Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-4
Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-4
Uploaded by
Adam Michael GreenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology: Dynamics, Analysis, and ForecastingFrom EverandMidlatitude Synoptic Meteorology: Dynamics, Analysis, and ForecastingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Technical, Aerodynamic & Performance Aspects of a Helicopter: A Manual for Helicopter Pilots and Engineers Who Want to Know MoreFrom EverandThe Technical, Aerodynamic & Performance Aspects of a Helicopter: A Manual for Helicopter Pilots and Engineers Who Want to Know MoreRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CPB30004 Process Dynamics and Control Experiment 4: Gas Pressure Process Control Lab ReportDocument18 pagesCPB30004 Process Dynamics and Control Experiment 4: Gas Pressure Process Control Lab ReportSiti Hajar Mohamed100% (19)
- Main Pump (Destroke Pressure) - Test and Adjust..Document12 pagesMain Pump (Destroke Pressure) - Test and Adjust..brahim100% (1)
- FWC Air Cooled Exchanger PDFDocument49 pagesFWC Air Cooled Exchanger PDFdinakaranpatel100% (1)
- Flatpack: Link Surface Control Systems and Downhole EquipmentDocument1 pageFlatpack: Link Surface Control Systems and Downhole EquipmentkirankirkNo ratings yet
- External LouversDocument2 pagesExternal LouversAmr Adeeb Abd-ElaahNo ratings yet
- Design of Hyperbolic Cooling TowerDocument58 pagesDesign of Hyperbolic Cooling TowerSanthi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Supersonic Wind Tunnel: Experiment No: 4 Date: 21/08/2018 AimDocument5 pagesCalibration of Supersonic Wind Tunnel: Experiment No: 4 Date: 21/08/2018 Aimbad guyNo ratings yet
- Basic Data:: Calculation of Gust Effect FactorDocument4 pagesBasic Data:: Calculation of Gust Effect FactorassadeqNo ratings yet
- Wind Load CalculationDocument4 pagesWind Load CalculationPriya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Wind Load CalculationDocument3 pagesWind Load CalculationGajera HarshadNo ratings yet
- Ip 21151006Document15 pagesIp 21151006Abuturab SharikmaslatNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part28Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part28Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Assignmet 3 and 4 For Survey Oguti Thomas NDCE Otee Isaac NDCE Olila Denis NDAR QN1a) - State The Aid of The Two-Peg TestDocument7 pagesAssignmet 3 and 4 For Survey Oguti Thomas NDCE Otee Isaac NDCE Olila Denis NDAR QN1a) - State The Aid of The Two-Peg TestOtee IsaacNo ratings yet
- Soil Bearing Capacity CalcuationsDocument26 pagesSoil Bearing Capacity CalcuationsBishal Thapa MagarNo ratings yet
- Modul Ks No - 17Document8 pagesModul Ks No - 17minhvinh7793No ratings yet
- cp3 Wind Load CalculationsDocument1 pagecp3 Wind Load CalculationsSumedha MayadunnaNo ratings yet
- Report 3Document14 pagesReport 3sahilbarbade.ee101No ratings yet
- Horizontal Curve Setting Line/ Legs Distance (M) Station Chainage Deflection Angle Radius Tangent Length Length of Curve Apex (E) BC MC EC From ToDocument38 pagesHorizontal Curve Setting Line/ Legs Distance (M) Station Chainage Deflection Angle Radius Tangent Length Length of Curve Apex (E) BC MC EC From ToRam Prasad NeupaneNo ratings yet
- MWH S Water Treatment Principles and Design Third Edition - 2012 - Crittenden - Appendix C Physical Properties of WaterDocument2 pagesMWH S Water Treatment Principles and Design Third Edition - 2012 - Crittenden - Appendix C Physical Properties of WaterbastianpurwaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of WaterDocument1 pagePhysical Properties of WaterJampier32No ratings yet
- R Rec P.838 2Document6 pagesR Rec P.838 2Madeline CurryNo ratings yet
- Chapter One (Roof Slab Analysis and Design)Document33 pagesChapter One (Roof Slab Analysis and Design)yohannisadmass122123No ratings yet
- Estimation of Quantities For EarthworkDocument2 pagesEstimation of Quantities For Earthworkmichael getachewNo ratings yet
- Moment at Each SectionDocument9 pagesMoment at Each SectionSanket BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Midspan Clearance - Calc SheetDocument1 pageMidspan Clearance - Calc SheetJoyce ChepkiruiNo ratings yet
- App3Document2 pagesApp3hamidrezaee008No ratings yet
- r050212103 Aircraft Engineering DrawingDocument11 pagesr050212103 Aircraft Engineering DrawingSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Lot B Estimated Safe Soil Bearing CapacityDocument5 pagesLot B Estimated Safe Soil Bearing CapacityBenedict OgbaghaNo ratings yet
- ME 370: Adams Lab.: 2021: Session 5Document5 pagesME 370: Adams Lab.: 2021: Session 5Aadhya SinghNo ratings yet
- Phu Luc 2Document11 pagesPhu Luc 2Bao Tran TranNo ratings yet
- SlopeDocument2 pagesSlopeARUN RAWATNo ratings yet
- Verification - Hand Calculations Slope StabilityDocument11 pagesVerification - Hand Calculations Slope StabilitymarcoNo ratings yet
- Design Wind Pressure: Aseana Bpo BuildingDocument5 pagesDesign Wind Pressure: Aseana Bpo BuildingRyan De Vera PagalNo ratings yet
- Base Shear An OtherDocument58 pagesBase Shear An OthermohammedNo ratings yet
- Base Shear - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument20 pagesBase Shear - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsmohammedNo ratings yet
- Bridge Technology: Comprehensive Design Example For Prestressed Concrete (PSC) Girder Superstructure BridgeDocument40 pagesBridge Technology: Comprehensive Design Example For Prestressed Concrete (PSC) Girder Superstructure BridgeSajib DasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER OneDocument18 pagesCHAPTER Oneyohannisadmass122123No ratings yet
- PQ2 - 4A4-Zamiera PDFDocument6 pagesPQ2 - 4A4-Zamiera PDFZamiera ZamranNo ratings yet
- Module Mounting Structure Staad Report - Al. StructureDocument23 pagesModule Mounting Structure Staad Report - Al. StructureGhanshyam SinghNo ratings yet
- March A. Observed Climatologic Data & Relevant Parameters: If Solar Radiation Rs Is Not AvailableDocument18 pagesMarch A. Observed Climatologic Data & Relevant Parameters: If Solar Radiation Rs Is Not AvailableApril Rose PlacerNo ratings yet
- Factor de Seguridad1Document7 pagesFactor de Seguridad1HAMMER BRAYAN VASQUEZ TORIBIONo ratings yet
- Direct Step MethodDocument4 pagesDirect Step MethodShoaib MateenNo ratings yet
- Levelling ReportDocument11 pagesLevelling Reportfadliezan1No ratings yet
- Typical RC Column Design Calculation SheetDocument1 pageTypical RC Column Design Calculation SheetINIMFON JAMESNo ratings yet
- HW2 Ans RevDocument14 pagesHW2 Ans RevanonymoussionNo ratings yet
- Final Winter 2021Document3 pagesFinal Winter 2021Maya TantawiNo ratings yet
- Aisc - 7-10-Wind Load CalculationDocument18 pagesAisc - 7-10-Wind Load CalculationameyyammaiNo ratings yet
- Jabel - Column Reinforcement DesignDocument27 pagesJabel - Column Reinforcement Designjamesbeth162No ratings yet
- 52402-BDK-PIP-CS-010 Pipe Wall Thickness Rev 0Document3 pages52402-BDK-PIP-CS-010 Pipe Wall Thickness Rev 0sudjonoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SolutionDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Example - CylinderDocument18 pagesWind Load Example - CylinderAnonymous f3uZJugqvNo ratings yet
- Liquefaction AnalysisDocument8 pagesLiquefaction AnalysisStructural SpreadsheetsNo ratings yet
- Steam Table From PerryDocument2 pagesSteam Table From PerryIndrawNo ratings yet
- 11711515ppt2019 190914160308Document28 pages11711515ppt2019 190914160308JeTengine EaterNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 - AirportDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 - AirportSaroj AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Firing Tables mk19Document11 pagesFiring Tables mk19SSOpticsNo ratings yet
- NSCP 2015 - Wind Load Design PDFDocument6 pagesNSCP 2015 - Wind Load Design PDFNedžadDžokoNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Design NSCP 2015Document6 pagesWind Load Design NSCP 2015MARKCHRISTMASNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Design NSCP 2015 PDFDocument6 pagesWind Load Design NSCP 2015 PDFMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Design NSCP 2015 PDFDocument6 pagesWind Load Design NSCP 2015 PDFdan0427No ratings yet
- Principles and Practice of Variable Pressure / Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (VP-ESEM)From EverandPrinciples and Practice of Variable Pressure / Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (VP-ESEM)No ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 5Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 5Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 4Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 4Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 3Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 3Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 1Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 1Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 5Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 5Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 10Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 10Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 8Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 8Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 2Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 2Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 9Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 9Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 7Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 7Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 6Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 6Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 1Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 1Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 3Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 3Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 4Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 4Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part33Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part33Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 2Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 2Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-3Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-3Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-6Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-6Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-5Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-5Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-2Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-2Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-7Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-7Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part32Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part32Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part27Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part27Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-1Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-1Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part25Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part25Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part21Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part21Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part28Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part28Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part26Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part26Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part29Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part29Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part22Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part22Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones para Componentes Puros PCPEquationFitDocument27 pagesEcuaciones para Componentes Puros PCPEquationFitMariano prolasNo ratings yet
- Civil Sem 3Document30 pagesCivil Sem 3malik mohsinNo ratings yet
- AHRI Standard 1280 - 2014 (R2022) (SI.I-P)Document23 pagesAHRI Standard 1280 - 2014 (R2022) (SI.I-P)TamNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Seepage On The Stability of Sea WallDocument24 pagesThe Effect of Seepage On The Stability of Sea WallChris FindlayNo ratings yet
- Setting Up A Reservoir Simulation ModelDocument30 pagesSetting Up A Reservoir Simulation ModelMariam Tatty LeonNo ratings yet
- Well Test Interpretation - SchlumbergerDocument128 pagesWell Test Interpretation - SchlumbergerLaode Faisal RahmanNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Lab PDFDocument4 pagesAir Compressor Lab PDFbernabas100% (2)
- Introduction To General Organic and Biochemistry 11Th Edition Bettelheim Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesIntroduction To General Organic and Biochemistry 11Th Edition Bettelheim Test Bank Full Chapter PDFarthur.hendricks257100% (20)
- Chapter 5 - Internal Forced ConvectionDocument38 pagesChapter 5 - Internal Forced ConvectionEihabARaoufMustafaNo ratings yet
- SPE 68504 Jet Drilling Tool: Cost-Effective Lateral Drilling Technology For Enhanced Oil RecoveryDocument9 pagesSPE 68504 Jet Drilling Tool: Cost-Effective Lateral Drilling Technology For Enhanced Oil RecoveryAnonymous VNu3ODGavNo ratings yet
- ABB 2600 Series-SealsDocument40 pagesABB 2600 Series-SealsDarkhan Serikbayev100% (1)
- Unsteady Three-Dimensional Numerical Model Development For The Investigation of The Gas Jet Wiping Process On The Flow Behaviors Near The Galvanizing Bath SurfaceDocument10 pagesUnsteady Three-Dimensional Numerical Model Development For The Investigation of The Gas Jet Wiping Process On The Flow Behaviors Near The Galvanizing Bath SurfaceJJNo ratings yet
- HCL Unloading StudyDocument17 pagesHCL Unloading StudykalaiNo ratings yet
- 1995 International Symposium (14th) Military Aspects of Blast and Shock (MABS) Held in Las Cruces, New MexicoDocument731 pages1995 International Symposium (14th) Military Aspects of Blast and Shock (MABS) Held in Las Cruces, New MexicoFirebrand38No ratings yet
- No Solution, No Points.: Saint Mary's UniversityDocument1 pageNo Solution, No Points.: Saint Mary's UniversityMark Anthony TajonNo ratings yet
- Barfield Pressure Tester 2311FADocument22 pagesBarfield Pressure Tester 2311FAguicordovaNo ratings yet
- Astm F1173 PDFDocument15 pagesAstm F1173 PDFRunchis DunchisNo ratings yet
- 54 PDFDocument8 pages54 PDFMuhammad Iqbal PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document46 pagesCH 5Chala1989No ratings yet
- G446 2104 PDS 0150 0027 Rev 02Document14 pagesG446 2104 PDS 0150 0027 Rev 02Magesh VenuNo ratings yet
- B.E. Gelfand - Blast Waves Attenuation in Two-Phase MediaDocument17 pagesB.E. Gelfand - Blast Waves Attenuation in Two-Phase MediaYamveaNo ratings yet
- Igces Physics Mock QPDocument16 pagesIgces Physics Mock QPWilliam ChongNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics of Buried PipesDocument11 pagesStructural Mechanics of Buried PipesSheikh Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- TF100-121E 64143 BTTM Load ValveDocument4 pagesTF100-121E 64143 BTTM Load ValveMardel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Vilter Refrigeration Piping Data Manual en US 5419418 02Document89 pagesVilter Refrigeration Piping Data Manual en US 5419418 02AmmoniaR717No ratings yet
- Radial Near Wellbore Stimulation by Acoustic Waves SPE 86492 MSDocument7 pagesRadial Near Wellbore Stimulation by Acoustic Waves SPE 86492 MSBolsec14No ratings yet
Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-4
Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-4
Uploaded by
Adam Michael GreenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-4
Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-4
Uploaded by
Adam Michael GreenCopyright:
Available Formats
3146 evsjv‡`k †M‡RU, AwZwi³, †deªæqvwi 11, 2021
Enclosed Buildings: Walls & Roofs
Notes:
1. Pressures shown are applied to the horizontal and vertical projections, for exposure
A, at h=9.1m, I=1.0, and Kzt = 1.0. Adjust to other conditions using Equation 6.2.3.
2. The load patterns shown shall be applied to each corner of the building in turn as the reference
corner. (See Figure 6.2.10)
3. For the design of the longitudinal MWFRS use θ = 0°, and locate the zone E/F, G/H boundary at
the mid-length of the building.
4. Load cases 1 and 2 must be checked for 25° < θ ≤ 45°. Load case 2 at 25° is provided only for
interpolation between 25° to 30°.
5. Plus and minus signs signify pressures acting toward and away from the projected surfaces,
respectively.
6. For roof slopes other than those shown, linear interpolation is permitted.
7. The total horizontal load shall not be less than that determined by assuming ps = 0 in zones B & D.
8. The zone pressures represent the following:
Horizontal pressure zones – Sum of the windward and leeward net (sum of internal and external)
pressures on vertical projection of:
A - End zone of wall C - Interior zone of wall
B - End zone of roof D - Interior zone of roof
Vertical pressure zones – Net (sum of internal and external) pressures on horizontal projection of:
E - End zone of windward roof G - Interior zone of windward roof
F - End zone of leeward roof H - Interior zone of leeward roof
9. Where zone E or G falls on a roof overhang on the windward side of the building, use EOH and
GOH for the pressure on the horizontal projection of the overhang. Overhangs on the leeward
and side edges shall have the basic zone pressure applied.
10. Notation:
a: 10 percent of least horizontal dimension or 0.4h, whichever is smaller, but not less than
either 4% of least horizontal dimension or 0.9 m.
h: Mean roof height, in feet (meters), except that eave height shall be used for roof angles <10°.
θ: Angle of plane of roof from horizontal, in degrees.
BNBC 2020 Part VI Chapter 2
evsjv‡`k †M‡RU, AwZwi³, †deªæqvwi 11, 2021 3147
Adjustment Factor for Building Height and Exposure,
Mean roof height (m) Exposure
A B C
4.6 1.00 1.21 1.47
6.0 1.00 1.29 1.55
7.6 1.00 1.35 1.61
9.1 1.00 1.40 1.66
10.7 1.05 1.45 1.70
12.2 1.09 1.49 1.74
13.7 1.12 1.53 1.78
15.2 1.16 1.56 1.81
16.8 1.19 1.59 1.84
18.3 1.22 1.62 1.87
Figure 6.2.2 Design wind pressure for main wind force resisting system- Method 1
(h ≤ 18.3 m)
Enclosed Buildings: Walls & Roofs
Notes:
1. Pressures shown are applied normal to the surface, for exposure A, at h = 9.1m, I = 1.0, and Kzt =
1.0. Adjust to other conditions using Equation 6.2.4.
2. Plus and minus signs signify pressures acting toward and away from the surfaces, respectively.
3. For hip roofs with θ ≤ 25°, Zone 3 shall be treated as Zone 2.
4. For effective wind areas between those given, value may be interpolated, otherwise use the value
associated with the lower effective wind area.
5. Notation:
a: 10 percent of least horizontal dimension or 0.4h, whichever is smaller, but not less than either 4%
of least horizontal dimension or 0.9 m.
h: Mean roof height, in feet (meters), except that eave height shall be used for roof angles <10°.
θ: Angle of plane of roof from horizontal, in degrees.
BNBC 2020 Part VI Chapter 2
3148 evsjv‡`k †M‡RU, AwZwi³, †deªæqvwi 11, 2021
Roof Overhang Net Design Wind Pressure, Pnet30 (kN/m2)
(Exposure A at h = 9.1 m with l= 1.0)
Roof Zone Effective Basic Wind Speed V (m/s)
Wind area (m2) 40.23 44.7 49.17 53.64 58.11 62.58 67.05 75.99
Pitch
2 0.930 -1.005 -1.239 -1.502 -1.785 -2.096 -2.431 -2.790 -3.584
2 1.860 -0.986 -1.220 -1.473 -1.756 -2.058 -2.388 -2.742 -3.522
Roof 0 to 7 degrees
2 4.648 -0.962 -1.191 -1.440 -1.713 -2.010 -2.330 -2.675 -3.436
2 9.296 -0.947 -1.168 -1.412 -1.680 -1.971 -2.287 -2.627 -3.373
3 0.930 -1.656 -2.043 -2.470 -2.943 -3.450 -4.005 -4.594 -5.905
3 1.860 -1.297 -1.603 -1.938 -2.311 -2.708 -3.144 -3.609 -4.632
3 4.648 -0.828 -1.024 -1.240 -1.474 -1.727 -2.005 -2.302 -2.957
3 9.296 -0.479 -0.584 -0.708 -0.842 -0.986 -1.144 -1.311 -1.684
Figure 6.2.3 Design wind pressure for components and cladding - Method 1 (h ≤ 18.3 m)
Roof Overhang Net Design Wind Pressure, Pnet30 (kN/m2)
(Exposure A at h = 9.1 m with l= 1.0)
Roof Zone Effective Basic Wind Speed V (m/s)
Pitch Wind area 40.23 44.7 49.17 53.64 58.11 62.58 67.05 75.99
(m2)
2 0.930 -1.302 -1.603 -1.943 -2.311 -2.713 -3.144 -3.613 -4.637
2 1.860 -1.302 -1.603 -1.943 -2.311 -2.713 -3.144 -3.613 -4.637
Roof > 7 to 27 degrees
2 4.648 -1.302 -1.603 -1.943 -2.311 -2.713 -3.144 -3.613 -4.637
2 9.296 -1.302 -1.603 -1.943 -2.311 -2.713 -3.144 -3.613 -4.637
3 0.930 -2.187 -2.699 -3.268 -3.885 -4.560 -5.292 -6.072 -7.800
3 1.860 -1.971 -2.436 -2.948 -3.507 -4.115 -4.775 -5.479 -7.039
3 4.648 -1.689 -2.086 -2.526 -3.005 -3.526 -4.091 -4.694 -6.034
3 9.296 -1.479 -1.823 -2.206 -2.627 -3.082 -3.574 -4.106 -5.268
BNBC 2020 Part VI Chapter 2
evsjv‡`k †M‡RU, AwZwi³, †deªæqvwi 11, 2021 3149
2 0.930 -1.182 -1.460 -1.766 -2.101 -2.464 -2.861 -3.282 -4.216
2 1.860 -1.148 -1.416 -1.713 -2.038 -2.393 -2.775 -3.182 -4.091
Roof >27 to 45 degrees 2 4.648 -1.101 -1.359 -1.641 -1.952 -2.292 -2.660 -3.052 -3.924
2 9.296 -1.062 -1.311 -1.587 -1.890 -2.220 -2.574 -2.952 -3.795
3 0.930 -1.182 -1.460 -1.766 -2.101 -2.464 -2.861 -3.283 -4.216
3 1.860 -1.148 -1.416 -1.713 -2.038 -2.393 -2.775 -3.182 -4.091
3 4.648 -1.101 -1.359 -1.641 -1.952 -2.292 -2.660 -3.053 -3.923
3 9.296 -1.062 -1.311 -1.589 -1.890 -2.220 -2.574 -2.952 -3.795
Adjustment Factor for Building Height and Exposure,
Mean roof height (m) Exposure
A B C
4.6 1.00 1.21 1.47
6.1 1.00 1.29 1.55
7.6 1.00 1.35 1.61
9.15 1.00 1.40 1.66
10.7 1.05 1.45 1.70
12.2 1.09 1.49 1.74
13.7 1.12 1.53 1.78
15.2 1.16 1.56 1.81
16.8 1.19 1.59 1.84
18.3 1.22 1.62 1.87
Unit Conversion – 1.0 ft =0.3048 m; 1.0 ft2 = 0.0929 m2; 1.0 psf = 0.0479 kN/m2
Figure 6.2.3 (Contd.) Design wind pressure for components and cladding-Method 1
(h ≤ 18.3 m)
BNBC 2020 Part VI Chapter 2
3150 evsjv‡`k †M‡RU, AwZwi³, †deªæqvwi 11, 2021
Topographic Multipliers for Exposure B
H/Lh K1 Multiplier x/Lh K2 Multiplier z/Lh K3 Multiplier
2-D 2-D 3-D 2-D All 2-D 2-D 3-D
Ridge Escarp. Axisym. Escarp. Other Ridge Escarp. Axisym.
Hill Cases Hill
0.20 0.29 0.17 0.21 0.00 1.00 1.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
0.25 0.36 0.21 0.26 0.50 0.88 0.67 0.10 0.74 0.78 0.67
0.30 0.43 0.26 0.32 1.00 0.75 0.33 0.20 0.55 0.61 0.45
0.35 0.51 0.30 0.37 1.50 0.63 0.00 0.30 0.41 0.47 0.30
0.40 0.58 0.34 0.42 2.00 0.50 0.00 0.40 0.30 0.37 0.20
0.45 0.65 0.38 0.47 2.50 0.38 0.00 0.50 0.22 0.29 0.14
0.50 0.72 0.43 0.53 3.00 0.25 0.00 0.60 0.17 0.22 0.09
3.50 0.13 0.00 0.70 0.12 0.17 0.06
4.00 0.00 0.00 0.80 0.09 0.14 0.04
0.90 0.07 0.11 0.03
1.00 0.05 0.08 0.02
1.50 0.01 0.02 0.00
2.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
Notes:
1. For values of H/Lh, x/Lh and z/Lh other than those shown, linear interpolation is permitted.
2. For H/Lh > 0.5, assume H/Lh = 0.5 for evaluating K1 and substitute 2H for Lh for evaluating K2 and
K3 .
3. Multipliers are based on the assumption that wind approaches the hill or escarpment along the
direction of maximum slope.
4. Notation:
H: Height of hill or escarpment relative to the upwind terrain, in meters.
Lh: Distance upwind of crest to where the difference in ground elevation is half the height of hill
or escarpment, in meters.
K1: Factor to account for shape of topographic feature and maximum speed-up effect.
K2: Factor to account for reduction in speed-up with distance upwind or downwind of crest.
K3: Factor to account for reduction in speed-up with height above local terrain.
x: Distance (upwind or downwind) from the crest to the building site, in meters.
z: Height above local ground level, in meters.
W: Horizontal attenuation factor.
Equation:
γ: Height attenuation factor
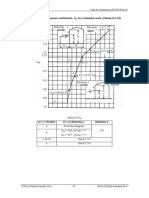
0/" 5 (1 + 01 0 02 ) ; K1 determined from Table below; 0 5 ¸1 −
| |
¹ ; 02 5
P Òë//B Á êBÁ
BNBC 2020 Part VI Chapter 2
evsjv‡`k †M‡RU, AwZwi³, †deªæqvwi 11, 2021 3151
Parameters for Speed-Up Over Hills and Escarpments
Hill Shape K1/(H/Lh) γ μ
Upwind of Downwind
Exposure A Exposure B Exposure C
crest of Crest
2-dimensional ridges 1.30 1.45 1.55 3 1.5 1.5
(or valleys with negative
H in K1/(H/Lh)
2-dimensional 0.75 0.85 0.95 2.5 1.5 4
escarpments
3-dimensional axisym. 0.95 1.05 1.15 4 1.5 1.5
Hill
Figure 6.2.4 Topographic factor, Kzt - Method 2
Enclosed, Partially Enclosed, and Open Buildings: Walls & Roofs
Enclosure Classification GCpi Notes:
1. Plus and minus signs signify pressures acting
Open Building 0.00
toward and away from the internal surfaces,
Partially Enclosed Building +0.55
respectively.
-0.55
2. Values of GCpi shall be used with qz or qh as
Enclosed Building +0.18 specified in Sec 2.4.11.
-0.18 3. Two cases shall be considered to determine the
critical load requirements for the appropriate
condition:
(i) a positive value of GCpi applied to all internal
surfaces
(ii) a negative value of GCpi applied to all internal
surfaces.
Figure 6.2.5 Internal pressure coefficient, GCpi main wind force resisting system
component and cladding - Method 2 (All Heights)
BNBC 2020 Part VI Chapter 2
3152 evsjv‡`k †M‡RU, AwZwi³, †deªæqvwi 11, 2021
Enclosed, Partially Enclosed Buildings: Walls & Roofs
Wall Pressure Coefficients, Cp
Surface L/B Cp Use With
Windward Wall All values 0.8 qz
Leeward Wall 0-1 -0.5 qh
2 -0.3
>4 -0.2
Side Wall All values -0.7 qh
Figure 6.2.6 External Pressure Coefficients, Cp main wind force resisting system -
Method 2 (All Heights)
BNBC 2020 Part VI Chapter 2
You might also like
- Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology: Dynamics, Analysis, and ForecastingFrom EverandMidlatitude Synoptic Meteorology: Dynamics, Analysis, and ForecastingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Technical, Aerodynamic & Performance Aspects of a Helicopter: A Manual for Helicopter Pilots and Engineers Who Want to Know MoreFrom EverandThe Technical, Aerodynamic & Performance Aspects of a Helicopter: A Manual for Helicopter Pilots and Engineers Who Want to Know MoreRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CPB30004 Process Dynamics and Control Experiment 4: Gas Pressure Process Control Lab ReportDocument18 pagesCPB30004 Process Dynamics and Control Experiment 4: Gas Pressure Process Control Lab ReportSiti Hajar Mohamed100% (19)
- Main Pump (Destroke Pressure) - Test and Adjust..Document12 pagesMain Pump (Destroke Pressure) - Test and Adjust..brahim100% (1)
- FWC Air Cooled Exchanger PDFDocument49 pagesFWC Air Cooled Exchanger PDFdinakaranpatel100% (1)
- Flatpack: Link Surface Control Systems and Downhole EquipmentDocument1 pageFlatpack: Link Surface Control Systems and Downhole EquipmentkirankirkNo ratings yet
- External LouversDocument2 pagesExternal LouversAmr Adeeb Abd-ElaahNo ratings yet
- Design of Hyperbolic Cooling TowerDocument58 pagesDesign of Hyperbolic Cooling TowerSanthi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Supersonic Wind Tunnel: Experiment No: 4 Date: 21/08/2018 AimDocument5 pagesCalibration of Supersonic Wind Tunnel: Experiment No: 4 Date: 21/08/2018 Aimbad guyNo ratings yet
- Basic Data:: Calculation of Gust Effect FactorDocument4 pagesBasic Data:: Calculation of Gust Effect FactorassadeqNo ratings yet
- Wind Load CalculationDocument4 pagesWind Load CalculationPriya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Wind Load CalculationDocument3 pagesWind Load CalculationGajera HarshadNo ratings yet
- Ip 21151006Document15 pagesIp 21151006Abuturab SharikmaslatNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part28Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part28Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Assignmet 3 and 4 For Survey Oguti Thomas NDCE Otee Isaac NDCE Olila Denis NDAR QN1a) - State The Aid of The Two-Peg TestDocument7 pagesAssignmet 3 and 4 For Survey Oguti Thomas NDCE Otee Isaac NDCE Olila Denis NDAR QN1a) - State The Aid of The Two-Peg TestOtee IsaacNo ratings yet
- Soil Bearing Capacity CalcuationsDocument26 pagesSoil Bearing Capacity CalcuationsBishal Thapa MagarNo ratings yet
- Modul Ks No - 17Document8 pagesModul Ks No - 17minhvinh7793No ratings yet
- cp3 Wind Load CalculationsDocument1 pagecp3 Wind Load CalculationsSumedha MayadunnaNo ratings yet
- Report 3Document14 pagesReport 3sahilbarbade.ee101No ratings yet
- Horizontal Curve Setting Line/ Legs Distance (M) Station Chainage Deflection Angle Radius Tangent Length Length of Curve Apex (E) BC MC EC From ToDocument38 pagesHorizontal Curve Setting Line/ Legs Distance (M) Station Chainage Deflection Angle Radius Tangent Length Length of Curve Apex (E) BC MC EC From ToRam Prasad NeupaneNo ratings yet
- MWH S Water Treatment Principles and Design Third Edition - 2012 - Crittenden - Appendix C Physical Properties of WaterDocument2 pagesMWH S Water Treatment Principles and Design Third Edition - 2012 - Crittenden - Appendix C Physical Properties of WaterbastianpurwaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of WaterDocument1 pagePhysical Properties of WaterJampier32No ratings yet
- R Rec P.838 2Document6 pagesR Rec P.838 2Madeline CurryNo ratings yet
- Chapter One (Roof Slab Analysis and Design)Document33 pagesChapter One (Roof Slab Analysis and Design)yohannisadmass122123No ratings yet
- Estimation of Quantities For EarthworkDocument2 pagesEstimation of Quantities For Earthworkmichael getachewNo ratings yet
- Moment at Each SectionDocument9 pagesMoment at Each SectionSanket BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Midspan Clearance - Calc SheetDocument1 pageMidspan Clearance - Calc SheetJoyce ChepkiruiNo ratings yet
- App3Document2 pagesApp3hamidrezaee008No ratings yet
- r050212103 Aircraft Engineering DrawingDocument11 pagesr050212103 Aircraft Engineering DrawingSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Lot B Estimated Safe Soil Bearing CapacityDocument5 pagesLot B Estimated Safe Soil Bearing CapacityBenedict OgbaghaNo ratings yet
- ME 370: Adams Lab.: 2021: Session 5Document5 pagesME 370: Adams Lab.: 2021: Session 5Aadhya SinghNo ratings yet
- Phu Luc 2Document11 pagesPhu Luc 2Bao Tran TranNo ratings yet
- SlopeDocument2 pagesSlopeARUN RAWATNo ratings yet
- Verification - Hand Calculations Slope StabilityDocument11 pagesVerification - Hand Calculations Slope StabilitymarcoNo ratings yet
- Design Wind Pressure: Aseana Bpo BuildingDocument5 pagesDesign Wind Pressure: Aseana Bpo BuildingRyan De Vera PagalNo ratings yet
- Base Shear An OtherDocument58 pagesBase Shear An OthermohammedNo ratings yet
- Base Shear - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument20 pagesBase Shear - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsmohammedNo ratings yet
- Bridge Technology: Comprehensive Design Example For Prestressed Concrete (PSC) Girder Superstructure BridgeDocument40 pagesBridge Technology: Comprehensive Design Example For Prestressed Concrete (PSC) Girder Superstructure BridgeSajib DasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER OneDocument18 pagesCHAPTER Oneyohannisadmass122123No ratings yet
- PQ2 - 4A4-Zamiera PDFDocument6 pagesPQ2 - 4A4-Zamiera PDFZamiera ZamranNo ratings yet
- Module Mounting Structure Staad Report - Al. StructureDocument23 pagesModule Mounting Structure Staad Report - Al. StructureGhanshyam SinghNo ratings yet
- March A. Observed Climatologic Data & Relevant Parameters: If Solar Radiation Rs Is Not AvailableDocument18 pagesMarch A. Observed Climatologic Data & Relevant Parameters: If Solar Radiation Rs Is Not AvailableApril Rose PlacerNo ratings yet
- Factor de Seguridad1Document7 pagesFactor de Seguridad1HAMMER BRAYAN VASQUEZ TORIBIONo ratings yet
- Direct Step MethodDocument4 pagesDirect Step MethodShoaib MateenNo ratings yet
- Levelling ReportDocument11 pagesLevelling Reportfadliezan1No ratings yet
- Typical RC Column Design Calculation SheetDocument1 pageTypical RC Column Design Calculation SheetINIMFON JAMESNo ratings yet
- HW2 Ans RevDocument14 pagesHW2 Ans RevanonymoussionNo ratings yet
- Final Winter 2021Document3 pagesFinal Winter 2021Maya TantawiNo ratings yet
- Aisc - 7-10-Wind Load CalculationDocument18 pagesAisc - 7-10-Wind Load CalculationameyyammaiNo ratings yet
- Jabel - Column Reinforcement DesignDocument27 pagesJabel - Column Reinforcement Designjamesbeth162No ratings yet
- 52402-BDK-PIP-CS-010 Pipe Wall Thickness Rev 0Document3 pages52402-BDK-PIP-CS-010 Pipe Wall Thickness Rev 0sudjonoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SolutionDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Example - CylinderDocument18 pagesWind Load Example - CylinderAnonymous f3uZJugqvNo ratings yet
- Liquefaction AnalysisDocument8 pagesLiquefaction AnalysisStructural SpreadsheetsNo ratings yet
- Steam Table From PerryDocument2 pagesSteam Table From PerryIndrawNo ratings yet
- 11711515ppt2019 190914160308Document28 pages11711515ppt2019 190914160308JeTengine EaterNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 - AirportDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 - AirportSaroj AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Firing Tables mk19Document11 pagesFiring Tables mk19SSOpticsNo ratings yet
- NSCP 2015 - Wind Load Design PDFDocument6 pagesNSCP 2015 - Wind Load Design PDFNedžadDžokoNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Design NSCP 2015Document6 pagesWind Load Design NSCP 2015MARKCHRISTMASNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Design NSCP 2015 PDFDocument6 pagesWind Load Design NSCP 2015 PDFMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Design NSCP 2015 PDFDocument6 pagesWind Load Design NSCP 2015 PDFdan0427No ratings yet
- Principles and Practice of Variable Pressure / Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (VP-ESEM)From EverandPrinciples and Practice of Variable Pressure / Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (VP-ESEM)No ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 5Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 5Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 4Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 4Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 3Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 3Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 1Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 1Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 5Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 5Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 10Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 10Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 8Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 8Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- AFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 2Document4 pagesAFSL Godown Soil Test - Part - 2Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 9Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 9Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 7Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 7Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 6Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 6Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 1Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 1Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 3Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 3Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 4Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 4Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part33Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part33Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- IS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 2Document7 pagesIS875 (Part3) - Wind Loads On Buildings and Structures - IIT Kanpur-Part 2Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-3Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-3Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-6Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-6Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-5Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-5Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-2Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-2Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-7Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-7Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part32Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part32Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part27Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part27Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-1Document7 pagesWind Load Clauses, Formulas and Equations - Part-1Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part25Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part25Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part21Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part21Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part28Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part28Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part26Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part26Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part29Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part29Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part22Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part22Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones para Componentes Puros PCPEquationFitDocument27 pagesEcuaciones para Componentes Puros PCPEquationFitMariano prolasNo ratings yet
- Civil Sem 3Document30 pagesCivil Sem 3malik mohsinNo ratings yet
- AHRI Standard 1280 - 2014 (R2022) (SI.I-P)Document23 pagesAHRI Standard 1280 - 2014 (R2022) (SI.I-P)TamNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Seepage On The Stability of Sea WallDocument24 pagesThe Effect of Seepage On The Stability of Sea WallChris FindlayNo ratings yet
- Setting Up A Reservoir Simulation ModelDocument30 pagesSetting Up A Reservoir Simulation ModelMariam Tatty LeonNo ratings yet
- Well Test Interpretation - SchlumbergerDocument128 pagesWell Test Interpretation - SchlumbergerLaode Faisal RahmanNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Lab PDFDocument4 pagesAir Compressor Lab PDFbernabas100% (2)
- Introduction To General Organic and Biochemistry 11Th Edition Bettelheim Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesIntroduction To General Organic and Biochemistry 11Th Edition Bettelheim Test Bank Full Chapter PDFarthur.hendricks257100% (20)
- Chapter 5 - Internal Forced ConvectionDocument38 pagesChapter 5 - Internal Forced ConvectionEihabARaoufMustafaNo ratings yet
- SPE 68504 Jet Drilling Tool: Cost-Effective Lateral Drilling Technology For Enhanced Oil RecoveryDocument9 pagesSPE 68504 Jet Drilling Tool: Cost-Effective Lateral Drilling Technology For Enhanced Oil RecoveryAnonymous VNu3ODGavNo ratings yet
- ABB 2600 Series-SealsDocument40 pagesABB 2600 Series-SealsDarkhan Serikbayev100% (1)
- Unsteady Three-Dimensional Numerical Model Development For The Investigation of The Gas Jet Wiping Process On The Flow Behaviors Near The Galvanizing Bath SurfaceDocument10 pagesUnsteady Three-Dimensional Numerical Model Development For The Investigation of The Gas Jet Wiping Process On The Flow Behaviors Near The Galvanizing Bath SurfaceJJNo ratings yet
- HCL Unloading StudyDocument17 pagesHCL Unloading StudykalaiNo ratings yet
- 1995 International Symposium (14th) Military Aspects of Blast and Shock (MABS) Held in Las Cruces, New MexicoDocument731 pages1995 International Symposium (14th) Military Aspects of Blast and Shock (MABS) Held in Las Cruces, New MexicoFirebrand38No ratings yet
- No Solution, No Points.: Saint Mary's UniversityDocument1 pageNo Solution, No Points.: Saint Mary's UniversityMark Anthony TajonNo ratings yet
- Barfield Pressure Tester 2311FADocument22 pagesBarfield Pressure Tester 2311FAguicordovaNo ratings yet
- Astm F1173 PDFDocument15 pagesAstm F1173 PDFRunchis DunchisNo ratings yet
- 54 PDFDocument8 pages54 PDFMuhammad Iqbal PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document46 pagesCH 5Chala1989No ratings yet
- G446 2104 PDS 0150 0027 Rev 02Document14 pagesG446 2104 PDS 0150 0027 Rev 02Magesh VenuNo ratings yet
- B.E. Gelfand - Blast Waves Attenuation in Two-Phase MediaDocument17 pagesB.E. Gelfand - Blast Waves Attenuation in Two-Phase MediaYamveaNo ratings yet
- Igces Physics Mock QPDocument16 pagesIgces Physics Mock QPWilliam ChongNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics of Buried PipesDocument11 pagesStructural Mechanics of Buried PipesSheikh Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- TF100-121E 64143 BTTM Load ValveDocument4 pagesTF100-121E 64143 BTTM Load ValveMardel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Vilter Refrigeration Piping Data Manual en US 5419418 02Document89 pagesVilter Refrigeration Piping Data Manual en US 5419418 02AmmoniaR717No ratings yet
- Radial Near Wellbore Stimulation by Acoustic Waves SPE 86492 MSDocument7 pagesRadial Near Wellbore Stimulation by Acoustic Waves SPE 86492 MSBolsec14No ratings yet