Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOLOGY
BIOLOGY
Uploaded by
Phantom0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesEukaryotic cells contain organelles surrounded by membranes within the cell cytoplasm. The cell membrane forms the outer boundary and is selectively permeable. It regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. The nucleus houses genetic material and directs cellular activities. Other organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria help produce proteins and energy to power cellular functions. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex with internal membranes and organelles that perform specialized functions.
Original Description:
Original Title
BIOLOGY(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEukaryotic cells contain organelles surrounded by membranes within the cell cytoplasm. The cell membrane forms the outer boundary and is selectively permeable. It regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. The nucleus houses genetic material and directs cellular activities. Other organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria help produce proteins and energy to power cellular functions. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex with internal membranes and organelles that perform specialized functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesBIOLOGY
BIOLOGY
Uploaded by
PhantomEukaryotic cells contain organelles surrounded by membranes within the cell cytoplasm. The cell membrane forms the outer boundary and is selectively permeable. It regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. The nucleus houses genetic material and directs cellular activities. Other organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria help produce proteins and energy to power cellular functions. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex with internal membranes and organelles that perform specialized functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
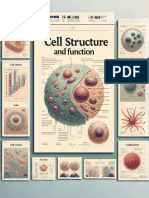
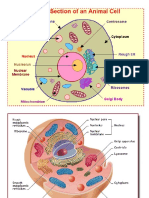
Cell Structures and Functions Eukaryotic cells
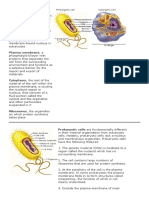
Cell shape and size CELL MEMBRANE
o Cellular diversity is also reflected in the o Also called as plasma membrane
different sizes of cells o It separates the cell from its external
o As a cell grows, its volume increases faster environment
than does its surface area o It is the outermost covering of animal cells
o The larger the cell, the greater the surface area while that of plant cells is called cell wall
required to maintain it and vice versa o Selectively permeable membrane that
regulates the entrance and exit of substances
INTERNAL ORGANIZATION into the cell
o Provides shape and flexibility to the cell
o Prokaryotic Cells – lack a nuclear envelope
o 1925, Evert Gorter and Francois Grendel –
and membrane-bound organelles, an example
of which is the bacterial cell. hypothesized that the cell membrane is
o Eukaryotic Cells – generally longer and have composed of a lipid bilayer
very distinct nuclei that are clearly surrounded They studied the lipids from
by nuclear membranes. erythrocytes (red blood cells) and
They also have numerous membrane- found out that the plasma membrane
bound organelles found in the has a layer facing inward, away from
cytoplasm aqueous environment (hydrophobic-
Protists, plants, fungi, and animals water fearing); outer layer facing
have eukaryotic cells outward, toward the outside
Binary fission environment (hydrophilic-water
loving)
Prokaryotic cells o 1935, Hugh Davson and James Danielli –
proposed a sandwich-like model of the cell
o The absence of a membrane-bound nucleus membrane
mainly distinguishes prokaryotic cells from Davson-Danielli model, describes the
eukaryotic cells cell membrane as a phospholipid
o Capsule – a sticky outer layer that provides bilayer sandwiched by a coat of protein
protection on either surface
o Cell wall – a structure that confers rigidity and o Singer-Nicolson Model – describes the
shape to the cell plasma membrane as a mosaic of proteins that
o Plasma membrane – a structure that serves as are embedded or attached to a fluid bilayer of
permeability barrier lipid
o Nucleoid – a DNA-containing region within It hypothesizes that proteins are
the cytoplasm globular entities, floating in and on the
o Cytoplasm – the region where chromosomes lipid bilayer
(DNA), ribosome, and various inclusions are
found
Cytoplasm
o Ribosome – the site where protein is o Ground substance and the biggest part of the
synthesized cell where organelles and cellular inclusions
o Pilus – a hair-like appendage that functions in are found
adhesion
o Flagellum – facilitates movement of bacteria Cytoplasmic organelles
o Endoplasmic Reticulum – is a network of o Ribosomes – most numerous of all
intercommunicating channels in the cytoplasm cytoplasmic structures
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – They are the sites where proteins are
described as such due to the presence made
of ribosomes. It plays a role in the They could be found attached to the
production of protein, as well as in its endoplasmic reticulum or free in the
folding, quality control, and dispatch cytoplasm
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum – o Centriole – has a central role in cell division
more tubular and non-granular where it participates in the formation of the
structure due to the absence of mitotic spindle
ribosomes. It plays a role in the o Microtubules – are long, slender, protein
manufacture and metabolism of lipids tubes
o Golgi Apparatus – is composed of sets of Together with the microfilaments, they
cisternae (folds) and numerous vesicles filled form the cytoskeleton of the cell
with fluid and suspended substances They are composed of linear polymers
Responsible for the processing, of tubulin
packaging, and sorting of secretory These also form the cores of the cilia
materials for use within and outside of and flagella of sperm cells and play a
the cell role in maintaining cell shape
o Mitochondrion – powerhouse of the cell o Microfilaments – support the cell to maintain
It contains enzymes that help in the its structure and shape as it provides resiliency
chemical oxidation of food molecules against forces that can alter the shape
and produces energy in the form of o Glycogen granules – which are abundant in
ATP liver cells, play an important role in the
Cristae – are numerous folds of the glucose cycle
inner membrane o Pigments – are substances that do not require
Matrix – is the space inside the inner staining by dyes because they already possess
membrane their own color
o Lysosomes – small, spherical, membrane-
bound organelles which contain a number of Nucleus
enzymes for intercellular digestion
Lyzozomes – enzyme produced by o Found in most eukaryotic cells
lysosomes o It is the site where nucleic acids are
Perixisomes – breakdown the toxins synthesized and, therefore, directs all the
that may harm the cell activities of the cell
o Secretory Granules – are large dense o Also serves as a site for the storage of
granules with membrane. These fuse with the hereditary factors
cell membrane to secrete substance such as o It is the source of ribonucleic acid (RNA), a
enzymes, proteins, and signaling molecules out molecule responsible for various cellular
of the cell functions such as genetic coding and
o Lipid Droplets – store fatty acids and sterols expression
o Nuclear Membrane – is the two-layered outer
Cytoplasmic inclusions limit of the nucleus separating it from the
cytoplasm
o Are non-membranous substances and
it contains ribosomes on its outer
structures suspended in the cytoplasm with membrane
varying functions it is also continuous with the
endoplasmic reticulum
the dense, protein-rich substance inside xanthophylls, and various red
the nucleus is the nucleoplasm, where pigments
the spherical, non-membrane bound Leucoplasts – store food such as
nucleolus (structures responsible for starches, lipids, and proteins
ribosome formation) is suspended
o Nuclear Pores – act as selective channels Cell modifications and adaptations
between the cytoplasm and the inside of the
o For instance, cells that absorb nutrients in the
nucleus, selectively allowing molecules which
small intestine have microvilli.
contain the correct localization signals to pass
These are extensions on the cell
in and out
membrane that help increase the
o Found inside the nucleus is the chromatin,
surface area of the cell, thus,
which is made up of DNA and proteins, and
facilitating increased absorption of
forms chromosomes during cell divisions
nutrients
o Nerve Cells, which are mostly elongated,
facilitate the transmission of impulses from
Structures found in plant cells the brain and the spinal cord to the different
parts of the body
o Cell Wall – is the outermost, rigid covering o Red Blood Cells (RBCs) – allows for easy
of plant cells movement through blood vessels
It is primarily composed of cellulose o Tracheal Cells have cilia that beat and drive
embedded in hardening compounds air impurities or foreign particles and mucus
such as pectin and lignin secretions up the trachea to the mouth where
Plant cells produce two types of cell they can be coughed out
walls, the primary and secondary o Sperm Cells have a tail, the flagellum, which
walls with a lamella sandwiched in propels it toward the egg cell for fertilization
between o Root Hairs (Specialized Cells) elongated
The primary wall is the first to form, outgrowths from the outer layer of cells in a
particularly, during the growth period root that help absorb water and minerals
of the cell. When the growth ceases, o Cell-Cell Junctions – the points where two
the secondary wall is formed. When cells come together, forming tissues and
secondary walls are formed, organs
expansion in cell size can no longer
be expected
o Water Vacuoles – are larger and more
centrally located in plant cells than in animal
cells
Vacuoles store enzymes and waster
products
o Plastids – they carry out the photosynthetic
function in plants
Chloroplasts – contain the green
pigment, chlorophyll which is
designed to absorb sunlight in the
initial step of photosynthesis
Chromoplasts – synthesize and store
pigments such as yellow, carotene,
You might also like
- Understanding ICD 10 CM and ICD 10 PCS A Worktext Spiral Bound Version 3rd Edition Bowie Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesUnderstanding ICD 10 CM and ICD 10 PCS A Worktext Spiral Bound Version 3rd Edition Bowie Solutions ManualDebits100% (7)
- Cell Structures & Organelles FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Structures & Organelles Functionsnasimzand78100% (1)
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell The Unit of LifeRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Unit of Life WorksheetDocument24 pagesThe Unit of Life WorksheetNeeraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Upload It 1Document5 pagesUpload It 1John Rey Bandong100% (1)
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesdeveshjayakumaryadavNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0Document14 pagesBiology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0gana63693No ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesFundamental Unit of Lifechabalalalulama5No ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- PRPM110L Module 3 & 4Document10 pagesPRPM110L Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document89 pagesUnit 2No Name100% (1)
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument5 pagesBiochemistry Reviewer202370092No ratings yet
- 1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeDocument100 pages1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument11 pagesThe CellVardan ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure N Functions2Document5 pagesCell Structure N Functions2fariha khanNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- L2 - Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellhgfhfgDocument65 pagesL2 - Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellhgfhfgNoriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesBhavanya RavichandrenNo ratings yet
- M PRtpbo Fxo F46 YBll E9 HDocument5 pagesM PRtpbo Fxo F46 YBll E9 Hrudrakumbhar2005No ratings yet
- Cell - Fundamental Unit of Life Part 2Document46 pagesCell - Fundamental Unit of Life Part 2hritwikgupta09No ratings yet
- Byjus Cell Rectified 43Document19 pagesByjus Cell Rectified 43Abhay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESDocument7 pagesProkaryotic&Eukaryotic DIFFERENCESChristian John Sitjar Dumo100% (1)
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypessandraNo ratings yet
- Biology: Prokaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesBiology: Prokaryotic CellsVictoria IlaganNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifelpc4944No ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-08 Cell: Structure and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-08 Cell: Structure and FunctionsHasharaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure2Document6 pagesCell Structure2CRYSTAL A. ARIETANo ratings yet
- Module 1 Biology NotesDocument16 pagesModule 1 Biology NotesPahulbir ThindNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of Life - Chapter - 8Document9 pagesCell The Unit of Life - Chapter - 8Shambhvi PathakNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellDocument11 pagesEukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellAvyanna MillerNo ratings yet
- عملي ٢Document4 pagesعملي ٢adelshayea555No ratings yet
- Parts of Plant Cell and Its FunctionsDocument2 pagesParts of Plant Cell and Its FunctionsThiody Hope Mongas50% (2)
- Cell StructuresDocument81 pagesCell Structuresnurshuhada zainuddinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 8 Cell The Unit of Lifeaatishsubash9b35832No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDocument8 pagesCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajNo ratings yet
- 3011 Doc 20240327 Wa0021.Document24 pages3011 Doc 20240327 Wa0021.vavc720No ratings yet
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsapi-95529788100% (1)
- CellDocument22 pagesCellrapidalerthubNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell - The Unit of LifeshanvimalhotraNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 L5 NIADocument31 pagesBio 103 L5 NIAsubrotoghosh2001No ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- 1.cell PhysiologyDocument5 pages1.cell PhysiologyNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesCell Structure and Functionnaveedalikhoso365100% (1)
- Cells PDFDocument107 pagesCells PDFida hadiNo ratings yet
- DNA, The Genetic MaterialDocument6 pagesDNA, The Genetic MaterialMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Major-Parts-Of-The-Cell - ReviewerDocument5 pagesMajor-Parts-Of-The-Cell - Reviewerjadenn busiaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellAnthony QuiroyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument16 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationanippoNo ratings yet
- Review of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument25 pagesReview of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsevil twinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LectureDocument13 pagesModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument16 pagesCellanantchouhdary1709No ratings yet
- Biology Study Guide Test 2Document9 pagesBiology Study Guide Test 2sharrone halimNo ratings yet
- CELL Study MaterialDocument12 pagesCELL Study MaterialShyamasree SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Biology Pt.2Document17 pagesBiology Pt.2Mafer MorenoNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument8 pagesCELLRajendra Chikkamath100% (1)
- 11 Biology Notes Ch08 Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes Ch08 Cell Structure and FunctionsChristopher PushparajNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- HSK 1 Vocabularies February 142019 With LogoDocument179 pagesHSK 1 Vocabularies February 142019 With LogoPhantomNo ratings yet
- Biology ContinuationDocument2 pagesBiology ContinuationPhantomNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument14 pagesArtsPhantomNo ratings yet
- 1.literary FormsDocument21 pages1.literary FormsPhantomNo ratings yet
- The Swinging Flashlight Test: Learning Objective: Facts About The PupilDocument3 pagesThe Swinging Flashlight Test: Learning Objective: Facts About The Pupilsiti hazard aldinaNo ratings yet
- Out of BodyDocument30 pagesOut of Bodyayeyen100% (4)
- GADPHDocument36 pagesGADPHTatane Díaz OjedaNo ratings yet
- 2013 h2 BiologyDocument1,838 pages2013 h2 BiologyJustt Mee100% (1)
- The Effect of Spinal Manipulative Therapy OnDocument22 pagesThe Effect of Spinal Manipulative Therapy OncpfisioNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Ornamental Bulbous Plant Bulb (Disambiguation)Document4 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Ornamental Bulbous Plant Bulb (Disambiguation)Alexandra Maria NeaguNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Revision Test - NutritionDocument4 pagesClass-10 Revision Test - NutritionVarshini PeraNo ratings yet
- Simplified FenclDocument18 pagesSimplified Fenclrina febriatiNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 1 - Reviewed by CommitteeDocument13 pagesSCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 1 - Reviewed by CommitteeBayani VicencioNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project - 12.05.2022Document16 pagesInvestigatory Project - 12.05.2022OMKAR CHAUDHARINo ratings yet
- Properties of EnzymesDocument7 pagesProperties of Enzymeslcassidy9074No ratings yet
- Electric Shock ChartDocument1 pageElectric Shock Chartbrsharma100% (2)
- Children of A Lessor GodDocument30 pagesChildren of A Lessor GodMunir KhattakNo ratings yet
- Piter - LR - Pure Tone Audiometry and MaskingDocument44 pagesPiter - LR - Pure Tone Audiometry and MaskingArief FakhrizalNo ratings yet
- BiomarkerDocument84 pagesBiomarkerAdriani HartantoNo ratings yet
- Citrate Anticoagulation During CRRTDocument12 pagesCitrate Anticoagulation During CRRTpmunizNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Pathomechanics of Elbow JointDocument44 pagesBiomechanics and Pathomechanics of Elbow JointAshwini BajajNo ratings yet
- Wieland 2013, The Phylogenetic System of MantodeaDocument220 pagesWieland 2013, The Phylogenetic System of MantodeaFernandoBrumNo ratings yet
- Hyperemia CongestionDocument40 pagesHyperemia CongestionBikash PuriNo ratings yet
- EmotionsDocument58 pagesEmotionsthivyaashini SellaNo ratings yet
- Enzymic Method For Quantitative Determination of Nanogram Amounts of Total and Oxidized GlutathioneDocument21 pagesEnzymic Method For Quantitative Determination of Nanogram Amounts of Total and Oxidized GlutathioneJosué Velázquez100% (1)
- Sensing and Perceiving: Sensation PerceptionDocument33 pagesSensing and Perceiving: Sensation PerceptionmarioNo ratings yet
- 60 Samples Questions and Answers For MRCOphth IDocument26 pages60 Samples Questions and Answers For MRCOphth Imacheso0% (1)
- BP303TPDocument1 pageBP303TPShubham KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Approach To HeadacheDocument49 pagesApproach To Headachegea pandhita sNo ratings yet
- 1 Lower Limb BONESDocument79 pages1 Lower Limb BONESZaid AbdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocument22 pagesTrigeminal NeuralgiaamandarestykbNo ratings yet
- DCCTDocument8 pagesDCCTZulimp SA DE CVNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument41 pagesPneumoniapaanar100% (2)