Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04d - Symmetrical Components Exercise Solution - r3
04d - Symmetrical Components Exercise Solution - r3
Uploaded by
Pool Martinez AlejandroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04d - Symmetrical Components Exercise Solution - r3
04d - Symmetrical Components Exercise Solution - r3
Uploaded by
Pool Martinez AlejandroCopyright:
Available Formats
SYMMETRICAL COMPONENTS EXERCISE SOLUTION
Problem 1:
Va = 67 V @ 0 degrees Ia = 1 A @ -10 degrees
Vb = 67 V @ -120 degrees Ib = 1 A @ -130 degrees
Vc = 67 V @ +120 degrees Ic = 1 A @ +110 degrees
Using the symmetrical components equations, manually calculate the positive, negative, and
zero-sequence components that you expect the relay to see for this balanced three-phase
condition. Draw a phasor diagram representing both the phase and sequence components for
the voltages and currents.
1
Va 0 = (67 @ 0 + 67 @ 240 + 67 @ 120) = 0 @ 0
3
Vc Ic
1
Va1 = (67 @ 0 + 1 @ 120 * 67 @ 240 + 1 @ 240 * 67 @ 120)
3
1
Va1 = (67 @ 0 + 67 @ 0 + 67 @ 0) = 67 @ 0 Va
3
Va 2 =
1
(67 @ 0 + 1 @ 240 * 67 @ 240 + 1 @ 120 * 67 @ 120)
Ia
3
1 Ib
Va 2 = (67 @ 0 + 67 @ 120 + 67 @ 240) = 0 @ 0
3 Vb
1
Ia 0 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 230 + 1 @ 110) = 0 @ 350
3
1
Ia1 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 120 *1 @ 230 + 1 @ 240 *1 @ 110)
3 Va1
1
Ia1 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 350 + 1 @ 350) = 1 @ 350
3 Ia1
1
Ia 2 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 240 *1 @ 230 + 1 @ 120 *1 @ 110)
3
1
Ia 2 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 110 + 1 @ 230) = 0 @ 350
3
Symmetrical Components Solution_r3 Page 1 of 3
Problem 2:
Va = 67 V @ 0 degrees Ia = 1 A @ -10 degrees
Vb = 67 V @ -120 degrees Ib = 1 A @ +110 degrees
Vc = 67 V @ +120 degrees Ic = 1 A @ -130 degrees
Using the symmetrical components equations, manually calculate the positive, negative, and
zero-sequence components that you expect a relay to see for this balanced three-phase
condition. Draw a phasor diagram representing both the phase and sequence components.
1
Va 0 = (67 @ 0 + 67 @ 240 + 67 @ 120) = 0 @ 0
3
Vc Ib
1
Va1 = (67 @ 0 + 1 @ 120 * 67 @ 240 + 1 @ 240 * 67 @ 120)
3
1 Va
Va1 = (67 @ 0 + 67 @ 0 + 67 @ 0) = 67 @ 0
3
Ia
1
Va 2 = (67 @ 0 + 1 @ 240 * 67 @ 240 + 1 @ 120 * 67 @ 120)
3 Ic
1 Vb
Va 2 = (67 @ 0 + 67 @ 120 + 67 @ 240) = 0 @ 0
3
1
Ia 0 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 230 + 1 @ 110) = 0 @ 350
3
1 Va2
Ia1 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 120 *1 @ 110 + 1 @ 240 *1 @ 230)
3
1 Ia2
Ia1 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 2300 + 1 @ 110) = 0 @ 350
3
1
Ia 2 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 240 *1 @ 110 + 1 @ 120 *1 @ 230)
3
1
Ia 2 = (1 @ 350 + 1 @ 350 + 1 @ 350) = 1 @ 350
3
Symmetrical Components Solution_r3 Page 2 of 3
Problem 3:
Using the symmetrical components equations, manually calculate the positive, negative, and
zero-sequence components that you expect a relay to see for this unbalanced condition. Draw
a phasor diagram representing both the phase and sequence components.
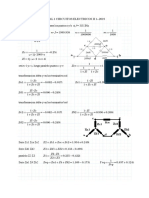
Va = 55.7 V @ 13 degrees Ia = 8.6 A @ +5 degrees
Vb = 44.9 V @ -89 degrees Ib = 7.7 A @ -165 degrees
Vc = 63.2 V @ +149 degrees Ic = 1.7 A @ +142 degrees
1
=
Va 0 (55.7 @13 + 44.9@ − 89 + 63.2@149)
= .3@12.0
3
1
=Va1 (55.7 @13 + 1@120* 44.9@ − 89 + 1@ 240*63.2@149)
3 Vc Ic
1
Va=1 (57.7 @13 + 44.9@ 31 + 63.2@ 29)= 54.1@ 24.1 Va
3
Ia
1 Ib
Va 2 = (55.7 @13 + 1@ 240 * 44.9 @ − 89 + 1@120 * 63.2 @149)
3
1
Va 2 = (55.7 @13 + 44.9 @151 + 63.2 @ 269) = 10.7 @ − 64.3
3
Vb
1
Ia 0 = (8.6 @ 5 + 7.7 @ − 165 + 1.7 @142) = 0.1@ − 136.9
3
1
Ia1 = (8.6 @ 5 + 1@120 * 7.7 @ − 165 + 1@ 240 *1.7 @142)
3 Va1
Ia2
1
Ia1 = (8.6 @ 5 + 7.7 @ − 45 + 1.7 @ 22) = 5.4 @ − 14.6
3
Ia1
1
Ia 2 = (8.6 @ 5 + 1@ 240 * 7.7 @ − 165 + 1@120 *1.7 @142) Va2
3
1
Ia 2 = (8.6 @ 5 + 7.7 @ 75 + 1.7 @ 262) = 4.1@ 32.2
3
Symmetrical Components Solution_r3 Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Power System Analysis and Design 6th Edition Glover Solutions ManualDocument37 pagesPower System Analysis and Design 6th Edition Glover Solutions Manualhelgasophie7478k0100% (31)
- 11th GateDocument48 pages11th GateSamejiel Aseviel LajesielNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 (Powers in Symmetrical Components) (Complete 2018)Document29 pagesLecture 4 (Powers in Symmetrical Components) (Complete 2018)Joshua Roberto Gruta100% (2)
- Viscosity by Efflux TimeDocument3 pagesViscosity by Efflux TimeAmit Jharbade67% (3)
- HW2 SolutionsDocument5 pagesHW2 SolutionsDilan Andres Valencia AguilarNo ratings yet
- 23344434Document13 pages23344434jenixson tamondong0% (1)
- M2 - 2.3.sym Components - Class 4Document11 pagesM2 - 2.3.sym Components - Class 4Anusha EnigallaNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment Final PDFDocument13 pagesGroup Assignment Final PDFdejene edossaNo ratings yet
- 普物實驗期初作業Document6 pages普物實驗期初作業宇峻No ratings yet
- Pembahasan WB Page 32 No 5Document7 pagesPembahasan WB Page 32 No 5riskyNo ratings yet
- Second Problem First Test First Semester 2015 Solution Jose Maria Rico MartinezDocument7 pagesSecond Problem First Test First Semester 2015 Solution Jose Maria Rico MartinezzeltaifyNo ratings yet
- TAEAMATRICESVALE1111Document8 pagesTAEAMATRICESVALE1111Cristian Alexander LenizNo ratings yet
- Tugas Rekayasa Trafik 1Document2 pagesTugas Rekayasa Trafik 1Dwi TriyantoNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 3 Unit 3 (Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Planar Force Systems)Document9 pagesMech 1 Module 3 Unit 3 (Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Planar Force Systems)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Usd SRBDocument29 pagesUsd SRBGLAISDALE KHEIZ CAMARAUANNo ratings yet
- Example On Biaxial Column Using Rec MethodDocument7 pagesExample On Biaxial Column Using Rec MethodmahletNo ratings yet
- Probleme Rezolvate AlgadDocument3 pagesProbleme Rezolvate AlgadCristian Giorgian LovinNo ratings yet
- Thevenin Norton Solved ProblemsDocument5 pagesThevenin Norton Solved Problemspotatochief420No ratings yet
- A334 Carino, Patricia Andrea Assignment On ForecastingDocument3 pagesA334 Carino, Patricia Andrea Assignment On ForecastingPatricia Andrea CariñoNo ratings yet
- Sample Question PaperDocument6 pagesSample Question PaperDavidNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit by Sajid DonDocument16 pagesAC Circuit by Sajid DonEngr Sajid100% (1)
- Usd DRBDocument15 pagesUsd DRBGLAISDALE KHEIZ CAMARAUANNo ratings yet
- Soluition Charpter 5 - 1Document3 pagesSoluition Charpter 5 - 1Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Technique Time Series Analysis Forecasting Errors Using EXCELDocument7 pagesForecasting Technique Time Series Analysis Forecasting Errors Using EXCELMohammed Al-FtesiNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers FormulaeDocument9 pagesRectifiers FormulaeSharath R SankarNo ratings yet
- Me-101 Tutorial 04 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMe-101 Tutorial 04 SolutionsVasanthi ChitturiNo ratings yet
- Parcial 1 2019 IDocument5 pagesParcial 1 2019 IAngel Gonzalez MolinaNo ratings yet
- ACpower HW SolutionsDocument13 pagesACpower HW Solutionsnkosingiphilephiri639No ratings yet
- Ejercicios II Fase: Anthony Pablo Romero Reynoso 6-124 6-144 7-60Document5 pagesEjercicios II Fase: Anthony Pablo Romero Reynoso 6-124 6-144 7-60anthony RomeroNo ratings yet
- Module IIDocument57 pagesModule IIHemanthNo ratings yet
- SupernodeDocument5 pagesSupernodeChiliveri VinodNo ratings yet
- MathDocument3 pagesMathGita ParamitaNo ratings yet
- פתרון בחינת מהטDocument16 pagesפתרון בחינת מהטliko uzielNo ratings yet
- Chapt03PP060205 PDFDocument9 pagesChapt03PP060205 PDFbassel_265988775No ratings yet
- 27 - Uap AlinDocument6 pages27 - Uap AlinJesica Evelyn WBNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1Iareto ArabwatiNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Engineering Lec2Document14 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering Lec2nasirvivacNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument7 pagesLinear AlgebraMANOJNo ratings yet
- PH - Algorithm (New)Document2 pagesPH - Algorithm (New)mail.information0101No ratings yet
- 58 B 8 Eef 6 BC 97 Fa 1 CDB 7 FDocument2 pages58 B 8 Eef 6 BC 97 Fa 1 CDB 7 Fapi-441441400No ratings yet
- HW 3 SolutionsDocument9 pagesHW 3 SolutionsnadunnnNo ratings yet
- Problem 5Document4 pagesProblem 5arafath1985No ratings yet
- Tabel PengamatanDocument3 pagesTabel PengamatanAbro Andriadi HarahapNo ratings yet
- Model Answer 4 - MPZ 4230 - 2009Document8 pagesModel Answer 4 - MPZ 4230 - 2009gayanlakNo ratings yet
- Question 3 (Annuity)Document2 pagesQuestion 3 (Annuity)putmelia0704No ratings yet
- Equilibrio de Cuerpos Rigidos 2Document7 pagesEquilibrio de Cuerpos Rigidos 2Ana Sofia Parra NiviaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrio de Cuerpos Rigidos 2Document7 pagesEquilibrio de Cuerpos Rigidos 2Ana Sofia Parra NiviaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrio de Cuerpos Rigidos 2Document7 pagesEquilibrio de Cuerpos Rigidos 2Ana Sofia Parra NiviaNo ratings yet
- Ray Adil Salin GanayDocument6 pagesRay Adil Salin GanayJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- تمرين 1 الارتباطDocument3 pagesتمرين 1 الارتباطخالد ببوشNo ratings yet
- Actividad Colaborativa Vectores, Matrices Y Determinantes: 1. Dados Los Siguientes Vectores Dados en Forma PolarDocument4 pagesActividad Colaborativa Vectores, Matrices Y Determinantes: 1. Dados Los Siguientes Vectores Dados en Forma PolarDiana HernndezNo ratings yet
- The Gauss-Seidel Method-Procedure & Example: δ =0 i = 2,3, ……………. G V =1, δ =0 i = G+1, G+2, ……… nDocument7 pagesThe Gauss-Seidel Method-Procedure & Example: δ =0 i = 2,3, ……………. G V =1, δ =0 i = G+1, G+2, ……… nSaikat MahmudNo ratings yet
- Cramer SDocument14 pagesCramer SFranz Daniel EbronNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Power System Analysis and Design 6th Edition Glover Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument60 pagesInstant Download PDF Power System Analysis and Design 6th Edition Glover Solutions Manual Full Chapterulziiabilas100% (5)
- (Chapter 7) Solution To Examples in Chapter 3Document24 pages(Chapter 7) Solution To Examples in Chapter 3Bara ThiNo ratings yet
- Yi X X Yi X Y: Grafico de DispercionDocument5 pagesYi X X Yi X Y: Grafico de Dispercionjlb1212No ratings yet
- Symmetrical ComponentDocument27 pagesSymmetrical ComponentTahir KedirNo ratings yet
- GPJ 1 Brother7Document11 pagesGPJ 1 Brother7Thao PhuongNo ratings yet
- Metodo de Rigideces: Grados de Libertad Nudo X Y 1 2 3 4Document8 pagesMetodo de Rigideces: Grados de Libertad Nudo X Y 1 2 3 4Miguel Sebastian Valera GarateaNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and Design 6Th Edition Glover Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument58 pagesPower System Analysis and Design 6Th Edition Glover Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDanielleNelsonxfiq100% (11)
- Exercises-6 Machine Problem-6 Cosejo, CharlenneM. BSEE-III EEN08Document29 pagesExercises-6 Machine Problem-6 Cosejo, CharlenneM. BSEE-III EEN08Charlenne CosejoNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- 3564-MC-309 - Interruptor de Caja MoldeadaDocument7 pages3564-MC-309 - Interruptor de Caja MoldeadaPool Martinez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Resistencia de ContactosDocument3 pagesResistencia de ContactosPool Martinez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- 06b - Relaying Fundamentals ANSI DEVICE CODES - r2Document2 pages06b - Relaying Fundamentals ANSI DEVICE CODES - r2Pool Martinez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- 04c - Symmetrical Components Exercise - r3Document3 pages04c - Symmetrical Components Exercise - r3Pool Martinez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- The in Uence of Project Autonomy On Project SuccessDocument8 pagesThe in Uence of Project Autonomy On Project SuccessPool Martinez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- I S S E P P: Mproved Ubcontractor Election Mploying Artnering RinciplesDocument11 pagesI S S E P P: Mproved Ubcontractor Election Mploying Artnering RinciplesPool Martinez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Moments, Levers and Gears 1 QPDocument21 pagesMoments, Levers and Gears 1 QPIbrahim MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Worksheet X AprilDocument3 pagesWorksheet X AprilAyushiNo ratings yet
- 2022 CH2213 Lecture22Document18 pages2022 CH2213 Lecture22KuNaL aGaLeNo ratings yet
- First Order Differential EquationsDocument17 pagesFirst Order Differential Equations20S1002 Joel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Automated Coagulation Detection SystemsDocument12 pagesAutomated Coagulation Detection SystemsSTARK DIAGNOSTICSNo ratings yet
- Design of Counterfort Retaining Wall PDFDocument14 pagesDesign of Counterfort Retaining Wall PDFAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Differential Pressure Gauge Model 712.15.160, Copper Alloy Model 732.15.160, Stainless Steel VersionDocument11 pagesDifferential Pressure Gauge Model 712.15.160, Copper Alloy Model 732.15.160, Stainless Steel VersionNayan DudhatraNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel and Timber StructuresDocument6 pagesDesign of Steel and Timber StructuresYi MokNo ratings yet
- Conversion From Latitude/Longitude To Cartesian CoordinatesDocument34 pagesConversion From Latitude/Longitude To Cartesian CoordinatesMinaAdlyNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stability of Quercetin HydratesDocument6 pagesThermal Stability of Quercetin HydratesNur MukminNo ratings yet
- On The Bridge Hill of The ViolinDocument12 pagesOn The Bridge Hill of The ViolinToto W. JuniartoNo ratings yet
- Design of Buried Pipeline Block AnchorDocument2 pagesDesign of Buried Pipeline Block Anchoragung_gpeNo ratings yet
- NIPV Smoke Cooling and Nozzle TechniquesDocument28 pagesNIPV Smoke Cooling and Nozzle TechniquesGeorge GartzounisNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument5 pagesConclusionkhairulhakam50% (2)
- 605187YSI Pro1020 Instruction Manual English WebDocument26 pages605187YSI Pro1020 Instruction Manual English WebSahibou WONINo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Formula SheetDocument1 pagePhysics 11 Formula SheetJack Song S.YNo ratings yet
- University of Santo TomasDocument5 pagesUniversity of Santo TomasChester GertesNo ratings yet
- Dipole Radiation in The Presence of A Conducting Half-SpaceDocument405 pagesDipole Radiation in The Presence of A Conducting Half-SpaceBélaid Hocine AnisNo ratings yet
- Classification Procedures For Expansive SoilsDocument7 pagesClassification Procedures For Expansive SoilsABDIRAHMANNo ratings yet
- 2798 Astm D - 2020Document6 pages2798 Astm D - 2020M0197 BatenkhNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements 1Document2 pagesClassification of Elements 1JACK FFNo ratings yet
- High Mast Lighting PolesDocument7 pagesHigh Mast Lighting PolesRaheem JunaidiNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 3 Sem Thermodynamics Rme302 2022Document2 pagesBtech Me 3 Sem Thermodynamics Rme302 2022mayankjain08248No ratings yet
- ASTEN JOHNSON - CentraFlowDocument5 pagesASTEN JOHNSON - CentraFlowKristina ivanovicNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Plates, Carbon Steel, For Intermediate-And Higher-Temperature ServiceDocument3 pagesPressure Vessel Plates, Carbon Steel, For Intermediate-And Higher-Temperature Servicekaushik21185No ratings yet
- De150101 BCMDocument7 pagesDe150101 BCMseve1No ratings yet
- PV Tali Danes H Solution ManualDocument197 pagesPV Tali Danes H Solution ManualSarhad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceDocument43 pagesChemistry: The Molecular ScienceMikaila Denise LoanzonNo ratings yet