Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 3 M4B TT 1
Chap 3 M4B TT 1
Uploaded by
Mai Phương AnhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap 3 M4B TT 1
Chap 3 M4B TT 1
Uploaded by
Mai Phương AnhCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH FOR BUSINESS
CHAP 3: MATHEMATIC OF FINANCE
I. Percentage
!"# %&'("
• Scale factor =
)'* %&'("
è Khi đề có 2 scale khác nhau thì tính mỗi scale rồi nhân lại với nhau ra overall
scale
Ex: The price of good increase by 20% and decrease by 35%, find the percentage
change in price?
The individual scale factors are 1.2 and 0.65 so the overall scale is
1.2 × 0.65 = 0.78
Hence, the price decrease 22%
a) The scale factor is 1 + 12% = 1.12. → 𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 ∶ 16.25 × 1.12 = 18.2
b) The scale factor is 1 + 5% = 1.05 → 𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛: 113 566 × 1.05 =
119,244
c) The scale factor is 1 + 15% = 1.15→ 𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 ∶ 87.9 × 1.15 = 101.985
d) The 1st scale factor is 1 – 30% = 0.7, the 2nd scale factor is 1 + 15% = 1.15
The overall scale factor is 0.7 x 1.15 = 0.805
The new price is: 2,300 x 0.805 = 1,851.5
e) The 1st scale factor is 1 – 18% = 0.82, the 2nd scale factor is 1 – 32% = 0.68
The overall scale factor is 0.82 x 0.68 = 0.5576
The new price is: 23,000 x 0.5576 = 12,824.8
If it depreciates 50% after 2 years, the scale factor is 1 – 50% = 0.5, so it is
different.
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
J&'(" KL M"&N O
• Index number = scale factor from base year x 100=J&'(" KL P&Q" M"&N × 100
Ø Base-weighted index (or Laspeyres index): xét Q theo base year, P thay đổi theo
từng năm
Ø Current – weighted index (or Paasche index): Q và P thay đổi
• Inflation (lạm phát): the pencentage increase in the level of prices over a 12 months
period
Nominal price
Xét base year là năm 2005:
2003: Real price = 230 x 1.04 x 1.03= 246.376
2004: Real price = 242 x 1.03= 249.26
2005: Real price = 251
RST
2006: Real price = U.VRS = 250.73
UVW
2007: Real price = U.VRS × U.VR = 101.38
µ Nhân hay chia đều là scale factor
µ Base year real price = Nominal price
µ Nếu trước base thì Nominal price nhân overall scale tới base
µ Nếu sau base thì Nominal price chia overall scale tới base
• Nominal price: giá thô chưa dính inflation
• Real price: giá sau khi dính inflation
!XYKL&' %&'("
• Inflation rate=
Z"&' %&'("
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
a) Scale factor = 1 + 0.45=1.45
New price = 1.45 x 18 000 = 26 100
b) To make a loss, the new price ≤ 18 000
18 000
→ 𝑁𝑒𝑤 𝑠𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 = = 0.69
26 100
→ 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 = 1 − 0.69 = 31%
a) Base year 2010
bV
Index of 2009 : × 100 = 83.3
bc
d×UVV
Tương tự cho các năm còn lại ( bấm máy bc
rồi thế X cho nhanh)
Year 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Price ($) 40 48 44 56 60 71 68
Index 83.3 100 91.7 117.7 125 147.9 135
number
UeS ×bc
b) 2015’s price is : = 68
UVV
c) 73→ $44
100 → ? ⇒ 60.27 ⇒ 2013
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
a)
Year 2004 2005 2006 2007
Spending 236 240 267 276
Index number 100 101.7 113 116.9
b)
Year 2004 2005 2006 2007
Spending 236 240 267 276
Inflation 4.7 4.2 3.4
Real spending 236 229.2 244.7 244.7
Index number 100 97.1 103.7 103.7
c) In real term, spending on education fell by 2.9% in 2005, increased by 6.8% in
2006 and remain unchanged in 2007
II. Compound interest
Ex: Gửi tiền ngân hành 10 000 000VND, lãi suất 10% /năm
• Simple interest: Mỗi năm rút 1 khoảng tiền lãi như nhau (ex: 1 triệu tiền lãi mỗi năm)
𝑆 = 𝑃 (1 + 𝑛𝑟)
• Compound interest: lãi chồng lãi, tiền lãi đầu kì tiếp tục đưa vào vốn để sinh lãi tiếp.
Do đó, năm tới sẽ tính lãi 10% từ vốn 11 000 000
𝑆 = 𝑃(1 + 𝑟)L
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
with P: principal value( vốn ban đầu)
S: future value: amount to which an investment will grow after earning interest
r: Interest rate
n: period
è Công thức tổng quát compound:
𝑟
S = P(1 + )qL
𝑘
k = 1: annually k = 4: quarterly k = 2: semi – annually
k = 12: monthly k = 52: weekly k = 365: daily
• Continous compouding: lãi kép liên tục
S = P𝑒 NL
• Annual percentage rate (APR): dùng khi vay mượn, so sánh APR vì nó chỉ ra được số
lãi hằng năm phải trả
• Annual equivalent( effective) rate (AER): dùng khi gửi tiết kiệm, tiền lãi mỗi năm được
bao nhiêu
𝑟
𝐴𝐸𝑅/𝐴𝑃𝑅 = (1 + )q − 1
𝑘
N
𝐸𝐴𝑅 = 𝑒 − 1
𝑆 = 𝑃 (1 + 𝑟)𝑛 = 50,000(1 − 5%)3 = 42,868.75
N 𝑘𝑛 v% 1x8
a) S=P (1 +q) =7000(1+ ) =13,947.94
U
N 𝑘𝑛 v% 2x8
b) S=P (1 +q) =7000(1+ R
) =14,156.59
N 𝑘𝑛 v% 12x8
c) S=P (1 + q) =7000(1+ UR ) =14,342.45
d) S = 𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑛 = 7000𝑒9%x8 = 14,381.0
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
N
𝐴𝐸𝑅 = (1 + q)q − 1
8.05 R
𝐴 = (1 + ) − 1 = 0.0821 → 𝐴𝐸𝑅 = 8.21%
100 × 2
7.95 UR
𝐵 = (1 + ) − 1 = 0.0825 → 𝐴𝐸𝑅 = 8.25%
100 × 2
⇒ 𝐵 ℎ𝑎𝑠 𝑔𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑟𝑒𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛
a) Scale factor in the second year = 0,6 x 0,7 = 0.42
UbTVV
Price of the car when it is new = V.bR
= 35 000
b) Scale factor after second year = (0,8)x (x: years)
14 700 x (0,8)x ≤ 14 700 x 25%. ⇔ (0,8)x ≤ 0,25. ⇔ x ≥ 6.2125
Therefore, the car will worth less than 25% of amount that I paid after 7 year
N
AER= 12.6%= (1 + q)q − 1 ⇒ 𝑟U = 12.6% ⇒ 𝑆U = 𝑃(1 + 12.6%)L = (1.126)L 𝑃
𝑆R = 𝑃𝑒 UV.S%L = 𝑃𝑒 V.UVSL
UU.S% bL
𝑆e = 𝑃(1 + b
)
Assume n=2⇒ 𝑆U = 1.268𝑃; 𝑆R = 1.234𝑃; 𝑆e = 1.255𝑃
Hence, choose S2
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
µ Đầu tư, chọn PV cao hơn
µ Vay tiền, chọn PV thấp hơn
III. Geometric series:
• Geometric series : cấp số nhân (vd: 3, 9, 27, 81, 243,... – multiply 3 each time)
• Arithmetic progression: cấp số cộng (vd: 4, 6, 8, 10,... – add 2 each time)
L~U
K L~U
(1 + 𝑟)L − 1
| 𝑎(1 + 𝑟) = 𝑎 + 𝑎 (𝑎 + 𝑟) + ⋯ + 𝑎(1 + 𝑟) = 𝑎• €
𝑟
K•V
• Sinking fund: gửi tiền hằng kì
Ø If the payment is made at the beginning of each period
(1 + 𝑟)L − 1
𝑆 = 𝐴(1 + 𝑟)
𝑟
Ø If the payment is made at the end of each period
(1 + 𝑟)L − 1
𝑆=𝐴
𝑟
(U‚V.Vc)ƒ„ ~U
a) S=5000(1 + 0.08) = 78 227,4
V.Vc
b) Interest rate per time= 0.08 : 2= 0.04
1st year: S1 = 5000 x (1 + 0,04 )20 (tiền năm đầu đầu tư 20 kì)
2nd year: S2 = 5000 x (1 + 0,04)18
10th year: S10 = 5000 x (1 + 0,04)2
S = S1 + S2 +...+ S10 = ∑UV 2𝑥
U 5000(1 + 0,04) = 78 941,1
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
c) 1st year: S1 = 5000 x e0,08.10
2nd year: S2 = 5000 x e0,08.9.
10th year: S10 = 5000 x e0,08
" ‡„.„ˆ.ƒ„ ~U
S = S1 + S2 +...+ S10 = 5000𝑒 V.Vc×UV × " ‡„.„ˆ ~U
= 79 701
• Loans: Vay một khoảng L hiện tại và mỗi kì trả một khoảng A
(1 + 𝑟)L − 1
𝐿 = (1 + 𝑟)L =𝐴
𝑟
𝐿
𝐴=
1 − (1 + 𝑟)~L
𝑟
• Payout figure: PV of all remaining repayments( sô tiền còn lại sau mootj
thời gian trả nợ)
1 − (1 + 𝑟)~L
𝑃𝑉‹ = 𝐴 • €
𝑟
With n: tổng số period
ΠUVV VVV
A= ƒ‡(ƒ•Ž)‡• = ƒ‡(ƒ•ˆ%)‡•‘
= 9,367.87
Ž ˆ%
Monthly payment= A/12= 780,65
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
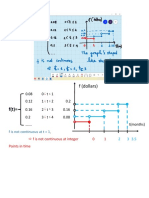
𝑆 = 5000(1.045)UV + ∑v‹•U 1000(1.045)‹ = 19 053,06
𝑆 = ∑v‹•V 5600 × 0,98‹ + ∑Ub v ‹
‹•U(5600 × 0.9) × 1.04 = 140 040,5
„.”ˆ ƒˆ
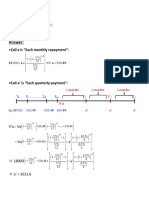
(U‚N)• ~U b.c% (U‚ ) ~U
𝑆 = 𝐴 (1 + 𝑟) N
→ 18 000 = 𝐴 ’1 + UR
“ ƒ•
„.”ˆ →𝐴=
ĥ
962.58
IV. Investment apparaisal
• Net present value(NPV): giá trị hiện tại ròng , dùng khi có Po, FV, xem
market rate là interest rate và so sánh NPV để quyết định đầu tư
𝑁𝑃𝑉 = 𝑃𝑉 − 𝑃V
𝐶U 𝐶R 𝐶L
𝑃𝑉 = + + ⋯ +
(1 + 𝑟) (1 + 𝑟)R (1 + 𝑟)L
P0 : khoảng đầu tư ban đầu
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
MATH FOR BUSINESS
• If NPV > 0: worth to invest (PV > P0)
• If NPV = 0: neutral
• If NPV < 0: not worth to invest (PV < P0)
• Internal rate of return (IRR): Tỉ suất thu nhập nội bộ => dùng khi NPV = 0, tính
interest rate và so sánh interest rate với market rate xem có nên đầu tư:
Ø If rIRR > rmarket : worth to invest
Ø If rIRR < rmarket : not worth to inves
ü Nếu đề không yêu cầu thì dùng NPV
ü Luôn mang về PV để so sánh
ü Bond, stock: xem như simple interest, cuối kì trả lại face value
• Annuity: a series of regular equal cash flows
MATH FOR BUSINESS TO NGOC THANH THANH
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Investment Science by David LuenbergerDocument94 pagesSolution Manual For Investment Science by David Luenbergerkoenajax96% (28)
- Games Strategies and Decision Making 2nd Edition Harrington Solutions Manual DownloadDocument18 pagesGames Strategies and Decision Making 2nd Edition Harrington Solutions Manual DownloadAmyBrightdqjm100% (37)
- Ilmi BooklistDocument26 pagesIlmi Booklistsaifulislam95786No ratings yet
- Final Exam Corporate Finance CFVG 2016-2017Document8 pagesFinal Exam Corporate Finance CFVG 2016-2017Hạt TiêuNo ratings yet
- GDE HandbookDocument19 pagesGDE Handbookisabelscosta8167100% (1)
- Midterm MathDocument4 pagesMidterm MathTuong TranNo ratings yet
- Exercises - 2 (Solutions) Chapter 6, Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesExercises - 2 (Solutions) Chapter 6, Practice QuestionsFoititika.netNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument29 pagesTime Value of Moneyrohan angelNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques For Management: Aditya K BiswasDocument31 pagesQuantitative Techniques For Management: Aditya K BiswasAnamica BhartiNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques For Management: Aditya K BiswasDocument22 pagesQuantitative Techniques For Management: Aditya K BiswasAnamica BhartiNo ratings yet
- A) Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3Document13 pagesA) Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3Usman KhiljiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Basic Financial MathsDocument21 pagesTutorial 1 - Basic Financial MathssagarchandratreyNo ratings yet
- Group 10 - HWchap 3Document33 pagesGroup 10 - HWchap 3Mai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- CA 3 and SolutionsDocument8 pagesCA 3 and SolutionsKatrin WidjajaNo ratings yet
- AB1201 Exam - Sem1 AY 2019-20 - ADocument4 pagesAB1201 Exam - Sem1 AY 2019-20 - Amelodysim2002No ratings yet
- (Midterm Discussions) : ©2023 Batangas State UniversityDocument42 pages(Midterm Discussions) : ©2023 Batangas State UniversityKea GuirreNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Methods of Comparing Alternative ProposalsDocument17 pagesChapter II Methods of Comparing Alternative ProposalsJOHN100% (1)
- Tugas Week 1 - Bagus SeptiawanDocument3 pagesTugas Week 1 - Bagus SeptiawanBagus SeptiawanNo ratings yet
- ECN801 - F2012 Midterm2Document15 pagesECN801 - F2012 Midterm2Zoloft Zithromax ProzacNo ratings yet
- Class Discussion 04 - TVM 2Document3 pagesClass Discussion 04 - TVM 2Sharmila BalaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Evaluation ProceduresDocument30 pagesAlternative Evaluation ProceduresNiranjan DahalNo ratings yet
- IPF Assignment 4Document12 pagesIPF Assignment 4Nitesh MehlaNo ratings yet
- Pe Civil Cost Analysis Fall 2012Document67 pagesPe Civil Cost Analysis Fall 2012Anonymous PkeI8e84Rs100% (1)
- Solution To Assignment-4 - (Revised)Document4 pagesSolution To Assignment-4 - (Revised)sgyn6cb4thNo ratings yet
- Risk and ReturnDocument39 pagesRisk and ReturnPrince ShahaNo ratings yet
- Bản Sao Math-Chap-3Document18 pagesBản Sao Math-Chap-3youngandbeautifull666No ratings yet
- Adex 58K Special Topics in Finance: Valuation - Theory and PracticeDocument19 pagesAdex 58K Special Topics in Finance: Valuation - Theory and PracticeKivanc GocNo ratings yet
- Sol Short Term FinancingDocument25 pagesSol Short Term FinancingRajendra LamsalNo ratings yet
- Solution For Exercise #2Document5 pagesSolution For Exercise #2Lorman MaylasNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT-2 MathematicsDocument14 pagesASSIGNMENT-2 MathematicsHiteshNo ratings yet
- Practice 07Document8 pagesPractice 07daddy bobaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument28 pagesTime Value of Moneyvaibhavmakkar54No ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 - Time Value of MoneyDocument27 pagesChapter - 6 - Time Value of MoneyMahe990No ratings yet
- Session 4 - Valuation ConceptsDocument23 pagesSession 4 - Valuation Conceptssanjeet_kaur_10No ratings yet
- CA Ipcc Costing Suggested Answers For Nov 20161Document12 pagesCA Ipcc Costing Suggested Answers For Nov 20161Sai Kumar SandralaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Time Value of Money in Project AppraisalDocument15 pagesThe Role of Time Value of Money in Project AppraisalsilvanokanuNo ratings yet
- Bond Price 100,000Document22 pagesBond Price 100,000HAMMADHRNo ratings yet
- CFM Session 8Document7 pagesCFM Session 8khanhnguyenfgoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 SolutionsDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 SolutionsSadia R ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Annuity PDFDocument6 pagesOrdinary Annuity PDFCarl Omar GobangcoNo ratings yet
- CFM Take-home Exercise 8(1)Document6 pagesCFM Take-home Exercise 8(1)camlansuc09999No ratings yet
- Simple Annuity: General MathematicsDocument18 pagesSimple Annuity: General MathematicsAezcel SunicoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Simple InterestDocument43 pages3.1 Simple InterestAhmed salah el zeinyNo ratings yet
- Final Practrice (Unit 4 and 5)Document9 pagesFinal Practrice (Unit 4 and 5)mjlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Time Value of MoneyDocument23 pagesChapter 3 Time Value of MoneyAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- BA303 - 1002057831 - Rahmandika Adipradana (Supplementary Examination)Document13 pagesBA303 - 1002057831 - Rahmandika Adipradana (Supplementary Examination)Pump AestheticsNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Nro 8 SolucionnnnnnDocument9 pagesEjercicio Nro 8 SolucionnnnnnSugar Leonardo Herrera CoaquiraNo ratings yet
- MTP Soln 1Document14 pagesMTP Soln 1Anonymous 8wg4eowIdzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2 Benefit Cost AnalysisDocument26 pagesChapter 3 2 Benefit Cost AnalysisRoland NasayaoNo ratings yet
- CF B21 TVDocument33 pagesCF B21 TVSoumya KhatuaNo ratings yet
- Assignement - QTM (Quantitive Techique MGT)Document23 pagesAssignement - QTM (Quantitive Techique MGT)Nimit Gupta100% (2)
- Equivalent Uniform Annual CostDocument40 pagesEquivalent Uniform Annual CostDr. Rogelio C. Golez, JrNo ratings yet
- Leverage: 1) Operating Leverage (Associated With Operating Risk) - 2) Financial Leverage (Associated With Financial Risk)Document18 pagesLeverage: 1) Operating Leverage (Associated With Operating Risk) - 2) Financial Leverage (Associated With Financial Risk)ShashankNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Topic 2 Equivalence Continuous Conounding and Discrete PaymentsDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Topic 2 Equivalence Continuous Conounding and Discrete Paymentsincrediblesmile1234No ratings yet
- Add Math ProjectDocument18 pagesAdd Math Projectashar sarbiniNo ratings yet
- FM Practice Sheet Booklet SOLUTIONS - Nov 2022Document135 pagesFM Practice Sheet Booklet SOLUTIONS - Nov 2022Dhruvi VachhaniNo ratings yet
- ACCA F2-FMA LRP Revision Mock - Answers S15Document12 pagesACCA F2-FMA LRP Revision Mock - Answers S15tazNo ratings yet
- ANSWERMKIDocument3 pagesANSWERMKIJe CourseNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6No ratings yet
- Những cách mở đầu câu Speaking giúp tăng điểm FluencyDocument4 pagesNhững cách mở đầu câu Speaking giúp tăng điểm FluencyMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Chap9 Resource Allocation HomeworkDocument6 pagesChap9 Resource Allocation HomeworkMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Project ManagerDocument3 pagesProject ManagerMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- BAFNIU21395-MAI PHUONG ANH-StatisticsForBusiness - Assignment1Document11 pagesBAFNIU21395-MAI PHUONG ANH-StatisticsForBusiness - Assignment1Mai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- HW8-Scheduling - NewDocument5 pagesHW8-Scheduling - NewMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document2 pagesStep 1Mai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Sample Data For Pivot TableDocument15 pagesSample Data For Pivot TableMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Test 17.10Document4 pagesVocabulary Test 17.10Mai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Final RevisionDocument67 pagesFinal RevisionMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewDocument9 pagesScience ReviewMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- 5,6,7 ProblemsDocument3 pages5,6,7 ProblemsMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Bài tập từ vựng HTĐ và HTTDDocument7 pagesBài tập từ vựng HTĐ và HTTDMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Slides Week2 DataCollectionDocument26 pagesSlides Week2 DataCollectionMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Group 10 - HWchap 3Document33 pagesGroup 10 - HWchap 3Mai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - UpdateDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - UpdateMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Four Types of Control Mechanisms Starbucks UsesDocument7 pagesFour Types of Control Mechanisms Starbucks UsesMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MathsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 MathsMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- ADocument5 pagesAMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- MFB NoteDocument29 pagesMFB NoteMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Example 2Document3 pagesExample 2Mai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2chapter3 - Group 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2chapter3 - Group 2Mai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- Chia Dong Tu Hien Tai Tiep DienDocument5 pagesChia Dong Tu Hien Tai Tiep DienMai Phương AnhNo ratings yet
- PR Vani 2 No 2Document9 pagesPR Vani 2 No 2ivania nuryantariNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4067211Document53 pagesSSRN Id4067211mnpxzdsqs8No ratings yet
- HW 11 SolutionDocument5 pagesHW 11 SolutionPepe BufordNo ratings yet
- 04 Steop enDocument29 pages04 Steop enMutesa ChrisNo ratings yet
- Present Value of A Single Amount TableDocument1 pagePresent Value of A Single Amount TableAntonette CastilloNo ratings yet
- Game Theory Lecture 5Document24 pagesGame Theory Lecture 5Jessica ChenNo ratings yet
- 1 Problem Set I CournotDocument32 pages1 Problem Set I CournotSagheer Hussain DaharNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Analisis Dan Investasi TambangDocument10 pagesJurnal Analisis Dan Investasi Tambangdwi indahNo ratings yet
- Fisher MarketDocument4 pagesFisher Marketgabby209No ratings yet
- Introduction To Corporate Finance 5th Edition Frino Test BankDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Corporate Finance 5th Edition Frino Test Bankbradleygillespieditcebswrf100% (20)
- Game TheoryDocument21 pagesGame Theorykprasad_53No ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document47 pagesChapter 03Be BetterNo ratings yet
- Mathematization of Islamic Economics PDFDocument5 pagesMathematization of Islamic Economics PDFislamicthinkerNo ratings yet
- Present Value Interest Factor TableDocument6 pagesPresent Value Interest Factor TableQaisar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Mathematical EconomicsDocument42 pagesMathematical EconomicsSani SonuNo ratings yet
- Game Theory 93 2 Slide01Document44 pagesGame Theory 93 2 Slide01amiref100% (1)
- Compound Vs Simple Interest 8% Per Year For 40 YearsDocument4 pagesCompound Vs Simple Interest 8% Per Year For 40 YearsLakshmikanth SNo ratings yet
- Understanding Economics: Game TheoryDocument144 pagesUnderstanding Economics: Game TheorySyed Amir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Solution 3 RasmussenDocument12 pagesSolution 3 Rasmussenalvaro roberioNo ratings yet
- MCQ Answers 2017 - 2013Document18 pagesMCQ Answers 2017 - 2013aleehaNo ratings yet
- Opman Quiz 1 ReviewDocument11 pagesOpman Quiz 1 ReviewReniella AllejeNo ratings yet
- Ab MTDFDocument2 pagesAb MTDFcornel mileaNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Math 423 Final ExamDocument3 pagesFormulas For Math 423 Final ExamJake FeldmanNo ratings yet
- Basic Finance FormulasDocument1 pageBasic Finance Formulasmafe moraNo ratings yet
- Sneaker With Replacement Chain and EAA 2023Document13 pagesSneaker With Replacement Chain and EAA 2023Smit SanganiNo ratings yet
- Penerapan Metode Single Exponential Smoothing Dalam Peramalan Penjualan BarangDocument9 pagesPenerapan Metode Single Exponential Smoothing Dalam Peramalan Penjualan BarangAna Nya AnaNo ratings yet
- Game Theory Lecture Notes UT AustinDocument11 pagesGame Theory Lecture Notes UT AustinooaminooNo ratings yet