Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHAPTER Test in Oral Communication in Context
CHAPTER Test in Oral Communication in Context
Uploaded by
Marilou Iamztol RecamaraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Case Studies TestDocument3 pagesCase Studies TestMayank Sharma0% (1)
- Each Student Should Strictly Follow The Format Given Below For His/her Research ProjectDocument7 pagesEach Student Should Strictly Follow The Format Given Below For His/her Research ProjectAnsari WarisNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2-Module 4 (Q1 Wk9)Document23 pagesPractical Research 2-Module 4 (Q1 Wk9)Mizchyne CaburogNo ratings yet
- PR 1 WK 4 - LASDocument10 pagesPR 1 WK 4 - LASAleah AguraNo ratings yet
- Action Plan Reading ProgramsDocument5 pagesAction Plan Reading ProgramsMA ASTERIA AGUSTINA CENALNo ratings yet
- Flipped PDFDocument18 pagesFlipped PDFIsabel GMNo ratings yet
- Applied - 11 - Research in Daily Life 1 - semII - CLAS8 - Analyzing and Drawing Out Patterns and Themes With Intellectual Honesty - v2 PNS PDFDocument15 pagesApplied - 11 - Research in Daily Life 1 - semII - CLAS8 - Analyzing and Drawing Out Patterns and Themes With Intellectual Honesty - v2 PNS PDFAnya LiggayuNo ratings yet
- Final Term Examination in ICT 11Document3 pagesFinal Term Examination in ICT 11Boyong ManatadNo ratings yet
- ORALCOMM - Chapter 1.5 Intercultural CommunicationDocument24 pagesORALCOMM - Chapter 1.5 Intercultural CommunicationJasminNo ratings yet
- The Flipped Classroom UNiv - LeichesterDocument28 pagesThe Flipped Classroom UNiv - LeichesterEmanuele ViciniNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Activity-Sheet-OCC PDFDocument1 pageModule 1-Activity-Sheet-OCC PDFAMYTHEEZ CAMOMOTNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Department of EducationDocument9 pagesPractical Research 2: Department of EducationLianne LagayanNo ratings yet
- 01032022095126SHS PR2 Q2 M6 Val - withPOSTTESTDocument14 pages01032022095126SHS PR2 Q2 M6 Val - withPOSTTESTJAMES JORDAN NasNo ratings yet
- P8yqp15lr Module 8 Creative WritingDocument8 pagesP8yqp15lr Module 8 Creative WritingSteve Laurence PontilloNo ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela Form 4 Daily Attendance of VolunteerDocument3 pagesBrigada Eskwela Form 4 Daily Attendance of VolunteerGileta MarananNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 1: Qualitative Research Designs, Sample, and Data Collection and Analysis ProceduresDocument14 pagesResearch in Daily Life 1: Qualitative Research Designs, Sample, and Data Collection and Analysis ProceduresAnya LiggayuNo ratings yet
- Flipped Inclusion Classroom Action Research Jeanette VillanuevaDocument16 pagesFlipped Inclusion Classroom Action Research Jeanette VillanuevaMr. BatesNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Module 5 StudentsDocument16 pagesPractical Research 2 Module 5 StudentsCharry CervantesNo ratings yet
- 306112-Barucboc National High School: in Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region S.Y.:2018-2019Document3 pages306112-Barucboc National High School: in Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region S.Y.:2018-2019CeloSaki100% (1)
- Practical Research 2: Second Quarter-Module 12 Formulating RecommendationsDocument21 pagesPractical Research 2: Second Quarter-Module 12 Formulating RecommendationsJAMES JORDAN NasNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Grade 12 Learning Module First QuarterDocument19 pagesPractical Research 2: Grade 12 Learning Module First QuarterItsClarenceNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Session Guide For Learning Action Cell Obs MathDocument5 pagesProposal For Session Guide For Learning Action Cell Obs MathJONATHAN NUNAGNo ratings yet
- Signed Off - Practical Research 2 G12 - 2ndsem - Mod2 - Finding Answers Through Data Collection - v3 PDFDocument10 pagesSigned Off - Practical Research 2 G12 - 2ndsem - Mod2 - Finding Answers Through Data Collection - v3 PDFKay Tracey UrbiztondoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1Document2 pagesPractical Research 1Joderon NimesNo ratings yet
- Frontmatters EIM LM 02.06.15Document5 pagesFrontmatters EIM LM 02.06.15Owen CajarteNo ratings yet
- Adoption ResearchDocument8 pagesAdoption ResearchJemuel FontilaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Department of EducationDocument7 pagesPractical Research 2: Department of EducationLianne LagayanNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document21 pagesPractical Research 2Celina LimNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Department of EducationDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2: Department of EducationLianne LagayanNo ratings yet
- Action PlanDocument2 pagesAction PlanPepito ManlolokoNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch2 g2 Clas8 DrawingConclusions v3Document11 pagesPracticalResearch2 g2 Clas8 DrawingConclusions v3Donabel ReanoNo ratings yet
- On Reshma AssignmentDocument5 pagesOn Reshma Assignmentreshma vijayanNo ratings yet
- Myles Flipped Classroom Paper Revised v3 WDocument7 pagesMyles Flipped Classroom Paper Revised v3 Wapi-299736788No ratings yet
- TQ - PR 2-Quarter 2Document8 pagesTQ - PR 2-Quarter 2Czarina Ciara AndresNo ratings yet
- Shs12 Pracresearch2 q1 SLM Mod Differentiates The Kinds of Variables and Their UsesDocument18 pagesShs12 Pracresearch2 q1 SLM Mod Differentiates The Kinds of Variables and Their UsesCharme Villareal LumbaoNo ratings yet
- Child LaborDocument7 pagesChild LaborJizabell MontifalconNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion MoaDocument8 pagesWork Immersion MoaBea ColanoNo ratings yet
- Fill in The Blank Test ItemsDocument1 pageFill in The Blank Test ItemschristianNo ratings yet
- Focus Group TemplateDocument6 pagesFocus Group TemplateVanna SaoNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom StrategyDocument17 pagesFlipped Classroom StrategyNi Nyoman ParwatiNo ratings yet
- CreativeWriting12 Q2 Mod4 Different-Orientations-Of-CW v2Document25 pagesCreativeWriting12 Q2 Mod4 Different-Orientations-Of-CW v2Rezirri100% (1)
- Practical Research 2: Second Quarter - Module 9 Presentation and Interpretation of DataDocument20 pagesPractical Research 2: Second Quarter - Module 9 Presentation and Interpretation of DataJAMES JORDAN NasNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom Model PDFDocument5 pagesFlipped Classroom Model PDFAlyssa AmigoNo ratings yet
- Chapters Page Final!!!!!!!!!Document42 pagesChapters Page Final!!!!!!!!!Karenclaire RestauroNo ratings yet
- Las Iwrbs Q2 W7Document3 pagesLas Iwrbs Q2 W7JayieepearlNo ratings yet
- Productive PedagogiesDocument31 pagesProductive Pedagogiesortho123No ratings yet
- 3I'S (Week 7-8)Document15 pages3I'S (Week 7-8)AldrinJosephLacuarinNo ratings yet
- SHS Agreement Form EquipmentDocument2 pagesSHS Agreement Form EquipmentPau SilvestreNo ratings yet
- PR1 MODULE 4 No ASDocument21 pagesPR1 MODULE 4 No ASJohnson James AngellanoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1: Quarter 3, LAS 6: Synthesizing Information and Writing Coherent Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesPractical Research 1: Quarter 3, LAS 6: Synthesizing Information and Writing Coherent Literature ReviewAleah AguraNo ratings yet
- Clinging To The Internet: Students and Teachers' Level of Awareness and Effects of CyberbullyingDocument8 pagesClinging To The Internet: Students and Teachers' Level of Awareness and Effects of CyberbullyingAlexa May SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Module 3 For UploadDocument19 pagesPractical Research Module 3 For UploadMa. Lourdes LazaroNo ratings yet
- Prac Research Module 1Document15 pagesPrac Research Module 1Dennis Jade Gascon NumeronNo ratings yet
- April Rose S. Egay: WITH HONORS Is Given ToDocument6 pagesApril Rose S. Egay: WITH HONORS Is Given ToWen Dy NavaNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Students-Parents Virtual Orientation S.Y 2021-2022Document43 pagesSenior High School Students-Parents Virtual Orientation S.Y 2021-2022dennisNo ratings yet
- PracRes2 11 Q3 M15Document16 pagesPracRes2 11 Q3 M15Hikaru Nikki Flores NakamuraNo ratings yet
- Research: Levita Blorecia-Grana, DM, CE SjitDocument56 pagesResearch: Levita Blorecia-Grana, DM, CE Sjitrex hussein lamosteNo ratings yet
- PR 2 5 To 8 PDFDocument30 pagesPR 2 5 To 8 PDFGladys Glo MarceloNo ratings yet
- Word QuizDocument4 pagesWord QuizSumiaspNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 On Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 On Nature and Elements of CommunicationTamina Lameka Dastan100% (1)
- Oral Com Lesson 3 Quarter 1Document13 pagesOral Com Lesson 3 Quarter 1Ivy Lorraine GuillenNo ratings yet
- SPEECH DELIVERY PPTXDocument25 pagesSPEECH DELIVERY PPTXMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- 20 Item QuizDocument4 pages20 Item QuizMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- ORAL COMM PPDocument23 pagesORAL COMM PPMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Impromptu SpeechDocument16 pagesImpromptu SpeechMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- How To Write Application LetterDocument17 pagesHow To Write Application LetterMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Critical ReadingDocument4 pagesCritical ReadingMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Speech StyleDocument4 pagesOral Com Speech StyleMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Elements of DramaDocument12 pagesElements of DramaMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading ActivityDocument1 pageCritical Reading ActivityMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument5 pages21st Century LiteratureMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- CHRISTIANITYDocument12 pagesCHRISTIANITYMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q1 Week5Document2 pagesMath8 Q1 Week5Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- 2nd QUARTER EXAMINATION TOSDocument1 page2nd QUARTER EXAMINATION TOSMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- WHLP Week 1-8 Quarter 1 Oral Comm.Document3 pagesWHLP Week 1-8 Quarter 1 Oral Comm.Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- FDocument1 pageFMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2: Practical Research 2Document40 pagesQuarter 2: Practical Research 2Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- English11 q1 Module 1 8 Oral Communication in Context v1 RevisedDocument41 pagesEnglish11 q1 Module 1 8 Oral Communication in Context v1 RevisedMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Pnpki: Philippine National Public Key InfrastructureDocument9 pagesPnpki: Philippine National Public Key InfrastructureMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- NEW - REVISED - Oral Comm Q2 Wk7Document8 pagesNEW - REVISED - Oral Comm Q2 Wk7Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Pbulic Key Infrastracture (Pnpki) : Red-ColoredDocument3 pagesPhilippine National Pbulic Key Infrastracture (Pnpki) : Red-ColoredMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument7 pagesAction ResearchMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Final Proposal Template 2Document4 pagesFinal Proposal Template 2Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Doggy MilDocument2 pagesDoggy MilMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Invasive Species 2 Volumes - From Africanized Honey Bees To Zebra Mussels (PDFDrive)Document873 pagesEncyclopedia of Invasive Species 2 Volumes - From Africanized Honey Bees To Zebra Mussels (PDFDrive)medNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial DNADocument6 pagesEntrepreneurial DNADylan GregerNo ratings yet
- Lorenz 1986Document10 pagesLorenz 1986Jessica Lienlaf RojasNo ratings yet
- Art Quarter3 UnitTestDocument2 pagesArt Quarter3 UnitTestPatrick RodriguezNo ratings yet
- SCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020Document11 pagesSCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020JoanNo ratings yet
- University of Illinois The Grainger College of EngineeringDocument5 pagesUniversity of Illinois The Grainger College of EngineeringVinamr SachdevaNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument22 pagesMechanismssilva, april joy c.No ratings yet
- Saribuhay (News) - FINALDocument1 pageSaribuhay (News) - FINALJEREMAEH DELOSANo ratings yet
- One Felco Wh4 Fdas Osm - RemovedDocument3 pagesOne Felco Wh4 Fdas Osm - Removedjezer busbusNo ratings yet
- Craft Revival ProjectDocument3 pagesCraft Revival Projectkoshalsra3No ratings yet
- Act 1Document5 pagesAct 1Yue YueNo ratings yet
- Hjørland, B. (1998) Theory and Metatheory of Information Science. A New Interpretation. Journal of Documentation 54 (5) 606-621.Document17 pagesHjørland, B. (1998) Theory and Metatheory of Information Science. A New Interpretation. Journal of Documentation 54 (5) 606-621.Raul TorresNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 Elements of ClimateDocument8 pages1 - 1 Elements of Climatekhalfani jumaNo ratings yet
- On The Ocean Floor - AltDocument2 pagesOn The Ocean Floor - AltLance0016No ratings yet
- Oral Communication Mod2 Week 2Document5 pagesOral Communication Mod2 Week 2Josie EscalaNo ratings yet
- For English CriticDocument2 pagesFor English CriticSari Sari Store VideoNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior and Sustainable MarketingDocument14 pagesConsumer Behavior and Sustainable Marketinglon choNo ratings yet
- Constructing Basestations July27 RanjithDocument6 pagesConstructing Basestations July27 RanjithAkash MahalikNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationDocument11 pages1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationMohamed Elsir100% (1)
- EC 02 - Species - GM BinderDocument114 pagesEC 02 - Species - GM BinderAlbyNo ratings yet
- 1 - PilotSPM206 Branch Circuit Power Meter Catalog (KVA) (230523 - CUN - B)Document4 pages1 - PilotSPM206 Branch Circuit Power Meter Catalog (KVA) (230523 - CUN - B)KhairilMunawarNo ratings yet
- (Bradford Books) Sidney I. Wiener, Jeffrey S. Taube - Head Direction Cells and The Neural Mechanisms of Spatial Orientation-The MIT Press (2005)Document503 pages(Bradford Books) Sidney I. Wiener, Jeffrey S. Taube - Head Direction Cells and The Neural Mechanisms of Spatial Orientation-The MIT Press (2005)Víctor FuentesNo ratings yet
- Hedlin Novian Napitupulu Tugas3Document7 pagesHedlin Novian Napitupulu Tugas3hedlinbarcelona10 hedlinNo ratings yet
- NeurotechnologyDocument3 pagesNeurotechnologyLorna Mae MontanezNo ratings yet
- Sepl Esr GSRDocument4 pagesSepl Esr GSRSyed Mohd MehdiNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 (Linked List)Document12 pagesLec 3 (Linked List)Dr LolaNo ratings yet
- Physiological FeelingsDocument202 pagesPhysiological Feelingsoscarin123456789No ratings yet
- Free Vibration Analysis of Dragonfly Wings Using Finite Element MethodDocument10 pagesFree Vibration Analysis of Dragonfly Wings Using Finite Element Methodhiral gohilNo ratings yet
- RPMI-1640: With L-Glutamine Without Glucose and Sodium Bicarbonate Product Code: AT150Document2 pagesRPMI-1640: With L-Glutamine Without Glucose and Sodium Bicarbonate Product Code: AT150Gayathri MaigandanNo ratings yet
CHAPTER Test in Oral Communication in Context
CHAPTER Test in Oral Communication in Context
Uploaded by
Marilou Iamztol RecamaraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER Test in Oral Communication in Context
CHAPTER Test in Oral Communication in Context
Uploaded by
Marilou Iamztol RecamaraCopyright:
Available Formats
First Quarter Examination
ORAL COMMUNICATION IN CONTEXT 11
DAPITAN CITY NATL HIGH SCHOOL
Name:_______________________________ Grade & Section: __________________
TEST I: TRUE OR FALSE: Shade TRUE if the statement is correct and shade FALSE if otherwise.
1. Communication is very vital to our everyday lives.
TRUE FALSE
2. We cannot live without communicating because we need to share thoughts, impart
information, persuade others of our beliefs, and show our love and affection.
TRUE FALSE
3. Communication is a systematic process in which individuals interact with and through
symbols to create and interpret meanings.
TRUE FALSE
4. Communication is symbolic and involves meanings.
TRUE FALSE
5. Communication happens only when two or more people talk with each other
TRUE FALSE
TEST II: Identify what is being described in each statement below. Shade the letter
that corresponds to your answer.
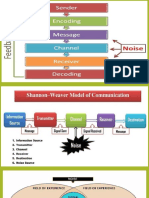
1. It is anything that impedes or gets in the way of accurately sending, receiving, and
interpreting the message, whether it be internal or external.
a. noise /interference
b. Listener/receiver
c. Speaker/sender
d. medium/language
2. He/She gets the message in the medium desired through the chosen channel, and
decodes the message.
a. noise /interference
b. Listener/receiver
c. Speaker/sender
d. medium/language
3. It is the situation or environment in which communication takes place, which includes
time, place, and event, as well as the sender’s and receiver’s feelings, perceptions,
beliefs, attitudes and relationships.
a. message
b. feedback
c. channel
d. context
4. It refers to the source of the message that is encoded into symbols that are verbal and/or
nonverbal.
a. noise /interference
b. Listener/receiver
c. Speaker/sender
d. medium/language
5. It is any information or anything the speaker/sender wants to communicate by using a
medium.
a. noise /interference
b. Listener/receiver
c. Speaker/sender
d. medium/language
6. It is the receiver’s response, verbally or nonverbally.
a. noise /interference
b. Listener/receiver
c. feedback
d. channel
TEST III: Read each given scenario/situation. Then, identify the kind of noise being
presented as INTERNAL NOISE or EXTERNAL NOISE. Shade the letter that corresponds to
your answer.
1. A teacher lectures while a passing motorcycle hoots its horns.
INTERNAL NOISE EXTERNAL NOISE
2. A student thinking about a quiz he has to take in the next class.
INTERNAL NOISE EXTERNAL NOISE
3. A child busily plays with his tablet while his mom is giving him instructions.
INTERNAL NOISE EXTERNAL NOISE
4. A speaker in a seminar explains a certain product when a cellular phone rings.
INTERNAL NOISE EXTERNAL NOISE
5. A professor lectures and coughs continuously
INTERNAL NOISE EXTERNAL NOISE
TEST II: Identify what is being described in each statement below. Shade the letter
that corresponds to your answer.
7. It is anything that impedes or gets in the way of accurately sending, receiving, and
interpreting the message, whether it be internal or external.
e. noise /interference
f. Listener/receiver
g. Speaker/sender
h. medium/language
8. He/She gets the message in the medium desired through the chosen channel, and
decodes the message.
e. noise /interference
f. Listener/receiver
g. Speaker/sender
h. medium/language
9. It is the situation or environment in which communication takes place, which includes
time, place, and event, as well as the sender’s and receiver’s feelings, perceptions,
beliefs, attitudes and relationships.
e. message
f. feedback
g. channel
h. context
10. It refers to the source of the message that is encoded into symbols that are verbal
and/or nonverbal.
e. noise /interference
f. Listener/receiver
g. Speaker/sender
h. medium/language
11. It is any information or anything the speaker/sender wants to communicate by
using a medium.
e. noise /interference
f. Listener/receiver
g. Speaker/sender
h. medium/language
12. It is the receiver’s response, verbally or nonverbally.
e. noise /interference
f. Listener/receiver
g. feedback
h. channel
6. The editor-in-chief of a magazine decides to pull out one article because the topic is too
sensitive for its readers.
a. Shannon-Weaver Model
b. Interactive Model
c. Schramm Model
d. Intermediary Model
7. A call center agent persuades a client through phone to purchase a new product from their
company.
a. Shannon-Weaver Model
b. Interactive Model
c. Schramm Model
d. Intermediary Model
8. High school best friends Millette and Geline met again after 20 years. They reminisced
about their high school days and shared some common experiences.
a. Shannon-Weaver Model
b. Interactive Model
c. Schramm Model
d. Intermediary Model
9. A reviewer of a peer-reviewed publication disapproves a study because it did not meet the
qualifications or standards set by the committee.
a. Shannon-Weaver Model
b. Interactive Model
c. Schramm Model
d. Intermediary Model
10. A well-known TV news anchor reports from a remote area where the signal is
erratic. Therefore, TV viewers had a problem understanding the news because of the
unclear signal.
a. Shannon-Weaver Model
b. Interactive Model
c. Schramm Model
d. Intermediary Model
11. A daughter sends a text message to her mother and asks permission to go to her
classmate’s house after school to finish a particular project. The daughter finds it hard to
decide if she can go because her mother has not replied to her message.
a. Shannon-Weaver Model
b. Interactive Model
c. Schramm Model
d. Intermediary Model
You might also like
- Case Studies TestDocument3 pagesCase Studies TestMayank Sharma0% (1)
- Each Student Should Strictly Follow The Format Given Below For His/her Research ProjectDocument7 pagesEach Student Should Strictly Follow The Format Given Below For His/her Research ProjectAnsari WarisNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2-Module 4 (Q1 Wk9)Document23 pagesPractical Research 2-Module 4 (Q1 Wk9)Mizchyne CaburogNo ratings yet
- PR 1 WK 4 - LASDocument10 pagesPR 1 WK 4 - LASAleah AguraNo ratings yet
- Action Plan Reading ProgramsDocument5 pagesAction Plan Reading ProgramsMA ASTERIA AGUSTINA CENALNo ratings yet
- Flipped PDFDocument18 pagesFlipped PDFIsabel GMNo ratings yet
- Applied - 11 - Research in Daily Life 1 - semII - CLAS8 - Analyzing and Drawing Out Patterns and Themes With Intellectual Honesty - v2 PNS PDFDocument15 pagesApplied - 11 - Research in Daily Life 1 - semII - CLAS8 - Analyzing and Drawing Out Patterns and Themes With Intellectual Honesty - v2 PNS PDFAnya LiggayuNo ratings yet
- Final Term Examination in ICT 11Document3 pagesFinal Term Examination in ICT 11Boyong ManatadNo ratings yet
- ORALCOMM - Chapter 1.5 Intercultural CommunicationDocument24 pagesORALCOMM - Chapter 1.5 Intercultural CommunicationJasminNo ratings yet
- The Flipped Classroom UNiv - LeichesterDocument28 pagesThe Flipped Classroom UNiv - LeichesterEmanuele ViciniNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Activity-Sheet-OCC PDFDocument1 pageModule 1-Activity-Sheet-OCC PDFAMYTHEEZ CAMOMOTNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Department of EducationDocument9 pagesPractical Research 2: Department of EducationLianne LagayanNo ratings yet
- 01032022095126SHS PR2 Q2 M6 Val - withPOSTTESTDocument14 pages01032022095126SHS PR2 Q2 M6 Val - withPOSTTESTJAMES JORDAN NasNo ratings yet
- P8yqp15lr Module 8 Creative WritingDocument8 pagesP8yqp15lr Module 8 Creative WritingSteve Laurence PontilloNo ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela Form 4 Daily Attendance of VolunteerDocument3 pagesBrigada Eskwela Form 4 Daily Attendance of VolunteerGileta MarananNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 1: Qualitative Research Designs, Sample, and Data Collection and Analysis ProceduresDocument14 pagesResearch in Daily Life 1: Qualitative Research Designs, Sample, and Data Collection and Analysis ProceduresAnya LiggayuNo ratings yet
- Flipped Inclusion Classroom Action Research Jeanette VillanuevaDocument16 pagesFlipped Inclusion Classroom Action Research Jeanette VillanuevaMr. BatesNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Module 5 StudentsDocument16 pagesPractical Research 2 Module 5 StudentsCharry CervantesNo ratings yet
- 306112-Barucboc National High School: in Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region S.Y.:2018-2019Document3 pages306112-Barucboc National High School: in Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region S.Y.:2018-2019CeloSaki100% (1)
- Practical Research 2: Second Quarter-Module 12 Formulating RecommendationsDocument21 pagesPractical Research 2: Second Quarter-Module 12 Formulating RecommendationsJAMES JORDAN NasNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Grade 12 Learning Module First QuarterDocument19 pagesPractical Research 2: Grade 12 Learning Module First QuarterItsClarenceNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Session Guide For Learning Action Cell Obs MathDocument5 pagesProposal For Session Guide For Learning Action Cell Obs MathJONATHAN NUNAGNo ratings yet
- Signed Off - Practical Research 2 G12 - 2ndsem - Mod2 - Finding Answers Through Data Collection - v3 PDFDocument10 pagesSigned Off - Practical Research 2 G12 - 2ndsem - Mod2 - Finding Answers Through Data Collection - v3 PDFKay Tracey UrbiztondoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1Document2 pagesPractical Research 1Joderon NimesNo ratings yet
- Frontmatters EIM LM 02.06.15Document5 pagesFrontmatters EIM LM 02.06.15Owen CajarteNo ratings yet
- Adoption ResearchDocument8 pagesAdoption ResearchJemuel FontilaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Department of EducationDocument7 pagesPractical Research 2: Department of EducationLianne LagayanNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document21 pagesPractical Research 2Celina LimNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Department of EducationDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2: Department of EducationLianne LagayanNo ratings yet
- Action PlanDocument2 pagesAction PlanPepito ManlolokoNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch2 g2 Clas8 DrawingConclusions v3Document11 pagesPracticalResearch2 g2 Clas8 DrawingConclusions v3Donabel ReanoNo ratings yet
- On Reshma AssignmentDocument5 pagesOn Reshma Assignmentreshma vijayanNo ratings yet
- Myles Flipped Classroom Paper Revised v3 WDocument7 pagesMyles Flipped Classroom Paper Revised v3 Wapi-299736788No ratings yet
- TQ - PR 2-Quarter 2Document8 pagesTQ - PR 2-Quarter 2Czarina Ciara AndresNo ratings yet
- Shs12 Pracresearch2 q1 SLM Mod Differentiates The Kinds of Variables and Their UsesDocument18 pagesShs12 Pracresearch2 q1 SLM Mod Differentiates The Kinds of Variables and Their UsesCharme Villareal LumbaoNo ratings yet
- Child LaborDocument7 pagesChild LaborJizabell MontifalconNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion MoaDocument8 pagesWork Immersion MoaBea ColanoNo ratings yet
- Fill in The Blank Test ItemsDocument1 pageFill in The Blank Test ItemschristianNo ratings yet
- Focus Group TemplateDocument6 pagesFocus Group TemplateVanna SaoNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom StrategyDocument17 pagesFlipped Classroom StrategyNi Nyoman ParwatiNo ratings yet
- CreativeWriting12 Q2 Mod4 Different-Orientations-Of-CW v2Document25 pagesCreativeWriting12 Q2 Mod4 Different-Orientations-Of-CW v2Rezirri100% (1)
- Practical Research 2: Second Quarter - Module 9 Presentation and Interpretation of DataDocument20 pagesPractical Research 2: Second Quarter - Module 9 Presentation and Interpretation of DataJAMES JORDAN NasNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom Model PDFDocument5 pagesFlipped Classroom Model PDFAlyssa AmigoNo ratings yet
- Chapters Page Final!!!!!!!!!Document42 pagesChapters Page Final!!!!!!!!!Karenclaire RestauroNo ratings yet
- Las Iwrbs Q2 W7Document3 pagesLas Iwrbs Q2 W7JayieepearlNo ratings yet
- Productive PedagogiesDocument31 pagesProductive Pedagogiesortho123No ratings yet
- 3I'S (Week 7-8)Document15 pages3I'S (Week 7-8)AldrinJosephLacuarinNo ratings yet
- SHS Agreement Form EquipmentDocument2 pagesSHS Agreement Form EquipmentPau SilvestreNo ratings yet
- PR1 MODULE 4 No ASDocument21 pagesPR1 MODULE 4 No ASJohnson James AngellanoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1: Quarter 3, LAS 6: Synthesizing Information and Writing Coherent Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesPractical Research 1: Quarter 3, LAS 6: Synthesizing Information and Writing Coherent Literature ReviewAleah AguraNo ratings yet
- Clinging To The Internet: Students and Teachers' Level of Awareness and Effects of CyberbullyingDocument8 pagesClinging To The Internet: Students and Teachers' Level of Awareness and Effects of CyberbullyingAlexa May SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Module 3 For UploadDocument19 pagesPractical Research Module 3 For UploadMa. Lourdes LazaroNo ratings yet
- Prac Research Module 1Document15 pagesPrac Research Module 1Dennis Jade Gascon NumeronNo ratings yet
- April Rose S. Egay: WITH HONORS Is Given ToDocument6 pagesApril Rose S. Egay: WITH HONORS Is Given ToWen Dy NavaNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Students-Parents Virtual Orientation S.Y 2021-2022Document43 pagesSenior High School Students-Parents Virtual Orientation S.Y 2021-2022dennisNo ratings yet
- PracRes2 11 Q3 M15Document16 pagesPracRes2 11 Q3 M15Hikaru Nikki Flores NakamuraNo ratings yet
- Research: Levita Blorecia-Grana, DM, CE SjitDocument56 pagesResearch: Levita Blorecia-Grana, DM, CE Sjitrex hussein lamosteNo ratings yet
- PR 2 5 To 8 PDFDocument30 pagesPR 2 5 To 8 PDFGladys Glo MarceloNo ratings yet
- Word QuizDocument4 pagesWord QuizSumiaspNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 On Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 On Nature and Elements of CommunicationTamina Lameka Dastan100% (1)
- Oral Com Lesson 3 Quarter 1Document13 pagesOral Com Lesson 3 Quarter 1Ivy Lorraine GuillenNo ratings yet
- SPEECH DELIVERY PPTXDocument25 pagesSPEECH DELIVERY PPTXMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- 20 Item QuizDocument4 pages20 Item QuizMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- ORAL COMM PPDocument23 pagesORAL COMM PPMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Impromptu SpeechDocument16 pagesImpromptu SpeechMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- How To Write Application LetterDocument17 pagesHow To Write Application LetterMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Critical ReadingDocument4 pagesCritical ReadingMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Speech StyleDocument4 pagesOral Com Speech StyleMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Elements of DramaDocument12 pagesElements of DramaMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading ActivityDocument1 pageCritical Reading ActivityMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument5 pages21st Century LiteratureMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- CHRISTIANITYDocument12 pagesCHRISTIANITYMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q1 Week5Document2 pagesMath8 Q1 Week5Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- 2nd QUARTER EXAMINATION TOSDocument1 page2nd QUARTER EXAMINATION TOSMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- WHLP Week 1-8 Quarter 1 Oral Comm.Document3 pagesWHLP Week 1-8 Quarter 1 Oral Comm.Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- FDocument1 pageFMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2: Practical Research 2Document40 pagesQuarter 2: Practical Research 2Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- English11 q1 Module 1 8 Oral Communication in Context v1 RevisedDocument41 pagesEnglish11 q1 Module 1 8 Oral Communication in Context v1 RevisedMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Pnpki: Philippine National Public Key InfrastructureDocument9 pagesPnpki: Philippine National Public Key InfrastructureMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- NEW - REVISED - Oral Comm Q2 Wk7Document8 pagesNEW - REVISED - Oral Comm Q2 Wk7Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Pbulic Key Infrastracture (Pnpki) : Red-ColoredDocument3 pagesPhilippine National Pbulic Key Infrastracture (Pnpki) : Red-ColoredMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument7 pagesAction ResearchMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Final Proposal Template 2Document4 pagesFinal Proposal Template 2Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Doggy MilDocument2 pagesDoggy MilMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Invasive Species 2 Volumes - From Africanized Honey Bees To Zebra Mussels (PDFDrive)Document873 pagesEncyclopedia of Invasive Species 2 Volumes - From Africanized Honey Bees To Zebra Mussels (PDFDrive)medNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial DNADocument6 pagesEntrepreneurial DNADylan GregerNo ratings yet
- Lorenz 1986Document10 pagesLorenz 1986Jessica Lienlaf RojasNo ratings yet
- Art Quarter3 UnitTestDocument2 pagesArt Quarter3 UnitTestPatrick RodriguezNo ratings yet
- SCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020Document11 pagesSCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020JoanNo ratings yet
- University of Illinois The Grainger College of EngineeringDocument5 pagesUniversity of Illinois The Grainger College of EngineeringVinamr SachdevaNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument22 pagesMechanismssilva, april joy c.No ratings yet
- Saribuhay (News) - FINALDocument1 pageSaribuhay (News) - FINALJEREMAEH DELOSANo ratings yet
- One Felco Wh4 Fdas Osm - RemovedDocument3 pagesOne Felco Wh4 Fdas Osm - Removedjezer busbusNo ratings yet
- Craft Revival ProjectDocument3 pagesCraft Revival Projectkoshalsra3No ratings yet
- Act 1Document5 pagesAct 1Yue YueNo ratings yet
- Hjørland, B. (1998) Theory and Metatheory of Information Science. A New Interpretation. Journal of Documentation 54 (5) 606-621.Document17 pagesHjørland, B. (1998) Theory and Metatheory of Information Science. A New Interpretation. Journal of Documentation 54 (5) 606-621.Raul TorresNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 Elements of ClimateDocument8 pages1 - 1 Elements of Climatekhalfani jumaNo ratings yet
- On The Ocean Floor - AltDocument2 pagesOn The Ocean Floor - AltLance0016No ratings yet
- Oral Communication Mod2 Week 2Document5 pagesOral Communication Mod2 Week 2Josie EscalaNo ratings yet
- For English CriticDocument2 pagesFor English CriticSari Sari Store VideoNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior and Sustainable MarketingDocument14 pagesConsumer Behavior and Sustainable Marketinglon choNo ratings yet
- Constructing Basestations July27 RanjithDocument6 pagesConstructing Basestations July27 RanjithAkash MahalikNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationDocument11 pages1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationMohamed Elsir100% (1)
- EC 02 - Species - GM BinderDocument114 pagesEC 02 - Species - GM BinderAlbyNo ratings yet
- 1 - PilotSPM206 Branch Circuit Power Meter Catalog (KVA) (230523 - CUN - B)Document4 pages1 - PilotSPM206 Branch Circuit Power Meter Catalog (KVA) (230523 - CUN - B)KhairilMunawarNo ratings yet
- (Bradford Books) Sidney I. Wiener, Jeffrey S. Taube - Head Direction Cells and The Neural Mechanisms of Spatial Orientation-The MIT Press (2005)Document503 pages(Bradford Books) Sidney I. Wiener, Jeffrey S. Taube - Head Direction Cells and The Neural Mechanisms of Spatial Orientation-The MIT Press (2005)Víctor FuentesNo ratings yet
- Hedlin Novian Napitupulu Tugas3Document7 pagesHedlin Novian Napitupulu Tugas3hedlinbarcelona10 hedlinNo ratings yet
- NeurotechnologyDocument3 pagesNeurotechnologyLorna Mae MontanezNo ratings yet
- Sepl Esr GSRDocument4 pagesSepl Esr GSRSyed Mohd MehdiNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 (Linked List)Document12 pagesLec 3 (Linked List)Dr LolaNo ratings yet
- Physiological FeelingsDocument202 pagesPhysiological Feelingsoscarin123456789No ratings yet
- Free Vibration Analysis of Dragonfly Wings Using Finite Element MethodDocument10 pagesFree Vibration Analysis of Dragonfly Wings Using Finite Element Methodhiral gohilNo ratings yet
- RPMI-1640: With L-Glutamine Without Glucose and Sodium Bicarbonate Product Code: AT150Document2 pagesRPMI-1640: With L-Glutamine Without Glucose and Sodium Bicarbonate Product Code: AT150Gayathri MaigandanNo ratings yet