the business owners was relevant to include in the study.
The research I found on the topic was limited.
10. Some countable nouns in English such as earnings, goods, odds, surroundings,
proceeds, contents, and valuables only have a plural form and take a plural verb.
Examples:
The earnings for this quarter exceed expectations.
The proceeds from the sale go to support the homeless population in the city.
Locally produced goods have the advantage of shorter supply chains.
11. In sentences beginning with "there is" or "there are," the subject follows the verb.
Since "there" is not the subject, the verb agrees with what follows the verb.
Examples:
There is little administrative support. There are many factors affecting teacher
retention.
12. A collective noun acting as a single unit takes a singular verb. However, the plural
verb is used when the individual if the focus is on the individuals in the group.
Examples:
The group meets every week.
The committee participate in various volunteer activities in private lives.
13. In the present tense, verbs agree with their subjects in NUMBER (singular/plural)
and in PERSON (first, second, or third). The present tense ending –s (or –es) is used on
a verb if the subject is THIRD PERSON SINGULAR. Otherwise, the verb takes NO
ENDING.
14. A few indefinite pronouns such as All, Any, None and Some may be singular or
plural DEPENDING on the noun or pronoun they refer to.
Examples:
Some of the apples were sold.
Some of the flour was spilled.
15. Titles of works, story, article or establishment, even when plural in form, takes a
singular subject
Example:
BSP Enterprises is owned by Mr. Santos.
16. Adjectives used as subjects take plural verbs.
Example: The brave are honored.
17. Fractions may take singular or plural verbs depending on the of-phrase.
Examples:
Two-thirds of the school’s population speaks Pangalatok.
Two-thirds of the children are in grade school.
18. Words or phrases expressing periods of time, weight, measurement and amounts of
money are usually regarded as singular.
Examples:
Five years is a long engagement period.
Five thousand pesos is the prize money.
19. The expression the number takes a singular verb; the expression a number takes a
plural verb.
Examples:
The number of applicants is big.
A number of applicants are very young.
20. Nouns plural in form but singular in meaning.
Example: Statistics is showing an increase in inflation.
You might also like
- ECRIF Framework - TheoryDocument2 pagesECRIF Framework - TheoryKatherin Sandoval Bustos100% (1)
- How Much Can We Boost IQ and Scholastic AchievementDocument124 pagesHow Much Can We Boost IQ and Scholastic AchievementOnofrash VasileNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect GrammarDocument12 pagesPresent Perfect GrammarAlba Milena Rodriguez MorenoNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT and VERB AgreementDocument3 pagesSUBJECT and VERB AgreementKai BautistaNo ratings yet
- Sva RulesDocument2 pagesSva Ruleskayra dale larrauriNo ratings yet
- Basic English GrammarDocument214 pagesBasic English GrammarAsraf AliNo ratings yet
- English CGDocument247 pagesEnglish CGJestia Lyn EngracialNo ratings yet
- Use of AdverbsDocument14 pagesUse of AdverbsAntony PandiarajanNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument11 pagesSubject Verb AgreementSaud KhanNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument6 pagesAdjectivesBabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence PatternDocument27 pagesBasic Sentence PatternRichel CataluñaNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument10 pagesPrepositionsAnastasiia MazurovaNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect - Key IELTS Vocabulary Because: NotesDocument18 pagesCause and Effect - Key IELTS Vocabulary Because: NotesBharti Dogra100% (1)
- SpeakingDocument55 pagesSpeakingBảo Lê QuốcNo ratings yet
- Teaching Speaking and Writing SkillsDocument34 pagesTeaching Speaking and Writing SkillsVen KeraNo ratings yet
- Verb Phrase in EnglishDocument20 pagesVerb Phrase in Englishsardar ps4No ratings yet
- Topics Vocabulary-DucVuDocument81 pagesTopics Vocabulary-DucVuĐức VũNo ratings yet
- Teaching AdultsDocument63 pagesTeaching AdultsAnNgôNo ratings yet
- Sentence StructureDocument114 pagesSentence StructurePrabavathi PappuNo ratings yet
- One Word SubstitutionsDocument18 pagesOne Word Substitutionstechhacks gamingNo ratings yet
- Boost Your Vocabulary Cambridge IELTS 16 - Dinh Thang - A&M IELTS-trang-1,8-47Document41 pagesBoost Your Vocabulary Cambridge IELTS 16 - Dinh Thang - A&M IELTS-trang-1,8-47nguyễn quỳnhNo ratings yet
- Udl Template 1Document11 pagesUdl Template 1api-630048293No ratings yet
- MLA and APA FormatDocument41 pagesMLA and APA FormatZī Līú M. Lī100% (1)
- Phrases Clauses and SentenceDocument11 pagesPhrases Clauses and SentenceCamille CruzNo ratings yet
- Structure of EnglishDocument9 pagesStructure of EnglishCherry Mae PalilioNo ratings yet
- Biology VocabDocument17 pagesBiology VocabMuhammad Amin Suhaimi100% (1)
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument23 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesThảo BíchNo ratings yet
- Chuong1 Teaching Vocabulary PDFDocument32 pagesChuong1 Teaching Vocabulary PDFThảo TrịnhNo ratings yet
- English For Academic Purposes: Meeting 11 Basic Grammar PointsDocument36 pagesEnglish For Academic Purposes: Meeting 11 Basic Grammar PointsTheodorus AgungNo ratings yet
- GD TopicsDocument17 pagesGD TopicsbeadsindiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Part A - Reading: Guessing Word Meaning Using Word Prefixes & RootsDocument8 pagesLesson 2: Part A - Reading: Guessing Word Meaning Using Word Prefixes & RootsViệt Anh CNHNo ratings yet
- Grammatical ConceptsDocument38 pagesGrammatical Conceptsjoy canda50% (2)
- Human Should Not Eat AnimalsDocument9 pagesHuman Should Not Eat AnimalsMuskan AroraNo ratings yet
- English CapsuleDocument41 pagesEnglish CapsuleVipul Priya KumarNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement RulesDocument10 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement RulesMa. Luz CalvoNo ratings yet
- Grammar OneDocument63 pagesGrammar OneÇ Fìtààh Hààjì ÀbďìNo ratings yet
- Context CluesDocument11 pagesContext CluescheyeenNo ratings yet
- Pronouns and Types of PronounsDocument9 pagesPronouns and Types of PronounsHolística Melisa PasikNo ratings yet
- 700 Vocab PDF Antonym and Synonym 33 PDFDocument157 pages700 Vocab PDF Antonym and Synonym 33 PDFsaikiranNo ratings yet
- L 08910 Hyper Poetry Text Tula Blog and 2Document19 pagesL 08910 Hyper Poetry Text Tula Blog and 2Christine Mae LlabanNo ratings yet
- IELTS Speaking - Speaking Part 2-2Document19 pagesIELTS Speaking - Speaking Part 2-2Hairatun NisaNo ratings yet
- 750-Article Text-5622-1-10-202008Document29 pages750-Article Text-5622-1-10-202008Dafa Shafwan AlfaridzyNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechMUHAMMAD HASNAINNo ratings yet
- Good CommentsDocument15 pagesGood CommentsJumana MasterNo ratings yet
- Lexical RelationDocument47 pagesLexical Relationsudan rajNo ratings yet
- Rules of Subject Verb Agreement Are All You NeedDocument8 pagesRules of Subject Verb Agreement Are All You Needalexandra jacobNo ratings yet
- 【完整版】有道考神2023年1 4月口语题库&Part1范例答案Document51 pages【完整版】有道考神2023年1 4月口语题库&Part1范例答案ivy vistoNo ratings yet
- Dinosuars Before Dark TeachersbookDocument17 pagesDinosuars Before Dark TeachersbookR SNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Are Words That Describe NounsDocument16 pagesAdjectives Are Words That Describe NounsAntonio NeshevskiNo ratings yet
- English Common Error RulesDocument11 pagesEnglish Common Error RulesWahid AhmedNo ratings yet
- IELTS-Listening-Ebook May - Aug22Document137 pagesIELTS-Listening-Ebook May - Aug22Sam OctaNo ratings yet
- Verb and SituationDocument6 pagesVerb and Situationluthfia zahraNo ratings yet
- Verb 1Document9 pagesVerb 1desriandasyafitriNo ratings yet
- 1english7 Q1w7Document12 pages1english7 Q1w7Aejo AbayNo ratings yet
- INFINITIVEDocument8 pagesINFINITIVEYuni NurhandayaniNo ratings yet
- An Adjective Clause Describes A NounDocument8 pagesAn Adjective Clause Describes A NounVivi HidayantiNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechTEA AN QI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVESDocument17 pagesADJECTIVESIsuru AbhimanNo ratings yet
- StructuresDocument7 pagesStructuresThùy DươngNo ratings yet
- IELTS Speaking Vocabulary Family & FriendsDocument5 pagesIELTS Speaking Vocabulary Family & FriendsM_GHAREB72No ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument10 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementIan Jim BaysonNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument12 pagesSubject Verb AgreementMiya Chocho XDNo ratings yet
- The Master Key System by Charles F HaanelDocument390 pagesThe Master Key System by Charles F Haanelthaworldismine100% (4)
- Arizmendi CV 2016Document5 pagesArizmendi CV 2016api-340301569No ratings yet
- DLL For COTDocument7 pagesDLL For COTAngelbert B Villena100% (1)
- The Lost Writings of Wu Hsin Volume Three: in The Shadow of The Formless (Sample)Document34 pagesThe Lost Writings of Wu Hsin Volume Three: in The Shadow of The Formless (Sample)Roy Melvyn100% (6)
- Research Proposal CoverDocument15 pagesResearch Proposal CoverXuan ThanhNo ratings yet
- Debate Syllabus 2012-2013: "Success Is Peace of Mind Which Is A Direct Result of Self-Satisfaction in KnowingDocument3 pagesDebate Syllabus 2012-2013: "Success Is Peace of Mind Which Is A Direct Result of Self-Satisfaction in Knowingmanuelgilbert76No ratings yet
- Module 3 Prof Educ 6 Part 2 Focus On The LearnerDocument14 pagesModule 3 Prof Educ 6 Part 2 Focus On The LearnerJohn Abe NasayaoNo ratings yet
- The Situational ApproachDocument14 pagesThe Situational ApproachLaloo CNNo ratings yet
- Informational Text Features Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesInformational Text Features Lesson Planjray427No ratings yet
- Animal CommunicationDocument3 pagesAnimal CommunicationDEVI TEJASWININo ratings yet
- Wa0011.Document3 pagesWa0011.mulondo abubakerNo ratings yet
- Usherkober Background3 Motivation 5 22 12Document22 pagesUsherkober Background3 Motivation 5 22 12api-250421371No ratings yet
- Haptics: Technology Based On TouchDocument4 pagesHaptics: Technology Based On TouchijsretNo ratings yet
- WE Can Do It!: Ctivity Descriptive MeasuresDocument3 pagesWE Can Do It!: Ctivity Descriptive MeasuresXel Joe BahianNo ratings yet
- Contoh RPHDocument12 pagesContoh RPHLanun BluesNo ratings yet
- Finger Phonics Big Book 5 - JL6871 - AE Print IssuuDocument8 pagesFinger Phonics Big Book 5 - JL6871 - AE Print IssuumaymyatmoessssawNo ratings yet
- Sas 4Document2 pagesSas 4Marjurey JustolNo ratings yet
- DLL Catch Up Friday Grade 2Document6 pagesDLL Catch Up Friday Grade 2Sheene Penaranda Diatera Petisme100% (4)
- Leader MemberExchangeDocument36 pagesLeader MemberExchangeAbdullah MakkiNo ratings yet
- Soft Skill-ChapterDocument19 pagesSoft Skill-ChaptervenkatNo ratings yet
- An Investigation On The Learning Styles of B.ed. TraineesDocument6 pagesAn Investigation On The Learning Styles of B.ed. TraineesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument18 pagesCase Studyapi-229121329100% (1)
- FITCH The Art of Questioning 1879Document82 pagesFITCH The Art of Questioning 1879Studentul2000No ratings yet
- The Dyslexic Reader 2006 - Issue 42Document28 pagesThe Dyslexic Reader 2006 - Issue 42Davis Dyslexia Association International100% (5)
- Verbo Midterm ExamDocument2 pagesVerbo Midterm ExamChris BentulaNo ratings yet
- Gujarathi 2Document82 pagesGujarathi 2Rajasekaran PrakasamNo ratings yet
- Problem With Parallel Structures: A. Objectives of The StudyDocument4 pagesProblem With Parallel Structures: A. Objectives of The StudyShani Berliana100% (1)
- Úvod Do Anglického JazykaDocument24 pagesÚvod Do Anglického JazykaTomas CsomorNo ratings yet