Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 11
Lec 11
Uploaded by
Ashutosh ChowdhuryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lec 11
Lec 11
Uploaded by
Ashutosh ChowdhuryCopyright:
Available Formats
SWC 211 Soil and Water Conservation Engineering
RAINWATER HARVESTING
What is Rainwater Harvesting?
It is the principle of collecting and using precipitation (rainfall from a catchment’s
surface.
An old technology is gaining popularity in a new way. Rainwater harvesting is
enjoying a renaissance of sorts in the world, but it traces its history to biblical times.
Extensive rainwater harvesting apparatus existed 4000 years ago in the Palestine and
Greece. In ancient Rome, residences were built with individual cisterns and paved
courtyards to capture rainwater to augment water from city’s aqueducts. As early as the
third millennium BC, farming communities in Baluchistan and Kutch impounded
rainwater and used it for irrigation dams.
Storage
Groundwater Reservoirs
Rooftop rainwater collected may be recharged to groundwater reservoir through:
• Abandoned dug well
• Abandoned/ running hand pump
• Recharge shaft
• Defunct bore well
• Trench/ pit with injection well
Small storages tank above ground level (suitable for individual houses)
A simple rooftop rainwater harvesting as practiced in some villages using split
pipe or GI valley sheets or Bamboo directing the flow from rooftop to a small drum or
plastic tank.
If there is a group of houses, the owners can collectively lead the rainwater into a
subsurface tank situated in a common place.
Another simple method of storage is letting the rainwater into the exiting well
through a filter media consisting of the following.
Layer 1: Layer of sand – fine to medium (150 to 300 mm)
Department of Soil & Water Conservation Engineering
SWC 211 Soil and Water Conservation Engineering
Layer 2: Layer of gravel (200 mm)
Layer 3: Layer of medium pebbles bed (500 mm)
There are certain limitations in adopting storage method, in places where the
monsoon period is only 3 to 4 months as we require a large quantity of storage tanks of
bigger dimensions, and preservation of water in the tanks for longer period is also
hazardous. Hence, we have to go in for recharging method.
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
The groundwater available in urban localities and Metropolis could not cope up
with the ever increasing demand and results in the over-exploitation of groundwater with
inadequate replenishment due to urbanization. The rainwater runs off into sea as the
ground area available for percolation for recharging is meager/ insignificant. Hence the
rooftop rainwater harvesting method is best suitable for conservation of rainwater and
recharging the groundwater aquifer.
Runoff coefficient for various surfaces
Type of catchment Coefficients (m sec-1)
Roof catchments
Tiles 0.80 – 0.90
Corrugated metal sheets 0.70 – 0.80
Ground surface coverlings
Concrete 0.60 – 0.80
Brick Pavements 0.50 – 0.60
Untreated ground catchments
Soil on slopes less than 10 per cent 0.00 – 0.30
Rocky natural catchments 0.20 – 0.50
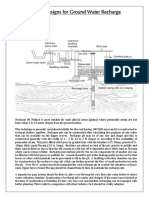
Under this method, the rain pouring on the top of the roof (whatever be the roof
material) is drained thorough down pipes into a recharging pit (1 x 1 x 1 m) or
0.60 x 0.60 x 0.60 m made up of broken brick jelly for 0.60 m from the bottom of the top
layer is filled with river sand for 0.40 m height of the pit covered by perforated precast
RCC slab.
Department of Soil & Water Conservation Engineering
SWC 211 Soil and Water Conservation Engineering
If the water source for the building is a bore well, the recharging pit is extended to
at least 10 – 15 m depth by means of a tube well or 200 mm. Diameter filled with broken
brick jelly and pebbles.
Rainwater harvesting for individual house of < 100 m2 (Recharging pit method)
Pit Size: 1 x 1 x 1 m
S. No. Description Quantity Rate Amount
1. Earthwork excavation for percolation pit 1 m3 41 41
2. Filling the pit with 40 mm size brick jelly 0.6 m3 312.42 188
3. Filling the pit top with river sand 0.4 m3 326.92 131
4. Perforated precast RCC slab 40 mm thick for 1 m3 175 175
covering the pit
5. Connecting the drain pipe to the pit through 150 10 m 400 4000
mm diameter PVC pipe including earth works,
laying, joining and sand gravel packing
6. Unforeseen items 465
Total Rs. 5000
Rainwater harvesting for multi storied building of size 20 x 30 m
(Recharging trench method) Trench size: All round the building 1 x 1 x 1.5 m
S. No. Description Quantity Rate Amount
1. Earthwork excavation for open trench 126 41 5766
2. Filling the trench with brick jelly 84 312.42 26243
3. Filling the trench with river sand 42 326.92 1373
4. Provision of PVC pipe 150 mm diameter 24 m 275 6600
including bends and clamps
Department of Soil & Water Conservation Engineering
SWC 211 Soil and Water Conservation Engineering
5. Filling with pebbles in the top layer of the 10 m 1500 15000
trench
6. Unforeseen items and petty supervision charges 8260
Total Rs. 75000
Recharge trench cum injection well
This technique is ideally suited for areas where permeable sandy horizons within
3 to 5 m below ground level and continuous up to the water level under unconfined
conditions, by which copious water available can be easily recharged.
In this technique, 1 to 2 m, wide and 2 to 3 m, deep trench is excavated, the length
of which depends on the site availability and volume of water to be handled. An
injection well of 100 to 150 mm diameter is constructed, piercing through the layers of
impermeable horizons to the potential aquifer reaching about 3 to 5 metres below water
levels (1 to 10 m) from the bottom of the trenches. Depending upon the volume of water
to be injected, the number of injection wells can be increased to enhance the recharging
rate.
Benefits of rainwater harvesting
• Groundwater level is increased
• Recharges the well
• Reduces crack formation in walls and structures
• Dilutes the salt content of water in the wells i.e. improves the groundwater quality
• Improves moisture content in the soil
• Aids the growth of plants and trees
• Seawater intrusion into the land is arrested
• Reduces the soil erosion
• Improves the groundwater quality
Department of Soil & Water Conservation Engineering
You might also like
- Explain Briefly About Preloading. A. Preloading of Soil Is Merely Applying An External Loading For A Long Duration ToDocument10 pagesExplain Briefly About Preloading. A. Preloading of Soil Is Merely Applying An External Loading For A Long Duration Tohimabindugvsd71No ratings yet
- Stowing PracticeDocument7 pagesStowing PracticeNitesh Shah100% (3)
- Pse Module 13.2: Fluid Mechanics 02Document5 pagesPse Module 13.2: Fluid Mechanics 02Ronald VilladolidNo ratings yet
- Sand Dams or Silt TrapsDocument6 pagesSand Dams or Silt TrapscherogonyaNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY. Ground ImprovementDocument6 pagesCASE STUDY. Ground ImprovementRashdanNo ratings yet
- Winsem2014-15 Cp0670 17-Apr-2015 Rm01 U4 l4 Rainwater-HarvestingDocument12 pagesWinsem2014-15 Cp0670 17-Apr-2015 Rm01 U4 l4 Rainwater-HarvestingShiv ShivNo ratings yet
- Irrigation NotesDocument28 pagesIrrigation NotesCristy JeanNo ratings yet
- Water Pan For Runoff Water Harvesting PDFDocument4 pagesWater Pan For Runoff Water Harvesting PDFmulwa2009No ratings yet
- Engg MeasuresDocument94 pagesEngg MeasuresDilin Sathyanath100% (1)
- Vaccum TechniqueDocument25 pagesVaccum TechniqueDeepak JoghuNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering Semester Vii Civil EngineeringDocument52 pagesIrrigation Engineering Semester Vii Civil EngineeringHod CivilNo ratings yet
- Recharge WellDocument7 pagesRecharge WellanbujeNo ratings yet
- Rain Water Harvesting Techniques To Augment Ground Water 1Document10 pagesRain Water Harvesting Techniques To Augment Ground Water 1Manoj YadavNo ratings yet
- Embankment in Soft SoilDocument65 pagesEmbankment in Soft SoilMd. Shiraz JinnathNo ratings yet
- Technical Designs For Ground Water RechargeDocument4 pagesTechnical Designs For Ground Water RechargeMardiaNo ratings yet
- Subsurface DrainsDocument28 pagesSubsurface DrainsMarie PeneyraNo ratings yet
- Dewatering TechniquesDocument17 pagesDewatering TechniquesTrudeep DaveNo ratings yet
- Rainwater HarvestingDocument53 pagesRainwater HarvestingNik Soni100% (2)
- Ground Improvement Techniques 01Document57 pagesGround Improvement Techniques 01tharadev2512No ratings yet
- The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Infrastructure MSCDocument48 pagesThe Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Infrastructure MSCEng Ahmed abdilahi IsmailNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document10 pagesCH 9salmanistiaq0No ratings yet
- DewateringDocument6 pagesDewateringIsife OlisaemekaNo ratings yet
- SLF Soak Away For Sewage EffluentDocument10 pagesSLF Soak Away For Sewage EffluentaberraNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Rain PDFDocument34 pagesUnit 4 Rain PDFNaGamani KanDanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-GBT Part-IiDocument14 pagesUnit 2-GBT Part-Iiaraq3501No ratings yet
- ##Contour Trenches - Rainwater HarvestingDocument6 pages##Contour Trenches - Rainwater HarvestingalbttiNo ratings yet
- Soil Improvement Techn: IquesDocument7 pagesSoil Improvement Techn: IquescybotbNo ratings yet
- Methods of DewateringDocument11 pagesMethods of DewateringjinkumalakarNo ratings yet
- Dewatering For ConstructionDocument14 pagesDewatering For ConstructionpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- UNDERGROUND DRAINAGE SYSTEMS Rev 3Document14 pagesUNDERGROUND DRAINAGE SYSTEMS Rev 3Coolwecaleza Chinene100% (1)
- Rainwater HarvestingDocument4 pagesRainwater HarvestingCHARUCHOUHANNo ratings yet
- Groundwate DamsDocument4 pagesGroundwate DamsikaspuspasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 (83-87Document5 pagesChapter 8 (83-87Affinity HydroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 08Document2 pagesTutorial 08jsyadav.nithNo ratings yet
- Geotechnics Project: Faculty of Civil and Enviromental EngineeringDocument21 pagesGeotechnics Project: Faculty of Civil and Enviromental EngineeringFarah Sofhia Mohd ZinNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution Control Method Adopted by NTPC Ltd. in Ash Dyke (Starter & WorkingDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Control Method Adopted by NTPC Ltd. in Ash Dyke (Starter & WorkingSukesh NayakNo ratings yet
- Grey Water Management Resource Book GoIDocument38 pagesGrey Water Management Resource Book GoIsalilNo ratings yet
- Assignment On CE 6402 - Dec 14 2022Document3 pagesAssignment On CE 6402 - Dec 14 2022Mirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Rain Water HarvestingDocument9 pagesRain Water HarvestingAnna Jane Tan100% (1)
- 13 Dewatering of FoundationsDocument65 pages13 Dewatering of FoundationsZahoor AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture-10 Canal LiningDocument19 pagesLecture-10 Canal LiningTamour KhalilNo ratings yet
- Sub Surface Dams PDFDocument5 pagesSub Surface Dams PDFKwabena OtchereNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank HandoutDocument8 pagesSeptic Tank HandoutDebkumar MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Disposal System For Rural AreasDocument10 pagesWaste Water Disposal System For Rural AreasRishabhNo ratings yet
- Slideshare Upload Login SignupDocument26 pagesSlideshare Upload Login SignupAbok AduogoNo ratings yet
- DewateringtechniquespptDocument45 pagesDewateringtechniquespptMadhu AsopaNo ratings yet
- Lec-04 & 05 Draiage & DewateringDocument33 pagesLec-04 & 05 Draiage & DewateringRahat fahimNo ratings yet
- GIT - A2 KEY & Scheme of ValuationDocument6 pagesGIT - A2 KEY & Scheme of ValuationsantoshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document38 pagesLecture 2Khalid ArafatNo ratings yet
- Methodology of ConstructionDocument19 pagesMethodology of Constructionsumit249100% (1)
- Construction Dewatering: CM 420 - T S L 7: C D G FDocument8 pagesConstruction Dewatering: CM 420 - T S L 7: C D G FKaiser AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Technical Sheet. Ministry of HousingDocument9 pagesTechnical Sheet. Ministry of HousingVishal Goriah100% (2)
- Chapter 3 WcuDocument12 pagesChapter 3 WcuKubaNo ratings yet
- Land and Highway Drainage DrainageDocument16 pagesLand and Highway Drainage DrainageIcen AlincastreNo ratings yet
- The Vienna Donau City Tower 2000mm Flat SlabsDocument16 pagesThe Vienna Donau City Tower 2000mm Flat SlabsSakisNo ratings yet
- Types of Subsurface Drainage SystemsDocument12 pagesTypes of Subsurface Drainage SystemsRajesh Khadka100% (1)
- Successful Cementing in Areas Prone To Shallow Saltwater Flows in Deep-Water Gulf of MexicoDocument8 pagesSuccessful Cementing in Areas Prone To Shallow Saltwater Flows in Deep-Water Gulf of MexicoEmad JamshidiNo ratings yet
- Unit II DewateringDocument13 pagesUnit II Dewateringadhishankar50No ratings yet
- Seminar 20PGCEC17Document23 pagesSeminar 20PGCEC17tauheedrameezNo ratings yet
- Concrete Construction for the Home and the FarmFrom EverandConcrete Construction for the Home and the FarmNo ratings yet
- Ecorain Water Solutions PVT LTDDocument65 pagesEcorain Water Solutions PVT LTDAshutosh ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Rain Water Harvesting 18th Dec 2021Document2 pagesRain Water Harvesting 18th Dec 2021Ashutosh ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentAshutosh ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2095311913605535 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2095311913605535 MainAshutosh ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentAshutosh ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Bottom OutletsDocument3 pagesBottom OutletsJezylu Jireh Lasola AnitoNo ratings yet
- MMBC Case StudyDocument2 pagesMMBC Case StudyPavan TNo ratings yet
- BS EN 446 - 1997 Grout For Prestressing TendonsDocument12 pagesBS EN 446 - 1997 Grout For Prestressing TendonsKamagara Roland AndrewNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineer Exam Vertical Forces (Gravity/Other) Review ClassDocument6 pagesStructural Engineer Exam Vertical Forces (Gravity/Other) Review ClassSabreena NasrinNo ratings yet
- Design Data:: Hhuofw01Document3 pagesDesign Data:: Hhuofw01SAYALI KULKARNINo ratings yet
- TBL 31 B HA en DC 004 A Safety Valve Design CalculationDocument37 pagesTBL 31 B HA en DC 004 A Safety Valve Design CalculationDangolNo ratings yet
- Thermal Bridging Guide: September 2018Document22 pagesThermal Bridging Guide: September 2018HANINo ratings yet
- Details of Installed HVAC EquipmentDocument1 pageDetails of Installed HVAC EquipmentAnsari1918No ratings yet
- B - 4 - Thermal-Bridge-Free - Construction - 20091019 OKDocument43 pagesB - 4 - Thermal-Bridge-Free - Construction - 20091019 OKDoru FecheteNo ratings yet
- Concrete FormsDocument11 pagesConcrete FormsmurdicksNo ratings yet
- Sample Resume For Civil Engineer - ConnectCVDocument2 pagesSample Resume For Civil Engineer - ConnectCVRo AnNo ratings yet
- Beam ColumnDocument35 pagesBeam ColumnDhinesh KalaimaranNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Colweld Piling SDN BHD Colweld Geotech SDN BHDDocument13 pagesCompany Profile: Colweld Piling SDN BHD Colweld Geotech SDN BHDAdam LimNo ratings yet
- PBDby NR Newson PDFDocument399 pagesPBDby NR Newson PDFYHTRTR100% (2)
- An Overview of Vibration and Seismic Applications of Niti Shape Memory AlloyDocument13 pagesAn Overview of Vibration and Seismic Applications of Niti Shape Memory AlloyEstephanie_GrassiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cement Article Directory: Subject Article Title/link DescriptionDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Cement Article Directory: Subject Article Title/link Descriptionv1963No ratings yet
- Rehabilitation and Retrofitting of Buildings DR K M Soni, Chief Engineer, CPWD, West Zone I, MumbaiDocument8 pagesRehabilitation and Retrofitting of Buildings DR K M Soni, Chief Engineer, CPWD, West Zone I, MumbaiSabyasachi Naik (Zico)No ratings yet
- Deep Cement Mixing MethodDocument14 pagesDeep Cement Mixing MethodKhoi DuongNo ratings yet
- Peb 1234330943765774 1Document29 pagesPeb 1234330943765774 1Vikas Singh Chandel100% (1)
- GcsDocument88 pagesGcsshazniSNo ratings yet
- NJ2212GK: General DataDocument5 pagesNJ2212GK: General DataJaum DamianiNo ratings yet
- Ideal FluidDocument2 pagesIdeal FluidaathiraNo ratings yet
- Ref - Integrity Problems of Concrete Piles - FPrimeC - FPrimeC Solutions IncDocument7 pagesRef - Integrity Problems of Concrete Piles - FPrimeC - FPrimeC Solutions IncM MNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Ceramic ShrinkageDocument4 pagesLab Report Ceramic Shrinkagenadeem ranaNo ratings yet
- Only / Underline Format: Chapter C8 Rain LoadsDocument30 pagesOnly / Underline Format: Chapter C8 Rain LoadssharethefilesNo ratings yet
- ZXXXXDocument12 pagesZXXXXMikael MarkovNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow ExperimentDocument3 pagesPipe Flow ExperimentprofmundyNo ratings yet
- CE6451-Fluid Mechanics and MachineryDocument17 pagesCE6451-Fluid Mechanics and Machinerysridevi73No ratings yet
- BOPDrawing TemplateDocument65 pagesBOPDrawing TemplateCristian Barbuceanu100% (1)