Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dissertation On Mudra Loan
Dissertation On Mudra Loan
Uploaded by
Aarti DivyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dissertation On Mudra Loan
Dissertation On Mudra Loan
Uploaded by
Aarti DivyaCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Dissertation On Mudra LOAN
Mba (Savitribai Phule Pune University)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
DISSERTATION REPORT
ON
REVIEW OF PERFORMANCE OF PRADHAN MANTRI
MUDRA
YOJANA
DISSERTATION SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE
REQUIREMENT FOR THE AWARD OF THE DEGREE OF
MASTER OF BUSINESS
ADMINISTRATION OF
SAVITRIBAI PHULE PUNE UNIVERSITY
SUBMITTED BY
MS. POOJA DNYANESHWAR BHORDE
(MBA – FINANCE)
UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF
PROF. VIKAS DESHPANDE
SMT. HIRABEN NANAVATI INSTITUTE OF
MANAGEMENT AND RESEARCH FOR
WOMEN, PUNE-411052
2016 -2018
STUDENT DECLARATION
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
I, the undersigned Ms. Pooja Dnyaneshwar Bhorde, hereby declare that, the
dissertation work entitled “REVIEW OF PERFORMANCE OF PRADHAN MANTRI
MUDRA YOJANA.” is an authentic work that has been carried out during the period of
January 2018 to March 2018. The project has been submitted in partial fulfillment of
the requirements for the award of the Degree of Master of Business Administration to
Savitribai Phule Pune University.
The Project has been done under the guidance of Prof. Vikas Deshpande Sir.
The matter presented in this project report has not been submitted by me for the award of
any other degree elsewhere.
Place : HNIMR, Pune
Date :
CERTIFICATE
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
This is to certify that the dissertation on the project titled “REVIEW OF THE
PERFORMANCE OF PRADHAN MANTRI MUDRA YOJANA” is an original work of Ms.
Pooja Dnyaneshwar Bhorde; and is being submitted in partial fulfillment for the award of
the Master’s Degree in Business Administration of Savitribai Phule Pune University. The
report has not been submitted earlier either to this University/Institution for the
fulfillment of the requirement of a course of study.
Signature of the Faculty Guide Signature of the Director
Date: Date:
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The completion of any inter-disciplinary project depends upon cooperation, co-
ordination and combined efforts of several sources of knowledge. The success and final
outcome of this project required a lot of guidance and assistance from many people and I
am extremely fortunate to have got this all along the completion of my project work. With
deep sense of gratitude I would like to thank all these intellectuals who their best to help
during my dissertation work.
To start off, it’s a privilege for me to express my deepest sense of gratitude to Prof.
Vikas Deshpande Sir, my project mentor from HNIMR, Pune for his versatile viewpoint
and understanding of the subject matter, his guidance, continuous encouragement and
supervision throughout the course.
I am extremely thankful to Dr. Jagdish Pol, Director, HNIMR, Pune for
continuously motivating me, without which this work would not have been possible.
Last but not least, I would like to thank my friends and family members for their
support, and excellent co-operation to build up my morale and who’ve helped me directly
in making the project successful.
Signature of the Student
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
TABLE OF CONTE`NT
SR. NO. CONTENT PAGE NO.
• ABBREVIATIONS
• LIST OF TABLES
• LIST OF FIGURES
• EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
CHAPTER NO. 1. INTRODUCTION
CHAPTER NO. 2. REVIEW OF LETERATURE
CHAPTER NO. 3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Objectives
3.2 Scope of the Research
3.3 Type of Research
3.4 Date Sources
CHAPTER NO. 4 RESEARCH DESIGN
CHAPTER NO. 5. DATA ANALYSIS
CHAPTER NO. 6. SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
CHAPTER NO. 7. SUGGESTIONS
CHAPTER NO. 8. CONCLUSION
• BIBLIOGRAPHY
• APPENDICES
ABBREVIATIONS
• MUDRA : Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd.
• IMF : International Monitory Fund
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
• MFI : Micro Finance Institution
• NBFI : Non Banking Financial Institution
• MSME : Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises
• PMMY : Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
• DFS : Department of Financial Services, Government of India
• GOI : Government of India
• SHG : Self Help Group
• MSMED : Micro, Small, Medium Enterprises Development
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE NO. TITLE PAGE NO.
1.1 Categories of MUDRA Scheme
1.2 Process Flow Diagram
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
1.3 MUDRA offerings
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE NO. TITLE PAGE NO.
1.1 Loan Sanctioned and Disbursed ) Up – To Dec, 2015 )
1.2 Loan Sanctioned and Disbursed ) Up – To Dec, 2016 )
5.1 Region wise Performance by Banks (No. of accounts )
5.2 Region wise Performance by Banks (Amount
Disbursed)
5.3 Region wise Performance – Banks & MFIs ( No. of
Accounts )
5.4 Region wise Performance – Banks & MFIs ( Amount
Disbursed )
5.5 Financing for New Entrepreneurs
5.6 Financing of Women
5.7 Loans to Minority
5.8 PMMY – PMJDY OD Account
5.9 Disbursement through MUDRA Card
5.10 Share of SC/ST/OBC
5.11 Categories of MUDRA Loans and
Beneficiaries 2015 – 16
LIST OF CHARTS
CHART NO. TITLE PAGE NO.
5.1 All Banks – Performance region wise (No. of A/c)
5.2 All Banks – Disbursement region wise ( Amt. in ₹
Crore)
5.3 All Banks – Performance region wise (No. of A/c)
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
5.4 All Banks – Disbursement region wise ( Amt. in ₹
Crore)
5.5 New Entrepreneurs ( No. of Accounts )
5.6 New Entrepreneurs ( Disbursement Amount in ₹
Crore )
5.7 Women Entrepreneurs ( No. of Accounts )
5.8 New Entrepreneurs (Disbursement Amount in ₹
Crore )
5.9 Minority ( No. of Accounts )
5.10 Minority ( Disbursement Amount in ₹ Crore )
5.11 PMJDY OD Account
5.12 Disbursement through MUDRA Card
5.13 PMMY – Category wise
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana
(PMMY) on 8 April 2015. The objective of the scheme is to develop and refinance all banks
and micro-finance institutions (NBFC-MFIs) in the business of lending to micro/small
business entities engaged in manufacturing, trading, and service activities. The scheme is
based on the premise that providing institutional finance to micro/small business units
will turn these entities into instruments of growth, employment generation, and
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
development. Micro Save conducted an independent, point-in-time assessment of the
PMMY to analyse its effectiveness.
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) aims to develop and refinance all financial
institutions (FIs) in the business of lending to micro/small business entities engaged in
manufacturing, trading, and service activities. This Policy Brief highlights the
effectiveness, impacts and challenges of the PMMY and assesses its capacity to finance
those unable to get loans under the conventional system.
The core theme of the project is based on study and analysis of review of
performance of Mudra Loan and sanctioning procedure of Mudra Loan.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
CHAPTER
NO.1
INTRODUCTIO
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
CHAPTER NO.1
INTRODUCTION
Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd (MUDRA):
The Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd (MUDRA) was set up by the
Government of India (GOI). MUDRA has been initially formed as a wholly owned subsidiary
of Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) with 100 % capital being
contributed by it. Presently, the authorized capital of MUDRA is 1000 crores and paid-up
capital is 750 crore, fully subscribed by SIDBI. More capital is expected to enhance the
functioning of MUDRA.
MUDRA is expected to serve millions of small borrowers through better governed
MFIs offering suitable products at affordable costs and thereby ensure growth and
strengthening of the microfinance sector in India. The business domain of MUDRA consists
of income generating micro enterprises engaged in manufacturing, trading and services
sectors for loans up to Rs. 10 lakhs. From fiscal 2016-17 micro enterprises involved in
activities allied to agriculture too have also been brought within the ambit of PMMY loans.
The overdraft amount of Rs. 5000 sanctioned under PMJDY is also treated as part of
MUDRA loans PMMY.
• Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) :
The setting up of MUDRA Bank was a part of the 2015-16 Union Budget
proposal made by Honorable Finance Minister of India. The goal of government is to use
MUDRA as a tool to fund the unfunded. All Non- Corporate Small Business Segment)
comprising of proprietorship or partnership firms running as small manufacturing units,
service sector units, shopkeepers, fruits/vegetable vendors, truck operators, food service
units, repair shops, machine operators, small industries, food processors and others in
rural and urban areas, are eligible for assistance under MUDRA. Bank branches would
facilitate collateral free loans under MUDRA scheme as per customer requirements. Under
the aegis of Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY), MUDRA has created 3 loan products
i.e. Shishu (covering loans up to Rs. 50, 000) Kishore (covering loans above Rs. 50, 000 and
up to Rs. 5 lakhs) Tarun (covering loans above Rs. 5 lakhs to Rs. 10 lakhs) as per the stages
of growth and funding needs of the beneficiary micro unit.
Roles and Responsibilities of MUDRA:
MUDRA has been formed with the primary objective of developing the micro
enterprise sector in the country by extending various supports including financial support
in the form of refinancing, so as to achieve the goal of “funding the unfunded”. The GOI
Press the release of 2nd March 2015 has laid down the roles and responsibilities of MUDRA.
Subsequently, GOI has also decided that MUDRA will provide refinance support, monitor
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
the PMMY data by managing the web portal, facilitate offering guarantees for loans
granted under PMMY and take up other activities assigned it from time to time.
In order to make the monitoring more effective, a dedicated portal www.mudra.org. in
was put in place to capture the data on the performance under PMMY on a weekly basis to
have consolidated data of nationwide disaggregated retail transactions details, including
data on new entrepreneurs, women entrepreneurs, SC/ST, Minority, MUDRA card etc. The
data so collected was analyzed and reported to GOI. The progress was closely followed up
with the banks for improvement, if any. A team of officers at ‘Mission Mudra’ was
constituted and placed with DFS for an overall supervision and follow up of the
programme on behalf of GOI.
Focus is on :
MUDRA Bank was formed with a mandate to refinance and regulate micro finance
institutions and get financial assistance to small units that are typically excluded from the
mainstream banking system.
Big corporate groups provide jobs to only 1.25 crore people, while small
entrepreneurs employ 12 crore people and face problems getting financial assistance from
banks and other formal sources, PM Narendra Modi said. This has stifled growth and
limited. In order to strength this type of entrepreneurs by assisting them financially
MUDRA bank has been started.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
MUDRA VISION
“To be an integrated financial and support services provider par
excellence benchmarked with global best practices and standards for the
bottom of the pyramid universe for their comprehensive economic and
social development.”
MUDRA MISSION
“To create an inclusive, sustainable and value based entrepreneurial culture,
in collaboration with our partner institutions in achieving economic success
and financial security.”
MUDRA PURPOSE
Our basic purpose is to attain development in an inclusive and
sustainable manner by supporting and promoting partner institutions
and creating an ecosystem of growth for micro enterprises sector.
• MUDRA – PRODUCT
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Under the aegis of Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana, MUDRA has already created its initial
products/schemes. Depending upon the category of business, MUDRA schemes provides
loan in 3 categories.
Tarun
Loans
(Covering
loans from
Rs. 5 lakhs to
Kisho 10 lakhs)
re
(Covering loans
Shishu from Rs.
Loans 50,000/- to
5laks)
(Covering
loans from Rs.
50,000/- )
Fig 1.1 Categories of MUDRA scheme
• Shishu :
This Shishu loan is specially designed for the people who want loans at their early
stage or beginning stage. Indian Government wants to support these businesses
more than the other businesses. Mudra scheme provides 60% funds towards the
Shishu loan. Applicants get loan up to Rs. 50,000 under this stage.
• Kishor :
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Kishor loan is the issue for the people who are already started their business but it
has be established yet. This will cover the loans of above Rs. 50,000 and up to Rs. 5
lakh.
• Tarun :
In this stage, an applicant will get highest loan amount. All small business which
have been set up and established will fall into this category. This loan variant is
designed to meet funding needs to business that has grown out of Development
Stages and Growth Stage.
How & Where to get loans under
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana
(PMMY)
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Process Flow Diagram
Borrower
To approach any of the following lending institution in their region
Scheduled Scheduled Micro
Lending Institutions shall extend financial assistance under PMMY to eligible borrowers
Commerci Urban Co- Financial
al Banks Region Operative Institution
(Public / al Banks/ Viz, NBFCs,
Private Rural State Co- MFIs,
Banks operative Societies,
Banks Trusts
Borrower Borrower Borrower Borrower
MUDRA is launched
For information onwith a purpose
MUDRA to make
products better
and any kindthe
of mall business
assistance, thein the country so that
a borrower
large number of people
can either can getcontact
approach/ employed and self
MUDRA – employed
office at Mumbaiandor to add in the GDP of
the identified MUDRA Nodal Officers, whose details are made
available at MUDRA’s Website.
• MUDRA AND SMALL BUSINESS
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
the country. MUDRA would benefit small manufacturing units, fruits and vegetable sellers,
shopkeepers, beauty parlours, hair salon, hawkers, and urban areas with financing
requirements maximum of ₹ 10 lakh depends upon the business categories ( i.e Kishore,
Shishu and Tarun ) of the entrepreneurs.
TABLE NO. 1.1
LOAN SANCTION AND DISBURSED ( UP – TO DEC, 2015 )
Shishu Kishore Tarun Total
No. of Loan 12296461 1261600 224416 11782477
sanctioned
Amount of
Loan 20799 26714 17445 64958
Sanctioned
Amount of
Loan 19917 25266 16131 61314
Disbursed
As the table 1.1 shows that amount of loan disbursed under Kishore products is more than
the Shishu and Tarun products in absolute figure upto dec. 2015 within period of nine
months as the Yojana started in April, 2015
TABLE NO. 1.2
LOAN SANCTION AND DISBURSED ( UP – TO DEC, 2016 )
Shishu Kishore Tarun Total
No. of Loan 19852783 1303722 42344793 63501298
sanctioned
Amount of
Loan 40614 24365 16417 81396
Sanctioned
Amount of
Loan 40109 22907 15592 78608
Disbursed
As the table 1.2 shows that amount of loan disbursed under Shishu product is more than
the Kishore and Tarun product in absolute figure up to dec. 2016. While comparing to
previous calendar year it is found that total loan disbursed is 78608 in 2016 but 61314 in
Dec. 2015. There is total increase more than 28%.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
MUDRA Offering
Refinanc Mahil Busine Equip
e a ss me nt
Sector Micr schemes Uddy loans Financ
/A o for a mi for e
ctivity Credit RRBs/ Sche Trader scheme
Focuse schem Co- me s Food s and
Community Textiles for
dLand es Fig 1.3 : MUDRA Offerings
transport Social & Products Product
sector/ Personal sector sector
Activity Service Activity
1. Sector / Activity Focused Schemes:
To maximize coverage of beneficiaries and tailor products to meet requirements
of specific business activities, sector / activity focused schemes would be rolled out. To
begin with, based on higher concentration of businesses in certain activities / sectors,
schemes are being proposed for:
• Land Transport Sector / Activity :
These activities will inter alia support units for purchase of transport vehicles
for goods and personal transport such as auto rickshaw, small goods transport vehicle, 3
wheelers, e-rickshaw, passenger cars, taxis etc.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
• Community, Social & Personal Service Activities :
Community, Social & Personal Service Activities such as saloons, beauty
parlours, gymnasium, boutiques, tailoring shops, dry cleaning, cycle and motorcycle
repair shop, DTP and Photocopying Facilities, Medicine shops, Courier Agents etc.
• Food Products Sector :
Food products sectors support would be available for undertaking activities
such as papad making, achaar making, jam / jelly making, agricultural produce
preservation at rural level, sweet shops, small service food stalls and day to day catering /
canteen services, cold chain vehicles, cold storages, ice making units, ice cream making
units, biscuit, bread and bun making etc.
• Textile Products Sector / Activity :
Textile product sector provide support for undertaking activities such as
handloom, power loom, chikan work, zari and zardozi work, traditional embroidery and
hand work, traditional dyeing and printing, apparel design, knitting, cotton ginning,
computerized embroidery, stitching and other textile non garment products such as bags,
vehicle accessories, furnishing accessories etc.
2. Micro Credit Scheme:
It creates financial support to MFIs for on lending to individuals / groups of
individuals / JLGs / SHGs for creation of qualifying assets as per RBI guidelines towards
setting up / running micro enterprises as per MSMED Act and non-farm income
generating activities.
3. Refinance Scheme for RRBs / Co-operative Banks :
It enhancing liquidity of RRBs / Scheduled Co-operative Banks by refinancing
loan extended to micro enterprises as per MSMED Act with beneficiary loan size upto 10
lakh per enterprise / borrower for manufacturing and service sector enterprises.
4. Mahila Uddyami Scheme :
It gives the timely and adequate financial support to the MFIs, for on lending to
women / group of women / JLGs / SHGs for creation of qualifying assets as per RBI
guidelines towards setting up / running micro enterprises as per MSMED Act and non-
farm income generating activities.
5. Business loans for Traders and Shopkeepers :
It gives timely and adequate financial support for on lending to individuals for
running their shops / trading & business activities / service enterprises and non-farm
income generating activities with beneficiary loan size of upto 10 lakh per enterprise /
borrower.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
6. Equipment Finance Scheme for Micro Units :
It gives timely and adequate financial support for on lending to individuals
for setting up micro enterprises by purchasing necessary machinery / equipment’s with
per beneficiary loan size of upto 10 lakh.
Eligibility for Mudra Loan Yojana :
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana is Indian Government scheme in order to provide the
financial aid through loans. Basically, Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana has three facilities
available for catering to enterprises at different stages of growth and financial needs.
• Non-farm income generating activities
• Indian citizens
• Non-cooperate entities
• Small business owners like vegetable vendors, truck operators, fruit vendors,
shopkeepers, repair shops, paper/food processing units, artisans etc. are eligible for
Mudra Bank Loan Yojana.
• Funds to be invested for business activities.
All Indian citizens like, men, women, private limited company, proprietary concern,
partnership firms and other entities can apply for Mudra Bank Loan Yojana.
To avail Mudra bank loan applicant must have the below-mentioned eligibility :
• Monthly income of the applicant should have above INR 17000 or INR 15 lakhs as
annual turnover. The profit after for non-individual should be Rs. 1 lakh per year
and for self employed it is Rs 2 lakh.
• Applicant age should be 23 to 28 years at the time of loan sanction and should not
more than 65 years at the loan maturity time.
• Applicants have to spend the year in the current residence or having one year
service relationship with bank which they are applying for loan.
• In case the salaried individuals minimum occupational stability must be 2 years,
business stability must be 5 years service stability for doctors.
Required documents for Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana :
• Identity proof : PAN card, Adhar card, Voter ID, Passport, Driving License.
• Cast certificate
• Address proof : Recent telephone bill, property tax, electricity bill, Voter ID,
Passport, Adhar card etc.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
• Recent passport size photos of partners/Directors/Proprietor.
• Bank statement – 6 months.
• Copies of registration certificates/ relevant licenses/other document.
• Companies address proof and identity proof.
• Balance sheet of previous 2 years.
• Income tax returns.
• sales tax returns for previous 3 years.
• Memorandum and Articles of association of the company/partnership//Deed of
partners etc.
• If there is any loan in your business name then you need to provide 2 years
projection of your balance sheet.
• If you have to purchase any machinery then provide the details of supplier name,
machinery price, and machinery details.
How to apply Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana :
Here are the steps to apply the Mudra Bank Loan Yojana for all categories (Shishu,
Kishor and Tarun).
• Applicants need to visit the private or commercial bank nearest to his/her location.
• Submit your business ideas with the loan application form.
• Along with the form you need to submit the some required documents (as
mentioned above).
• All formalities follow as per the bank instructions.
• After document verification, your loan will be sanctioned and made available to
loan seeker.
For accessing above stated products following things are available :
1. Mudra Card
2. Portfolio Credit Guarantee
3. Credit Enhancement
Mudra Loan Card :
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
This Mudra loan card acts as the credit card with the pre-approved loan amount. It also
acts as the debit cards and allows ATM withdrawals. The Mudra Card will work with
Rupay platform and can be used or point of sales.
This card will allow users to:
• Can be used as credit card to avail the overdraft facility.
• Swipe the card at PoS.
• Withdraw cash from ATMs
Benefits that flow to society from MUDRA Bank :
• Loans from Mudra Bank will help to bridge the shortfall in loans for small
businesses, who are unable to get institutional credit.
• It also provides credit of up to Rs. 10 lakh to small entrepreneurs, benefitting small
manufacturing units, small shopkeepers, fruits and vegetable vendors, truck
operators, hawkers, artisans in rural and urban areas.
• It also act as a partner with State and regional-level coordinators to grant financial
assistance to last-mile financiers of small and micro business enterprises.
• It offers a Credit Guarantee scheme for providing guarantees to loans being offered
to micro businesses.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Space for Photo Space for Photo Space for Photo
(Signature of Proprietor/Partner/Director whose photo is affixed above)
Date:
Place:
CHECK LIST : (The check list is only indicative and not exhaustive and depending
upon the local requirements at different places addition could be made as per
necessity.)
1) Proof of identity: Self certified copy of Voter’s ID card / Driving License / PAN Card /
Aadhar Card / Passport.
2)Proof of Residence: Recent telephone bill, property tax receipt (not older than 2
months), Voter’s ID card, Aadhar Card & Passport of Proprietor/Partners/Directors.
3)Proof of SC/ST/OBC/Minority.
4)Proof of Identity/Address of the Business Enterprise – Copies of relevant
licenses/registration certificates/other documents pertaining to the ownership,identity
and address of business unit.
5)Applicant should not be defaulter in any Bank/Financial Institution.
6)Statement of accounts (for last six months), from the existing banker, if
any.
7) Last two years balance sheets of the units along with income tax/sales tax return etc.
(Applicable for all cases from Rs. 2 Lacs and above).
8) Projected balance sheets for one year in case of working capital limits and for the period
of the loan in case of term loan (Applicable for all cases from Rs. 2 Lacs and above).
9) Sales achieved during the current financial year up to the date of submission of
application.
10) Project report (for the proposed project) containing details of technical & economic
viability.
11) Memorandum and articles of association of the company/Partnership Deed of Partners
etc.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
12) In absence of third party guarantee, Asset & Liability statement from the borrower
including Directors & Partners may be sought to know the net-worth.
13) Photos (two copies) of Proprietor/ Partners/ Directors.
Acknowledgement Slip for loan Application under Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana
Office Copy:
Application (system Date of Application
generated/manual)
Number
Name of the Loan Amt. Requested
Applicant(s) for
Signature of Signature of Branch
Applicant(s) official
Acknowledgement Slip for loan Application under Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana
Applicants Copy:
Application (system Date of Application
generated/manual)
Number
Name of the Loan Amt. Requested
Applicant(s) for
Signature of Signature of Branch
Applicant(s) official
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
To respond to the design of PMMY and mitigate the risks associated with unsecured
lending, banks have devised interesting customer selection strategies. The primary
strategy of banks is to select their potential MUDRA customers on the basis of branch
staff’s knowledge of customers and potential borrowers transaction history. Customers
who are well known to branch staff and have healthy transaction record are preferred
over others.
Known 2. Bank’s customer 3. Business is close
by / visible
closely to having savings from branch
manager & account for long
In the second and final stage of customer selection, banks follow a “50 meter rule”, under
which customers are screened on the basis of their proximity to the bank’s branches.
Customers whose business is within “50 meters”, or is visible.
Had Bank Account before taking MUDRA (n=617)
15
YES
No
85
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Main Objectives of MUDRA Yojana Scheme:
• Guidelines for micro financing
This will decide how much microfinance’s should be invested and where, the eligibility,
verification and processing of the Mudra Scheme will be done initially.
• MFI entities registration
The entrepreneurs who think that they are eligible under this scheme can apply for
registration. If verified and approved, they will be beneficiaries of this scheme.
• Formulation and supervising a credit guarantee scheme for loans to micro
enterprises
Micro enterprises are businesses on a very small scale that employ hardly a handful of
people. When loans are extended to such enterprises, a guarantee of credit must go hand
in hand.
• Supporting development and promotional activities in sector
Mudra Yojana Scheme doesn’t just end with refinancing and collecting the payment. It also
involves actively supporting any form of development in the sector to which it has
refinanced. The ultimate aim is the development of our nation and this scheme strives in
all possible ways to achieve that.
• Creating good architecture of last mile credit delivery
Quite a few government schemes do not get implemented completely due to various
reasons and somewhere along the way, the focus seems to get completely lost. The Mudra
Scheme has taken upon itself as one of its objective.
• MFI entities supervision
The supervision of the microfinance’s is done carefully. It is made sure that each eligible
candidate receives the stipulated amount without any delay or hassle.
• MFI entities accreditation
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
To ensure that the applicants are eligible for refinancing under this particular scheme,
various verification processes are implemented and accreditation is given.
• To prevent indebtedness and ensure timely recovery
Mudra is a refinancing scheme and not a direct lending scheme. As with any other means
of lending money, in case of unwarranted situations if the borrower is unable to pay the
money back, debts tend to accumulate over time looming like a dark cloud over the
borrower. One of the objectives of the Mudra is to ensure timely recovery of the
microfinance’s to prevent mounting debts.
• Guidelines for micro financing
This will decide how much micro finances should be invested and where. The eligibility,
verification and processing of the Mudra Scheme will be done initially
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
CHAPTER NO.2
REVIEW OF
LITERATUR
E
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
CHAPTER NO.2
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
MUDRA Bank is to provide refinance to last mile 8 providers of finance for
microenterprises loans. Commercial banks, regional rural banks, cooperative banks,
NBFCs and microfinance institutions are eligible to obtain refinance for loans under three
categories: up to Rs 50,000, Rs. 50,000 to Rs. 0.5 million and Rs. 0.5 million to Rs. 1 million.
The three categories are expected to cater to microenterprises at different stages of
development, though 60% of MUDRA Bank’s funding is earmarked to cater to the first
category. The loans are meant to be for nonfarm income-generating activities.
• Dr. J. Venkatesh and MS. R. Lavanya Kumari (2017)
They has showed that besides the schemes that are being introduced for the
overall growth and development of the MSME sector, initiatives have been launched which
focus solely on entrepreneurs. The schemes will contribute to the well-being of the
individuals engaged in small scale industries which will positively affect the progress of
the whole economy.
• R. Rupa (2017)
He has showed that the MUDRA schemes is very much successful in Tamil Nadu. It
is found that the MFIs have contributed substantially to increase the number of accounts
financed under the PMMY.
• William Ohene-Adu and Susana Amankwah(2017)
He is commented that, the market environment is techno sarvey and customers
are well aware and value sensitive with wide range of choice between services providers
hence, the customer satisfaction is depends upon the service quality provided to customers.
Uppal R. K. have comment on bank as retail store and further focused on advantages of
this approach in understanding and building relationship with customers to solve their
problems and to remain relevant.
• Rudrawar & M. A. A. (2016)
They have concluded that the desired transformation can be achieved from PMMY
scheme. If applied properly at the bottom level, it may act as a game changing idea and
may increase, boost and prosper the Indian economy. It should include less documentation
and easily accessible. In coming few years, MUDRA will be a catalyst for the development
of employment, GDP and entrepreneurship at large. Studied the biggest obstacle for the
development of micro and small enterprises was lack of financial assistance. They
introduced the small business contribution to nation GDP. This paper identified the
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
importance of this sector and strategic tool for small business. Also reveals the role of
MUDRA Bank towards small enterprises.
• Mol S. TP (2016)
He has explained that there are certain problems like financial illiteracy, lack of
awareness and customer acquisition is high. Reserve Bank of India has initiated various
initiatives to enhanced financial inclusion. He has displayed that financial inclusion has
increase in India in the last few years with many new innovations like mobile banking,
ultra small branches etc. but still it is far from adequate. He has clarified that there are
some issues like money related Illiteracy, absence of mindfulness and client securing is
high. Reserve Bank of India has started different activities to improved money related
consideration. Information and communication technology offers the opportunities
enhancement of financial inclusion.
• Anup Kumar (2016)
He has displayed that the small businesses from the foundation of the economic
strata needs to be enhanced and supported. A major number of initiatives have been taken
in the past few years are a step in the right direction. He has Throws a light on the
performance of the small-scale sector. This sector contributes the traffic jam to the growth
of the country. But it has very little financial support. This paper focused on to know about
MUDRA Yojana.
• Verma S. (2015)
He has focused that the design of MUDRA Bank will not only cater to the financial
problems of MSMEs but also give moral support to vast pool of young population to
materialize their dreams of becoming an entrepreneur.
• Mehar L (2015)
Mehar has showed that the financial inclusion in India has increased in the last few
years with new innovations like mobile banking, ultra small branches etc. It will be in
charge of creating, upgrading and renegotiating every single Micro undertaking zone by
supporting the Micro Finance Institutions which are occupied with the matter of providing
loan to smaller scale/private firms. MUDRA is framed to accomplish the objective of
“funding the unfunded”. It deals with the web-based interface for checking the PMMY
information. It takes different duties or exercises allowed to it. He reported that the
expectations the consumers should be understood and powerful strategies are to be
implemented by the banks. The value of services provided should be measured in terms of
quality and quantity. The business domain of MUDRA consists of income generating micro
enterprises engaged in manufacturing, trading and services sectors for loans up to Rs. 10
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
lakhs. From fiscal 2016-17 micro enterprises involved in activities allied to agriculture too
have also been brought within the ambit of PMMY loans. The overdraft amount of Rs. 5000
sanctioned under PMJDY is also treated as part of MUDRA loans PMMY. It was put in place
to capture the data on the performance under PMMY on a weekly basis to have
consolidated data of nationwide disaggregated retail transactions details, including data
on new entrepreneurs, women entrepreneurs, SC/ST, Minority, MUDRA card etc. The data
so collected was analyzed and reported to GOI.
The progress was closely followed up with the banks for improvement, if
any. A team of officers at ‘Mission Mudra’ was constituted and placed with DFS for an
overall supervision and follow up of the programme on behalf of GOI. Subsequently, it was
also decided that the MUDRA loans given by MFIs also needs to be captured as most of the
MFIs are MUDRA partners. Accordingly, MFIN was given the responsibility for following up
with the NBFC- MFI and getting their data on the portal. Similarly, Sa-Dhan was made
responsible for collecting the data and on- boarding the same for the non NBFC MFIs.
• Krishna R. R. and V. V. Ganesh Murthy (2015)
He commented that, the market environment is techno sarvey and customers are
well aware and value sensitive with wide range of choice between services providers
hence, the customer satisfaction is depends upon the service quality provided to customers.
He comment on bank as retail store and further focused on advantages of this approach in
understanding and building relationship with customers to solve their problems and to
remain relevant. He admits the fact that, for sustainable development of banking sector
mainly depend upon the trust and loyalty of the customer relationship.
• Hauptman(2015)
He proposed a scheme of approved dealers to assist the Lead Banks in providing
finance and guidance to farmers and small industrialists. In providing finance and
guidance effectively, the banks would have to collect the required information, ensure
recovery of loans and interest, assist in obtaining after sales service and keep a watch on
the working of the assisted enterprise. This work can be made easier by creating and
supporting a set of approved dealers. He requested the RBI to give clear and specific
definition of the different components of priority sectors. Some of the bankers are not clear
about the precise scope of Mudra scheme. Guidance from the RBI would help them to
increase their involvement in farm credit on right lines. He conducted a study among the
village artisans of Karnataka and found that they are receiving an insignificant per cent of their
total credit requirements from banks. Thus artisans are living under the influence of moneylenders.
The opinion that the aim of the banking policy should be to uplift the under privileged class of the
society in rural India from subsistence existence to surplus existence. The concept of priority sector
should include only the real poor of the country and by providing them necessary financial
assistance; they can be lifted from the pitches of animal existence to the heights of human
existence. He made it clear that institutional financing does not mean replacing individual
moneylenders with institutionalized moneylenders. Institutional financing should enable the
agriculturists to
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
move on to a level of new technology that will increase agricultural output and employment. This
means productivity of both land and human beings. Data relating to finance must be able to
provide a basis for assessing how much financing has really contributed to additional output and
employment. He pointed out that the role of commercial banks in the priority sectors is not
confined merely to the provision of finance. They have to evaluate the feasibility of the project and
assist the entrepreneurs to select the right type of project. He also emphasized the need for proper
co-ordination between government agencies and banks for better results in the development of
priority sectors .
in his study on the achievement of commercial banks since nationalization has found that
the banks, which have relatively low priority sector lending have been the ones with higher than
the average credit deposit ratios. Another finding noticed among the banks is that in regard to the
priority sectors, a few branches of banks achieved impressive ratios, to the neglect of the rest of the
areas. Again there is considerable concentration of priority sector advances in a few a States. He
reminded the banks about their socio-economic responsibility in the up-liftment of the poorest
strata of the society. A substantial portion of the people lives in abject poverty and the first priority
should be to provide productive employment opportunities to the very poor- whether they are in
rural or urban areas. Banks should equip themselves fully to serve as instruments of development
for the poorer sections of people. Singh and Balraj11 (1979) conducted a study on commercial
bank lending in Hisser district of Haryana and concluded that villagers are relieved from the
exploitation of moneylenders by the operation of a nationalized bank. At the same time they also
reported other problems such as uneasy, untimely and no availability of loans, expensive and
cumbersome procedures, excessive and useless formalities, unsuitable procedure of loan
repayment and the absence of easy accessibility of banking facilities.
• Kalyanaraman and sudhaami (2015)
He reveal that customer satisfaction is the state of mind that customer have
about the bank when their expectations have been met or exceeded over lifetime of
services. It helps bank to identify opportunities for services innovation and retention of
customers. The most important and common objectives of MUDRA Yojana are equity and
access for the poor and cost sharing has an implicit budgetary objective in regard to public
funding replacement. That is, reduction in public expenditure on higher education and
reallocation of education expenditure from higher to lower levels of education.
Notwithstanding the importance for budgetary objectives, however, the studies do not
offer a supporting or confronting empirical evidence on achieving the budgetary
objectives. The loans scheme receives a considerably higher level of government subsidy
than the loans schemes in the other case study countries. The primary objective of social
control and nationalization is to ensure a better alignment of the commercial banking
system to meet the needs of the economy. It is the duty of the banks to see that credit flows
into channels, which are most productive and most helpful to our growth and
development. To promote the welfare of the people who are socially and economically
backward, the concept of priority sector lending was evolved. Quantitative targets were
set for lending to priority sector and separate sub targets were also set for lending to
agriculture and weaker sections of the society. As a result, lending to the borrowers in
priority sectors have increased substantially. Increased flow of credit to the different
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
sectors assisted the developmental activities and thereby expanded the income as well as
the standard of living of the people.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
CHAPTER NO.3
RESEARCH
METHODOLOG
Y
CHAPTER NO. 3
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY
1. To know Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana.
2. To know the MUDRA product under PMMY.
3. To study the factors that is taken into the consideration before giving the Mudra loan.
4. To observe the documents collected for the sanctioning of loans.
3.2 SCOPE OF THE STUDY
1. The scope of the project can be understood in terms of its relevance to the growth og
knowledge about Mudra Loan.
2. The study covers the period of last 3 years from 2015 to till. There are several reasons
for selecting this period.
3. During the past 3 years the Bank has gone global as a result the company has
witnessed many economies and political changes.
3.3 TYPE OF RESEARCH
The type of research is Exploratory Research
3.4 DATA SOURCES
The study is based on secondary data. The data is collected from various sources
newspapers, magazines and internet websites including website of MUDRA Yojana. For
presentation table is used and for analysis percentage method used.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
CHAPTER NO. 4
RESEARCH
DESIGN
CHAPTER NO. 4
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
RESEARCH DESIGN
• NEED OF THE STUDY
The project forms very vital aspects during the curriculum of MBA. At the end of
the 1st year students are required to undergo a summer training programme of 60 days.
This training is an integral part of MBA course and its importance lies in the fact that it
gives the students the first exposure to an organization.
The training undertaken in Bank of Maharashtra is with few objectives. They are :
1. To get the opportunity or real life business experience.
2. To be able to apply theoretical knowledge obtained in institute practically in actual
business environment.
3. To have a comprehensive understanding of the company.
4. To get acquainted with real organizational problems, perceptions and challenges.
5. To get an opportunity to interact with dynamic managers and all other dynamic levels
of the organization and gain knowledge through their real life experience.
• LIMITATION OF THE STUDY:
1. The study period is limited i.e, only for 2 months.
2. The study was related to the financial services sector where the financial institution
has not given each and every information of their working procedure.
3. As the data was not made available through the primary sources. Some of the data
was collected through the secondary.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
❖ NEED OF
CHAPTER
NO.5 DATA
CHAPTER NO.5
ANALYSIS
DATA ANALYSIS
Review of performance of PMMY during 2015-17
The data collected through portal has been analyzed and some of the salient features are
as under:
1. Overall Achievement vis a vis target
The overall performance of the Yojana indicates that the target has been achieved during
the year. As against t0078he target of ` 122188 crore, the Banks and MFIs together have
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
disbursed ` 132954.73 crore, thereby achieving 109%. The achievements by Public Sector
Banks indicate a substantial credit growth in this segment. Based on the data collected
from the PSBs, it was seen that the disbursement by these banks in this segment was
around ` 33,000 crore during the 2014-15 which has recorded a growth of 70% during
2015-17. The other lending institutions have also achieved high credit growth in this
segment due to the initiative of Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana.
2. Regional
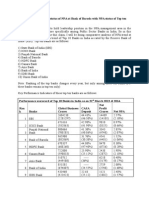
coverage TABLE NO.
5.1
Region wise performance by banks (No. of accounts)
Category North West East South Total
Shishu 2382453 1864905 1893789 2563432 8704579
Kishor 414020 331002 375376 852109 1972507
Tarun 120636 95641 60320 132814 409411
Total 2917109 2291548 2329485 3548355 11086497
%Share 26% 21% 21% 32% 100%
North: Chandigarh, Haryana, HP, J&K, Delhi, UP, Uttarakhand, Punjab and Rajasthan
West: Dadra & Nagar Haveli, D&Diu, Gujarat, Lakshadweep, MP, Maharashtra
East:
NE States, Odisha, WB, Sikkim, Bihar and Jharkhand South:
Karnataka, Kerala, Pudicherry, TN, Telangana, AP, and Andaman & Nicobar
CHART NO. 5.1
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
All Banks - Performance regionwise (No. of A/c)
132814
South852109
2563432
60320
East375376 Shishu
1893789 Kishore Tarun
95641
West 331002
1864905
120636
North 414020
2382453
0 500000 10000001500000200000025000003000000
,
The regional coverage of the programme indicates that all the four regions had wide coverage,
although there had been an edge for the Southern region. The other three regions were almost at
par to each other.
TABLE NO. 5.2
Region wise performance by Banks (Amount Disbursed)
Category North West East South Total
Shishu 4090.28 3478.55 3746.97 5668.02 16983.82
Kishor 9436.71 7312.05 7116.48 16426.35 40291.59
Tarun 9022.46 7143.29 4219.29 9389.86 29774.9
Total 22549.45 17933.89 15082.74 31484.23 87050.31
% Share 26% 21% 17% 36% 100%
Average
Disbursed/
account (₹ 77 78 65 89 79
in
Thousands)
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
CHART NO. 5.2
All Banks - Disbursement regionwise ( Amt in ₹ Cr)
9389.86
South16426.35
5668.02
4219.29
East7116.48Shishu
3746.97Kishor
Column1
7143.29
West7312.05
3478.55
9022.46
North 9436.71
4090.28
0 200040006000800010000 12000 14000 16000 18000
As regards the amount disbursed, North and West regions were at par with that of the
number of accounts financed, under the Yojana. However, the Southern region had a larger
share in the amount disbursed by banks.
The per account average amount disbursed also showed a similar pattern.
TABLE NO. 5.3
Region wise performance – Banks and MFIs ( No. of accounts )
Category North West East South Total
Shishu 6270143 7326264 8411412 10393227 32401046
Kishor 434221 353201 387317 894722 2069461
Tarun 120883 95994 60397 133143 410417
Total 6825247 7775459 8859126 11421092 34880924
% Share 20% 22% 25% 33% 100%
CHART NO. 5.3
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
All Banks - Performance regionwise ( N0 of A/c)
133143
South894722
10393227
60397
East387317 Shishu
8411412 Kishor Tarun
95994
West353201
7326264
120883
North434221
6270143
0 20000004000000600000080000001000000012000000
TABLE NO. 5.4
Region wise Performance – Banks & MFIs ( Amount Disbursed)
Category North West East South Total
Shishu 12037.22 14581.37 14491.25 20917.85 62027.69
Kishor 9612.64 7494.02 7200.78 16765.84 41073.28
Tarun 9041.88 7171.12 4224.92 9415.84 29853.76
Total 30691.74 29246.51 25916.95 47099.53 132954.7
% Share 23% 22% 19% 35% 100%
Average
Amount
Disbursed / 45 38 29 41 38
Amount (₹
in
Thousands)
CHART N0. 5.4
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
All Banks - Disbursement region wise ( Amt in ₹ Cr)
9415.84
South16765.84
20917.85
4224.92
East7200.78 Shishu
14491.25 Kishor Tarun
7171.12
West7494.02
14581.37
9041.88
North 9612.64
12037.22
0 5000 10000 15000 20000 25000
The data indicate that the MFI has contributed substantially to the number of accounts
financed under the Yojana. However, due to the smaller amount disbursed by them, it has
steeply brought down the per capita average loan under the programme, with an average
of `38000/ account, as against `79000/account in case of Bank Accounts.
But MFIs have contributed substantially in the financing of Shishu category loans.
3. Individual Bank wise performance in terms of disbursement of loan:
The State Bank of India with 12281.18 crore stands out among all the banks in lending
under PMMY. It is followed by Canara Bank with ` 7506.64 crore and Punjab National
Bank with ` 3593.42 crore.
Among the Private Sector Banks, HDFC Bank with ` 5356.89 crore tops the list, followed by
` 3921.51 crore by ICICI Bank, ` 3594.64 crore by Indus Ind Bank, and ` 2229.17 crore by
Axis Bank.
As regards RRBs, Uttar Bihar Gramin Bank with ` 1350.90 crore had the highest lending
under PMMY, followed by Karnataka Vikas Gramin Bank at ` 1070.05 crore and ` 1051.88
crore by Pragathi Krishna Gramin Bank at 1051.88 crore.
4. Financing for New entrepreneurs
MUDRA loan is meant for ‘funding the unfunded’. It is available for both new units and
expansion of existing units. The data of new entrepreneurs supported under PMMY,
indicate that out of 3.49 crore accounts financed during the year, 1.25 crore accounts were
for new entrepreneurs, which work out to 36%.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
TABLE NO. 5.5
New Entrepreneurs
Bank Type
No. of A/c Disbursement
Amt in ₹ Cr
Public Sector Bank 3822226 35463.13
Private Sector Bank and Foreign Bank 17774000 8000.88
Regional Rural Bank 720430 5088.39
NBFC – MFI 6049094 10213.16
Non NBFC – MFI 105518 142.52
Total 12474668 58908.08
CHART NO. 5.5
New Entrepreneurs - No. of A/c
105518 3822226
6049094
Public sector Bank
Private Sector Bank and Foreign
720430 Bank
Regional Rural Bank
NBFC – MFI
Non NBFC – MFI
17774000
CHART NO. 5.6
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
New Entrepreneurs - Disbursement Amt in ₹ Cr
142.52
10213.16
Public Sector Bank
Private Sector Bank and Foreign
5088.39 Bank
Regional Rural Bank
NBFC – MFI
Non NBFC – MFI
35463.13
8000.88
After the DFS gave permission to allow the classification of existing loans below INR 1
million as MUDRA, the total MUDRA loan portfolio (both in amount and in numbers ) as
reported by banks and NBFC-MFIs has three loan categories.
a) Refinanced Loans:
MUDRA loans extended by banks and NBFC-MFIs (up to INR 1 million ) to new
borrowers with the loans they received from MUDRA refinancing agency.
b) New MUDRA Loans:
MUDRA loans extended by banks and NBFC-MFIs over and above their refinancing
limit (with their own funds) to new “first-time borrowers” who were so far excluded from a
formal financial system.
c) Classification of the existing loans as MUDRA:
Classification of the already existing loan (up to INR 1 million) disbursed before 8
April 2015 (the date of MUDRA launch ) or renewal o existing loan (up to INR 1million ) on
and after 8 April 2015 as a MUDRA loan.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
RCNlawsnMifUecDdRloAans
Total MUDRA Loan
(INR 1329.5 billion; 100%)
NwMClUasDRifAedoacnsl
ans
Currently, banks and NBFC-MFIs report at an aggregate level without specific details on
number and amount of: a) the refinance loans; b) the new MUDRA loans and c) the
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
existing loans classified as MUDRA. For example, State Bank of India (SBI) annual report
(2015-17) highlights that SBI has distributed a total of INR 122.8 billion in MUDRA loans
to approximately one million borrower in FY 15-17.
Similarly, the NBFC-MFIs reported lending to as many as 23.79 million MUDRA customers
in FY 15-16 ( MUDRA performance report for the financial year 15-17) within just 11
months MUDRA started from 8th April 2015.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
5. Financing of Women
Providing financial support to women entrepreneurs was one of the main objectives of
PMMY. The data indicate that 2.76 crore women were funded out of the total number of
3.48 crore accounts, which is a whopping79%. MFIs contributed significantly for the
financing women under PMMY.
TABLE NO. 5.6
Women Entrepreneurs
Bank Type
No. of A/c Disbursement
Amt in ₹ Cr
Public Sector Bank 1475907 10352.09
Private Sector Bank and Foreign Bank 2153790 6450.74
Regional Rural Bank 292127 2462.19
NBFC – MFI 22962461 42047.05
Non NBFC – MFI 743980 1878.36
Total 27628265 63190.43
CHART NO. 5.7
Women Entrepreneurs - N0. of A/c
7439810475907
2153790
292127
Public Sector Bank
Private Sector Bank and
Foreign Bank
Regional Rural Bank
NBFC – MFI
Non NBFC – MFI
22962461
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
CHART NO. 5.8
Women Entrepreneurs - Disbursement in ₹ Cr
1878.36
10352.09
Public Sector Bank
Private Sector Bank and
6450.74 Foreign Bank
Regional Rural Bank
NBFC – MFI
Non NBFC – MFI
2462.19
42047.05
6. Loans to Minority
The loans provided by Banks and MFIs under PMMY for minorities indicate that 40.88
lakh accounts were of minorities, which is nearly 12%.
TABLE NO. 5.7
Minority
Bank Type
No. of A/c Disbursement
Amt in ₹ Cr
Public Sector Bank 498634 5313.69
Private Sector Bank and Foreign Bank 448106 2122.73
Regional Rural Bank 147011 1424.18
NBFC – MFI 2920382 4580.73
Non NBFC – MFI 74077 118.97
Total 4088210 13560.30
CHART NO. 5.9
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16732363
Minority - No. of A/c
74077
498634
Public Sector Bank
448106 Private Sector Bank and
Foreign Bank
147011 Regional Rural Bank
NBFC – MFI
Non NBFC – MFI
2920382
CHART NO. 5.10
Minority - Disbursement Amt in ₹ Cr.
118.97
4580.73 Public Sector Bank
5313.69 Private Sector Bank and
Foreign Bank
Regional Rural Bank
NBFC – MFI
Non NBFC – MFI
1424.18
2122.73
7. OD against PMJDY account
Among the loaners availing of financial assistance under PMMY included 24.17 lakh O/D
facilities against their PMJDY accounts. The amount disbursed under this arrangement
was to the tune of ` 274.02 crore, the average per account works out to be ` ₹ 1134.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
TABLE NO.
PMMY - PMJDY OD Accounts
PMJDY OD Account
Bank Type
Public Sector Bank 227.62
Private Sector Bank and Foreign Bank 0.1
Regional Rural Bank 46.3
Total 274.02
CHART NO. 5.11
PMJDY OD Account
46.3
0.1
Public Sector Bank
Private Sector Bank and
Foreign Bank
Regional Rural Bank
227.62
8. Disbursement through MUDRA card
MUDRA Card is an innovative product introduced during the year to take care of the
frequent and flexible credit needs of small borrowers. The card is issued as a Debit card on
RuPay platform and can be used for drawl of funds and also repayment as and when there
is surplus, so that the loan amount can be managed judiciously. The card was introduced
during the year which was adopted by most of the PSBs, RRBs and a few Private Sector
Banks too. The total number of card issued during the year was at 5.17 lakh for an amount
of ` 1476.96 cr. An amount of ` 1391.25 crore was withdrawn by the borrowers. The
average amount of MUDRA card works out to ` 28567 per card.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
TABLE NO. 5.9
MUDRA Card
Bank Type MUDRA Cards
Public Sector Bank 1290.07
Private Sector Bank and Foreign Bank 0
Regional Rural Bank 101.18
Total 1391.25
CHART NO. 5.12
MUDRA Card
101.18
Public Sector Bank
Private Sector Bank and
Foreign Bank
Regional Rural Bank
1290.07
9. Share of SC/ST/OBC
The NSSO survey of 2013 indicated that more than 60% of the micro enterprise units
belonged to weaker sections. The data obtained under PMMY shows that 1.84 crore
accounts financed by all the agencies under PMMY was for SC/ST/OBC categories, which is
nearly 53% of the accounts financed.
TABLE NO. 5.10
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
PMMY – Category wise
SC ST OBC
Bank type
No. of Disburse No. of Disburse No. of Disburse
account ment accounts ment account ment Amt.
s Amt. in Amt. in ₹ s in ₹ Cr
₹ Cr
Cr
Public Sector 360306 3028.38 159962 1364.22 901691 7238.35
Bank
Private
Sector Bank 584695 1672.37 165103 438.99 1106900 3759.34
and Foreign
Bank
Regional 171655 1227.81 87300 664.73 87300 3285.69
Rural Bank
NBFC - MFI 4892200 8606.31 1241112 2239.07 8006075 15271.67
Non NBFC - 105881 156.92 24869 35.02 131225 207.46
MFI
611473 14691.79 1678346 4742.03 106084 29762.52
Total 7 16
CHART NO. 5.13
PMMY - Categoory wise No. of Ac
0
0
0
0
0
131225
8006075
OBC No. of Ac 87300
1106900
901691
24869
1241112
ST No .of Ac 87300
165103
159962
105881
4892200
SC No. of Ac 171655
3 584695
60306
01000000 2000000 3000000 4000000 5000000 6000000 7000000 8000000 9000000
Public Sector BankPrivate Sector Bank and Foreign Bank Regional Rural BankNBFC - MFI
Non NBFC - MFI
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
CHART NO. 5.14
PMMY - Category wise Disbursement in ₹ Cr
0
0
0
0
0
207.46 15271.67
OBC Disbursement in Rs. Cr 3285.69
3759.34 7238.35
35.02
2239.07
ST Disbursement in Rs. Cr 664.73
438.99
1364.22
156.92
8606.31
SC Disbursement in Rs. Cr 1227.81
1672.37
3028.38
0 200040006000800010000 12000 14000 16000 18000
Public Sector BankPrivate Sector Bank and Foreign Bank
Regional Rural BankNBFC - MFI Non NBFC - MFI
TABLE NO. 5.11
CATEGORIES OF MUDRA LOANS AND BENEFICIARIES 2015 – 16
Category No. of Accounts Amount Disbursed
(₹ crore )
Shishu 324.02 62,028
Kishore 20.69 41,073
Tarun 4.10 29,854
Total 348.81 1,32,955
Out of the above
New entrepreneurs 124.75 58,908
(36%)
Women entrepreneurs 276.28 63,190
(79%)
Share of SC/ST/OBC 184.00 49,196.33
(53%)
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
CHAPTER NO.6
SUMMARY
OF
FINDINGS
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
CHAPTER NO.6
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
• Both banks and NBFC – MFIs have built huge MUDRA loan portfolio, but only a
small part of these loans appear to be “new MUDRA loans”, extended to “first-time
borrowers”, i.e., financially excluded. In absence of clear reporting by both banks
and NBFC – MFIs on the number and amount of MUDRA loans extended to
financially excluded borrowers, it will be difficult to truck the progress of MUDRA’s
mission to “fund the unfunded”.
• MUDRA has made positive impact on bottom-line of micro, small and medium
enterprises (MSMEs). However, the loan amount sanctioned is not always aligned
to the business requirements of the MSMEs financed.
• PMMY has “delivered successfully” on key product features envisaged. However, low
programme awareness and monitoring makes customers prone to fraud and
malpractices.
• Banks perform better than NBFC-MFIs on customer targeting, product and process
features.
• Banks perceive MUDRA loans as high risk and low value, requiring extremely high
involvement from staff. Therefore, banks have been extremely conservative in
extending MUDRA loans. Banks pre-select customers, avoid marketing the scheme,
and seek to fund only businesses located very close to their branches to mitigate the
risk of non-performing assets.
• MUDRA loans provide an excellent, but, as yet, unrealized business proposition for
banks. In absence of a suitable incentive structure to extend MUDRA loans, banks
refrain from opening their doors to all potential MUDRA customers.
• A series of policy changes could better motivate banks to promote MUDRA loans.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
CHAPTER
NO.7
SUGGESTION
S
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
CHAPTER NO.7
SUGGESTIONS
• Scheme can be extended to personal sector other than farms and factories. They
can start a loan funding of less than Rs. 50,000 so that the gap of 0-50k can be
fulfilled.
• There should be more concentration on the minority sector.
• MUDRA card can be used more intensively in the future.
• Women entrepreneurs should be more encouraged to wipe out the difficulties faced
by them.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
CHAPTER
NO.8
CONCLUSION
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
CHAPTER NO.8
CONCLUSION
The small businesses form the foundation of the economic development needs to be
strengthened and supported. A large number of schemes have been taken in the past few years
are a step in the right direction. MUDRA Yojana is the most recent scheme to boost up the small
and micro business units in India. This scheme has been taken to focus exclusively on
entrepreneurs. This type of scheme will add to the well – being of the individuals engaged in small
scale industries which will positively shape the progress of the economy as a whole. MUDRA as a
financial tool is found very effective in its early stages across the country. MUDRA creates a vision
of formalizing the informal and thereby funding the unfunded. Its role as an apex refinancer,
providing low-cost finance is likely to be its USP, thereby hoping to fill a yawning gap in India’s
microfinance space. These measures will greatly increase the confidence of our young educated
and skilled workers who are able to become the first generation enterprises, and existing small
businesses will be able to expand their activities. Just as banking the unbanked, MUDRA banks
main aim is funding the unfunded. This will definitely make a dramatic change and will help in
making a developed India.
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
BIBLIOGRAPHY
• Benefits of Mudra Bank – How to Take Loan from Mudra Bank. ( n. d. ).
Retrieved December 14, 2015.
• Annual Report of PMMY 2015 – 16
• International Journal of Research in Economics and Social Sciences, 5(7), 185 –
191. Mudra Offerings, State Wise PMMY Report. (n.d.). Retrieved December 20,
2015.
• “MUDRA: Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency” , International Journal
in Commerce, IT & Social Sciences, Vol.2, Issue 10, pp. 23-27
Website:
• http://www.mudra.org.in/PMMY Report
• http://www.mudra.org.in/AboutUs/Genesis
• http://www.mudra.org.in/Offerings
Downloaded by Aarti Divya (aartidivya110297@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Stage Gate ScorecardDocument5 pagesStage Gate ScorecarddayalumeNo ratings yet
- McDonalds HistoryDocument14 pagesMcDonalds Historytalha riaz100% (1)
- Model Company ProfileDocument15 pagesModel Company ProfileadeelNo ratings yet
- Interim Report 21BSP3460 - Pooja SureshDocument19 pagesInterim Report 21BSP3460 - Pooja SureshChahat PartapNo ratings yet
- CalPERS Board Meeting Agendas 2006 Through 2010Document1,001 pagesCalPERS Board Meeting Agendas 2006 Through 2010mflaherman6436No ratings yet
- Assignment of PMJY, PMMY and PMBSYDocument47 pagesAssignment of PMJY, PMMY and PMBSYPrakash Kumar HindujaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Customer Satisfaction at Oriental BankDocument62 pagesProject Report On Customer Satisfaction at Oriental BankYashraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Punjab National BankDocument44 pagesPunjab National BankRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Profitability of Life Insurance Companies in India - An Analytical StudyDocument15 pagesProfitability of Life Insurance Companies in India - An Analytical StudySatellite CafeNo ratings yet
- "Mudra Scheme-A Mission For Banking The Un-Banked": CFA A. Jajoo, Assistant Professor - Jagran Institute of ManagementDocument7 pages"Mudra Scheme-A Mission For Banking The Un-Banked": CFA A. Jajoo, Assistant Professor - Jagran Institute of ManagementAnu JajooNo ratings yet
- Npa ProjectDocument67 pagesNpa ProjectYemmiganur townNo ratings yet
- Micro FinanceDocument30 pagesMicro FinanceSakshi BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Loans and Advances of Commercial BanksDocument22 pagesComparative Study of Loans and Advances of Commercial BanksNoaman AkbarNo ratings yet
- Organisational Setup and Management of The State Bank of IndiaDocument6 pagesOrganisational Setup and Management of The State Bank of IndiapandisivaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Management of Assets and Liabilities in Relation To Performance and Profitability in ICICI BankDocument116 pagesA Study of Management of Assets and Liabilities in Relation To Performance and Profitability in ICICI BankdadismyheroNo ratings yet
- Study On The Performance of Retail Loans of Federal Bank LTD For The Last Five Years-NissarDocument66 pagesStudy On The Performance of Retail Loans of Federal Bank LTD For The Last Five Years-NissarNissar Ahammed100% (1)
- Microfinance and Its ImpactDocument117 pagesMicrofinance and Its ImpactkrishnanNo ratings yet
- Non-Performing Assets - Dissertation - Final ReportDocument51 pagesNon-Performing Assets - Dissertation - Final ReportShubham SakhujaNo ratings yet
- Economics Board ProjectDocument24 pagesEconomics Board ProjecttashaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis PNBDocument32 pagesFinancial Analysis PNBTarandeepNo ratings yet
- Dena BankDocument25 pagesDena BankJaved ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Project in HDFC BankDocument88 pagesProject in HDFC BanksiddharthNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Bank of BarodaDocument5 pagesComparative Analysis of Bank of BarodaArpita ChristianNo ratings yet
- Project Report Bank of BarodaDocument40 pagesProject Report Bank of BarodaAbhijeet JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Financial Inclusion in India - Role of RBIDocument6 pagesFinancial Inclusion in India - Role of RBIPeehu GulatiNo ratings yet
- Kotak Mahindra Bank 121121123739 Phpapp02Document112 pagesKotak Mahindra Bank 121121123739 Phpapp02RahulSinghNo ratings yet
- PNB Bank ProjectDocument20 pagesPNB Bank ProjectUlhasNo ratings yet
- "The Jalgaon Janata Sahakari Bank LTD, Savda": " Study of Retail Banking"Document73 pages"The Jalgaon Janata Sahakari Bank LTD, Savda": " Study of Retail Banking"Ujwal MahajanNo ratings yet
- Anmol Setia Project On New Scheme Launch by Present Govement Like Jhan Dhan and Bima Yojana - Undertaken in Oriental Bank of Commerce .Document87 pagesAnmol Setia Project On New Scheme Launch by Present Govement Like Jhan Dhan and Bima Yojana - Undertaken in Oriental Bank of Commerce .ANMOLNo ratings yet
- Detail Study of HDFC Mutual FundDocument83 pagesDetail Study of HDFC Mutual FundRaushan KushwahaNo ratings yet
- NPA of Jammu and Kashmir BankDocument22 pagesNPA of Jammu and Kashmir BankE-sabat RizviNo ratings yet
- Project Report OnDocument91 pagesProject Report OnSurajNo ratings yet
- Fmbo Question Bank and McqsDocument19 pagesFmbo Question Bank and McqspraveenNo ratings yet
- 7 Sbi, ProjectDocument54 pages7 Sbi, ProjecturjanagarNo ratings yet
- Project Report-I On Human Resource Management in UCO Bank: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument57 pagesProject Report-I On Human Resource Management in UCO Bank: Submitted To: Submitted byshubham.sinha0078No ratings yet
- Project Report On "Credit Risk Management in State Bank of India"Document65 pagesProject Report On "Credit Risk Management in State Bank of India"Sandeep YadavNo ratings yet
- Rashid Solanki Roll No. 294 Bandhan Bank Final Year ProjectDocument60 pagesRashid Solanki Roll No. 294 Bandhan Bank Final Year Projectsarah IsharatNo ratings yet
- Co Operative BankDocument49 pagesCo Operative BankJASPREETNo ratings yet
- "Financial Statement Analysis of Bank of Maharashtra": A Project Report OnDocument65 pages"Financial Statement Analysis of Bank of Maharashtra": A Project Report OnShashi RanjanNo ratings yet
- The Scope of Microfinance in The Indian Context-A StudyDocument47 pagesThe Scope of Microfinance in The Indian Context-A StudySunny Prasad ShawNo ratings yet
- Introduction of IDBI BankDocument4 pagesIntroduction of IDBI Bankomy123100% (2)
- Final ProjectDocument55 pagesFinal Projectpurva maratheNo ratings yet
- PREET 2nd Project FinalDocument73 pagesPREET 2nd Project Final308 Kiranjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Bandhan Bank Mini Project by NitishDocument90 pagesBandhan Bank Mini Project by NitishNITISH CHANDRA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- SHG Group Project Report PDF PDF Microfinance MicrocreditDocument1 pageSHG Group Project Report PDF PDF Microfinance MicrocreditGurleen Kaur BrarNo ratings yet
- Bank of Baroda Training and Development (Repaired)Document7 pagesBank of Baroda Training and Development (Repaired)SHANKAR PRINTINGNo ratings yet
- Study of Personal Loan and Analysis of People Perception On HDFC & Sbi BankDocument7 pagesStudy of Personal Loan and Analysis of People Perception On HDFC & Sbi BankJoshua GeddamNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON: "A Study of Comparative Analyis of Kotak Mahindra Bank With Its Competitor'S"Document63 pagesProject Report ON: "A Study of Comparative Analyis of Kotak Mahindra Bank With Its Competitor'S"Nitesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Project Report On NEXADocument47 pagesProject Report On NEXASoumen SahuNo ratings yet
- Emerging Issues in Indian Banking SectorDocument31 pagesEmerging Issues in Indian Banking SectorShradha JindalNo ratings yet
- Bandhan Case Study: Prepared By: Bakshi Satpreet Singh (10MBI1005)Document17 pagesBandhan Case Study: Prepared By: Bakshi Satpreet Singh (10MBI1005)Sachit MalikNo ratings yet
- A Study On Role and Effects of Microfinance Banks in Rural Areas in India 1Document63 pagesA Study On Role and Effects of Microfinance Banks in Rural Areas in India 1Rohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Retail Banking of Allahabad BankDocument50 pagesRetail Banking of Allahabad Bankaru161112No ratings yet
- Impact of Npa On Profitability:Empirical Study of Private Sector Banks in IndiaDocument63 pagesImpact of Npa On Profitability:Empirical Study of Private Sector Banks in IndiaTarun MirgNo ratings yet
- Dhaval File 123Document72 pagesDhaval File 123Rahul NishadNo ratings yet
- Profitability Ratio Fieldwork Report Preparation For Bank.Document27 pagesProfitability Ratio Fieldwork Report Preparation For Bank.Arpan GhimireNo ratings yet
- Sravanya MTDocument60 pagesSravanya MTPUTTU GURU PRASAD SENGUNTHA MUDALIAR100% (8)
- Black Book D 60 Mansi Upadhyay-4Document83 pagesBlack Book D 60 Mansi Upadhyay-4Mansi UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Between Private Sectors Bank and Public Sector BanksDocument36 pagesComparative Study Between Private Sectors Bank and Public Sector BanksjudeNo ratings yet
- Black Book Project 3Document69 pagesBlack Book Project 3Pragya SinghNo ratings yet
- My PRJCTDocument85 pagesMy PRJCTpawan_aujlaNo ratings yet
- Shruti Project Panjab National BankDocument71 pagesShruti Project Panjab National BankShobhit Goswami100% (2)
- An Analytical Study On Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana: Summer Project Report ONDocument45 pagesAn Analytical Study On Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana: Summer Project Report ONRavi Joshi100% (1)
- Projectfinancialinclusion 161005151647 PDFDocument43 pagesProjectfinancialinclusion 161005151647 PDFAkash BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Zero Base BudgetingDocument3 pagesZero Base BudgetingAarti DivyaNo ratings yet
- Aarti Divya MBA-AB Minor Project QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesAarti Divya MBA-AB Minor Project QuestionnaireAarti DivyaNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument3 pagesDisaster ManagementAarti DivyaNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument8 pagesMarketing ManagementAarti DivyaNo ratings yet
- Season in Retail From SAPDocument12 pagesSeason in Retail From SAPKarunGaurNo ratings yet
- Weekly PlusDocument12 pagesWeekly PlusRandora LkNo ratings yet
- Extended Withholding Tax Configuration - SAP FIDocument18 pagesExtended Withholding Tax Configuration - SAP FInaysarNo ratings yet
- Profood International CorporationDocument26 pagesProfood International CorporationYew MercadoNo ratings yet
- Carta de PasantiaDocument2 pagesCarta de PasantiaGertrudis PiñaNo ratings yet
- ISEC-655 Security Governance Management Assignment 1 GuidelinesDocument2 pagesISEC-655 Security Governance Management Assignment 1 GuidelinesAyushi JainNo ratings yet
- Chanos WSJ Article 1985Document12 pagesChanos WSJ Article 1985Franklin ForwardNo ratings yet
- Ethics Between Theory and Practice Social Responsibility in The Romanian Business EnvironmentDocument11 pagesEthics Between Theory and Practice Social Responsibility in The Romanian Business EnvironmentViorica MituNo ratings yet
- Google AdsDocument9 pagesGoogle AdsMADHUR SAPRANo ratings yet
- The Impact of Training and Development On Organizational PerformanceDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Training and Development On Organizational PerformanceMuhammad Asad88% (24)
- Ingles Infografia - EE - FF - Samuel ToctoDocument2 pagesIngles Infografia - EE - FF - Samuel Toctosamuel denilson tocto peñaNo ratings yet
- Ivey MSC Western UniversityDocument16 pagesIvey MSC Western UniversityDyanChenNo ratings yet
- Disruption in The Automotive Industry: How Digital Is Changing Car SalesDocument24 pagesDisruption in The Automotive Industry: How Digital Is Changing Car SalesEduardo D'CastroNo ratings yet
- (ACCCOB2 K36) Chapter 2 ExercisesDocument9 pages(ACCCOB2 K36) Chapter 2 ExercisessophiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. New Perspective On Marketing in The Service EconomyDocument14 pagesChapter 1. New Perspective On Marketing in The Service EconomyEdles Kyla NicoleNo ratings yet
- 4-CONSUMER CREDIT (Introduction To Consumer Credit)Document31 pages4-CONSUMER CREDIT (Introduction To Consumer Credit)Farahliza RosediNo ratings yet
- SonyDocument1 pageSonyamran mohammedNo ratings yet
- UNOPS - Esourcing - Vendor Guide - v1.7 - EN GDocument46 pagesUNOPS - Esourcing - Vendor Guide - v1.7 - EN GDawitNo ratings yet
- Brochure 59th Campus Feb-Mar 2024Document8 pagesBrochure 59th Campus Feb-Mar 2024abhishekkumarlear7974775179nNo ratings yet
- Managing A Professional Services FirmDocument37 pagesManaging A Professional Services FirmSaurabh MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Retailing Wholesaling: Chapter PreviewDocument34 pagesRetailing Wholesaling: Chapter PreviewMikaelaNo ratings yet
- ECMDocument14 pagesECMSuryanarayana TataNo ratings yet
- B2B Exchange (Business To Business)Document2 pagesB2B Exchange (Business To Business)ayu3117No ratings yet
- PHYSICAL EVIDENCE and SERVICESCAPESDocument17 pagesPHYSICAL EVIDENCE and SERVICESCAPESPreet Kaur0% (1)
- SAP SD Functional Consultant Resume - Hire IT People - We Get IT DoneDocument9 pagesSAP SD Functional Consultant Resume - Hire IT People - We Get IT DonenavanNo ratings yet
- Payroll Management System Project DocumentationDocument2 pagesPayroll Management System Project DocumentationBhagyashri MendheNo ratings yet