Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity 2.1 Ray Diagram of Curved Mirrors Group 5
Activity 2.1 Ray Diagram of Curved Mirrors Group 5
Uploaded by
Uel James Subosa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views5 pagesThe document summarizes the characteristics of images formed by concave and convex mirrors based on the position of the object. For concave mirrors, when the object is between the focal point (F) and center of curvature (C), the image is real, inverted, and bigger than the object. When the object is between F and the vertex (V) for a convex mirror, the image is upright, smaller than the object, and real. Everyday examples of curved mirrors listed include car headlights, magnifying glasses, makeup mirrors, and passenger side wing mirrors on cars.
Original Description:
Aksbamajsnaksbms
Original Title
Activity-2.1-Ray-Diagram-of-Curved-Mirrors-Group-5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the characteristics of images formed by concave and convex mirrors based on the position of the object. For concave mirrors, when the object is between the focal point (F) and center of curvature (C), the image is real, inverted, and bigger than the object. When the object is between F and the vertex (V) for a convex mirror, the image is upright, smaller than the object, and real. Everyday examples of curved mirrors listed include car headlights, magnifying glasses, makeup mirrors, and passenger side wing mirrors on cars.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views5 pagesActivity 2.1 Ray Diagram of Curved Mirrors Group 5
Activity 2.1 Ray Diagram of Curved Mirrors Group 5
Uploaded by
Uel James SubosaThe document summarizes the characteristics of images formed by concave and convex mirrors based on the position of the object. For concave mirrors, when the object is between the focal point (F) and center of curvature (C), the image is real, inverted, and bigger than the object. When the object is between F and the vertex (V) for a convex mirror, the image is upright, smaller than the object, and real. Everyday examples of curved mirrors listed include car headlights, magnifying glasses, makeup mirrors, and passenger side wing mirrors on cars.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Activity 2.
1-Ray Diagram of Curved Mirrors (Group 5)
Keith De Guzman(Answered concave mirror no. 3&4 and a question)
Althea Pineda (Answered concave mirror no. 5 and a question)
Stephanie Pacana (Answered concave no. 1&2 and a question)
Uel James Subosa (Answered convex no. 1 and a question)
Donato Minerva (Did not contribute)
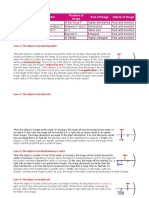
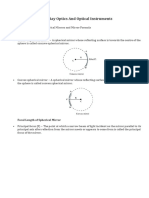
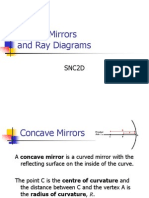
Concave Mirrors Characteristics
1. Object is farther than C. L- Farther than C
O- Inverted
S- smaller than the object
T- Real
2. Object at C (center of L- The object is at the center of C
curvature) O- Inverted
S- same size
T- Real
3. Object is between C & F. L- Between C and F
O- Inverted
S- Bigger
T- Real
4. Object at F. L- at F
O- Inverted
S- Bigger
T- Image
5. Object is between F & V. L- near at F
O- Upright
S- smaller
T-Real
Convex Mirror
(follow the rays for convex
mirrors)
1. Farther than C in front of the L- Farther than C in front of mirror
mirror O- Upright
S- Smaller
T- Real
2. Between F & V in front of the L- Between the F in front of the
mirror. mirror
O- Upright
S- same size
T- Real
Questions:
1. Does the position of the object affect the location, orientation,
size, and type (LOST) of the image? How?
Yes, it does because when you move the object the LOST of the
image changes based on the position.
2. For concave mirrors, in what position of the object is the image
real, inverted and bigger? For concave mirrors, when the object is
located anywhere between F and C, the image is real, inverted,
enlarged in size, and located beyond C.
3. In which position of the object is its image smaller?
When the image is getting farther away to the mirror it will start to
shrink due to how far it’s going.
4. Give examples in everyday life where curved mirrors are used.
-Headlights in the car.
-Magnifying glass
-Make up mirrors
-commonly occurring examples of convex mirrors are the passenger
side wing mirrors of cars.
You might also like
- Light Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument34 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction NotesMurli100% (5)
- Clark Benedict Lachica Quarter 2 Science Module 4Document5 pagesClark Benedict Lachica Quarter 2 Science Module 4Allen Ben Balcita100% (2)
- FSS CST TutorialDocument10 pagesFSS CST TutorialIftikhar Ahmed100% (1)
- Qualitative Characteristics (Orientation, Type, and Magnification) of Images Formed by LensesDocument7 pagesQualitative Characteristics (Orientation, Type, and Magnification) of Images Formed by LensesJulienne BarangasNo ratings yet
- Urved Mirrors Concave and Convex: Sophia Marie D. Verdeflor Grade 10-1 STEDocument23 pagesUrved Mirrors Concave and Convex: Sophia Marie D. Verdeflor Grade 10-1 STEImman Ray Loriezo AguilarNo ratings yet
- Curvedmirrors 160510115732 PDFDocument23 pagesCurvedmirrors 160510115732 PDFIan Frederick Sidayon CerveraNo ratings yet
- Curvedmirrors 160510115732Document23 pagesCurvedmirrors 160510115732Lidelyn Jane CañalitaNo ratings yet
- M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Document10 pagesM.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Rafiya95z MynirNo ratings yet
- Ray Diagramming For Concave and Convex MirrorsDocument56 pagesRay Diagramming For Concave and Convex MirrorsJocel BaquilarNo ratings yet
- Concave and Convex MirrorsDocument3 pagesConcave and Convex MirrorsghgguNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Lens Science Iv FinalDocument27 pages1.5 Lens Science Iv FinalJohn Lester GenizeraNo ratings yet
- Clark Benedict Lachica Quarter 2 Science Module 4Document5 pagesClark Benedict Lachica Quarter 2 Science Module 4Allen Ben BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Principal RaysDocument21 pagesPrincipal Raysmayalexa726No ratings yet
- 2Q - Lesson 1.5 - Ray Diagram-RulesandlocationsDocument45 pages2Q - Lesson 1.5 - Ray Diagram-Rulesandlocationsaiza cabatinganNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23Document46 pagesLecture 23Manivannan S MNo ratings yet
- Subject: PHYSICS: Topic: Convex LensDocument29 pagesSubject: PHYSICS: Topic: Convex LensEdu 4 UNo ratings yet
- Lens andDocument17 pagesLens andRandy AugustNo ratings yet
- Lenses: Evelyn C. Avila-Bellen, Rpae, LPTDocument23 pagesLenses: Evelyn C. Avila-Bellen, Rpae, LPTEvelynNo ratings yet
- Uploads - Online Class (2021 - 2022) - Dab6a67 - Teacher - 10094Document8 pagesUploads - Online Class (2021 - 2022) - Dab6a67 - Teacher - 10094Al TheaNo ratings yet
- Converging and Diverging LensesDocument27 pagesConverging and Diverging LensesDedar RashidNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument58 pagesLensesmacmac bugananNo ratings yet
- Forliveteaching 3 220616045804 9ea2c7ebDocument32 pagesForliveteaching 3 220616045804 9ea2c7ebPrincess Rehanne PadiosNo ratings yet
- Light Human Eye and Colourful World Electricity Magnetic Effect of Current FinalDocument16 pagesLight Human Eye and Colourful World Electricity Magnetic Effect of Current FinalworkforayusheditzNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY Ex-1 To 4-1Document3 pagesACTIVITY Ex-1 To 4-1GajiniNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 3Document34 pagesQ2 Module 3Ryza AcunaNo ratings yet
- Imageformationinlens 110819210040 Phpapp01Document14 pagesImageformationinlens 110819210040 Phpapp01richardNo ratings yet
- Plane Mirrors.: Today's LectureDocument29 pagesPlane Mirrors.: Today's LectureDedar RashidNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Curved Mirror LessonDocument44 pages2.5. Curved Mirror Lesson6h4gxcf7jbNo ratings yet
- F1 ADUCTANTE Lyka Marie T. - Activity 5 Mirror Ray DiagramDocument4 pagesF1 ADUCTANTE Lyka Marie T. - Activity 5 Mirror Ray DiagramShane GendranoNo ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument72 pagesLight WavesJeffrey MaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 (B) Aim: TheoryDocument3 pagesActivity 3 (B) Aim: TheoryMeghan KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Mirrors and Lenses StudentDocument60 pagesLesson 6 Mirrors and Lenses StudentJean Marc ReyNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Optics NotesDocument5 pagesScience 10 - Optics NotesRina Marie Besin CartesianoNo ratings yet
- Image Formed by Spherical MirrorsDocument15 pagesImage Formed by Spherical MirrorsAthul VincentNo ratings yet
- G10-Q2-L6 - Plane and Curved MirrorsDocument44 pagesG10-Q2-L6 - Plane and Curved MirrorsMark GalangNo ratings yet
- Light - ReflectionDocument6 pagesLight - ReflectionVenkataNo ratings yet
- Jolime A. SawayDocument6 pagesJolime A. Sawaydummycamera982No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lenses 2023 2024Document68 pagesUnit 3 Lenses 2023 2024Da YongNo ratings yet
- QUIAO Mirrors Ppt12-Autosaved-1Document35 pagesQUIAO Mirrors Ppt12-Autosaved-1Larry GuimbardaNo ratings yet
- Plane Mirrors.: Today's AgendaDocument45 pagesPlane Mirrors.: Today's AgendaRaym CallejaNo ratings yet
- 36 LensesDocument38 pages36 Lensessamsulsman1btgNo ratings yet
- Class13 Science G10 NotesDocument14 pagesClass13 Science G10 Notesemmazou18No ratings yet
- 10 Cbse Physics CH - 1 & 2 Revision MaterialDocument33 pages10 Cbse Physics CH - 1 & 2 Revision Material12-Criswin v geo-8ANo ratings yet
- Images Formed by Curved MirrorsDocument3 pagesImages Formed by Curved MirrorsKent100% (2)
- Spherical Mirrors: Concave MirrorDocument3 pagesSpherical Mirrors: Concave MirrorLeah ClovisNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10Document19 pagesStudy Material Class 10Shivam Tiwari100% (2)
- Images Formed by A Convex and Concave MirrorsDocument1 pageImages Formed by A Convex and Concave MirrorsMallipudi SphoorthiNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light in LensesDocument24 pagesRefraction of Light in LensesCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Alat OptiksDocument24 pagesAlat OptiksDini Ayu KusumawardhaniNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument22 pagesLight Reflection and Refractionapi-246793885100% (1)
- Concave Diagrams - KeyDocument3 pagesConcave Diagrams - KeyOnie BerolNo ratings yet
- Convex LensesDocument32 pagesConvex LensesCrisanta LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction 03 - Class Notes - (Udaan 2024)Document16 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction 03 - Class Notes - (Udaan 2024)Anant GhatiyaNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument41 pagesRay Opticssangitat082No ratings yet
- Curved Mirrors and Ray DiagramsDocument34 pagesCurved Mirrors and Ray Diagramsapi-263850753No ratings yet
- Grade IV MathDocument5 pagesGrade IV MathIGNACIO JULLIE MAENo ratings yet
- Optics Unit Test ReviewDocument5 pagesOptics Unit Test Reviewaymenikram5656No ratings yet
- Lenses: Lesson 5 (3 Hours)Document19 pagesLenses: Lesson 5 (3 Hours)DonnaNo ratings yet
- Concave Ray DiagramsDocument6 pagesConcave Ray DiagramsMarilyn Castro LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 1From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 11.2 Atomic Structure Solution - PremiumDocument16 pages11.2 Atomic Structure Solution - PremiumJonathan ParkerNo ratings yet
- The Digital Zone SystemDocument5 pagesThe Digital Zone SystemElsonB100% (1)
- 1st Seminar MicroscopeDocument50 pages1st Seminar MicroscopeManas DixitNo ratings yet
- Akansha Resonance Project FInalDocument18 pagesAkansha Resonance Project FInalPramod PandeyNo ratings yet
- Physics Demo Experiment Class 12Document9 pagesPhysics Demo Experiment Class 12Monty Mechanic50% (2)
- Classification of Elements and PeriodictyDocument32 pagesClassification of Elements and PeriodictyDarshan PatilNo ratings yet
- Output 11 Einstein Jimenez Asher DaraoDocument7 pagesOutput 11 Einstein Jimenez Asher DaraoJohn MarquezNo ratings yet
- BohrvswavemechanicalDocument5 pagesBohrvswavemechanicalapi-277220146No ratings yet
- Screen Film RadiographyDocument18 pagesScreen Film RadiographykhananuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1.1Document13 pagesExperiment 1.1yash parmarNo ratings yet
- PH6151 QuestionsDocument2 pagesPH6151 Questionsvenkateswaran k.sNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument23 pagesIonic BondingMark DichosonNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Camera Lens FilterDocument10 pagesChoosing A Camera Lens FilterPiyush UjawaneNo ratings yet
- Lasers NotesDocument8 pagesLasers Notesiram fatimaNo ratings yet
- The Atom and The Mole BookDocument8 pagesThe Atom and The Mole Bookapi-526691999No ratings yet
- Alberti PhdthesisDocument234 pagesAlberti PhdthesisUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: ENGR45 Materials Engineering Spring 04Document5 pagesAtomic Structure: ENGR45 Materials Engineering Spring 04KaliDasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Fiber Optics Po Fop TM AeDocument1 pageUnderstanding Fiber Optics Po Fop TM AeAghna Tiyas MandalNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument25 pagesAtomic Structuremichaeldevid7890No ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Resonant Transmission and Ramsauer-TownsendDocument6 pagesChapter 17: Resonant Transmission and Ramsauer-TownsendJefersonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document10 pagesExperiment 8venosyah devanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - MicrosDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 - MicrosCOLLEEN GULLENNo ratings yet
- Lession 2.1 1: Welcome To This LessonDocument19 pagesLession 2.1 1: Welcome To This LessongurungeNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Are As BelowDocument5 pagesImportant Questions Are As BelowReiki Channel Anuj BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Studying The Mechanisms of Titanium Dioxide As Ultraviolet-Blocking Additive For Films and Fabrics by An Improved SchemeDocument10 pagesStudying The Mechanisms of Titanium Dioxide As Ultraviolet-Blocking Additive For Films and Fabrics by An Improved SchemeHoang VuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - DPP 10 (Of Lec 13) - Arjuna JEE 2024Document2 pagesChemical Bonding - DPP 10 (Of Lec 13) - Arjuna JEE 2024byansh644No ratings yet
- Introduction To Optics EHB 227E: Wave MotionDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Optics EHB 227E: Wave MotionErtuğrul AlperNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties of Materials Calculated From First Principles TheoryDocument49 pagesOptical Properties of Materials Calculated From First Principles TheoryJH ShinNo ratings yet
- M0123 PhysicsDocument7 pagesM0123 PhysicsMIOR AHMAD RIDZUAN BIN MIOR MOHAMED TAHIR KPM-GuruNo ratings yet