Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Janipin - Quiz 4
Janipin - Quiz 4
Uploaded by
JANIPIN, Dave Karl M.Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Direct, Digital & Data-Driven Marketing 5thDocument1,418 pagesDirect, Digital & Data-Driven Marketing 5thDOUCHES FROIDES100% (2)
- prEN 6115Document15 pagesprEN 6115malotNo ratings yet
- Advac Guerero Chapter 15Document18 pagesAdvac Guerero Chapter 15Drew BanlutaNo ratings yet
- Contactor DutyDocument3 pagesContactor DutySteevan NelsonNo ratings yet
- BSE Design Guides (HKU)Document2 pagesBSE Design Guides (HKU)李梓誠0% (1)
- American Girl Presentaton Team-6Document9 pagesAmerican Girl Presentaton Team-6Ashish Kaushal RanjanNo ratings yet
- Galaura QUIZ 4Document2 pagesGalaura QUIZ 4JANIPIN, Dave Karl M.No ratings yet
- Bigger Perspective Why Are Circuits Important?Document5 pagesBigger Perspective Why Are Circuits Important?Shaezer AlpayNo ratings yet
- Principles of ElectricityDocument25 pagesPrinciples of ElectricityKeziah LafortezaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electricity: Background To Electricity, Circuits, and How To CalculateDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Electricity: Background To Electricity, Circuits, and How To CalculatetuNo ratings yet
- Distribusi Tenaga ListrikDocument10 pagesDistribusi Tenaga ListrikSundara Sudibya JayaNo ratings yet
- Ia 9 ReviewerDocument4 pagesIa 9 ReviewerElline PataganaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 PhysiscsDocument5 pagesChapter 7 PhysiscsSara KorkesNo ratings yet
- Electrical GlossaryDocument11 pagesElectrical Glossarysrogan2323No ratings yet
- Bmat Physics KnowledgeDocument25 pagesBmat Physics KnowledgeSummer GUO [07C15M]No ratings yet
- Electrical and Mechanical Systems in BuildingsDocument11 pagesElectrical and Mechanical Systems in BuildingsarchitectjeyNo ratings yet
- Topic: Basic Electrical and Electronics Simple Circuit I. Circuit A. Define CircuitDocument7 pagesTopic: Basic Electrical and Electronics Simple Circuit I. Circuit A. Define CircuitReymark LayupanNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY - Electrical Connection and Safety ApplicationDocument40 pagesELECTRICITY - Electrical Connection and Safety ApplicationakelariveraNo ratings yet
- Circuits Part IDocument8 pagesCircuits Part IBanusmatiSanmugamNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document13 pagesLab 2devchithNo ratings yet
- What Is Voltage Drop?: Conductor ResistanceDocument8 pagesWhat Is Voltage Drop?: Conductor ResistanceMohamed A. HusseinNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument19 pagesCircuitsRoden FernandezNo ratings yet
- Only Electrons Can Be Gained or Lost by Atoms Using Simple TechniquesDocument18 pagesOnly Electrons Can Be Gained or Lost by Atoms Using Simple TechniquesJackie GiallombardoNo ratings yet
- CLASS 9 CBSE CH-12 ElectricityDocument63 pagesCLASS 9 CBSE CH-12 ElectricityannigarwalNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument7 pagesEnergyMike OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Cfe Bu2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCfe Bu2 ReviewerMaria Katrina Ilumin VersozaNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of TransformerDocument28 pagesEfficiency of TransformerJane Erestain BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument96 pagesLab ManualASWANI RAJAN50% (2)
- Torino ElectricDocument85 pagesTorino ElectricScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Ee PrelimsDocument5 pagesEe Prelimselaizaagudo17No ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Notes Chapter 7 Electricity: 7.1 ElectrostaticsDocument10 pagesForm 3 Science Notes Chapter 7 Electricity: 7.1 ElectrostaticsJu Li TanNo ratings yet
- Electrical System BasicsDocument63 pagesElectrical System BasicsDuggineni RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ece ReviewerDocument4 pagesEce ReviewerKwinn EspinosaNo ratings yet
- INTRODocument35 pagesINTROSubharth SahaNo ratings yet
- MALVINO-Book ReviewDocument30 pagesMALVINO-Book ReviewAylie PilobelloNo ratings yet
- Types of Electrical LoadsDocument2 pagesTypes of Electrical LoadsChandaKunda50% (2)
- Week 14Document25 pagesWeek 14ali burhan tahirNo ratings yet
- A6.1 Basic Electrical TechnologyDocument65 pagesA6.1 Basic Electrical TechnologyRajeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical SystemDocument16 pagesElectrical SystemCjoy MañiboNo ratings yet
- BASIC Elec. TermsDocument5 pagesBASIC Elec. TermsRamces SolimanNo ratings yet
- G1 5 ReviewerDocument68 pagesG1 5 Reviewerangelyn violaNo ratings yet
- ARE-Ch10 Electrical SystemsDocument13 pagesARE-Ch10 Electrical Systemsmdmasood3295No ratings yet
- Topic ElectricityDocument8 pagesTopic ElectricityChumaNo ratings yet
- Basic Priciples of ElectricityDocument39 pagesBasic Priciples of ElectricityTejaswi PoludasuNo ratings yet
- Circuits QRDocument60 pagesCircuits QRDon Mariano Marcos Elementary SchoolNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits SummaryDocument3 pagesElectrical Circuits SummaryArcangEl RicaLynNo ratings yet
- Electrical Terms: Ohm'S Law (George Simon Ohm'S) - Relation Between Pressure CurrrentDocument8 pagesElectrical Terms: Ohm'S Law (George Simon Ohm'S) - Relation Between Pressure CurrrentJM ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Electrical TerminologiesDocument11 pagesElectrical TerminologiesVincent Ganasi LipawenNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Question and Answer - POWER SYSTEM QUESTION and ANSWERDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Question and Answer - POWER SYSTEM QUESTION and ANSWERchico brilliantoNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitDocument13 pagesElectric Circuitdead poolNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument50 pagesElectric CircuitsClaudineNo ratings yet
- Current. Voltage and ResistanceDocument2 pagesCurrent. Voltage and ResistanceJR ALMANZARNo ratings yet
- FLEX Course Material ABUTLI2S BUILDING UTILITIES 2Document13 pagesFLEX Course Material ABUTLI2S BUILDING UTILITIES 2Roger Delos Reyes FercolNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics I ReviewerDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics I ReviewerAyana Nylazir BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument19 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel CircuitsArchiemedez BatanganNo ratings yet
- Building Services Ii: Unit 1 - Electrical and Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring SystemsDocument72 pagesBuilding Services Ii: Unit 1 - Electrical and Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring Systemsmaria nancyNo ratings yet
- Building Services Ii: Unit 1 - Electrical and Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring SystemsDocument58 pagesBuilding Services Ii: Unit 1 - Electrical and Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring SystemsArun PrakashNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits CH 17.4 8thDocument16 pagesElectric Circuits CH 17.4 8ththegedusNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument17 pagesElectrical EnergykuevoradzogloriaNo ratings yet
- Physics SummaryDocument2 pagesPhysics SummaryresacyanniNo ratings yet
- Topics To Be Covered: Unit-2: Basic Circuit ElementsDocument11 pagesTopics To Be Covered: Unit-2: Basic Circuit ElementsParthaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument53 pagesBasic Principles of ElectricityRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1Document7 pagesEngineering Utilities 1Vanissa MontillaNo ratings yet
- Think EntrepreneuriallyDocument29 pagesThink EntrepreneuriallyDipali SikandNo ratings yet
- Grade 7&8 Week 2Document18 pagesGrade 7&8 Week 2RUSELLE HOROHORONo ratings yet
- mtb2 Quarter 4 Week 1 2Document3 pagesmtb2 Quarter 4 Week 1 2Carino ArleneNo ratings yet
- The Impact of National Culture PDFDocument30 pagesThe Impact of National Culture PDFJovanaNo ratings yet
- SECOND Semester, AY 2022-2023: Mission VisionDocument34 pagesSECOND Semester, AY 2022-2023: Mission Visionjeyyy BonesssNo ratings yet
- Industrial Marketing 5-6Document2 pagesIndustrial Marketing 5-6Mary Grace Ygot ParachaNo ratings yet
- CV Review 35Document1 pageCV Review 35Pean CkNo ratings yet
- Powers and Functions of Registrar Under Trade Union ActDocument20 pagesPowers and Functions of Registrar Under Trade Union ActJagriti SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Eutectic 19910: A Hard Nickel-Chromium Coating For Resistance To AbrasionDocument2 pagesEutectic 19910: A Hard Nickel-Chromium Coating For Resistance To AbrasionFactel SANo ratings yet
- PN8603-X-2 xPON OLT Product Specifications: Topvision Technologies Co., LTDDocument7 pagesPN8603-X-2 xPON OLT Product Specifications: Topvision Technologies Co., LTDmylife900No ratings yet
- Back Stepping - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesBack Stepping - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMario RossiNo ratings yet
- Power Query & BIDocument14 pagesPower Query & BIzubair muhammad0% (2)
- Nora Esd ProfileDocument4 pagesNora Esd ProfileProjectinsightNo ratings yet
- Delphi XE HandbookDocument135 pagesDelphi XE HandbookRadovan JaicNo ratings yet
- KBT65DP15 15RT0Document1 pageKBT65DP15 15RT0Andre LanaNo ratings yet
- NullDocument2 pagesNullapi-27552272No ratings yet
- Exam 2018 s1 Op2 NewDocument12 pagesExam 2018 s1 Op2 NewmakgethwawhitneyNo ratings yet
- Recereum WhitePaperDocument23 pagesRecereum WhitePaperLord VNo ratings yet
- 096 Floor Statement On Presidents Decision To Increase Troops in Iraq Obama SpeechDocument3 pages096 Floor Statement On Presidents Decision To Increase Troops in Iraq Obama SpeechDivya Deepika MaddireddyNo ratings yet
- GBP Statement: Account SummaryDocument16 pagesGBP Statement: Account SummaryKris TheVillainNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Regrind Materials in PVC Extrusion ProcessingDocument1 pageUtilization of Regrind Materials in PVC Extrusion ProcessingAntonius PrakosaNo ratings yet
- 05 Hydrologic LossesDocument39 pages05 Hydrologic LossesMaan HinolanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Air CompressorDocument15 pagesUnit 5 Air Compressormadhume01No ratings yet
- Lab - Manual LP V (2019PATERN)Document39 pagesLab - Manual LP V (2019PATERN)Vaishnavi DhimateNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering Module 1Document32 pagesEarthquake Engineering Module 1Ed AnthonyNo ratings yet
Janipin - Quiz 4
Janipin - Quiz 4
Uploaded by
JANIPIN, Dave Karl M.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Janipin - Quiz 4
Janipin - Quiz 4
Uploaded by
JANIPIN, Dave Karl M.Copyright:
Available Formats
Dave Karl M.
Janipin 09/13/2022
BSCE - CEM 3A Quiz 4
Name, describe and distinguish between types of electrical circuits and
compute circuit loads. give atleast 5 examples for each type.
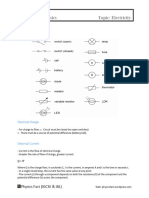
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
TYPES OF ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
Close Circuits - refers to a load that operates independently within a circuit.
In this case, the load determines the value of the current flow.
Examples :
- A Flashlight is ON.
- When you have a camera directly connected to a TV on the property that
shows images from the video camera.
- A camera installed to monitor crowd behavior
- Battery
- PVC cell
Open Circuits - when there is a faulty electrical wire or electronic
component in a circuit or the switch is OFF, then it is called Open Circuit.
Examples :
-A bulb power with a battery controlled by a switch.
-A string of electric lights that don't work if one bulb goes out.
- The circuit of lamp with switch in OFF state.
-A flashlight that is off.
-Unplugged Wires
Short Circuits - is when there is a low resistance connection between two
conductors that are supplying electrical power to a circuit. This would
generate an excess of voltage streaming and cause excessive flow of
current in the power source. The electricity will flow through a ‘short’ route
and cause a short circuit.
Examples :
- Water or other fluids encountering electrical wiring.
- Vermin or pests chewing through wires
- Old or damaged outlets, switches, lights, appliances, or other electrical
devices
- Deterioration of electrical cable sheathing
- Loose connections in an electrical box
Series Circuits - When 2 or more loads Bulbs are connected to each other
in a series, then it is called a Series Circuit. In a series circuit, if one load or
bulb gets fuse, then rest of the bulbs will not get power supply and will not
glow.
Examples : Water Heater, Flashlight, Well Water Pump, Freezers, and
Refrigerators
Dave Karl M. Janipin 09/13/2022
BSCE - CEM 3A Quiz 4
Parallel Circuits - A parallel circuit is one in which two or more loads such
as bulbs are connected to one another in series. All loads in this kind of
circuit must have a voltage capacity that is equivalent to the input supply.
Different load powers are possible. If one load or bulb in a parallel circuit
blows a fuse, the remaining lights will still receive power and continue to
glow.
Examples :
- Wiring of Car headlights
- Wiring of speaker
- Christmas Lights
- Plug sockets/outlets
-Alarm system
COMPUTER CIRCUIT LOADS
TYPES OF COMPUTER CIRCUIT LOADS
RESISTIVE LOADS - loads consisting of any heating element are classified
as resistive loads. These include incandescent lights, toasters, ovens, space
heaters and coffee makers. A load that draws current in a sinusoidal waxing-
and-waning pattern in concert with a sinusoidal variation in voltage – that is,
the maximum, minimum and zero points of the voltage and current values
over time line up – is a purely resistive one and includes no other elements.
Examples : Iron Box, Geyser, Heater, Domestic Boiler, & Electric Stove
INDUCTIVE LOADS - loads that power electrical motors are inductive loads.
These are found in a variety of household items and devices with moving
parts, including fans, vacuum cleaners, dishwashers, washing machines and
the compressors in refrigerators and air conditioners. In contrast to resistive
loads, in a purely inductive load, current follows a sinusoidal pattern that
peaks after the voltage sine wave peaks, so the maximum, minimum and
zero points are out of phase.
Examples : Motors, Transformers, Arc furnaces , Generators, & Solenoid
valve
CAPACITIVE LOADS - In a capacitive load, current and voltage are out of
phase as with an inductive load. The difference is that in the case of a
capacitive load, the current reaches its maximum value before the voltage
does. The current waveform leads the voltage waveform, but in an inductive
load, the current waveform lags it.
Examples : Battery Bank, Capacitor Bank, Buried Cables, Synchronous
Condenser, & capacitors used in various circuits such as motor starters
You might also like
- Direct, Digital & Data-Driven Marketing 5thDocument1,418 pagesDirect, Digital & Data-Driven Marketing 5thDOUCHES FROIDES100% (2)
- prEN 6115Document15 pagesprEN 6115malotNo ratings yet
- Advac Guerero Chapter 15Document18 pagesAdvac Guerero Chapter 15Drew BanlutaNo ratings yet
- Contactor DutyDocument3 pagesContactor DutySteevan NelsonNo ratings yet
- BSE Design Guides (HKU)Document2 pagesBSE Design Guides (HKU)李梓誠0% (1)
- American Girl Presentaton Team-6Document9 pagesAmerican Girl Presentaton Team-6Ashish Kaushal RanjanNo ratings yet
- Galaura QUIZ 4Document2 pagesGalaura QUIZ 4JANIPIN, Dave Karl M.No ratings yet
- Bigger Perspective Why Are Circuits Important?Document5 pagesBigger Perspective Why Are Circuits Important?Shaezer AlpayNo ratings yet
- Principles of ElectricityDocument25 pagesPrinciples of ElectricityKeziah LafortezaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electricity: Background To Electricity, Circuits, and How To CalculateDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Electricity: Background To Electricity, Circuits, and How To CalculatetuNo ratings yet
- Distribusi Tenaga ListrikDocument10 pagesDistribusi Tenaga ListrikSundara Sudibya JayaNo ratings yet
- Ia 9 ReviewerDocument4 pagesIa 9 ReviewerElline PataganaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 PhysiscsDocument5 pagesChapter 7 PhysiscsSara KorkesNo ratings yet
- Electrical GlossaryDocument11 pagesElectrical Glossarysrogan2323No ratings yet
- Bmat Physics KnowledgeDocument25 pagesBmat Physics KnowledgeSummer GUO [07C15M]No ratings yet
- Electrical and Mechanical Systems in BuildingsDocument11 pagesElectrical and Mechanical Systems in BuildingsarchitectjeyNo ratings yet
- Topic: Basic Electrical and Electronics Simple Circuit I. Circuit A. Define CircuitDocument7 pagesTopic: Basic Electrical and Electronics Simple Circuit I. Circuit A. Define CircuitReymark LayupanNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY - Electrical Connection and Safety ApplicationDocument40 pagesELECTRICITY - Electrical Connection and Safety ApplicationakelariveraNo ratings yet
- Circuits Part IDocument8 pagesCircuits Part IBanusmatiSanmugamNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document13 pagesLab 2devchithNo ratings yet
- What Is Voltage Drop?: Conductor ResistanceDocument8 pagesWhat Is Voltage Drop?: Conductor ResistanceMohamed A. HusseinNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument19 pagesCircuitsRoden FernandezNo ratings yet
- Only Electrons Can Be Gained or Lost by Atoms Using Simple TechniquesDocument18 pagesOnly Electrons Can Be Gained or Lost by Atoms Using Simple TechniquesJackie GiallombardoNo ratings yet
- CLASS 9 CBSE CH-12 ElectricityDocument63 pagesCLASS 9 CBSE CH-12 ElectricityannigarwalNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument7 pagesEnergyMike OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Cfe Bu2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCfe Bu2 ReviewerMaria Katrina Ilumin VersozaNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of TransformerDocument28 pagesEfficiency of TransformerJane Erestain BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument96 pagesLab ManualASWANI RAJAN50% (2)
- Torino ElectricDocument85 pagesTorino ElectricScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Ee PrelimsDocument5 pagesEe Prelimselaizaagudo17No ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Notes Chapter 7 Electricity: 7.1 ElectrostaticsDocument10 pagesForm 3 Science Notes Chapter 7 Electricity: 7.1 ElectrostaticsJu Li TanNo ratings yet
- Electrical System BasicsDocument63 pagesElectrical System BasicsDuggineni RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ece ReviewerDocument4 pagesEce ReviewerKwinn EspinosaNo ratings yet
- INTRODocument35 pagesINTROSubharth SahaNo ratings yet
- MALVINO-Book ReviewDocument30 pagesMALVINO-Book ReviewAylie PilobelloNo ratings yet
- Types of Electrical LoadsDocument2 pagesTypes of Electrical LoadsChandaKunda50% (2)
- Week 14Document25 pagesWeek 14ali burhan tahirNo ratings yet
- A6.1 Basic Electrical TechnologyDocument65 pagesA6.1 Basic Electrical TechnologyRajeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical SystemDocument16 pagesElectrical SystemCjoy MañiboNo ratings yet
- BASIC Elec. TermsDocument5 pagesBASIC Elec. TermsRamces SolimanNo ratings yet
- G1 5 ReviewerDocument68 pagesG1 5 Reviewerangelyn violaNo ratings yet
- ARE-Ch10 Electrical SystemsDocument13 pagesARE-Ch10 Electrical Systemsmdmasood3295No ratings yet
- Topic ElectricityDocument8 pagesTopic ElectricityChumaNo ratings yet
- Basic Priciples of ElectricityDocument39 pagesBasic Priciples of ElectricityTejaswi PoludasuNo ratings yet
- Circuits QRDocument60 pagesCircuits QRDon Mariano Marcos Elementary SchoolNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits SummaryDocument3 pagesElectrical Circuits SummaryArcangEl RicaLynNo ratings yet
- Electrical Terms: Ohm'S Law (George Simon Ohm'S) - Relation Between Pressure CurrrentDocument8 pagesElectrical Terms: Ohm'S Law (George Simon Ohm'S) - Relation Between Pressure CurrrentJM ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Electrical TerminologiesDocument11 pagesElectrical TerminologiesVincent Ganasi LipawenNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Question and Answer - POWER SYSTEM QUESTION and ANSWERDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Question and Answer - POWER SYSTEM QUESTION and ANSWERchico brilliantoNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitDocument13 pagesElectric Circuitdead poolNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument50 pagesElectric CircuitsClaudineNo ratings yet
- Current. Voltage and ResistanceDocument2 pagesCurrent. Voltage and ResistanceJR ALMANZARNo ratings yet
- FLEX Course Material ABUTLI2S BUILDING UTILITIES 2Document13 pagesFLEX Course Material ABUTLI2S BUILDING UTILITIES 2Roger Delos Reyes FercolNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics I ReviewerDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics I ReviewerAyana Nylazir BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument19 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel CircuitsArchiemedez BatanganNo ratings yet
- Building Services Ii: Unit 1 - Electrical and Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring SystemsDocument72 pagesBuilding Services Ii: Unit 1 - Electrical and Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring Systemsmaria nancyNo ratings yet
- Building Services Ii: Unit 1 - Electrical and Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring SystemsDocument58 pagesBuilding Services Ii: Unit 1 - Electrical and Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring SystemsArun PrakashNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits CH 17.4 8thDocument16 pagesElectric Circuits CH 17.4 8ththegedusNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument17 pagesElectrical EnergykuevoradzogloriaNo ratings yet
- Physics SummaryDocument2 pagesPhysics SummaryresacyanniNo ratings yet
- Topics To Be Covered: Unit-2: Basic Circuit ElementsDocument11 pagesTopics To Be Covered: Unit-2: Basic Circuit ElementsParthaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument53 pagesBasic Principles of ElectricityRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1Document7 pagesEngineering Utilities 1Vanissa MontillaNo ratings yet
- Think EntrepreneuriallyDocument29 pagesThink EntrepreneuriallyDipali SikandNo ratings yet
- Grade 7&8 Week 2Document18 pagesGrade 7&8 Week 2RUSELLE HOROHORONo ratings yet
- mtb2 Quarter 4 Week 1 2Document3 pagesmtb2 Quarter 4 Week 1 2Carino ArleneNo ratings yet
- The Impact of National Culture PDFDocument30 pagesThe Impact of National Culture PDFJovanaNo ratings yet
- SECOND Semester, AY 2022-2023: Mission VisionDocument34 pagesSECOND Semester, AY 2022-2023: Mission Visionjeyyy BonesssNo ratings yet
- Industrial Marketing 5-6Document2 pagesIndustrial Marketing 5-6Mary Grace Ygot ParachaNo ratings yet
- CV Review 35Document1 pageCV Review 35Pean CkNo ratings yet
- Powers and Functions of Registrar Under Trade Union ActDocument20 pagesPowers and Functions of Registrar Under Trade Union ActJagriti SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Eutectic 19910: A Hard Nickel-Chromium Coating For Resistance To AbrasionDocument2 pagesEutectic 19910: A Hard Nickel-Chromium Coating For Resistance To AbrasionFactel SANo ratings yet
- PN8603-X-2 xPON OLT Product Specifications: Topvision Technologies Co., LTDDocument7 pagesPN8603-X-2 xPON OLT Product Specifications: Topvision Technologies Co., LTDmylife900No ratings yet
- Back Stepping - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesBack Stepping - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMario RossiNo ratings yet
- Power Query & BIDocument14 pagesPower Query & BIzubair muhammad0% (2)
- Nora Esd ProfileDocument4 pagesNora Esd ProfileProjectinsightNo ratings yet
- Delphi XE HandbookDocument135 pagesDelphi XE HandbookRadovan JaicNo ratings yet
- KBT65DP15 15RT0Document1 pageKBT65DP15 15RT0Andre LanaNo ratings yet
- NullDocument2 pagesNullapi-27552272No ratings yet
- Exam 2018 s1 Op2 NewDocument12 pagesExam 2018 s1 Op2 NewmakgethwawhitneyNo ratings yet
- Recereum WhitePaperDocument23 pagesRecereum WhitePaperLord VNo ratings yet
- 096 Floor Statement On Presidents Decision To Increase Troops in Iraq Obama SpeechDocument3 pages096 Floor Statement On Presidents Decision To Increase Troops in Iraq Obama SpeechDivya Deepika MaddireddyNo ratings yet
- GBP Statement: Account SummaryDocument16 pagesGBP Statement: Account SummaryKris TheVillainNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Regrind Materials in PVC Extrusion ProcessingDocument1 pageUtilization of Regrind Materials in PVC Extrusion ProcessingAntonius PrakosaNo ratings yet
- 05 Hydrologic LossesDocument39 pages05 Hydrologic LossesMaan HinolanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Air CompressorDocument15 pagesUnit 5 Air Compressormadhume01No ratings yet
- Lab - Manual LP V (2019PATERN)Document39 pagesLab - Manual LP V (2019PATERN)Vaishnavi DhimateNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering Module 1Document32 pagesEarthquake Engineering Module 1Ed AnthonyNo ratings yet