Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digestive Reviewer
Digestive Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jay Ivan Milen Gamboa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThe document summarizes the human digestive system, including the organs and structures involved in digestion and their functions. It describes the pathway of digestion from the mouth through the esophagus, stomach, small intestine including the duodenum, jejunum and ileum, large intestine, and rectum. It provides details on teeth, saliva, gastric juices, enzymes, and accessory organs such as the liver, gallbladder and pancreas that aid in the breakdown and absorption of food.
Original Description:
Original Title
Digestive-reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the human digestive system, including the organs and structures involved in digestion and their functions. It describes the pathway of digestion from the mouth through the esophagus, stomach, small intestine including the duodenum, jejunum and ileum, large intestine, and rectum. It provides details on teeth, saliva, gastric juices, enzymes, and accessory organs such as the liver, gallbladder and pancreas that aid in the breakdown and absorption of food.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageDigestive Reviewer
Digestive Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jay Ivan Milen GamboaThe document summarizes the human digestive system, including the organs and structures involved in digestion and their functions. It describes the pathway of digestion from the mouth through the esophagus, stomach, small intestine including the duodenum, jejunum and ileum, large intestine, and rectum. It provides details on teeth, saliva, gastric juices, enzymes, and accessory organs such as the liver, gallbladder and pancreas that aid in the breakdown and absorption of food.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
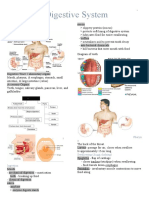
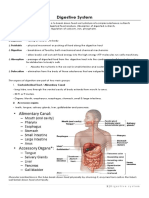
Mastication - grinding of food into Pathway: SMALL INTESTINE - 6m long
smaller pieces Oral Cavity Duodenum -first & shortest segment
Bolus - mixture of food and saliva Lips (25cm)
Chyme - semifluid of digested food & Cheeks Jejunum - between the duo and ileum
digestive secretions Vestibule (2.5 m)
Peristalsis - begins in the esophagus Ileum - final section (3.5 cm)
when a bolus of food is swallowed Tongue Villi - finger-like foldings
Stomach - bean-shaped; storage; 4 TYPES OF PAPILLAE
primary digestion Fungiform - sweet & sour, TIP ENZYMES
Large intestine - vital task to absorb Filiform - covers most of DORSAL Peptidases - breaks pepsin
water and nutrients; converts surface Carbohydrases - break down
digested food to feces Vallate - BACK of palatine, v shape Maltase- maltose->glucose
Bile - produced by the liver, aids formation towards throat Lactose- galactose->glucose
digestion of lipids in small intestine Foliate - SIDE Sucrase- fructose->glucose
Gall bladder- hollow organ where bile Lipases - breaks lipids
is stored before it is released into the TEETH Nucleases - breaks nucleic acid -
small intestine (temporary) Deciduous - milk teeth, shed after >nucleotides
Permanent - pushes milk teeth
Methods of nutrition: Incisors - front teeth (first 1, humans LIVER
Autotrophs - produce own food have 8) -neutralizes chyme acidity
Heterotrophs - dependent Canines - cuspids (fangs, 2) (3rd) -aids in fat absorption
Carnivore,Herbivore,Omnivore* Premolar - crushing & tearing food (8, -emulsifes fats and hastens digestive
Coprophagy - feeds on feces 6th) action of enzymes
*unable to absorb nutrients (dogs, Molar - grinding, chewing (wisdom -stimulate peristalsis, where a great
pigs, rabbits, beavers) tooth) percentage of glycogen is stored
Ruminants - from plant-based food -center of fat & carbohydrate
by fermenting it in specialized STRUCTURES metabolism
stomach prior to digestion (cattle, External:
sheep, goat, moose, giraffe, buffalo) Crown *Gall bladder
Sanguivore - consumes blood Cusps *Bile
(mosquito,bat,leech) Root *Cholecystokinin - stimulates release
Frugivore - fruit eater (male Neck of bile into the intestine & secretion
mosquito, passerine birds) of enzymes by the pancreas
Filter feeders - straining suspended Internal:
matters, feed on planktons Pulp cavity PANCREAS
Vermivores - feed on worms Dentin Exocrine - with pancreatic ducts
Scavenger - consumes corpses Enamel - typsin, chrymotipsin,
Decomposers - consume Cementum carboxypeptidase
dead/decaying organism, bacteria Alveoli - sockets
Gingiva/gums Pancreatic amylase
Human Digestion; IDAAE Periodontal ligament Panceatic lipase
Ingestion -take in food Periodontal disease Pancreatic bicarbonate
Digestion - breakdown food Secretin - stimulates secretion in
Absorption - absorb nutrients STOMACH pancreas
Assimilation - utilization Sphincters - cardiac and phyloric
Egestion/Elimination - eliminate Endocrine - islets of langerhans
4 REGIONS (CFBP) *produces and controls INSULIN and
Under Ingestion: Cardiac - mucous secreting glands; GLUCAGON
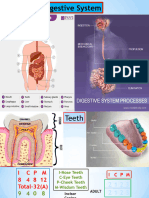
Mouth - mechanical digestion closest in espohagus Insulin - (absorption of) sugar
*Teeth - breaking up food Fundus - largest art; contain gastric Glucagon - raises blood glucose
glands
Mouth - chemical digestion Body LARGE INTESTINE - 5 feet
*Saliva - allows bolus to pass from Pylorus - secretes 2 types of mucus Cecum
mouth to espohagus easily and hormone gastrin Appendix
Amylase - digests starch Colon
Mucin - slippery protein, protects soft COMPOSITION OF GASTRIC JUICE Descending and Sigmoid crypts
lining of DS, lubricates food for easy Chief cells Rectum
swallowing Pepsinogen - converted pepsin by GA Anal Canal
Buffers - neutralizes acid to prevent Rennin - curdles milk
tooth decay
Anti-bacterial chemicals - kill bacteria Parietal cells - pyramidal cells; source
Stomach - produces mucosa that of GA
helps in breaking down food Goblet cells - produces mucus
Gastrin - secreted in pylorus;
Accesory organs: secretion of parietal cells
Tongue - membrane skeleton
Teeth Hunger pangs - contraction of empty
Salivary glands: stomach
Parotid - near the ears Borborygmus - stomach rumbling
Sublingual - under the tongue
Submandibular - under mandible
You might also like
- DIGESTIVE SYSTEM of VERTEBRATE-COMPARATIVE ANATOMYDocument58 pagesDIGESTIVE SYSTEM of VERTEBRATE-COMPARATIVE ANATOMYpratiwi kusuma64% (11)
- Role of BisoprololDocument43 pagesRole of BisoprololFidel Martua Marpaung67% (3)
- ILAMEDDocument6 pagesILAMEDPriya HariNo ratings yet
- Ucm 499295 PDFDocument58 pagesUcm 499295 PDFThea Margareth MartinezNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 6 & 7 NUTRISI TERNAK DASARDocument45 pagesPertemuan 6 & 7 NUTRISI TERNAK DASARsyintiaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: 1. Mouth 2. Pharynx (Throat)Document5 pagesDigestive System: 1. Mouth 2. Pharynx (Throat)Usita, Zackary, T.No ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument16 pagesAnaphy ReviewerBr1nfoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive Systemhimig the melodyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Pharyn XDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Pharyn XPanda 911No ratings yet
- Simple Non-Ruminants: Principles of Animal Nutrition Dr. Cristine W. MaramagDocument30 pagesSimple Non-Ruminants: Principles of Animal Nutrition Dr. Cristine W. MaramagMc Kjell Dagman RaveloNo ratings yet
- Digestive System-1Document18 pagesDigestive System-1Rishi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 Digestive Study Test GuideDocument6 pagesBio 101 Digestive Study Test Guideamorris0906No ratings yet
- Digestive System in Non-RuminantsDocument5 pagesDigestive System in Non-RuminantsTumisang TlhabanoNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument48 pagesAnimal Nutritionalkirstenlexie.galvezNo ratings yet
- Digestive TermsDocument2 pagesDigestive TermsTorio Kristine Anne P.No ratings yet
- Unit 3. Digestion and AbsorptionDocument45 pagesUnit 3. Digestion and AbsorptionDiana HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Food PathDocument7 pagesFood PathLovelle SanchezNo ratings yet
- Digestion: Hsslive - in Rajini A.P, HSST Zoology, Govt. Aphss Elappully, PalakkadDocument11 pagesDigestion: Hsslive - in Rajini A.P, HSST Zoology, Govt. Aphss Elappully, PalakkadShan RomioNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- S4 Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesS4 Digestive Systemcam broquelNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDigestive SystemCXT EnterpriseNo ratings yet
- General Biology: 1. Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology: 1. Digestive SystemJuno Merdien GarciaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ Sheet of PaperDocument33 pagesQUIZ Sheet of PaperGab FgilzcheNo ratings yet
- Ana DigesDocument2 pagesAna DigesSTEM-G.04 Kiarrah Katrina BotinNo ratings yet
- Digestive System FINALDocument43 pagesDigestive System FINALSean Lorenzo TumacderNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Ncm-216)Document10 pagesMetabolism (Ncm-216)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- GastrointestinalDocument39 pagesGastrointestinalالمسوول الاعلاميNo ratings yet
- Digestive System For Ycb Net Yoga and Other Science StudentDocument18 pagesDigestive System For Ycb Net Yoga and Other Science StudentSaudamini SinhaNo ratings yet
- 9 Enzymes and DigestionDocument6 pages9 Enzymes and DigestionSheniqua GreavesNo ratings yet
- Digestion Rev Horses ProteinDocument8 pagesDigestion Rev Horses ProteinKyle Gwyneth BobierNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument49 pagesExamJunaisah P. PangaponNo ratings yet
- 1.study of Physiological Functions of Digestive System of Farm AnimalsDocument58 pages1.study of Physiological Functions of Digestive System of Farm AnimalsKashifNo ratings yet
- Digestion Unit NotesDocument8 pagesDigestion Unit NotesBen SmithNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Digestive Systemheyraheyra70No ratings yet
- Digestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Document3 pagesDigestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Kaikiyi Sykay PachecoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in HumansDocument4 pagesNutrition in Humanselise limNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument49 pagesDigestive SystemDaniel WakaWakaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy FinalsDocument20 pagesAnaphy FinalsHazel Anne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesHuman Digestive SystemLeafrast GamingNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument4 pagesDigestionMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ReviewerDocument2 pagesDigestive System ReviewerDivino BauzonNo ratings yet
- Animal Digestion: AGR Vet ScienceDocument38 pagesAnimal Digestion: AGR Vet ScienceRauven Jean Erodias FadriquelaNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 1: Vonny Verania Khuangga 405130005Document101 pagesPemicu 1: Vonny Verania Khuangga 405130005Vonny Verania KhuanggaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Notes On Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesIGCSE Biology Notes On Digestive SystemTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Digestive System 2021Document51 pagesTopic 5 - Digestive System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Animal Digestive SystemsDocument70 pagesAnimal Digestive SystemsAnnaGuese100% (1)
- System, Consists of A Digestive Tube Called GI Tract or Alimentary Canal and Several Accessory Organs (LiverDocument5 pagesSystem, Consists of A Digestive Tube Called GI Tract or Alimentary Canal and Several Accessory Organs (LiverJm AshiiNo ratings yet
- Can Hold 4l of Food (Maximum)Document4 pagesCan Hold 4l of Food (Maximum)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- Group6 DiDocument9 pagesGroup6 DiAngel Ann Gertos Inojales INo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Water We Take Plays Important Role inDocument12 pagesDigestive System: Water We Take Plays Important Role inMouli ChandraNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Presented By: Areeba Aqil 15-B.ED-14 B.Ed Iv Semester GC-9755Document15 pagesDigestive System: Presented By: Areeba Aqil 15-B.ED-14 B.Ed Iv Semester GC-9755Uzma SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Digestion 3 322Document87 pagesDigestion 3 322SAROL, Gwen Alessandra V.No ratings yet
- Digestion WiwiDocument23 pagesDigestion WiwiSCE1-0622 Amni Insyirah Binti Mohd NasarudinNo ratings yet
- 02 Sistem DigestiveDocument16 pages02 Sistem DigestiveAnnisaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument6 pagesDigestive System NotesZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of The Different Livestock Systems: By: Kristy BairdDocument24 pagesA Comparison of The Different Livestock Systems: By: Kristy BairdReynaldy ChristianNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemGabrielle Anne CarlosNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NewDocument26 pagesDigestive System NewJonathan Farne CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NutritionDocument20 pagesChapter 2 NutritionAzie Nurul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Endocrine SystemDocument36 pagesDigestive and Endocrine SystemAldrei Vina Pauleah BorjaNo ratings yet
- Ana DigesDocument3 pagesAna DigesFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Digestive System Post LabDocument29 pagesDigestive System Post LabMaxine MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Young Adulthood 1Document7 pagesYoung Adulthood 1Jay Ivan Milen GamboaNo ratings yet
- Early ChildhoodDocument13 pagesEarly ChildhoodJay Ivan Milen GamboaNo ratings yet
- NanotechnologyDocument2 pagesNanotechnologyJay Ivan Milen GamboaNo ratings yet
- Information AgeDocument38 pagesInformation AgeJay Ivan Milen GamboaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate ExperimentDocument16 pagesCarbohydrate ExperimentJay Ivan Milen GamboaNo ratings yet
- Theory BackgroundDocument1 pageTheory BackgroundJay Ivan Milen GamboaNo ratings yet
- ROJA RANI Abstract For PosterDocument4 pagesROJA RANI Abstract For Postersaikrishnamedico100% (1)
- Grodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of OphthalmologyDocument24 pagesGrodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of OphthalmologyTeguh Imana NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate: PresentationDocument3 pagesSodium Bicarbonate: Presentationmadimadi11100% (1)
- Edwardus T. Adar 1308012050: Consultant Dr. Stef D. Soka, SP.BDocument21 pagesEdwardus T. Adar 1308012050: Consultant Dr. Stef D. Soka, SP.BAlbert RanggaNo ratings yet
- Common Periodontal Instruments PDFDocument6 pagesCommon Periodontal Instruments PDFMuhammed Mansoor100% (1)
- Care ReportDocument23 pagesCare ReportSindi Muthiah UtamiNo ratings yet
- Isotonic NaclDocument61 pagesIsotonic NaclAlliah CasingNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Ventilador Draguer Evita 2 Dura PDFDocument6 pagesBrochure - Ventilador Draguer Evita 2 Dura PDFCarlos Andres Jaimes RicoNo ratings yet
- Sports-Related InjuriesDocument2 pagesSports-Related Injurieslil trxshNo ratings yet
- Komposisi Dan Fungsi Darah 1Document49 pagesKomposisi Dan Fungsi Darah 1Adelia MnNo ratings yet
- Lilbm3: Adita Ayu Aprilia 30101407112Document16 pagesLilbm3: Adita Ayu Aprilia 30101407112Adita AyuNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Life Stages of Women To Enhance Your PracticeDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Life Stages of Women To Enhance Your PracticeGina Magda RianaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Draft Write Up Bedes 1-1Document65 pagesThesis Draft Write Up Bedes 1-1CESAR NDJOKONo ratings yet
- Hematenics Vitamins How To ChooseDocument27 pagesHematenics Vitamins How To ChooseRohit BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Bacteria of Medical Importance - PPTX, MONDAYDocument113 pagesGram Negative Bacteria of Medical Importance - PPTX, MONDAYGeorge C. KasondaNo ratings yet
- New Simple Technique For Syndactyly Release.97398Document8 pagesNew Simple Technique For Syndactyly Release.97398dr. Joko WibowoNo ratings yet
- Facial Vascular Danger Zones For Filler Injections: Uwe Wollina - Alberto GoldmanDocument8 pagesFacial Vascular Danger Zones For Filler Injections: Uwe Wollina - Alberto GoldmanLuis Fernando WeffortNo ratings yet
- BOLILE ESOFAGUL Mia TareDocument12 pagesBOLILE ESOFAGUL Mia Tareelisabeth-ward-skipNo ratings yet
- Weight Loss Without PlateauDocument85 pagesWeight Loss Without Plateauryarok1No ratings yet
- Why Is My Dog Foaming at The Mouth WagwcxidDocument3 pagesWhy Is My Dog Foaming at The Mouth Wagwcxidchequeorange5No ratings yet
- Ocular Prosthesis Case HistoryDocument5 pagesOcular Prosthesis Case HistorydrsmritiNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Pro Kinetic Therapy-Motilin-Like DrugsDocument6 pagesGastrointestinal Pro Kinetic Therapy-Motilin-Like Drugstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Disorder KrishnaDocument16 pagesMendelian Disorder KrishnaTanmay kalraNo ratings yet
- Reproduction, Technology, and The SocietyDocument38 pagesReproduction, Technology, and The SocietyJep LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Infographic: How You Can Die Running A MarathonDocument1 pageInfographic: How You Can Die Running A MarathonedsunonlineNo ratings yet
- CPR, Aed, enDocument87 pagesCPR, Aed, enKing DonNo ratings yet
- Jelkd Jeo QWNDocument25 pagesJelkd Jeo QWNcd_armand1885No ratings yet