Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability File 3 Bayes
Probability File 3 Bayes
Uploaded by
Juank Z Bk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views14 pagesThe document discusses different probability concepts including:
- Joint probability is the probability of two or more events occurring together.
- Independent events are not affected by previous events, so the probability of each event remains the same.
- Dependent events are when the probability of an event is affected by previous events.
- Conditional probability is the probability of an event given that another event has occurred.
Original Description:
Some probability exercises from Principles of Biostatistics using Microsoft Excel
Original Title
Probability file 3 Bayes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different probability concepts including:
- Joint probability is the probability of two or more events occurring together.
- Independent events are not affected by previous events, so the probability of each event remains the same.
- Dependent events are when the probability of an event is affected by previous events.
- Conditional probability is the probability of an event given that another event has occurred.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views14 pagesProbability File 3 Bayes
Probability File 3 Bayes
Uploaded by
Juank Z BkThe document discusses different probability concepts including:
- Joint probability is the probability of two or more events occurring together.
- Independent events are not affected by previous events, so the probability of each event remains the same.
- Dependent events are when the probability of an event is affected by previous events.
- Conditional probability is the probability of an event given that another event has occurred.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Probability is calculated as the number of desired outcomes divided by the total possible
outcomes, in the case where all outcomes are equally likely.
Joint Probability, the probability of two (or more) events is called the joint probability. The
joint probability of two or more random variables is referred to as the joint probability
distribution. Probabilities are combined using multiplication, therefore the joint probability of
independent events is calculated as the probability of event A multiplied by the probability of
event B. Independent Events are not affected by previous events.
Independent events example: You toss a coin and it comes up "Heads" three times ... what is
the chance that the next toss will also be a "Head"? The chance is simply ½ (or 0.5) just like
ANY toss of the coin.
Example: In the experiment of drawing two cards, find the probability of drawing and ace of
spades and a red card.
Mutually exclusive events, are those events that cannot or do not occur at the same time.
Example: Find the probability of a person who is mortally sick and at the same completely
healthy.
Dependent Events where what happens depends on what happened before, such as taking
cards from a deck makes less cards each time. This is related to Conditional probability,
which is known as the possibility of an event or outcome happening, based on the existence
of a previous event or outcome. It is calculated by multiplying the probability of the
preceding event by the renewed probability of the succeeding, or conditional, event.
Sources:
https://machinelearningmastery.com/joint-marginal-and-conditional-probability-for-machine-learning/#:~:text=Marginal%20p
https://byjus.com/maths/mutually-exclusive-events/
https://byjus.com/maths/conditional-probability/
arning/#:~:text=Marginal%20probability%20is%20the%20probability,presence%20of%20a%20second%20event.
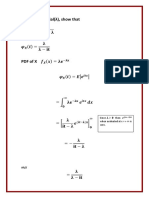
Bayes’ theorem describes the probability of occurrence of an event related to any condition. Source
It is also considered for the case of conditional probability. Bayes theorem is also known as https://byjus.com/math
the formula for the probability of “causes”. For example: if we have to calculate the
probability of taking a blue ball from the second bag out of three different bags of balls,
where each bag contains three different colour balls viz. red, blue, black.
https://byjus.com/maths/bayes-theorem/
A manufacturing company discovers that 40% of its new employees turn out to be good
workers and 60% turn out to be poor workers. All current workers receive a reasoning test. Of
the good workers, 80% approve, 40% of the poor workers approve. Assume that these figures
will be true in the future. If the company makes the test part of its hiring procedure and only
hires people who meet the above requirements and also pass the test, what percentage of the
new hires will turn out to be good workers?
The following information refers to three shipping terminals operated by a certain company. Your
internal auditor randomly selects a set of shipping documents, checking that the selected set contains an
error. Find the probability that the error occurred at the marine terminal.
Terminal % shipment % error
Tierra 60 4
Aire 30 9
Mar 10 12
Specificity = 1 - False Positive = 1 - P(positive test l no disease) = P(negative test l no disease)
Sensitivity = 1 - False Negative = 1- P(negative test l disease) = P(positive test l disease)
You might also like
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1nurul.purbaya100% (2)
- Leson 1.1 Notes Probability and Statistics - Virtual SC CourseDocument3 pagesLeson 1.1 Notes Probability and Statistics - Virtual SC CourseAlibinSabahNo ratings yet
- ProbabilitiesDocument18 pagesProbabilitiesAkshat Pandey0% (1)
- TSP in Excel PDFDocument23 pagesTSP in Excel PDFJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Tesla Multiplication MethodDocument3 pagesTesla Multiplication MethodJuank Z Bk0% (1)
- T DistributionDocument4 pagesT DistributionEr Rajesh BuraNo ratings yet
- Whats ProbabilityDocument5 pagesWhats ProbabilityBabita RayNo ratings yet
- QMB FL. Chap 03Document78 pagesQMB FL. Chap 03Manula JayawardhanaNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Probability ConceptsDocument42 pagesA Survey of Probability ConceptsBor ShonNo ratings yet
- ProbDocument62 pagesProbSherlene Antenor SolisNo ratings yet
- Probability: Mrs - Kiranmayi PatelDocument35 pagesProbability: Mrs - Kiranmayi PatelShubhamNo ratings yet
- National College of Business Administration & Economics: Probability & StatisticsDocument5 pagesNational College of Business Administration & Economics: Probability & StatisticsAleena HassanNo ratings yet
- MBA First Semester AssignmentDocument14 pagesMBA First Semester AssignmentMukeshKumarNo ratings yet
- 6 Modeling Uncertainty With ProbabilityDocument88 pages6 Modeling Uncertainty With ProbabilityMohammad Raihanul Hasan100% (1)
- Statistics Session 4: "There Are Three Kinds of Lies: Lies, Damned Lies, and Statistics."Document34 pagesStatistics Session 4: "There Are Three Kinds of Lies: Lies, Damned Lies, and Statistics."Christina Sliney-BissNo ratings yet
- 2 - Probability DistributionsDocument63 pages2 - Probability DistributionsGagan Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- Business Math DefinitionsDocument3 pagesBusiness Math DefinitionsWilliam Andrew Gutiera BulaqueñaNo ratings yet
- StatisticalDocument5 pagesStatisticalHazel Faith CellaNo ratings yet
- Tree Diagram ProbabilityDocument5 pagesTree Diagram Probabilityapi-140032165No ratings yet
- Concepts of ProbabilityDocument32 pagesConcepts of ProbabilityRushina SinghiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 BCC ProbabilityDocument10 pagesModule 5 BCC ProbabilityJean Rose RamillaNo ratings yet
- Ips-1, 2017Document21 pagesIps-1, 2017Mayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Probability Concepts and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesProbability Concepts and ApplicationsimtiazbscNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CH: Data Handling Topic: Probability: By: AkhileshDocument7 pagesMathematics CH: Data Handling Topic: Probability: By: AkhileshReshma SharmaNo ratings yet
- Probabilty NewDocument7 pagesProbabilty NewGoodluck EdwinNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts of Probability: Probability Is A Measure of The Likelihood That ADocument43 pagesFundamental Concepts of Probability: Probability Is A Measure of The Likelihood That ARobel MetikuNo ratings yet
- LS3 Probability JHSDocument34 pagesLS3 Probability JHSJaysanAledZurc100% (1)
- Mme 8201 2-Probability Concepts and ApplicationsDocument18 pagesMme 8201 2-Probability Concepts and ApplicationsJosephat KalanziNo ratings yet
- Point EstimationDocument13 pagesPoint EstimationTarun Goyal100% (1)
- History of ProbabilityDocument3 pagesHistory of ProbabilityJeffery Ooi100% (1)
- Maths Project File Term 2Document19 pagesMaths Project File Term 2Aditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Gate All Topics PDFDocument5 pagesGate All Topics PDFneelam aryaNo ratings yet
- Probability Applications in BusinessDocument4 pagesProbability Applications in BusinessAhsan Billah50% (2)
- Probability with Permutations: An Introduction To Probability And CombinationsFrom EverandProbability with Permutations: An Introduction To Probability And CombinationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - ProbabilityDocument19 pagesChapter 7 - ProbabilityKayla JhonsonNo ratings yet
- Probability Shortcut Tricks Tips Concept How To Solve Probability Question Short TrickDocument32 pagesProbability Shortcut Tricks Tips Concept How To Solve Probability Question Short TrickalmamunduthmNo ratings yet
- Probability and SamplingDocument20 pagesProbability and SamplingTsitsi AbigailNo ratings yet
- Percentage StatisticsDocument6 pagesPercentage StatisticsasdfghjkNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Probability and Decision MakingDocument10 pages5.0 Probability and Decision MakingBridget MatutuNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument10 pagesProbabilitySANIUL ISLAM100% (4)
- Statistics 3 - ProbabilityDocument31 pagesStatistics 3 - Probabilityأمجد هاتف منفي جفالNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document85 pagesChapter 15Oreomath AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Math - Subjuctive Probability MeaningDocument3 pagesMath - Subjuctive Probability MeaningAloysius RajNo ratings yet
- Individual Task - 03 Sinta Comara (12350421478)Document6 pagesIndividual Task - 03 Sinta Comara (12350421478)Rijan AnantaNo ratings yet
- Probability (Introduction) : Random Experiments Sample Spaces EventsDocument37 pagesProbability (Introduction) : Random Experiments Sample Spaces EventsrammableNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability With Mathematica - Hastings Sec1.1Document6 pagesIntroduction To Probability With Mathematica - Hastings Sec1.1Δημητρης ΛουλουδηςNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Conditional Probability and IndependenceDocument36 pagesChapter 03 - Conditional Probability and IndependenceBatu GünNo ratings yet
- Statistic AssignmentDocument6 pagesStatistic AssignmentZeeshan MughalNo ratings yet
- Probability and Probability DistributionDocument46 pagesProbability and Probability DistributionEdna Lip AnerNo ratings yet
- Scott Cunningham Causal Inference 2020 SEGUNDA PARTEDocument107 pagesScott Cunningham Causal Inference 2020 SEGUNDA PARTEAndrés LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Individual Task - 03 Wahyu Raihan Aprilio (12350410263)Document6 pagesIndividual Task - 03 Wahyu Raihan Aprilio (12350410263)Rijan AnantaNo ratings yet
- Superior University of Pakistan: Lecture No. 18 of The Course On Statistics and Probability by DR - Amjad HussainDocument61 pagesSuperior University of Pakistan: Lecture No. 18 of The Course On Statistics and Probability by DR - Amjad Hussainapi-26281458No ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics - Yayo 2Document7 pagesProbability and Statistics - Yayo 2riskyNo ratings yet
- Presented By, Name-Ankita Rath ROLL NO-17STAT008 P.G. Dept. of Statistics 2 YrDocument30 pagesPresented By, Name-Ankita Rath ROLL NO-17STAT008 P.G. Dept. of Statistics 2 YrSoumya Ranjan SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Module in Math ProbDocument5 pagesModule in Math ProbArtemist FowlNo ratings yet
- Definition of ProbabilityDocument10 pagesDefinition of ProbabilityAnand satputeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ProbabilityDocument17 pagesIntroduction To ProbabilitySaad AliNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Complete NotesDocument9 pagesEconometrics Complete NotesMunnah BhaiNo ratings yet
- Chi SquareDocument12 pagesChi SquareAlicia YeoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 IUB MAT 212Document35 pagesLecture 02 IUB MAT 212Mir Sahib0% (1)
- Probability FormulaDocument4 pagesProbability Formulaapi-140032165No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ProbabilityDocument112 pagesBasic Concepts of ProbabilityNo FreedomNo ratings yet
- What Is Random?: Chance and Order in Mathematics and LifeFrom EverandWhat Is Random?: Chance and Order in Mathematics and LifeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Gambling Theory: Know the Odds!From EverandIntroduction to Gambling Theory: Know the Odds!Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Session 1 SummaryDocument34 pagesSession 1 SummaryJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Levene S TestDocument42 pagesLevene S TestJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution Second Set of Exercises September 22Document9 pagesSampling Distribution Second Set of Exercises September 22Juank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Probability August 10thDocument21 pagesProbability August 10thJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Tukey KramerDocument14 pagesTukey KramerJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Discrete Probability Distributions Poisson SOLCDocument10 pagesDiscrete Probability Distributions Poisson SOLCJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- SOLC Discrete Probability Distributions BinomialDocument24 pagesSOLC Discrete Probability Distributions BinomialJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing SolutionDocument32 pagesHypothesis Testing SolutionJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2Juank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Function ExercisesDocument10 pagesCharacteristic Function ExercisesJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Clase Julio 5 Distribución NormalDocument28 pagesClase Julio 5 Distribución NormalJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Probabbility File 4 Solc NormDocument28 pagesProbabbility File 4 Solc NormJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution of The Mean CH 8 SolcDocument12 pagesSampling Distribution of The Mean CH 8 SolcJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Probability File 3 Bayes August 17Document17 pagesProbability File 3 Bayes August 17Juank Z BkNo ratings yet
- CLASS 1 May 26th SolcDocument3,297 pagesCLASS 1 May 26th SolcJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- Haga Clic para Agregar Texto Haga Clic para Agregar TextoDocument6 pagesHaga Clic para Agregar Texto Haga Clic para Agregar TextoJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- 24 Ultimate Data Science Projects To Boost Your Knowledge and SkillsDocument10 pages24 Ultimate Data Science Projects To Boost Your Knowledge and SkillsJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- New-York Chicago Topeka Seattle San-Diego: Unitary Shipping Costs - Parameter C (I, J)Document3 pagesNew-York Chicago Topeka Seattle San-Diego: Unitary Shipping Costs - Parameter C (I, J)Juank Z BkNo ratings yet
- March 2005 SATDocument47 pagesMarch 2005 SATJuank Z BkNo ratings yet
- BRM McqsDocument7 pagesBRM McqsKiran ansurkarNo ratings yet
- Module Diass 2nd QuarterDocument39 pagesModule Diass 2nd QuarterVictoria De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Nba Sar EceDocument329 pagesNba Sar EceHarshalNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Questions in Questionnaire DesignDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of Questions in Questionnaire DesignpratishthamalikNo ratings yet
- THE LEVEL OF AWARENESS AMONG THE TEENAGE MOTHERS OF TUBIGON, BOHOL IN RENDERING NEWBORN CARE (Part 1)Document13 pagesTHE LEVEL OF AWARENESS AMONG THE TEENAGE MOTHERS OF TUBIGON, BOHOL IN RENDERING NEWBORN CARE (Part 1)Wuawie MemesNo ratings yet
- DKA-FBF2007-#04-Prometheus BooksDocument71 pagesDKA-FBF2007-#04-Prometheus Booksapi-3766294100% (1)
- So What's The Deal With Gann and Gann AnalysisDocument12 pagesSo What's The Deal With Gann and Gann Analysissalima100% (1)
- United Bank Pakistan Brief History: Chairman-Deputy Chairman - President & CEO - DirectorDocument7 pagesUnited Bank Pakistan Brief History: Chairman-Deputy Chairman - President & CEO - DirectorAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- L4b - Perfomance Evaluation Metric - RegressionDocument6 pagesL4b - Perfomance Evaluation Metric - RegressionKinya KageniNo ratings yet
- Impact of Digital Technology and The Need For Periodical Review of Educational Curriculum in Nigeria Tertiary InstitutionsDocument6 pagesImpact of Digital Technology and The Need For Periodical Review of Educational Curriculum in Nigeria Tertiary InstitutionsEngr. Najeem Olawale AdelakunNo ratings yet
- KesihatanDocument20 pagesKesihatandalysa100% (1)
- Indian Leadership Styles PDFDocument17 pagesIndian Leadership Styles PDFRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Every Sector of The Industry Requires Some Spice of Innovation Which Results From Continuous ResearchDocument13 pagesEvery Sector of The Industry Requires Some Spice of Innovation Which Results From Continuous ResearchTAKUDZWANo ratings yet
- V2 Theeffectsofsocialmediavalidation V2Document15 pagesV2 Theeffectsofsocialmediavalidation V2Josue GarciaNo ratings yet
- 20-2 Course Outline 2017-18Document2 pages20-2 Course Outline 2017-18api-302976262No ratings yet
- Physics Ip - Copy FinalDocument22 pagesPhysics Ip - Copy Finalduraivigneshwaran2007No ratings yet
- Research Methods - STA630 Quiz 4Document244 pagesResearch Methods - STA630 Quiz 4Athar NazirNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument8 pagesBrainstormingparulkakNo ratings yet
- Professional PracticeDocument7 pagesProfessional PracticeMQ SpotifyNo ratings yet
- Considerations in Designing A CurriculumDocument2 pagesConsiderations in Designing A CurriculumMarina Maulad Marsal100% (1)
- Optimization of Multi-Tiered Supply Chain Networks With Equilibrium FlowsDocument16 pagesOptimization of Multi-Tiered Supply Chain Networks With Equilibrium FlowsSandhya BajajNo ratings yet
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)Document36 pagesStatistical Process Control (SPC)SYEDOUNMUHAMMAD ZAIDI100% (1)
- Thinking Skills and Creativity: Burak AyçiçekDocument10 pagesThinking Skills and Creativity: Burak AyçiçekLUCY AMANDA MUNOZ CAICEDONo ratings yet
- Financial Technology Performance of Commercial Banks I Nordic CountriesDocument126 pagesFinancial Technology Performance of Commercial Banks I Nordic CountriesOumaima MengouchiNo ratings yet
- REVISEDDocument63 pagesREVISEDAina De LeonNo ratings yet
- TQM IMP Questions - MBA III Semester-OUDocument2 pagesTQM IMP Questions - MBA III Semester-OUsrinivas nallakuntaNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Better Student and A Smarter PersonDocument19 pagesHow To Be A Better Student and A Smarter PersonGian Fiero100% (1)
- The Management of Productivity and Technology in Manufacturing PDFDocument333 pagesThe Management of Productivity and Technology in Manufacturing PDFmythee100% (2)