Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 9 Curriculum
Grade 9 Curriculum
Uploaded by
Jassien Moring FlorentinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 9 Curriculum
Grade 9 Curriculum
Uploaded by
Jassien Moring FlorentinoCopyright:
Available Formats
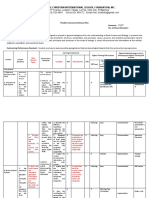
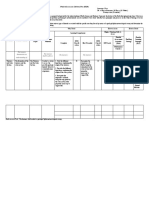
MATERIALS/
LEARNING VALUES STRATEGIES AND
CONTENT/ TOPIC ASSESSMENT TOOLS/ REFERENCES
COMPETENCIES INTEGRATION ACTIVITES
EQUIPMENTS
UNIT III: Our
Planet and Earth
Chapter 6
.Volcanoes - describe the - Appreciation - Quiz - Media Review - Power point - Science for
1.1 Type of different types of - Cooperation - Oral Recitation - Description Wheel presentation the 21st
volcanoes volcanoes; - Collaboration - Review and - Direct Instruction - Textbook Century
1.2 Volcanic - Awareness drills - Note-Taking - Laboratory Learners. 9
Eruption 1.3 Energy - differentiate - Love - Assignment Technique Manual Pages 228-
from volcanoes between active - Reflective teaching 252
and inactive - Cooperative
volcanoes teaching
- Power point
- explain what
presentation
happens when
- Socratic Method
volcanoes erupt
- illustrate how
energy from
volcanoes may be
tapped for human
use
Chapter 7:
- Oral recitation - Power point - Science for
2.Climate - Fluent Thinking - Quiz presentation the 21st
2.1 Factors that - explain how - Curiosity - Laboratory - Cooperative - Textbook Century
affect climate different factors - Awareness Activity Teaching Learners 9
2.2 Global climate affect the climate - Elaborative Thinking - Assignment - Demonstration Pages 269-
phenomenon of an area; - Appreciation method 280
- Service - Reflective teaching
- describe certain - Socratic Method
- Critical mind
climatic
- Collaboration
phenomena that
- Cooperation
occur on a global
level;
Chapter 8 - Organization - Review and - Board Work - Science for
- infer the - Textbook
3. Constellations - Creativity drills - Problem Solving the 21st
characteristics of
3.1 Characteristics - Logical thinking - Long Quiz - Board Work - Power Point Century
stars based on
of stars - Curiosity - Assignment - Socratic Method presentation Learner 9 -
the characteristics
3.2 Arrangement of - Elaborative thinking Pages 299-
of the Sun - Reflective teaching
stars in a group - Appreciation 310
- Cooperative learning
3.3 Changing
- infer that the - Direct Instruction
position of
arrangement of
constellations
stars in a group
during the night and
(constellation)
at different times of
does not change
the year
3.4 Beliefs and
practices about
constellations and
astrology
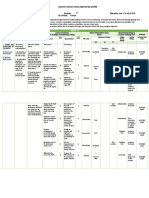
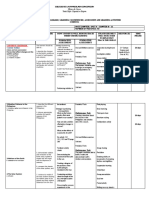
Unit IV: A Deeper
Look at Motion - Appreciation - Quiz - Textbook
and Energy - Cooperation - Drill - Power Point - Science for
- describe the - Collaboration - Assignment - Lecture Method Presentation the 21st
Chapter 9 horizontal and - Critical mind - Inductive Method Century 9
Two dimensional vertical motions of a - Awareness - Power Point Learners –
Motion and projectile Presentation Pages 322-
- Perseverance
Conservation of - Constructivist 333
- Maka-tao
Momentom - investigate the - Reflective Thinking
relationship between - Maka-Diyos
Projectile Motion - Collaborative
1.2.Impulse, the angle of release - Love
- Service Learning
Momentum and and the height and - Cooperative leaning
Impulse range of the - Problem solving
1.3.Conservation of projectile;
Linear Momentum
- relate impulse and
momentum to
collision of objects
(e.g., vehicular
collision)
- infer that the total
momentum before
and after collision is
equal;
- infer that the total
momentum before
and after collision is
equal;
- examine effects and
predict causes of
collision related
damages/injuries
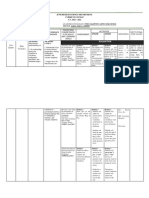
- Fluent Thinking - Oral Recitation - Textbook
- Curiosity - Quick - Power Point - Science for
- Originality - Assignment - Lecture Method Presentation the 21st
Chapter 10 - Collaborative
Energy, Heat, and - Awareness - Laboratory Century
- explain energy Activity Learning Learners -
Electricity - Elaborative
2.1 Changes in transformation in Thinking - Drill - Reflective Learning Pages 370-
form of various - Appreciation - Constructive 395
mechanical activities/events (e.g., - Preservation Teaching Method
energy waterfalls, archery, - Cooperative
2.2 Conservation amusement rides) - Collaborative
of energy - Service
- perform activities to
demonstrate
conservation of
mechanical energy
- infer that the total
mechanical energy
remains the same
during any process
- construct a model to
demonstrate that
heat can do work -
- infer that heat
transfer can be used
to do work, and that
work involves the
release of heat
- explain why
machines are never
100-percent efficient
-
- explain how heat
transfer and
energy
transformation
make heat
engines like
geothermal plants
work; and
- explain how
electrical energy
is generated,
transmitted, and
distributed.
You might also like
- A Case Study On Counselling PsychologyDocument9 pagesA Case Study On Counselling Psychologychilaz7775% (4)
- FIDP Earth and Life ScienceDocument10 pagesFIDP Earth and Life ScienceTeacher MelNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Science 10 CMDocument6 pages1st Quarter Science 10 CMHazel Nunez Telebangco100% (1)
- ACTIVITY 1 The Stages of Development and Developmental TasksDocument3 pagesACTIVITY 1 The Stages of Development and Developmental TasksJaymar Magtibay100% (2)
- Science 10 Curriculum MapDocument2 pagesScience 10 Curriculum MapDxtr Talens100% (1)
- How I Got 93 in SAP S 4HANA Financial Ac PDFDocument4 pagesHow I Got 93 in SAP S 4HANA Financial Ac PDFkrisho0% (1)
- John Levi Martin - The Explanation of Social Action-Oxford University Press (2011) PDFDocument411 pagesJohn Levi Martin - The Explanation of Social Action-Oxford University Press (2011) PDFMarcio Barbosa100% (2)
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map (CIDAM) : Semester: 1Document3 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map (CIDAM) : Semester: 1Mary-Rose Casuyon100% (1)
- Science 10 Glip 2122Document23 pagesScience 10 Glip 2122Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Cmap Science 10Document2 pagesCmap Science 10Zharina Ann Estavillo100% (1)
- Science 10 Cmap Crisanta Del RosarioDocument6 pagesScience 10 Cmap Crisanta Del Rosariogino avilaNo ratings yet
- Concepcion Holy Cross College, Inc. Barangay Minane, Concepcion, TarlacDocument2 pagesConcepcion Holy Cross College, Inc. Barangay Minane, Concepcion, TarlacAbigail PanesNo ratings yet
- Solar Planetary System.Document8 pagesSolar Planetary System.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- CM SCIENCE 9 3rd QuarterDocument7 pagesCM SCIENCE 9 3rd QuarterJenny Acosta Catacutan100% (1)
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2api-350696220No ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: HolidayDocument6 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: HolidayJudy Ann MañozaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Lesson PlanDocument27 pagesScience 10 Lesson PlanMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 1ST QuarterDocument26 pages1ST QuarterMa. Victoria RamosNo ratings yet
- Sample Curriculum Map (Science 10)Document7 pagesSample Curriculum Map (Science 10)Rose HeyNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document10 pagesScience 10Roylan RosalNo ratings yet
- 1ST QuarterDocument27 pages1ST QuarterMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Science 3M 9.1.2023Document2 pagesScience 3M 9.1.2023Yogeswary SitaramanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 G10Document7 pagesWeek 3 G10lucky remosNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map - Science 9 (3rd Quarter)Document7 pagesCurriculum Map - Science 9 (3rd Quarter)Welbert AmarNo ratings yet
- Science 10 First Quarter LP Week 1 To 8Document25 pagesScience 10 First Quarter LP Week 1 To 8Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 1ST QuarterDocument26 pages1ST QuarterSher SherwinNo ratings yet
- DLL Sept.19Document1 pageDLL Sept.19Ma'am Jessica GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography 12 Weather and Climate Unit Plan Lesson PlansDocument28 pagesPhysical Geography 12 Weather and Climate Unit Plan Lesson Plansapi-499589514No ratings yet
- Science Block Cot Plan Sy 2021Document2 pagesScience Block Cot Plan Sy 2021Maria Dhalia MarquezNo ratings yet
- Victoria Deleon Unit Plan For Edss5710 Section B 16 01 2021Document7 pagesVictoria Deleon Unit Plan For Edss5710 Section B 16 01 2021api-552950576No ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The Learners: The LearnersDocument2 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Shall Be Able To: The Learners: The LearnersFerdinand GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLL Q3 Week 2 Day4Document6 pagesDLL Q3 Week 2 Day4Cecilia Guevarra DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in Science 4th G7 EditedDocument5 pagesCurriculum Map in Science 4th G7 EditedLily RosemaryNo ratings yet
- Unit Progression-ScienceDocument4 pagesUnit Progression-Scienceapi-401642975No ratings yet
- Melt Chocolate LessonDocument3 pagesMelt Chocolate Lessonapi-390696333No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter DLP in Science 10Document28 pages1st Quarter DLP in Science 10yamikoNo ratings yet
- CURRICULUM-MAP-2 ScienceDocument8 pagesCURRICULUM-MAP-2 ScienceGian HipolitoNo ratings yet
- V Xh7Rxy4Vnii: 1. Comparing ThingsDocument4 pagesV Xh7Rxy4Vnii: 1. Comparing ThingsJohn Louise Templado AndradaNo ratings yet
- Sci - dll.1st QuarterDocument26 pagesSci - dll.1st QuarterEvefel Ruth SanchezNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map SCIENCE 9 3rd QuarterDocument2 pagesCurriculum Map SCIENCE 9 3rd QuarterCrispin Daniel MuñozNo ratings yet
- Syllabus-Math in Modern World - BSITDocument5 pagesSyllabus-Math in Modern World - BSITHarold LuceroNo ratings yet
- Sci. 10 DLL W2Document4 pagesSci. 10 DLL W2kathleen de jesusNo ratings yet
- TERM/WEEKS: Term 4, Week 3 Year Level: One LEARNING AREA/TOPIC: Science, Nature and Development of ScienceDocument7 pagesTERM/WEEKS: Term 4, Week 3 Year Level: One LEARNING AREA/TOPIC: Science, Nature and Development of ScienceCameron ShawNo ratings yet
- 6th Science GC 25 19 Al 23 de FEBRERODocument4 pages6th Science GC 25 19 Al 23 de FEBREROGabrielaVenegasNo ratings yet
- 1ST QuarterDocument33 pages1ST Quarteriwantantonio5No ratings yet
- DLL - Science 10 For EditDocument70 pagesDLL - Science 10 For EditJoanne Diaz JacintoNo ratings yet
- CMAP & WLT - GRADE 10 (1st QTR)Document4 pagesCMAP & WLT - GRADE 10 (1st QTR)Pamela MalihanNo ratings yet
- Earth&Life CIDAM EditedDocument19 pagesEarth&Life CIDAM EditedDanica Veneracion UmaliNo ratings yet
- 1st QuarterDocument37 pages1st Quarterrealclarksian12No ratings yet
- CURR MAP Sci 6 4gradingDocument4 pagesCURR MAP Sci 6 4gradingÄngēlïçå Prōvïdô PülgånNo ratings yet
- Science9 4th Quarter Learning MatrixDocument5 pagesScience9 4th Quarter Learning MatrixWilsonNo ratings yet
- Form 3 First Term Scheme MupandanyamaDocument15 pagesForm 3 First Term Scheme MupandanyamaMunashe MasiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum MapDocument6 pagesCurriculum MapMJ HagosNo ratings yet
- 1ST QuarterDocument26 pages1ST Quartercarl pahuyoNo ratings yet
- Edtp5002 Kirby Harripersad Final TPDocument47 pagesEdtp5002 Kirby Harripersad Final TPapi-553012998No ratings yet
- Curriculum Map SCIENCE 10Document5 pagesCurriculum Map SCIENCE 10Teacher MelNo ratings yet
- CIDAMDocument6 pagesCIDAMcruzjhay575No ratings yet
- Physical Science Subject AlignmentDocument4 pagesPhysical Science Subject AlignmentHenno Nickole Vince A. BugtongNo ratings yet
- Social Science Lesson Plan - Julissa CortesDocument4 pagesSocial Science Lesson Plan - Julissa Cortesmarlon acostaNo ratings yet
- Scheme-Physics-Form 2Document17 pagesScheme-Physics-Form 2Nestory mahunjaNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade World Geography Lesson Plans Week 4Document8 pages8th Grade World Geography Lesson Plans Week 4christopher salberNo ratings yet
- G10Block PlanSY22 23 (1stGWeek3) PECAJAS - EditedDocument7 pagesG10Block PlanSY22 23 (1stGWeek3) PECAJAS - EditedMarco GNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB Q2 Week 3Document10 pagesDLL - MTB Q2 Week 3Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Tos - MTB 2 - Q1Document3 pagesTos - MTB 2 - Q1Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Table-of-Specification MTB 1 Q2 SUM NO. 2Document1 pageTable-of-Specification MTB 1 Q2 SUM NO. 2Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan 4th GradingDocument7 pagesUnit Plan 4th GradingJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Periodical Exam 9Document4 pagesPeriodical Exam 9Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument16 pagesMitochondriaJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- UBD Stage 3Document4 pagesUBD Stage 3Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Learning Plan Structure of Matter Februayr 17 2021Document4 pagesSynchronous Learning Plan Structure of Matter Februayr 17 2021Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Pyrimidine BiosynthesisDocument45 pagesPyrimidine BiosynthesisJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SOPDocument15 pagesChapter 1 SOPJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Grade 7 First QuarterDocument10 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 7 First QuarterJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Asychronous Learning Plan Method of Plant Production 1Document3 pagesAsychronous Learning Plan Method of Plant Production 1Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Learning Plan Temperature Feb 24 2021Document6 pagesSynchronous Learning Plan Temperature Feb 24 2021Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Learning Plan Scientific Notation February 19 2021Document4 pagesSynchronous Learning Plan Scientific Notation February 19 2021Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Learning PlanDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Learning PlanJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Revised Table of SpecificationDocument3 pagesRevised Table of SpecificationJassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Teachers Manual in Filipino 10 PDFDocument2 pagesTeachers Manual in Filipino 10 PDFEdilyn HinotanNo ratings yet
- Pr5 HomonymyDocument45 pagesPr5 HomonymyMoi WarheadNo ratings yet
- Anton Makarenko - G.N. FilonovDocument9 pagesAnton Makarenko - G.N. FilonovsergevictorNo ratings yet
- Life Box NotesDocument141 pagesLife Box NotespoopingatrediffmailNo ratings yet
- PSLE English Paper PDFDocument19 pagesPSLE English Paper PDFanu0% (2)
- Presentation On SitaraDocument14 pagesPresentation On Sitarafahadali1234No ratings yet
- English Lecture (Special Occasion Speeches)Document3 pagesEnglish Lecture (Special Occasion Speeches)Ericka Cathlyne de VeraNo ratings yet
- Smarter Goals TemplateDocument2 pagesSmarter Goals TemplateHamada AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Receiving Stage: Listening: StagesDocument12 pagesThe Receiving Stage: Listening: StagesGladyss PunzalanNo ratings yet
- The Commonest Types of Metaphor in EnglishDocument21 pagesThe Commonest Types of Metaphor in EnglishmanuNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Class Installation ArtDocument2 pagesRubric For Class Installation ArtRon LopezNo ratings yet
- Thesis OutlineDocument2 pagesThesis OutlineEnDang SakinahNo ratings yet
- Abe Tabular SummaryDocument2 pagesAbe Tabular Summaryapi-294900383No ratings yet
- Top 55 IGCSE in French Oral Exam Questions CIE BoardDocument23 pagesTop 55 IGCSE in French Oral Exam Questions CIE BoardjayNo ratings yet
- Wren & Martin - WikipediaDocument4 pagesWren & Martin - WikipediaHARSH CHOURASIANo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Lesson 1Document22 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Lesson 1Niña Gloria Acuin ZaspaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: My House: Lesson 1: Getting Started - A Look InsideDocument62 pagesUnit 2: My House: Lesson 1: Getting Started - A Look InsideThủy- 0985 117 980/0326 930 309 Ms.No ratings yet
- General Problems I N Scientific An D Technica L Translatio NDocument7 pagesGeneral Problems I N Scientific An D Technica L Translatio NAbdelkader BennaoumNo ratings yet
- Parallel Assessment in English 10 Quarter 2 Module 2Document1 pageParallel Assessment in English 10 Quarter 2 Module 2Hazel SolisNo ratings yet
- Group IV - Activity 1 and 2Document5 pagesGroup IV - Activity 1 and 2Morgan MangunayNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Interviews CheatSheetDocument4 pagesBehavioral Interviews CheatSheetkinglegend3103No ratings yet
- Gold Exp B1 U3 Lang Test ADocument2 pagesGold Exp B1 U3 Lang Test APaweł KlinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Course DesigningDocument3 pagesChapter 8: Course DesigninghasnainNo ratings yet
- K N o W L e D G e - B A S e D D e S I G NDocument241 pagesK N o W L e D G e - B A S e D D e S I G NAndreea MitreanuNo ratings yet
- 2023 Accomplishment Report - VRPDocument3 pages2023 Accomplishment Report - VRPjeffreylois.maestradoNo ratings yet
- BUS 430 Assignment 1 LensCrafters Case StudyDocument6 pagesBUS 430 Assignment 1 LensCrafters Case Studyjanesthomas0% (1)