Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verb Tenses
Verb Tenses
Uploaded by
Angelica FilipeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pre-Int Unit11 BusinessWritingPunctuation PDFDocument2 pagesPre-Int Unit11 BusinessWritingPunctuation PDFZoeTziavara100% (2)
- Time Expressions: Adverbs of FrequencyDocument8 pagesTime Expressions: Adverbs of FrequencyCamila PiranNo ratings yet
- Do Form - Simple (Questions, Negatives) Have Form (Perfect, Perfect Contin) Be Form (Simpl, Contin)Document2 pagesDo Form - Simple (Questions, Negatives) Have Form (Perfect, Perfect Contin) Be Form (Simpl, Contin)malarvizhiNo ratings yet
- Acfrogdgthvxiqs-1yqvjkhvd Mlmzky9c C79l4nwxjhu2s-Mauhtqarai 35bmrjckd6a9aaorui5nc6ajenhswiyhk3o T7zf4hoa49ufvr2cdqbtbje7mzwfox0f-Cu4b5ii2sjtqgmgnqixDocument10 pagesAcfrogdgthvxiqs-1yqvjkhvd Mlmzky9c C79l4nwxjhu2s-Mauhtqarai 35bmrjckd6a9aaorui5nc6ajenhswiyhk3o T7zf4hoa49ufvr2cdqbtbje7mzwfox0f-Cu4b5ii2sjtqgmgnqixAfif Faishal DzakwanNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar and Useful ItemsDocument20 pagesBasic Grammar and Useful ItemsNicole MuroNo ratings yet
- All English Tenses 1Document2 pagesAll English Tenses 1VinNo ratings yet
- English Manual: Licenciada Filología Inglesa Colegiada #2811Document36 pagesEnglish Manual: Licenciada Filología Inglesa Colegiada #2811Gema Caro MolinaNo ratings yet
- PRESENT SIMPLE and CONTINUOUS CHARTDocument2 pagesPRESENT SIMPLE and CONTINUOUS CHARTSusiNo ratings yet
- Importante: Jamas Combinar Am/Is/Are Con Un Verbo en Forma Simple, Ejemplos: Is Cook, Are Go, Am Sleep - Esta Combinación No Es PosibleDocument5 pagesImportante: Jamas Combinar Am/Is/Are Con Un Verbo en Forma Simple, Ejemplos: Is Cook, Are Go, Am Sleep - Esta Combinación No Es PosibleModesta SaenzNo ratings yet
- Theory Present and Past Tenses RevisionDocument2 pagesTheory Present and Past Tenses RevisionAndarielle ConstanceNo ratings yet
- Ingles, Present Simple - 20240604 - 141433 - 0000Document22 pagesIngles, Present Simple - 20240604 - 141433 - 0000juanitodoggieNo ratings yet
- English Sentence Structures Ultima Version Completa 1Document3 pagesEnglish Sentence Structures Ultima Version Completa 1Ariel MeferNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument1 pageTENSESFacundo Nicolás de la FuenteNo ratings yet
- Table Tense Grammar Guides - 85605Document3 pagesTable Tense Grammar Guides - 85605Ferangizbonu BoltayevaNo ratings yet
- Resumen Examen 13-02Document2 pagesResumen Examen 13-02Tully - SanNo ratings yet
- Present Simple, Present Perfect, and Present ContinuousDocument8 pagesPresent Simple, Present Perfect, and Present ContinuousMateo Ariel BelossiNo ratings yet
- Apuntes de Ingles B2 (GRAMMAR)Document29 pagesApuntes de Ingles B2 (GRAMMAR)micobasauriNo ratings yet
- Ingles 1 ResumenDocument7 pagesIngles 1 Resumenjulieta.a.martinezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Adverbs and Expressions of FrequencyDocument22 pagesPresent Simple Adverbs and Expressions of FrequencyDania Huanca MeloNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument3 pagesPresent Simple: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeAlejandra MalettiNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple Tense: Did You Like Did He SeeDocument4 pagesThe Present Simple Tense: Did You Like Did He SeeMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present ContinousDocument1 pagePresent Simple Present ContinousHernández Martínez RamsésNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple Tense: Did You Like Did He SeeDocument4 pagesThe Present Simple Tense: Did You Like Did He SeeMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Present Simple Tabela VIIDocument1 pageUnit 1 Present Simple Tabela VIIJasmin IbrahimovicNo ratings yet
- Adjective+Preposition: Past SimpleDocument5 pagesAdjective+Preposition: Past SimpleSusana GrandãoNo ratings yet
- Tempos VerbaisDocument50 pagesTempos VerbaisJoao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Summary - Advanced 1Document20 pagesGrammar Summary - Advanced 1Strawberry's BlogNo ratings yet
- Present Simple - ResumenDocument1 pagePresent Simple - ResumenAndrea AguirreNo ratings yet
- Virtual PortfolioDocument16 pagesVirtual PortfolioDavid IonutNo ratings yet
- Present Progresive Vs Present ExerciseDocument2 pagesPresent Progresive Vs Present Exerciseteacher ATRIANO RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Simple: Don't /doesn'tDocument7 pagesVerb Tenses Simple: Don't /doesn'tMARIA CANALESNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Simple: Don't /doesn'tDocument7 pagesVerb Tenses Simple: Don't /doesn'tMARIA CANALESNo ratings yet
- Todas Las Formas VerbalesDocument14 pagesTodas Las Formas VerbalesCacoDemonNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument7 pagesPresent Perfectvj.perezcortesNo ratings yet
- Simple Present 1Document19 pagesSimple Present 1cu6295151No ratings yet
- All Verb TensesDocument3 pagesAll Verb TensesAndreu PadrenyNo ratings yet
- Resumen de Tiempos VerbalesDocument1 pageResumen de Tiempos VerbalesMaría MercedesNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Simple Past Tense (2) Geçmiş ZamanDocument3 pagesTenses: Simple Past Tense (2) Geçmiş ZamanMerve AcerNo ratings yet
- Direct Reported SpeechDocument1 pageDirect Reported SpeechMARIN VALDEZ DESIREE STEPHANIA MAVD050203MDFRLSA5No ratings yet
- PresentDocument27 pagesPresentJúlia TANo ratings yet
- Simple Present: InglêsDocument5 pagesSimple Present: InglêsJuliaNo ratings yet
- Repaso InglésDocument2 pagesRepaso InglésValentina CuelloNo ratings yet
- Hábitos o Rutinas Hechos Características Acciones Que Están Pasando Ahora Mismo. (En Progreso)Document1 pageHábitos o Rutinas Hechos Características Acciones Que Están Pasando Ahora Mismo. (En Progreso)Erick ZHNo ratings yet
- Direct Reported SpeechDocument1 pageDirect Reported SpeechMARIN VALDEZ DESIREE STEPHANIA MAVD050203MDFRLSA5No ratings yet
- Engleski - VremenaDocument8 pagesEngleski - VremenasreckoNo ratings yet
- Verbs ChartDocument1 pageVerbs ChartiraaaaatiNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument3 pagesPresent PerfectJuan Luis EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and ContinuousDocument2 pagesPast Simple and ContinuousLaura Roman DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Tenses PDFDocument14 pagesTenses PDFMalaaika SaleemNo ratings yet
- Review - Units 1 - 6Document32 pagesReview - Units 1 - 6Rolando Aparicio Cueto OsorioNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument5 pagesTensesNadia BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Presentes y Pasados Simple y ContinuoDocument11 pagesPresentes y Pasados Simple y ContinuoAida Álvarez LópezNo ratings yet
- İngi̇li̇zce Zamanlar TablosuDocument4 pagesİngi̇li̇zce Zamanlar TablosurealisemeNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses PresDocument20 pagesVerb Tenses PresMarcos AlamosNo ratings yet
- Review of TensesDocument3 pagesReview of Tenseschristian mendozaNo ratings yet
- Cuadro EstructurasDocument1 pageCuadro EstructurasEdiNo ratings yet
- Tenses ChartDocument2 pagesTenses ChartMichelleNo ratings yet
- The Following Table Summarizes The 16 Tenses in EnglishDocument9 pagesThe Following Table Summarizes The 16 Tenses in Englishsoto amilkarNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Continuous - Karen L. Hernández Chávez.Document5 pagesThe Present Perfect Continuous - Karen L. Hernández Chávez.Karen HernándezNo ratings yet
- 4u Physics Equations Formula SheetDocument2 pages4u Physics Equations Formula SheetAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- TC Exam Study NotesDocument3 pagesTC Exam Study NotesAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- Pre Flight Briefing Checklist For Solo FlightsDocument2 pagesPre Flight Briefing Checklist For Solo FlightsAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- Study Notes For Ground Portion of Flight TestDocument1 pageStudy Notes For Ground Portion of Flight TestAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- Generosity in Small Things by Sister Lucy of FatimaDocument2 pagesGenerosity in Small Things by Sister Lucy of FatimaAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- 2 Text OperationDocument42 pages2 Text OperationTensu AwekeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Sentence Patterns and Parts of SpeechDocument47 pagesLecture 2 Sentence Patterns and Parts of SpeechRedman BestNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: The TOEFL Course Is Designed To Prepare Students For The TOEFL PBT TestDocument9 pagesSyllabus: The TOEFL Course Is Designed To Prepare Students For The TOEFL PBT TestSulfi mahraniNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Learning & TeachingDocument6 pagesDifferentiated Learning & Teachingapi-281086391No ratings yet
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 2: (Answers For Teacher Reference)Document35 pagesEntrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 2: (Answers For Teacher Reference)Brooklon HardyNo ratings yet
- English Yearly Scheme of Work Year One 2020Document11 pagesEnglish Yearly Scheme of Work Year One 2020jeetveer1No ratings yet
- International Handbook of Bilingualism and Bilingual EducationDocument707 pagesInternational Handbook of Bilingualism and Bilingual Educationoanadragan100% (2)
- Summary RubricDocument1 pageSummary RubricAmmar Fitri0% (1)
- What Is PragmaticsDocument3 pagesWhat Is Pragmaticschew_93No ratings yet
- THE ORAL APPROACH SummaryDocument1 pageTHE ORAL APPROACH Summaryvb22009No ratings yet
- English360 Ebook PDFDocument269 pagesEnglish360 Ebook PDFZul AmranNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON FORMAT Grade 6Document4 pagesDETAILED LESSON FORMAT Grade 6Regine Malana100% (2)
- CMap Grade 8 EnglishDocument15 pagesCMap Grade 8 EnglishMia MingoaNo ratings yet
- Da Words Meaning GermanDocument10 pagesDa Words Meaning GermanLoki97 0No ratings yet
- Learning Log Module 18Document2 pagesLearning Log Module 18Giane Joana Alisoso DanaoNo ratings yet
- In Company 3.0: M CM IllanDocument162 pagesIn Company 3.0: M CM Illanglooria911No ratings yet
- LYAAADocument10 pagesLYAAAAan FchNo ratings yet
- Updated Active & PassiveDocument24 pagesUpdated Active & PassiveKaye Angelie AcederaNo ratings yet
- A Course To Survive Marina's ClassesDocument32 pagesA Course To Survive Marina's ClassesF Jhie After AliveNo ratings yet
- How To Teach PhonicsDocument26 pagesHow To Teach PhonicsbookbindingNo ratings yet
- If ClauseDocument4 pagesIf ClausesrNo ratings yet
- TSL 612 - Grammar Exercises 1-7Document20 pagesTSL 612 - Grammar Exercises 1-7Cosas de LaRubiaNo ratings yet
- WRITING - Unclear Pronoun ReferenceDocument4 pagesWRITING - Unclear Pronoun Referenceyoussef2No ratings yet
- Lexical AnalysisDocument38 pagesLexical Analysissaeed khanNo ratings yet
- Ingles 2Document73 pagesIngles 2Alguien AhíNo ratings yet
- MTB Mle 2019Document4 pagesMTB Mle 2019Christ Ian100% (2)
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q2 - W6 - D2Document8 pagesDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q2 - W6 - D2Neil HarveyNo ratings yet
- DLL Oral Comm Q2 Week 6Document3 pagesDLL Oral Comm Q2 Week 6Marichu FernandezNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Grammar Guides 140856Document16 pagesRelative Clauses Grammar Guides 140856Roberta OrlandoNo ratings yet
Verb Tenses
Verb Tenses
Uploaded by
Angelica FilipeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verb Tenses
Verb Tenses
Uploaded by
Angelica FilipeCopyright:
Available Formats
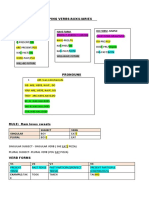
VERB TENSES
TENSES TYPES OF TENSES AUXILIARY VERB
PRESENT TENSE SIMPLE TENSES AUXILIARY VERB – TO DO
(NEGATIVE+ INTERROGATIVE)
PAST TENSE CONTINUOUS TENSES (ING) AUXILIARY VERB – TO BE
FUTURE TENSE PERFECT TENSES (PAST PARTICIPLE) AUXILIARY VERB – TO HAVE
AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE
PRESENT AUXILIARY VERBS
- PRESENT SIMPLE (1 verb) SIMPLE TENSES – TO DO ***** (ONLY USE:
in the NEGATIVE + INTERROGATIVE) ROUTINE
FACTS
TIME TABLE (HORÁRIOS)
…….ALL VERBS (EXCEPT ****) Do – does
EXCEPTIONS ******
-----TO BE
-----TO HAVE GOT
…….MODAL VERBS (MODAL VERBS)
- PRESENT CONTINUOUS CONTINUOUS TENSES – SOMETHING HAPPENING NOW
TO BE (PRESENT SIMPLE) + ESTAR+ A FAZER
(ing) (MAIN VERB+ING) (estar fazendo)
- PRESENT PERFECT **** PERFECT TENSES- TO HAVE
- present perfect continuous
*****
PAST
SIMPLE
…….ALL VERBS (EXCEPT ****) REGULAR VERBS: AFFIRMATIVE REGULAR /irregular VERBS:
NEGATIVE + INTERROGATIVE
AFFIRMATIVE: 1. Add ED / D /IED (consonant+y) DID NOT
1. REGULAR VERBS 1. NEGATIVE – DID NOT
2. IRREGULAR VERBS (Study 2. INTERROGATIVE- DID
list) 3. SHORT ANSWERS (Yes, I
did/ no, I didn’t)
-----TO BE ***** AM + IS = WAS
ARE = WERE
-----TO HAVE/HAS GOT ***** HAD (GOT)
…….MODAL VERBS *****
- PAST CONTINUOUS (ing) CONTINUOUS TENSES –
TO BE (PAST SIMPLE) +
(MAIN VERB+ING)
- present PERFECT **** PERFECT TENSES
- TO HAVE + MAIN VERB IN THE P.P.
(Past Participle)
- past PERFECT ****
PRESENT PERFECT
CONTINUOUS****
FUTURE
- WILL (may / might/ could)
-GOING TO To BE(conjugated) + GOING TO + main
verb in the infinitive
- PRESENT CONTINUOUS
- PRESENT SIMPLE
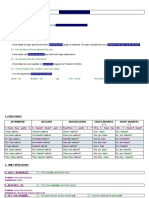
VERB TO BE
I AM I AM NOT AM I? AM I NOT? / YES, I AM
I’m I’M NOT** AREN’T I? NO, I’M NOT
(I AMN’T) (AMN’T i)
YOU ARE YOU ARE NOT Are AREN’T YES, WE ARE
You’re YOU AREN’T you/we/they? YOU/WE/THEY..? NO, WE AREN’T
HE/SHE/IT IS HE/SHE/IT IS NOT Is he/she/it? ISN’T YES, HE IS
He’s HE/SHE/IT…? NO, HE ISN’T
She’s ISN’T
It’s
WE/YOU/THEY WE/YOU/THEY
ARE ARE NOT
We’re -AREN’T
You’re
They’re
PRESENT SIMPLE -HAVE GOT
VERBS – PRESENT SIMPLE VERBS – PRESENT HAVE I,YOU,WE,THEY YES, I HAVE
AFFIRMATIVE SIMPLE GOT? NO, I HAVEN’T
HAVE /HAS + MAIN VERB IN THE NEGATIVE
INFINITIVE HAVEN’T I,YOU,WE,THEY YES, HE HAS
HAVE NOT /HAS NOT + GOT? NO, HE HASN’T
HAVE GOT MAIN VERB IN THE
I, YOU, WE, THEY = THE SAME AS INFINITIVE HAS HE,SHE,IT GOT?
THE NAME OF VERB (infinitive) HASN’T HE,SHE,IT GOT?
I HAVE GOT HAVEN’T GOT
I, YOU WE THEY = NAME
HE, SHE, IT = HAS OF VERB
HE HAS GOT
HE, SHE, IT = HASN’T
I’VE GOT got
YOU’VE
WE’VE
THEY’VE
HE’S GOT
SHE’S
IT’S
PRESENT SIMPLE – ALL OTHER
VERBS (not exceptions)
OTHER VERBS -affirmative + MAIN VERB IN THE HE WISHES
INFINITIVE WASHES
I, YOU WE THEY = NAME OF VERB
WATCHES
(INFINITIVE)
KISSES
BOXES
HE, SHE, IT = RULE
DO doo – DOES – daz
1. +S
2. + ES (S. SS, SH, CH, X, O-Z)
STUDY-STUDIES
3. +IES (consonant + y)
OTHER VERBS -negative + MAIN VERB
I, YOU, WE, THEY = DO+NOT (INFINITIVE)
(DON’T) eat (main verb in infinitive)
HE, SHE, IT = DOES +NOT (DOESN’T)
eat (main verb in infinitive)
OTHER VERBS -interrogative + MAIN VERB YES, I, YOU, WE, THEY DO
(INFINITIVE) NO, I DON’T
I do – do I? Don’t I?
He does- does he? Doesn’t he? YES, HE,SHE,IT DOES
eat (main verb in infinitive) NO, HE DOESN’T
MODAL VERBS ANY TENSE
INFINITIVE/PRESENT PAST SIMPLE (SEMI-MODAL
VERBS)
IGUAL PARA TODOS OS SEMPRE SEGUIDOS PARA NEGATIVO + PERGUNTAS-TROCAR SUJEITO E VERBO
SUJEITOS POR VERBO NOT
PRINCIPAL NO
INFINITIVO
CAN – CANNOT/CAN’T COULD – TO BE + ABLE TO + 1.ASK/give PERMISSION
COULDN’T MAIN VERB IN THE 2. CAPABILITY -saber fazer (Play the piano
INFINITIVE 3. PHYSICAL CAPABILITY (No legs)
conseguir
4. POSSIBILITY (what is possible)
SHALL SHOULD – Informal – SHALL-Used for I and WE
SHOULDN’T OUGHT TO + MAIN Shall I bring the drinks?
VERB IN THE *Shall we go for coffee?
INFINITIVE *let’s go for coffee!!!!!~
SHOULD - GIVE ADVICE
You should go to the doctor
MUST – (OBRIGATÓRIO) ----------------- HAVE TO + YOU MUST GO TO CLASSES
MUSTN’T –(PROÍBIDO INFINITIVE YOU MUSTN’T MISS CLASSES
MAY ----------------- 1.ASK PERMISSION FORMAL
MAY NOT 2. possibilidade (they may arrive today)
MIGHT ----------------- 1. possibilidade (they may arrive today)
MIGHT NOT
WILL – WILL NOT /WON’T WOULD – (FUTURE) ********
(ALWAYS FUTURE) WOULDN’T GOING TO,
PRESENT
CONTINUOUS
PREDICTIONS Expect
HOPES Hope
FEARS I’m
THREATS afraid
OFFERS Believe
PROMISES I’m sure
WARNINGS I know
COMMENTS I think
ON-THE-SPOT probably
DECISIONS
CONTINUOUS TENSES 1.VERB TO BE (PRESENT) (BEFORE -ING) PRESENT CONTINOUS:
+ MAIN VERB + ING 1. E (WRITE) WRIT+ING I am having lessons
1. PRESENT 2. CVC (SWIM+M+ING RIGHT NOW
CONTINUOUS 1.VERB TO BE (PAST) + RUN-RUNNING I am reading a nice book
MAIN VERB + ING HIT-HITTING They are building a
2. PAST WINNING house-
CONTINUOUS 3. LIE -LY+ING
DIE – DY+ING
4. Ski – skiing
NEGATIVE
TO BE + NOT
PAST SIMPLE
VERBS – PAST SIMPLE + MAIN VERB IN THE
AFFIRMATIVE INFINITIVE
HAVE GOT
I, YOU WE THEY HE, SHE, IT = HAD (GOT)
To be I, he, she, it WAS
We, you, they WERE
OTHER VERBS- AFFIRMATIVE 1. D (RULE)
1. REGULAR VERBS 2. ED (all) Exceptions when adding 'ed':
3. IED (CONSONANT + Y)
1.when the final letter is e, only add d
2. IRREGULAR VERBS
STUDY THE LIST 2.after a short, stressed vowel, the final consonant
is doubled
admit – admitted
final l is always doubled in British English (not in
American English):
travel - travelled
after a consonant, final y becomes i (but: not after
a vowel)
worry - worried
but: play - played
OTHER VERBS -negative + MAIN VERB (INFINITIVE)
I, YOU, WE, THEY, HE, SHE, IT
=DID+NOT
OTHER VERBS -interrogative + MAIN VERB (INFINITIVE)
I DID – DID I?
I didn’t – didn’t I?
PRESENT PERFECT
HAVE + main verb in HAVEN’T + P.P. HAVE I, YOU, WE, THEY YES, I, YOU, WE, THEY HAVE
the P.P. + P.P.? NO, I, YOU, WE, THEY HAVEN’T
HAS + main verb in HASN’T + P.P. HAS HE, SHE, IT + P.P.? YES, HE, SHE, IT HAS
the P.P NO, HE, SHE, IT HASN’T
PERFECT TENSES
PRESENT PERFECT + P.P. (past participle)
1. Regular verbs +ed
rd
1.HAVE/HAS (3 column)
PAST PERFECT NEGATIVE + NOT = HADN’T HAD + SUBJECT + P.P. ? YES, I HAD
1. HAD + p.p. NO, I HADN’T
EXPRESSIONS --- TENSES
WHEN TO USE PRESENT SIMPLE WHEN TO USE PRESENT CONTINUOUS
EXPRESSIONS FOR PRESENT SIMPLE EXPRESSIONS FOR PRESENT CONTINUOUS
ROUTINES
(How OFTEN do you….?
ALWAYS NOW ---
RIGHT NOW
NEVER AT THE MOMENT
SOMETIMES TODAY,
USUALLY THIS………….
THIS WEEK, MONTH, YEAR, SUMMER
OFTEN
FREQUENTLY
HARDLY EVER
EVERY …………………
DAY, WEEK, MONTH, YEAR, SEASON, SPRING, HOUR,
SUMMER, AUTUMN, WINTER
Every three minutes
ONCE A WEEK
TWICE A MONTH
THREE TIMES A YEAR
WHEN TO USE PRESENT PERFECT WHEN TO USE PAST SIMPLE
1. TO TALK ABOUT A PAST ACTION BUT WE DON’T 1. TO TALK ABOUT A SHORT PAST ACTION THAT
SAY WHEN IT HAPPENED ( either because we HAPPENED ONCE AND WE GIVE THE EXACT
don’t know or it’s not important) TIME IT HAPPENED
2. To talk about a situation that began in the past
but is still continuing.
3. TO TALK ABOUT AN ACTION IN THE RECENT PAST
EXPRESSIONS PRESENT PERFECT EXPRESSIONS PAST SIMPLE
ALREADY -Já (AFFIRMATIVE) LAST ……year, month, week
YET – AINDA NÃO (NEGATIVE+INTERROGATIVE) AGO … 2 weeks ago, 1 month ago ….
Yet YESTERDAY
JUST – ACABA DE ACONTECER THE DAY BEFORE (YESTERDAY)
THE PREVIOUS …DAY/MONTH/YEAR
SINCE- DESDE+ PONTO NO TEMPO
FOR-HÁ + QUANTIDADE IN 2019
At 8.00
EVER – ALGUMA VEZ? RECENTLY
NEVER In April
SO FAR In the morning
UNTIL NOW
I HAVE ALREADY/JUST seen --------
I haven’t seen the film YET
Have you seen the film YET?
Have you ever ---?
What is the most beautiful city you have ever visited?
PAST CONTINUOUS vs PAST SIMPLE
PAST CONTINUOUS PAST SIMPLE
I WAS HAVING A SHOWER WHEN THE PHONE RANG
THE PHONE RANG WHEN I WAS HAVING A SHOWER
I HAD A SHOWER WHILE MY SISTER WASHED THE DISHES
I WAS HAVING COFFEE WHILE MY SISTER WAS DOING THE DISHES
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple
Simple Past Present Perfect Simple
irregular verbs: see 2nd column of irregular verbs irregular verbs: form of 'have' + 3rd column of irregular verbs
I spoke I / you / we / they have spoken
he / she / it has spoken
regular verbs: infinitive + ed regular verbs: form of 'have' + infinitive + ed
I worked I / you / we / they have worked
he / she / it has worked
certain time in the past Certain event in the past or how often
Example: so far?
certain action took place or whether / how
I phoned Mary 2 minutes ago. often an action has happened till now?
just / already / not yet
Example:
I have just phoned Mary.
Simple Past Present Perfect Simple
certain event in the past whether / how often till now
Example: Example:
He went to Canada last summer. Have you ever been to Canada? / I have been to
Canada twice.
Emphasis on action or result?
Do you just want to express what happened in the past? Or do you want to emphasise the result
(a past action's consequence in the present)?
Simple Past Present Perfect Simple
Emphasis on action Emphasis on result
Example: Example:
I bought a new bike. (just telling I have bought a new bike. (With this sentence I actually
what I did in the past.) want to express that I have a new bike now.)
Signal Words
Simple Past Present Perfect Simple
yesterday just
... ago already
in 1990 up to now
the other day until now / till now
last ... ever
(not) yet
so far
lately / recently
Present perfect x Simple past
Você sempre deve utilizar o "present perfect" quando o período de uma ação for irrelevante ou não estiver
especificado.
Alternativamente, utilize sempre o "simple past" quando forem fornecidos ou solicitados os detalhes sobre
o período ou lugar de uma ação.
Compare:
Present perfect Simple past
We use the Present Perfect: We use Past Simple if we say
when something happened
1.To talk about experiences in life until now
2. we use the present perfect to ask about people’s
experiences. If the answer is yes, we use the past simple to
ask for more information-
I have lived in Lyon. I lived in Lyon in 1989.
They have eaten Thai food. They ate Thai food last night.
Have you seen 'Othello'? Where did you see 'Othello'?
We have been to Ireland. When did you go to Ireland?
Existe ainda uma diferença de atitude entre esses dois tempos verbais, que frequentemente consiste em um
fator importante na escolha do melhor tempo a ser utilizado.
Em "What did you do at school today?" utilizamos o "simple past" porque a pergunta se refere
às atividades, e o período escolar do dia está sendo considerado como encerrado.
Em "What have you done at school today?" utilizamos o "present perfect" porque a pergunta se
refere aos resultados: « mostre-os para mim». O momento em que a pergunta foi feita é considerado
como uma continuação do período escolar.
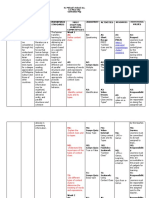
EXPRESSIONS - TENSES
Present Present continuous Past simple PRESENT PERFECT PAST PERFECT
simple Single action I don’t know WHEN it
I know when it happened
happened
Routine Today Last ……. JUST (has just By the time I was
Last year, month, week, happened)
night
Facts Now Yesterday, the day For – since WHEN I was ….
before yesterday For + period of time
SINCE + point in time
schedules THIS…month, year, Ago ……. Already
week Two weeks ago, 1 Yet
month ago Already – affirmative
Yet = negative + not
Yet - interrogative
EVERY DAY 3 times
ONCE a week
On Mondays
In the week
At the
weekend
Always Twice
Never once
Usually
sometimes
often
PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE VS PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS
PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS
I HAVE DONE I HAVE BEEN DOING
HE HAS DONE HE HAS BEEN DOING
I have been a teacher for 25 years I have been teaching for 25 years
What have you done? What have you been doing?
HAVE YOU EVER…? + P.P. - LATELY
HOW LONG HAVE YOU BEEN ----?
FOR TWO MONTHS NOW
MIXED PAST TENSES - NARRATIVE TENSES
Present simple or Present continuous
Past simple or Present perfect
Will or Going to
Going to or Present continuous
Past continuous – past simple * I was eating when he arrived
Past simple – past simple He washed the car while I made dinner
Past continuous – past continuous He was cooking while I was having a
shower
Past perfect – past simple ** I had eaten when he arrived
TIME LINE
PRESENT
PRESENT SIMPLE
1. ROUTINE
2. FACTS
3. SCHEDULES
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
1. HAPPENING NOW
2. BEGUN BUT NOT YET FINISHED
PAST
PAST SIMPLE
ACTION IN THE PAST-FINISHED
PAST CONTINUOUS
ACTION THAT WAS HAPPENING AT A
SPECIFIC TIME IN THE PAST
PRESENT PERFECT
AN ACTION THAT STARTED AT SOME TIME IN
THE PAST (WE DON’T KNOW WHEN) AND IS
STILL TRUE NOW
PAST PERFECT
AN ACTION THAT HAPPENED AT A SPECIFIC
TIME IN THE PAST
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS
FUTURE
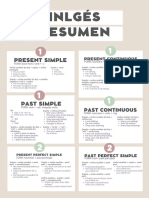
TENSES
Present Simple Tense
Present Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Simple Tense
Past Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Tense
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Simple Tense
Future Continuous Tense
Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
You might also like
- Pre-Int Unit11 BusinessWritingPunctuation PDFDocument2 pagesPre-Int Unit11 BusinessWritingPunctuation PDFZoeTziavara100% (2)
- Time Expressions: Adverbs of FrequencyDocument8 pagesTime Expressions: Adverbs of FrequencyCamila PiranNo ratings yet
- Do Form - Simple (Questions, Negatives) Have Form (Perfect, Perfect Contin) Be Form (Simpl, Contin)Document2 pagesDo Form - Simple (Questions, Negatives) Have Form (Perfect, Perfect Contin) Be Form (Simpl, Contin)malarvizhiNo ratings yet
- Acfrogdgthvxiqs-1yqvjkhvd Mlmzky9c C79l4nwxjhu2s-Mauhtqarai 35bmrjckd6a9aaorui5nc6ajenhswiyhk3o T7zf4hoa49ufvr2cdqbtbje7mzwfox0f-Cu4b5ii2sjtqgmgnqixDocument10 pagesAcfrogdgthvxiqs-1yqvjkhvd Mlmzky9c C79l4nwxjhu2s-Mauhtqarai 35bmrjckd6a9aaorui5nc6ajenhswiyhk3o T7zf4hoa49ufvr2cdqbtbje7mzwfox0f-Cu4b5ii2sjtqgmgnqixAfif Faishal DzakwanNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar and Useful ItemsDocument20 pagesBasic Grammar and Useful ItemsNicole MuroNo ratings yet
- All English Tenses 1Document2 pagesAll English Tenses 1VinNo ratings yet
- English Manual: Licenciada Filología Inglesa Colegiada #2811Document36 pagesEnglish Manual: Licenciada Filología Inglesa Colegiada #2811Gema Caro MolinaNo ratings yet
- PRESENT SIMPLE and CONTINUOUS CHARTDocument2 pagesPRESENT SIMPLE and CONTINUOUS CHARTSusiNo ratings yet
- Importante: Jamas Combinar Am/Is/Are Con Un Verbo en Forma Simple, Ejemplos: Is Cook, Are Go, Am Sleep - Esta Combinación No Es PosibleDocument5 pagesImportante: Jamas Combinar Am/Is/Are Con Un Verbo en Forma Simple, Ejemplos: Is Cook, Are Go, Am Sleep - Esta Combinación No Es PosibleModesta SaenzNo ratings yet
- Theory Present and Past Tenses RevisionDocument2 pagesTheory Present and Past Tenses RevisionAndarielle ConstanceNo ratings yet
- Ingles, Present Simple - 20240604 - 141433 - 0000Document22 pagesIngles, Present Simple - 20240604 - 141433 - 0000juanitodoggieNo ratings yet
- English Sentence Structures Ultima Version Completa 1Document3 pagesEnglish Sentence Structures Ultima Version Completa 1Ariel MeferNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument1 pageTENSESFacundo Nicolás de la FuenteNo ratings yet
- Table Tense Grammar Guides - 85605Document3 pagesTable Tense Grammar Guides - 85605Ferangizbonu BoltayevaNo ratings yet
- Resumen Examen 13-02Document2 pagesResumen Examen 13-02Tully - SanNo ratings yet
- Present Simple, Present Perfect, and Present ContinuousDocument8 pagesPresent Simple, Present Perfect, and Present ContinuousMateo Ariel BelossiNo ratings yet
- Apuntes de Ingles B2 (GRAMMAR)Document29 pagesApuntes de Ingles B2 (GRAMMAR)micobasauriNo ratings yet
- Ingles 1 ResumenDocument7 pagesIngles 1 Resumenjulieta.a.martinezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Adverbs and Expressions of FrequencyDocument22 pagesPresent Simple Adverbs and Expressions of FrequencyDania Huanca MeloNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument3 pagesPresent Simple: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeAlejandra MalettiNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple Tense: Did You Like Did He SeeDocument4 pagesThe Present Simple Tense: Did You Like Did He SeeMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present ContinousDocument1 pagePresent Simple Present ContinousHernández Martínez RamsésNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple Tense: Did You Like Did He SeeDocument4 pagesThe Present Simple Tense: Did You Like Did He SeeMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Present Simple Tabela VIIDocument1 pageUnit 1 Present Simple Tabela VIIJasmin IbrahimovicNo ratings yet
- Adjective+Preposition: Past SimpleDocument5 pagesAdjective+Preposition: Past SimpleSusana GrandãoNo ratings yet
- Tempos VerbaisDocument50 pagesTempos VerbaisJoao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Summary - Advanced 1Document20 pagesGrammar Summary - Advanced 1Strawberry's BlogNo ratings yet
- Present Simple - ResumenDocument1 pagePresent Simple - ResumenAndrea AguirreNo ratings yet
- Virtual PortfolioDocument16 pagesVirtual PortfolioDavid IonutNo ratings yet
- Present Progresive Vs Present ExerciseDocument2 pagesPresent Progresive Vs Present Exerciseteacher ATRIANO RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Simple: Don't /doesn'tDocument7 pagesVerb Tenses Simple: Don't /doesn'tMARIA CANALESNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Simple: Don't /doesn'tDocument7 pagesVerb Tenses Simple: Don't /doesn'tMARIA CANALESNo ratings yet
- Todas Las Formas VerbalesDocument14 pagesTodas Las Formas VerbalesCacoDemonNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument7 pagesPresent Perfectvj.perezcortesNo ratings yet
- Simple Present 1Document19 pagesSimple Present 1cu6295151No ratings yet
- All Verb TensesDocument3 pagesAll Verb TensesAndreu PadrenyNo ratings yet
- Resumen de Tiempos VerbalesDocument1 pageResumen de Tiempos VerbalesMaría MercedesNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Simple Past Tense (2) Geçmiş ZamanDocument3 pagesTenses: Simple Past Tense (2) Geçmiş ZamanMerve AcerNo ratings yet
- Direct Reported SpeechDocument1 pageDirect Reported SpeechMARIN VALDEZ DESIREE STEPHANIA MAVD050203MDFRLSA5No ratings yet
- PresentDocument27 pagesPresentJúlia TANo ratings yet
- Simple Present: InglêsDocument5 pagesSimple Present: InglêsJuliaNo ratings yet
- Repaso InglésDocument2 pagesRepaso InglésValentina CuelloNo ratings yet
- Hábitos o Rutinas Hechos Características Acciones Que Están Pasando Ahora Mismo. (En Progreso)Document1 pageHábitos o Rutinas Hechos Características Acciones Que Están Pasando Ahora Mismo. (En Progreso)Erick ZHNo ratings yet
- Direct Reported SpeechDocument1 pageDirect Reported SpeechMARIN VALDEZ DESIREE STEPHANIA MAVD050203MDFRLSA5No ratings yet
- Engleski - VremenaDocument8 pagesEngleski - VremenasreckoNo ratings yet
- Verbs ChartDocument1 pageVerbs ChartiraaaaatiNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument3 pagesPresent PerfectJuan Luis EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and ContinuousDocument2 pagesPast Simple and ContinuousLaura Roman DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Tenses PDFDocument14 pagesTenses PDFMalaaika SaleemNo ratings yet
- Review - Units 1 - 6Document32 pagesReview - Units 1 - 6Rolando Aparicio Cueto OsorioNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument5 pagesTensesNadia BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Presentes y Pasados Simple y ContinuoDocument11 pagesPresentes y Pasados Simple y ContinuoAida Álvarez LópezNo ratings yet
- İngi̇li̇zce Zamanlar TablosuDocument4 pagesİngi̇li̇zce Zamanlar TablosurealisemeNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses PresDocument20 pagesVerb Tenses PresMarcos AlamosNo ratings yet
- Review of TensesDocument3 pagesReview of Tenseschristian mendozaNo ratings yet
- Cuadro EstructurasDocument1 pageCuadro EstructurasEdiNo ratings yet
- Tenses ChartDocument2 pagesTenses ChartMichelleNo ratings yet
- The Following Table Summarizes The 16 Tenses in EnglishDocument9 pagesThe Following Table Summarizes The 16 Tenses in Englishsoto amilkarNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Continuous - Karen L. Hernández Chávez.Document5 pagesThe Present Perfect Continuous - Karen L. Hernández Chávez.Karen HernándezNo ratings yet
- 4u Physics Equations Formula SheetDocument2 pages4u Physics Equations Formula SheetAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- TC Exam Study NotesDocument3 pagesTC Exam Study NotesAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- Pre Flight Briefing Checklist For Solo FlightsDocument2 pagesPre Flight Briefing Checklist For Solo FlightsAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- Study Notes For Ground Portion of Flight TestDocument1 pageStudy Notes For Ground Portion of Flight TestAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- Generosity in Small Things by Sister Lucy of FatimaDocument2 pagesGenerosity in Small Things by Sister Lucy of FatimaAngelica FilipeNo ratings yet
- 2 Text OperationDocument42 pages2 Text OperationTensu AwekeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Sentence Patterns and Parts of SpeechDocument47 pagesLecture 2 Sentence Patterns and Parts of SpeechRedman BestNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: The TOEFL Course Is Designed To Prepare Students For The TOEFL PBT TestDocument9 pagesSyllabus: The TOEFL Course Is Designed To Prepare Students For The TOEFL PBT TestSulfi mahraniNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Learning & TeachingDocument6 pagesDifferentiated Learning & Teachingapi-281086391No ratings yet
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 2: (Answers For Teacher Reference)Document35 pagesEntrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 2: (Answers For Teacher Reference)Brooklon HardyNo ratings yet
- English Yearly Scheme of Work Year One 2020Document11 pagesEnglish Yearly Scheme of Work Year One 2020jeetveer1No ratings yet
- International Handbook of Bilingualism and Bilingual EducationDocument707 pagesInternational Handbook of Bilingualism and Bilingual Educationoanadragan100% (2)
- Summary RubricDocument1 pageSummary RubricAmmar Fitri0% (1)
- What Is PragmaticsDocument3 pagesWhat Is Pragmaticschew_93No ratings yet
- THE ORAL APPROACH SummaryDocument1 pageTHE ORAL APPROACH Summaryvb22009No ratings yet
- English360 Ebook PDFDocument269 pagesEnglish360 Ebook PDFZul AmranNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON FORMAT Grade 6Document4 pagesDETAILED LESSON FORMAT Grade 6Regine Malana100% (2)
- CMap Grade 8 EnglishDocument15 pagesCMap Grade 8 EnglishMia MingoaNo ratings yet
- Da Words Meaning GermanDocument10 pagesDa Words Meaning GermanLoki97 0No ratings yet
- Learning Log Module 18Document2 pagesLearning Log Module 18Giane Joana Alisoso DanaoNo ratings yet
- In Company 3.0: M CM IllanDocument162 pagesIn Company 3.0: M CM Illanglooria911No ratings yet
- LYAAADocument10 pagesLYAAAAan FchNo ratings yet
- Updated Active & PassiveDocument24 pagesUpdated Active & PassiveKaye Angelie AcederaNo ratings yet
- A Course To Survive Marina's ClassesDocument32 pagesA Course To Survive Marina's ClassesF Jhie After AliveNo ratings yet
- How To Teach PhonicsDocument26 pagesHow To Teach PhonicsbookbindingNo ratings yet
- If ClauseDocument4 pagesIf ClausesrNo ratings yet
- TSL 612 - Grammar Exercises 1-7Document20 pagesTSL 612 - Grammar Exercises 1-7Cosas de LaRubiaNo ratings yet
- WRITING - Unclear Pronoun ReferenceDocument4 pagesWRITING - Unclear Pronoun Referenceyoussef2No ratings yet
- Lexical AnalysisDocument38 pagesLexical Analysissaeed khanNo ratings yet
- Ingles 2Document73 pagesIngles 2Alguien AhíNo ratings yet
- MTB Mle 2019Document4 pagesMTB Mle 2019Christ Ian100% (2)
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q2 - W6 - D2Document8 pagesDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q2 - W6 - D2Neil HarveyNo ratings yet
- DLL Oral Comm Q2 Week 6Document3 pagesDLL Oral Comm Q2 Week 6Marichu FernandezNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Grammar Guides 140856Document16 pagesRelative Clauses Grammar Guides 140856Roberta OrlandoNo ratings yet