Professional Documents
Culture Documents
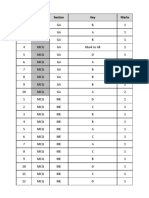
MCQ On Fluid Mechanics 5eea6a0c39140f30f369e136
MCQ On Fluid Mechanics 5eea6a0c39140f30f369e136
Uploaded by
Harsh Tiwari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views18 pagesfm mcq
Original Title
mcq-on-fluid-mechanics--5eea6a0c39140f30f369e136 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentfm mcq
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views18 pagesMCQ On Fluid Mechanics 5eea6a0c39140f30f369e136
MCQ On Fluid Mechanics 5eea6a0c39140f30f369e136
Uploaded by
Harsh Tiwarifm mcq
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 18
Deg)
Fluid Mechanics Questions
India's #1 Learning Platform
Start Complete Exam Preparation
eA een
Gikees eed ease)
Ce cienry Corea peor
Download App
MCQ Question 1 View this Question Online >
In the stability of floating bodies, the stable equilibrium is attained if the meta centre (M)
point ___ the centre of gravity (6).
1. lies above
2. coincides with
3. is parallel to
4. lies below
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 1 : lies above
coaching
India's Super Teachers for all
govt. exams Under One Roof
5 ee Nod
With the aim of helping you gain knowledge, Testbook brings various chapters from Fluid Mechanics
to help you ace your government job preparations. Stay tuned for more.
Fluid Mechanics MCQ Question 1 Detailed Solution
Explanation:
In the stability of floating bodies, the stable equilibrium Is attained if the metacentre (M) point lies
above the centre of gravity (6).
The partially submerged body resembles the floating body, where the weight of the body is balanced
by the buoyancy force acting in the upwards direction. The stability of the floating is governed by the
metacentre of the floating body.
Metacenter
+ It is the point about which a body starts oscillating when the body is tilted by a small angle.
+ itis the point where the line of action of buoyancy will meet the normal axis of the body when
the body is given a small angular displacement.
Stability of floating bodies:
os
Ley 7, 2 ke
(|
AL ld ty
Stable equilbrium Mis aboveG Unstable equllibium M is below G
1. Stable equilibrium: The metacentre is above the centre of gravity of the body, then the disturbing
couple is balanced by restoring couple, the will be in stable equilibrium.
2. Unstable equilibrium: The metacer
couple is supported by restoring coup!
is below the centre of gravity of the body, then t
the body will be in unstable equilibrium
disturbing
3. Neutral equilibrium: The metacentre and the centre of gravity coincides at the same point, then the
body is in neutral equilibrium.
Stability of submerged bodies:
In the case of the submerged body the centre of gravity and centre of buoyancy is fixed, therefore the
stability or instability is decided by the relative positions of the centre of buoyancy and the centre of
aravity.
1, Stable equilibrium: For stable equilibrium, the body the centre of buoyancy Is above the centre of
gravity. The disturbing couple is countered by the restoring couple.
Free surface
A Submerged body
in Stable Equilibrium
2. Unstable equilibrium: For unstable equilibrium, the centre of buoyancy is below the centre of ca C
of the body, the disturbing couple is supported by the restoring couple.
Free surface N
A Submerged body
in Unstable Equilibrium
3. Neutral equilibrium: when the centre of gravity and the centre of buoyancy coincide then it is the
state of neutral equilibrium.
Free surface
(a) (b) ©
A Submerged bod
in Neutral Equilibrium
eat ha) DR GoC DAR ce eescttcn
Start Complete Exam Preparation
aici (jee ieee
foe rcere
jownload App
MCQ Question 2 View this Question Online >
Bernoulli's equation is applied to
1. Venturimeter a
2. Orifice meter
3. Pitot tube meter © =~
4. All of the above
~
‘Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 4: All of the above
Se ck a ac
CONCEPT:
Bernoulli's principle: For a streamlined flow of an ideal liquid in a varying cross-section tube the total
energy per unit volume remains constant throughout the fluid,
+ This means that in steady flow the sum of all forms of mechanical energy in a fluid along
a streamline is the same at all points on that streamline.
From Bemoull's principle
P, P,
at teh + ive= A +ghy + 3V5
P a
© 4+gh+ hv? = constant. ~
EXPLANATION:
* From above it is clear that Bernoulli's equation states that the summation of pressure head,
kinetic head, and datum/potential head is constant for steady, incompressible, rotational, and
non-viscous flow.
* In other words, an increase in the speed of the fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in
pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy i. the total energy of a flowing system
remains constant until an external force is applied.
* So Bemoulli's equation refers to the conservation of energy.
* Allof the above are the measuring devices like Venturimeter, Orifice meter, and Pitot tube
meter works on the Bemoulli’s theorem. Therefore option 4 is correct.
eee ee eee) Cee oe
Start Complete Exam Preparation
Cay esd Eis
Crestetoras
MCQ Question 3 ‘View this Question Online >
Rain crops are spherical because of
1. viscosity
of
2. air resistance
3. swear
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 3 : surface tension forces
Fluid Mechanics MCQ Question 3 Detailed Solution
CONCEPT:
Surface tension (S):
+ Itis the property by virtue of which the free surface of a liquid at rest behaves like elastic
‘stretched membrane tending to contract so as to occupy the minimum surface area.
+ Surface tension is measured as the force acting per unit length of an imaginary line at)
the liquid surface. Bele
Surface tension(S) =
EXPLANATION:
+ The property of a fluid due to which it opposes the relative
layers is called viscosity (or fluid friction or internal frie
its different
option 1 is incorrect.
~ A-small liquid drop hias a spherical shape, as
have the minimum surface area and for
area. Therefore option 3 is correct.
Bjimportant Point
Applications of Surface Tension
tension the liquid surface tries to
, the sphere has a minimum surface
+ The warm soup tastes tasty because its surface tension is low at high temperatures and the
soup spreads on all parts of the tongue.
+ The phenomenon of rising or fall of liquid level inside a capillary tube when it is dipped in the
liquid is called capillary action.
+ The capillary actions due to surface tension.
* Capillary action draws the ink to the tips of fountain pen nibs from a reservoir or cartridge
within the pen.
2
es
De see RST ia)
PS ela me (CM hc uimede ele l iced)
Roe ete
een peso
Doers Cees
jownload App
MCQ Question 4 View this Question Online >
Ina stream line steady flow, two points A and B on a stream line are 1 m apart and the
flow velocity varies uniformly from 2 m/s to 5 m/s. What is the acceleration of fluid at
B? ‘ j
1. 3m/s? )
2. 6m/s?
4.15 m/s?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 4: 15 m/s?
Fluid Mechanics MCQ Question 4 Detailed Solution
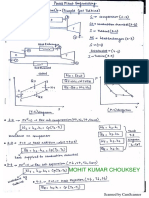
Concept:
For flow along a stream line acceleration Is given as
ifV=f(s,t)
then, WV = 20 ds + Wr de
wv _9
For steady flow ae =
=W yds
Then@= os * &
Since V = f(s) only for steady fl
= WV
a=-Vx@
Therefore
Calculation:
Given, Va = 2 m/s, Ve = 5 m/s, and distance s = 1m
wv _ 6-2) _9
ie
So acceleration of fluid at B is
ag=Vpx ¥ =5x3=15
a
&
ieee ae acta
Start Complete Exam Preparation
rsucd ey ee
Question Bank Ga eet
Dao
Download App
MCQ Question 5 View this Question Online >
A vertical triangular plane area, submerged in water, with one side in the free surface,
vertex downward and latitude ‘h’ was the pressure centre below the free surface by
1. W/4
2 h/3
3. 2h/3
4. h/2
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 4: h/2
Geometry ‘Centre of pressut
xz
I 2h
>
b
ee,
\ /\
“7\p +
=
—
b
( )) =
b
ww |
=
a ap
a
a
lat)
Ly
we
Po
eee een pact
Start Complete Exam Preparation
Ceca cot
PV ao barteod ae
is (=) cs)
Rosine
jownload App
Cresieace pr
MCQ Question 6 View this Question Online >
Assuming constant temperature condition and air to be an ideal gas, the variation in
atmospheric pressure with height calculated from fluid statics is
1. linears =
™.-
3. quadratic
4. cubic
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 2: exponential
Fluid Mechanics MCQ Question 6 Detailed Solution
Explanation:
al P
From hydrostatic law:
Rate of increase of pressure in a vertical direction equal to the weight density of the fluid at that
point.
4
For a compressible fluid, density (0) changes with the change of pressure and temperature. Thus, eq
(1) cannot be integrated directly.
~: Airis an ideal gas so,
p= piRT (~ PV=mRT)
dp __ op @ - t
> 2 =-BI> P=-gZk
s/#=[ pies inp=-Z
«p= @9RT | ©. the atmospheric pressure varies exponentially with height.
DL aC CR Goc Re eros
Start Complete Exam Preparation
a} Pac Oe 3} Pears
ier! pretre
jownload App
Cresieorag
MCQ Question 7 View this Question Online >
The piezometric head in a static liquid:
1. remains constant only in a horizontal plane
2. remains constant at all points in the liquid
3. decreases linearly with depth below a free surface _
4. increases linearly with depth below a free surface
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
xX 2: femains constant at all points in the liquid
Fluid Mechanics MCQ Question 7 Detailed Solution
Explanation:
The total energy of a flowing fluid can be represented in terms of head, which is given by
P4Pae
ww oy
The sum of the pressure head and hydrostatic pressure head is called the piezometric head. Itis
given by
Piezometrichead = 2, + 2
P
where =7= pressure energy per unit weight or pressure head
ye
27 = kinetic energy per unit weight or kinetic energy head
Z = potential eneray per unit weight or elevation head
The pressure at any point in a static fluid is ie \ ic law which is given by -
Z=—p9
2 P =-poz
+P =pgh
where P = pressure above atmospheric pressure and h = height of the point from the free surface
P,
At point A, pressure head = —* = h, and datum head = z,
Po
At point B, pressure head = —? = hg and datum head = z3
4
P
Piezometric head at point A = 37 + *=hg+Z,=H
; Py
Piezometric head at point B = 3g hetZy=H
-. piezometric head remains constant at all points in the liquid.
India’s #1 Learning Platform
Start Complete Exam Preparation
ECan
(ga) Dally Live Bored Pc
aa Ec Cirsieurg Pyettry
MCQ Question 8 View this Question Online >
The property by virtue of which liquid opposes relative motion between its different
layers is called
1. Surface tension
2. Cohesion
3. Viscosity
4. Capillarity >
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 3 : Viscosity
Fluid Mechanics MCQ Question 8 Detailed Solution
CONCEPT:
Viscous force (F):
+ When a layer of fluid slips or tends to slip on adjacent layers in contact, the two layers exert
tangential force on each other which tries to destroy the relative motion between them.
+ The property of a fluid due to which it opposes the relative motion between its different
layers is called viscosity (or fluid friction or intemal friction) and the force between the layers
‘opposing the relative motion is called viscous force.
+ The force acting between the different layers of a fluid is given by —
F=-nA®
Where n = coefficient of viscosity, A = area of the plane and dv/dx = velocity gradient.
+ A negative sign is employed because viscous force acts in a direction opposite to the flow of
liquid. ‘
+ The Sl.unit of viscosity |s poiselulle (PI). Its other units are Nsm* or Pas.
EXPLANATION:
+ Surface tension is the property by virtue of which liquid tries to minimize its
free surface area and itis measured as the force acting per unit length of an imaginary line
drawn on the liquid surface. Therefore option 7 isincorrect.
+ The force of attraction between molecules of same substance is celled the force of
cohesion. Therefore option 2 \s HBOyect.
+ From above it is clear that the by virtue of which liquid opposes relative motion
between its different layers is called viscosity. Therefore option 3 is correct.
+ If a tube of the very narrow bore (called capillary) is dipped in a liquid, itis found that the liquid
in the capillary either ascends or descends relative to the surrounding liquid. This
phenomenon is called capillarity. Therefore option 4 is incorrect.
vy
~ Bimportant Point
+ Cause of Viscosity: It is due to cohesion and molecular momentum exchange between fluid
layers.
* €.G.S Unit of viscosity is Poise = dyne-sec/em?
* One Poise = 0.1 Pa.s
* 1/100 Poise is called centipoises.
Pa
ee Lr het
Sela meas) (CM bel de)
Can cae ray
Cpu kes
poser
lownload App
ieereat ony
MCQ Question 9 View this Question Online >
For a pitot tube, the stagnation pressure head is 6.8 m, the static pressure head is 5
m, Cy = 0.9 and g = 10 == Calculate the velocity?
1. 9m/s
2. 11.24 m/s
3. 10.49 m/s
4. 5.4m/s
‘Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 4:5.4 m/s
Ro
‘
ae a al CRC a Korres ied
Sele merrell made erle lied)
i Pins ibe Dr
Dieser Cres eucrg Pyttra
jownload App
MCQ Question 10 View this Question Online >
The pitot tube is used to measure
1. velocity at stagnation point
2. stagnation pressure
3. static pressure
4. dynamic pressure
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option 2 : stagnation pressure
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MCQ On First Law of Thermodynamics 5eea6a1539140f30f369f474Document15 pagesMCQ On First Law of Thermodynamics 5eea6a1539140f30f369f474Harsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Production Engineering Manufacturing 5eea6a0d39140f30f369e295Document16 pagesMCQ On Production Engineering Manufacturing 5eea6a0d39140f30f369e295Harsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Vik QM U2Document12 pagesVik QM U2Harsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- AET Tata Steel 2018 Paper Aptitude Section PDFDocument40 pagesAET Tata Steel 2018 Paper Aptitude Section PDFHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- ME2 Key PublishedDocument3 pagesME2 Key PublishedHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Unit # 2Document85 pagesUnit # 2Harsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Dig Awardgca PDFDocument8 pagesDig Awardgca PDFHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Short Notes Part 1 @mohit Chouksey PDFDocument12 pagesPower Plant Short Notes Part 1 @mohit Chouksey PDFHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Key PDFDocument22 pagesSSC CGL Key PDFHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressDocument11 pagesThermal StressHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (Trusses and Frames) GATE 2005 TO 2019 by H S Rajput PDFDocument16 pagesEngineering Mechanics (Trusses and Frames) GATE 2005 TO 2019 by H S Rajput PDFHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument32 pagesNotesHarsh TiwariNo ratings yet