Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 8
Math 8
Uploaded by
Renelyn LeriaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 8
Math 8
Uploaded by
Renelyn LeriaCopyright:
Available Formats
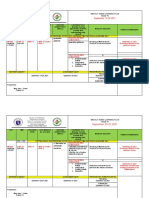
PROJECT SIKAP SUGGESTED LESSONS FOR NOT MASTERED COMPETENCIES
SECONDARY LEVEL - Grade 8
DAY OBJECTIVES ACTIVITIES
Illustrate and apply Teacher let the students answer the Activity 1:
the laws of
exponents. Note: Give the product of the following as fast as you can:
Basic Law of 1) 3 x 3 = _______
Exponent 2) 4 x 4 x 4 =________
3) 5 x 5 x 5 =________
4) 2 x 2 x 2 =________
1
5) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 =_________
The teacher explain the basic law of exponent.
a n=a x a x a x a …
In a n, a is called the base and n is called the exponent.
The learners answer the worksheet prepared by the teacher.
Illustrate and apply The teacher give the definition and explain the zero and the
the laws of negative property.
exponents.
Zero Property and Note: Any nonzero real number raised to a power of zero is
Negative property equal to 1.
0
x =1
Note: Any nonzero real number raised to a negative power
will be one divided by the number raised to the positive
2
power of the same number.
1
x (−a)= a
x
The teacher shows examples of each property
The learners answer the activity prepared by the teacher.
Illustrate and apply The teacher emphasizes the Power Law of Exponents.
the laws of
exponents. Note: If a number raise a power to a power, just multiply
Power of Powers the exponents.
( x ¿¿ m)n= xmn ¿
3 The teacher gives illustrative examples using the power law
of exponents.
The learners answer the worksheet prepared by the teacher.
Illustrate and apply The teacher emphasizes the Product Law of Exponents.
the laws of Note: When multiplying two numbers that have the same
exponents. base, simply add the exponents.
Product Law of m n
x ∙ x =x
m +n
4
Exponent The teacher gives examples in using the product law of
exponent.
The learners answer the worksheet prepared by the teacher.
Illustrate and apply The teacher emphasizes the Quotient Law of Exponents.
the laws of Note: When dividing two numbers that have the same base,
exponents. simply subtract the exponents.
5 Quotient Law of m n
x ÷ x =x
m−n
Exponent The teacher gives examples in using the quotient law of
exponent.
The learners answer the worksheet prepared by the teacher.
Illustrate and apply The teacher emphasizes the Power of a product property.
the laws of
exponents. Note: If the product of two nonzero real numbers is being
Power of a Product raised to an exponent, you can distribute the exponent to
6 each factor and multiply individually.
(xy )m=x m∗ y m
The teacher gives examples in using the power of a product
rule.
The learners answer the worksheet prepared by the teacher.
Illustrate and apply The teacher emphasizes the Power of a quotient property.
the laws of
exponents. Note: If the quotient of two nonzero real numbers are being
Power of a raised to an exponent, distribute the exponent to each
Quotient individual factor and divide individually.
7
() ( )
a a
x x
= a
y y
The teacher gives examples in using the power of a
quotient rule.
The learners answer the worksheet prepared by the teacher.
Find the sum of a The teacher gives illustrative examples in getting the sum of
polynomial. a given polynomial.
8 The learners find the sum of the given polynomial using the
steps provided by the teacher.
Find the difference The teacher gives illustrative examples in getting the
of a polynomial. difference of a given polynomial.
9
The learners find the sum of the given polynomial using the
steps provided by the teacher.
Find the product of The teacher gives illustrative examples in finding the
a polynomial. product of a polynomial.
10
The learners find the product of the given polynomial using
the steps provided by the teacher.
Find the quotient The teacher gives illustrative examples in getting the
of a polynomial. quotient of a given polynomial.
11
The learners find the quotient of the given polynomial using
the steps provided by the teacher.
Find the factors of The teacher shows flashcards containing numbers from 2 to
12 the numbers from 100 one at a time.
2 to 100. The learners give the factors of the numbers shown.
Find the GCF and The teacher shows the steps in finding the greatest common
LCM of the given factor and the least common multiple of a given number.
13 numbers.
The learners answer the worksheet provided by the teacher.
Find the factors of The teacher shows the steps and give illustrative examples
the given algebraic in finding the factors of a given algebraic expression using
14 expressions using the greatest common monomial factor.
greatest common The learners answer the worksheet provided by the teacher.
monomial factor.
Find the factors of The teacher shows the steps in getting the factors of perfect
perfect square square trinomials.
trinomials.
Note: To factor perfect square trinomials, get the square
root of the first and last terms, then list down the square root as
15
sum/difference of two terms.
The teacher gives examples of factoring perfect square
trinomials.
The learners answer the worksheet provide by the teacher.
Evaluate algebraic The teacher explains the steps in evaluating rational
expressions algebraic expressions.
involving integral
exponents The teacher let the students complete the table.
My Valu
Valu My
expressio e of My solution
e of a value
n b
2 3 2 3
a + b =2 +3
2 3 ¿ 4 +27 31
a 2+ b3 ¿ 31
16
3 4
2 4
−2 −2
a (−2 )
−3
= −3
b 3
−2 3
3
27
a -2 3 ¿
−3 (−2)
2 4
b
27
¿
4
3 2
−1 0
a b 2 3
Simplify rational The teacher explains the steps in simplifying rational
algebraic algebraic expressions.
17 expressions The teacher gives illustrative examples of simplifying
rational algebraic expressions.
The learners answer the worksheet provided by the teacher.
18 Find the product of The teacher explains the steps in getting the product of
rational algebraic rational algebraic expressions.
expresions. Note: The product of two rational expressions is the product
of the numerators divided by the product of the
denominators.
a
∗c
In symbols, b ac
= , bd ≠ 0.
d bd
The teacher gives illustrative examples of multiplying
rational algebraic expressions.
The learners answer the worksheet provided by the teacher.
Find the quotient The teacher explains the steps in getting the product of
of rational rational algebraic expressions.
algebraic Note: The quotient of two rational algebraic expressions is
expressions. the product of the dividend and the reciprocal of the divisor.
a
∗d
In symbols, a c b ad
19 ÷ = = , b , c , d ≠0.
b d c bc
The teacher gives illustrative examples of dividing rational
algebraic expressions.
The learners answer the worksheet provided by the teacher.
Find the sum and The teacher explains the steps in getting the product of
the difference of rational algebraic expressions.
rational algebraic Note:
expressions. 1. In adding or subtracting similar rational expressions,
add or subtract the numerators and write the answer in
the numerator of the result over the common
denominator.
a c a+c
In symbols, + = , b ≠ 0.
b b b
20 2. In adding or subtracting dissimilar rational expressions,
change the rational algebraic expressions into similar
rational algebraic expressions using the least common
denominator of LCD and proceed as in adding similar
fractions.
The teacher gives illustrative examples of adding and
subtracting rational algebraic expressions.
The learners answer the worksheet provided by the teacher.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Fractions and Decimals ScholasticDocument49 pagesFractions and Decimals ScholastichusseinNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 21st Slide DeckDocument17 pages21st Slide DeckRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Certificate Course 1Document1 pageCertificate Course 1Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Certificate Course 1Document1 pageCertificate Course 1Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Math 10Document6 pagesMath 10Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Certificate Course 1Document1 pageCertificate Course 1Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- 21st Session GuideDocument5 pages21st Session GuideRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- School Form 2 (SF2) Daily Attendance Report of LearnersDocument6 pagesSchool Form 2 (SF2) Daily Attendance Report of LearnersRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Contextualization Session GuideDocument5 pagesContextualization Session GuideRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment Q2 - Mapeh 10: Malangas National High SchoolDocument2 pagesSummative Assessment Q2 - Mapeh 10: Malangas National High SchoolRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
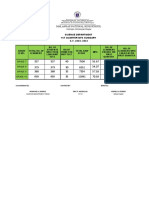
- Sikap Schedule 2022 2023Document16 pagesSikap Schedule 2022 2023Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Rating The Portfolio: Bureau of Human Resource and Organizational DevelopmentDocument26 pagesRating The Portfolio: Bureau of Human Resource and Organizational DevelopmentRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking. AFA, Agri MPSDocument4 pagesDressmaking. AFA, Agri MPSRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
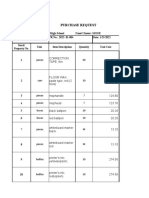
- Purchase Request 4 5 7Document12 pagesPurchase Request 4 5 7Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- September 13-20,2021: Generates Patterns. Generates PatternsDocument7 pagesSeptember 13-20,2021: Generates Patterns. Generates PatternsRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Minutes of Opening of Bid1Document2 pagesMinutes of Opening of Bid1Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- SLMs Report Q1 TemplateDocument1 pageSLMs Report Q1 TemplateRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Award and Other Documents1Document6 pagesAward and Other Documents1Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Name of Procuring Entity-1Document1 pageName of Procuring Entity-1Renelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- Notice To Conduct Post Qua PRACDocument2 pagesNotice To Conduct Post Qua PRACRenelyn LeriaNo ratings yet
- q4wk1 2 AssessmentDocument2 pagesq4wk1 2 Assessmentclariza de ocampoNo ratings yet
- Ws CL 11 TrigonometryDocument3 pagesWs CL 11 TrigonometryRamakrishna BatabyalNo ratings yet
- Math8 q1 Mod9 Writing-Linear-Equation v2Document21 pagesMath8 q1 Mod9 Writing-Linear-Equation v2Rainman InsanityNo ratings yet
- Math 9 q1 RemedialDocument6 pagesMath 9 q1 RemedialCathNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan of Grade 8 Week 1-9Document9 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan of Grade 8 Week 1-9Zaldy Roman MendozaNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsDocument17 pagesRD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsBhushan kumarNo ratings yet
- 20 Rational Exponents and Radical ExpressionDocument14 pages20 Rational Exponents and Radical Expressionbabyu1100% (2)
- Activity - Math 4march 8 12 - 2021Document6 pagesActivity - Math 4march 8 12 - 2021Nhovie Claire FlorencioNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 TestDocument5 pagesGrade 9 TestLito PepitoNo ratings yet
- Expressing A Ratio As A Fraction or Percentage PDF 1Document3 pagesExpressing A Ratio As A Fraction or Percentage PDF 1Elena IorgaNo ratings yet
- Integrals Involving RootsDocument83 pagesIntegrals Involving RootsAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- The g9 Joint Examination Pp1 MsDocument12 pagesThe g9 Joint Examination Pp1 Mswinrosenyaboke56No ratings yet
- CambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 08DDocument8 pagesCambMATHS10 5.1-5.3 2ED Test 08Dwill.clark6No ratings yet
- Exercises Chapter Quadratic Equation and Quadratic FunctionDocument4 pagesExercises Chapter Quadratic Equation and Quadratic Functionyehuda pramanaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities MADocument9 pagesTrigonometric Identities MAswiftmessiNo ratings yet
- OCR FSMQ Worked Solutions 4thDocument113 pagesOCR FSMQ Worked Solutions 4thafaflotfi_155696459No ratings yet
- DLP Math 8 PDFDocument289 pagesDLP Math 8 PDFKeisha LupangoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry For Class 11 PDFDocument4 pagesTrigonometry For Class 11 PDFHiNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials Rev ExDocument2 pagesFactoring Polynomials Rev ExCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Lecture NotesDocument75 pagesQuadratic Equation Lecture NotesExtra WorkNo ratings yet
- DETAILED-LP Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square RootsDocument5 pagesDETAILED-LP Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square RootsAngeline CruzNo ratings yet
- Target Exercises: Type 1.only One Correct OptionDocument18 pagesTarget Exercises: Type 1.only One Correct OptionharshmadhavNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Illustrating System of Linear Equations in Two Variables - M8AL-Ih-1Document11 pagesMathematics: Illustrating System of Linear Equations in Two Variables - M8AL-Ih-1ROMEO JR RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Tutor Number Surds #3 RationalisationDocument2 pagesGCSE Maths Tutor Number Surds #3 Rationalisationgcsemathstutor100% (1)
- G9 Math Q1 - Week 2-3 - Relationship of Coefficient and Roots of Q.E.Document25 pagesG9 Math Q1 - Week 2-3 - Relationship of Coefficient and Roots of Q.E.Mechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- G8 Math Q1 - Week 5 - Slope of A LineDocument43 pagesG8 Math Q1 - Week 5 - Slope of A LineWenilyn MananganNo ratings yet
- G. Solving Quadratic Inequalities (H) - 2Document7 pagesG. Solving Quadratic Inequalities (H) - 2985wtz8rcjNo ratings yet
- 2 FractionDocument16 pages2 FractionSubrataThakuraNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up #2 - 1: Write The Following Solutions in Interval Notation Then Graph On A Number Line: 1) 2) 3)Document4 pagesWarm-Up #2 - 1: Write The Following Solutions in Interval Notation Then Graph On A Number Line: 1) 2) 3)Samuel AdamsNo ratings yet