Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activate 1 Biology Chapter1 Answers
Activate 1 Biology Chapter1 Answers
Uploaded by
John LebizCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- b1 Cell Structure and Transport Exam QsDocument38 pagesb1 Cell Structure and Transport Exam QsMary Ann MaherNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz100% (1)
- Activate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz100% (1)
- AQA Biology: 1 Biological Molecules Exam-Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesAQA Biology: 1 Biological Molecules Exam-Style QuestionsreneehandsNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 Physics Chapter1 AnswersDocument5 pagesActivate 1 Physics Chapter1 AnswersPapi Parikh100% (1)
- Hostel Allocation System C++ ProjectDocument18 pagesHostel Allocation System C++ ProjectSuruchi Jha100% (1)
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 Chemistry Chapter1 AnswersDocument5 pagesActivate 1 Chemistry Chapter1 AnswersAlex Lim100% (1)
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Student Book Answers - Physics 1 Chapter 2Document5 pagesStudent Book Answers - Physics 1 Chapter 2Mhmd AlrashedNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Questions StudentDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Questions Studentapi-299996815No ratings yet
- The Robots Are Coming The Robots Are ComingDocument5 pagesThe Robots Are Coming The Robots Are Comingapi-272551013No ratings yet
- 9Bb-6 Leaves and RootsDocument1 page9Bb-6 Leaves and RootsHAMAD NoorNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz0% (1)
- Activate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- 4 - Unicellular Structural AdaptationsDocument12 pages4 - Unicellular Structural AdaptationsNayani Snigdha0% (1)
- P3 Chapter 1 End-Of-Chapter Test (Foundation)Document6 pagesP3 Chapter 1 End-Of-Chapter Test (Foundation)Paul LloydNo ratings yet
- Topic 8: Transport in PlantsDocument18 pagesTopic 8: Transport in PlantsCOXMIC FNNo ratings yet
- Biology IGCSE CellDocument30 pagesBiology IGCSE CellUmm ArafaNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocument51 pages12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- Test 1 Chapter 5: Cell Division Sub Topic: Mitosis: BPK/Biology Item /Method1-Analogy & Role Play1/MitosisDocument3 pagesTest 1 Chapter 5: Cell Division Sub Topic: Mitosis: BPK/Biology Item /Method1-Analogy & Role Play1/MitosisYan MLNo ratings yet
- Specialised-Cells-Worksheet - Combined ScienceDocument3 pagesSpecialised-Cells-Worksheet - Combined ScienceBachittar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Use The Table Above To Fill in The ChartDocument5 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet Use The Table Above To Fill in The ChartRachel Ann EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- KS3 Light 2Document46 pagesKS3 Light 2Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- 2.1 Formative Assessment Biology BookDocument1 page2.1 Formative Assessment Biology Bookabdullah adNo ratings yet
- Amoeba, Euglena, Spirogyra, Paramecium: CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesAmoeba, Euglena, Spirogyra, Paramecium: CharacteristicsMac SensNo ratings yet
- Specialised CellsDocument9 pagesSpecialised CellsJanah Pauline AbunganNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Light and SoundDocument11 pagesYear 8 Light and SoundCinara RahimovaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Digestion and Absorption Revision Notes PDFDocument24 pagesBiology - Digestion and Absorption Revision Notes PDFanna robertsonNo ratings yet
- Interdependence and Food WebsDocument3 pagesInterdependence and Food WebsArchieNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFDocument50 pagesCell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFRozel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells - WorksheetDocument4 pagesPlant and Animal Cells - WorksheetsabaNo ratings yet
- Checked - Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene Technology - Exam BookletDocument63 pagesChecked - Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene Technology - Exam BookletEllane leeNo ratings yet
- 3.2 MicroscopeDocument30 pages3.2 Microscopesudirman0103651972No ratings yet
- Sats QuestionsDocument9 pagesSats Questionsapi-3800318No ratings yet
- Chem12015 ExamDocument16 pagesChem12015 ExamAAVANINo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet: (Assume That The Sugar Molecules Can Pass Through The Cell Membrane in Each Case.)Document2 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Worksheet: (Assume That The Sugar Molecules Can Pass Through The Cell Membrane in Each Case.)Cavene Scott100% (1)
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Periodic Table ks3Document3 pagesWorksheet Periodic Table ks3Miku ChanNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Cell Membranes and Transport Worksheet: Name: - Class: XI SCIENCEDocument5 pagesAs-Level Biology Cell Membranes and Transport Worksheet: Name: - Class: XI SCIENCEDina Anggraini Pramitasari100% (2)
- Cie Alevel BiologyDocument24 pagesCie Alevel BiologyArun Ghatan100% (2)
- Living and Nonliving NotesDocument2 pagesLiving and Nonliving NotesRobNo ratings yet
- Patterns of InheritanceDocument26 pagesPatterns of InheritanceVidhya NairNo ratings yet
- Electricity Worksheet Page 2Document1 pageElectricity Worksheet Page 2Laura LucumiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 SCIENCE QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesGrade 9 SCIENCE QUESTIONSSharreah LimNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument14 pagesActive TransportRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument32 pagesStates of MatterKeith BansrajNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision GuideDocument22 pagesBiology Revision GuidePoornima AthikariNo ratings yet
- Biology As A2 CombinedDocument253 pagesBiology As A2 CombinedKulsoom JawedNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemAbdurahmaan RaikarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1Document14 pagesEdexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1seif nimerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Science Module Form 1 - Chapter 2Document13 pagesChapter 2: Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Science Module Form 1 - Chapter 2Thiba KrishnanNo ratings yet
- How Can We Study The Living WorldDocument9 pagesHow Can We Study The Living WorldFarah TaimoorNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Organism (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDocument16 pagesOrganisation of The Organism (Multiple Choice) 1 QPNatalie RossetteNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument14 pagesTransport in PlantsMuhammad Faizan KaleemNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesRumaisa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 November 1999Document5 pagesPaper 2 November 1999MSHNo ratings yet
- Science Equipments Mathematics Equipment: Item Description Qty. UnitDocument5 pagesScience Equipments Mathematics Equipment: Item Description Qty. UnitJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Science Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12From EverandScience Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12No ratings yet
- GR 9 NS Cell Worksheet MemoDocument4 pagesGR 9 NS Cell Worksheet MemoSyrus ZambiaNo ratings yet
- BC Science 8 Workbook AnswersDocument22 pagesBC Science 8 Workbook Answersi. zNo ratings yet
- 7 SolubilityDocument4 pages7 SolubilityJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Mynard JoDocument13 pagesMynard JoJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W9Document1 pageT1W9John LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W4 (Revision)Document4 pagesT1W4 (Revision)John LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W10Document1 pageT1W10John LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Booking Confirmation - 28342216136Document2 pagesBooking Confirmation - 28342216136John LebizNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Physics Worksheet 1Document3 pagesGrade 7 Physics Worksheet 1John LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz0% (1)
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- NPS International SchoolDocument2 pagesNPS International SchoolJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- 1a (I) (1) (A) (Ii) (1) (A) (Iii) (1) (Iv) (1) B (1) (1) (1) Number Mark 2 (A)Document2 pages1a (I) (1) (A) (Ii) (1) (A) (Iii) (1) (Iv) (1) B (1) (1) (1) Number Mark 2 (A)John LebizNo ratings yet
- Practice Abstract Reasoning Test 1 - With ExplanationsDocument9 pagesPractice Abstract Reasoning Test 1 - With ExplanationsEliah Lopez0% (1)
- Astrovega May 2024Document44 pagesAstrovega May 2024VARA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Final1 PDFDocument10 pagesFinal1 PDFAngelica SantiagoNo ratings yet
- JD Asistent Manager - ENDocument4 pagesJD Asistent Manager - ENMihaela RaduNo ratings yet
- PA - StocksDocument36 pagesPA - Stocksikolev57No ratings yet
- Xii CH 1 PPT 1Document92 pagesXii CH 1 PPT 1jiyanshi yadavNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Heineken BeerDocument13 pagesPresentation On Heineken BeerΣόλα ΚαρίμοβαNo ratings yet
- Bradburn Et Al v. North Central Regional Library District - Document No. 57Document28 pagesBradburn Et Al v. North Central Regional Library District - Document No. 57Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering ActivitiesDocument3 pagesData Gathering ActivitiesKyla PapaNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On Shri Ram Piston and Rings LimitedDocument89 pagesSummer Training Report On Shri Ram Piston and Rings LimitedKevin Joy75% (4)
- CONFIRMALDocument50 pagesCONFIRMALSri SaiNo ratings yet
- PPC DrainDocument6 pagesPPC Drainherysyam1980No ratings yet
- BT1 Handout - 01 Concrete (REV20210114)Document11 pagesBT1 Handout - 01 Concrete (REV20210114)Jano AgbigayNo ratings yet
- PROCESS AND ART. OSKAR HANSEN AND HIS CONCEPT OF VARIABLE ARCHITECTURE - Contemporary Lynx - Promoting Polish Art in The WorldDocument13 pagesPROCESS AND ART. OSKAR HANSEN AND HIS CONCEPT OF VARIABLE ARCHITECTURE - Contemporary Lynx - Promoting Polish Art in The WorldBen GreenNo ratings yet
- EG III Generator Unit ManualDocument15 pagesEG III Generator Unit ManualLIVIANo ratings yet
- Active Certificates: A Framework For DelegationDocument39 pagesActive Certificates: A Framework For DelegationBruno CrispoNo ratings yet
- Access 4 TEST MODULE 1Document5 pagesAccess 4 TEST MODULE 1Stai4eNo ratings yet
- Stage 1 English Curriculum Framework PDFDocument2 pagesStage 1 English Curriculum Framework PDFMangunatun KhasanahNo ratings yet
- APICS BSCM Chapter 1 NotesDocument11 pagesAPICS BSCM Chapter 1 NotesvayugaramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NematodesDocument5 pagesChapter 8 NematodesJuju GalangNo ratings yet
- Session-10 Assignment Name: Dharmi Javiya Enroll No: 92100133058Document3 pagesSession-10 Assignment Name: Dharmi Javiya Enroll No: 92100133058Dharmi JaviyaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Beauty Parlour Managment' She Guided Us in Preparation of The Project andDocument23 pagesAcknowledgement: Beauty Parlour Managment' She Guided Us in Preparation of The Project andKomal DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 5070 s12 QP 21 PDFDocument20 pages5070 s12 QP 21 PDFNeural Spark Physics CieNo ratings yet
- Bohemian Rhapsody (Ukulele Tab)Document4 pagesBohemian Rhapsody (Ukulele Tab)crojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Interstate-Mcbee Sensors: Serving The Diesel and Natural Gas Industry For Over 60 YearsDocument1 pageInterstate-Mcbee Sensors: Serving The Diesel and Natural Gas Industry For Over 60 YearsRicardoNo ratings yet
- NFL Network ResumeDocument2 pagesNFL Network Resumeapi-314448476No ratings yet
- En - mb997 F407VGT6 E01 SchematicDocument9 pagesEn - mb997 F407VGT6 E01 SchematicBharath Kumar Reddy MNo ratings yet
- 'NEXtCARE Corporate Profile 5Document1 page'NEXtCARE Corporate Profile 5Rajesh PotluriNo ratings yet
Activate 1 Biology Chapter1 Answers
Activate 1 Biology Chapter1 Answers
Uploaded by
John LebizOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activate 1 Biology Chapter1 Answers
Activate 1 Biology Chapter1 Answers
Uploaded by
John LebizCopyright:
Available Formats
Student book answers
Chapter 1
Biology B1 Unit Opener
Picture Puzzler: chin, egg, leaf, leg
Key Words The key word is cell.
Picture Puzzler: an amoeba cell
Close up
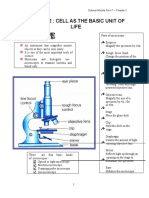
B1 1.1 Observing cells
In-text questions A cells
B Cork cells, that looked like tiny rooms.
C Looking carefully/in detail at an object.
D eye piece
Activity Magnification
(10 × 50 =) × 500
Summary 1 cells, building, observe, microscope, magnifies (5 marks)
questions 2a magnifies object (1 mark)
b holds microscope slide (or object) you are observing (1 mark)
c produce a clear image of the object (1 mark)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
Plant and animal cells share several components.
They each have a nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and mitochondria. Plant cells also
have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a vacuole.
Both cell types can respire.
This is due to the presence of mitochondria in both types of cells. Only plant cells can
photosynthesise.
This is because only plant cells have chloroplasts.
B1 1.2 Plant and animal cells
In-text questions A nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria
B Controls the cell/contains genetic material.
C cell wall, chloroplast, vacuole
D cell sap
Activity Prefixes
Bio- = life; biology, biography
Photo- = light; photograph, photographer
Micro- = small; microscope, microwave
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 1
Summary 1 vacuole – contains cell sap to keep the cell firm
questions nucleus – controls the cell’s activities
cell wall – rigid structure that supports the cell cytoplasm – where chemical reactions
take place chloroplast – where photosynthesis occurs
cell membrane – controls what comes in and out of a cell mitochondria – where
respiration occurs (7 marks)
2a leaf cells (1 mark)
b Leaf cells require chlorophyll to be able to photosynthesise. (1 mark)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
Animal cells and plant cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and
mitochondria. Plant cells also have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a vacuole.
Both cell types can respire (due to the presence of mitochondria).
Only plant cells can photosynthesise (due to the presence of chloroplasts).
B1 1.3 Specialised cells
In-text questions A Cells that can perform particular functions/jobs.
B Transmit messages/electrical impulses around the body.
C nucleus
D streamlined head and tail
E large surface area; packed with chloroplasts
Activity Detailed descriptions
Ciliated cells should appear as rectangular cells with nuclei inside and hairs on
top of the rectangles labelled cilia.
Summary 1 specialised, function, oxygen, chloroplasts, photosynthesis (5 marks)
questions 2 correct description of specialised features, for example, a red blood cell: no
nucleus, disc-like shape. (2 marks)
3 A labelled diagram for a sperm cell is drawn, with the following features: streamlined
head – enable it to move through water easily, tail – to ‘swim’, many mitochondria – for
respiration. (6 marks)
B1 1.4 Movement of substances
In-text questions A food particles/glucose and oxygen
B carbon dioxide
Activity Stink-bomb Alert!
In diffusion, particles travel from an area of high concentration to an area of low
concentration. Initially, the smell from the stink bomb is only found in the immediate
vicinity but eventually, the smell will spread until the concentration of stink bomb
particles becomes constant.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 1
Summary 1 high, low, diffusion (3 marks)
questions 2 The smell diffuses from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration. (3
marks)
3 Example answers (6 marks):
Water in the plant is used for photosynthesis, vacuole becomes less full, less
pressure on the cell wall, cell becomes floppy, therefore the plant wilts. Credit
correct use of diagrams.
B1 1.4 Movement of substances
In-text questions A Organism made up of only one cell.
B Any two from: cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane.
C Any from: euglena carries out photosynthesis/has chloroplasts/has an eye spot/has a
flagellum.
Activity Unicellular organisms
Some of the following points should be included: both unicellular organisms; amoeba
looks jelly-like with no fixed structure; euglena are green with a tail-like structure.
Summary 1 unicellular, one, binary, fission, engulf, photosynthesis (6 marks)
questions 2 Nucleus in the parent cell divides, cytoplasm divides, two (daughter cells) produced.
(3 marks)
3 QWC question (6 marks). Example answers:
Both unicellular, have a nucleus/cytoplasm, get rid of waste by excretory vesicles, only
euglena can photosynthesise, both can move, euglena by flagellum, amoeba by
pseudopods, both cells can engulf food.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
Student book answers
Chapter 1
B1 Chapter 1 summary
End-of-chapter 1 B (A cell is the smallest unit of an organism.) (1 mark)
questions 2a nucleus (1 mark) b trap light/photosynthesis (1 mark)
c W (vacuole) (1 mark)
d Two from: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane.
3a microscope (1 mark)
b add stain/dye/coloured liquid (1 mark)
c It could transmit a disease or cause an infection as blood is removed. (1 mark)
d Diagram should show a cell containing a nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane. (3
marks)
4a A cell whose structure is adapted to suit its function. (1 mark)
b red blood cell (1 mark), transport oxygen (1 mark) transmits messages (1 mark)
carry out photosynthesis (1 mark), packed with chloroplasts (1 mark)
c Water moves into the root hair cell by diffusion/osmosis.
It moves from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water
concentration, through a cell membrane. (3 marks)
5a No, it is unicellular/consists of one cell only. Plants are multicellular organisms. (2 marks)
b Any similarity from: nucleus; cell membrane; cytoplasm. (1 mark)
Any difference from: chloroplasts; eye spot; flagellum only present in euglena. (1 mark)
c The eye spot detects light. The flagella cause euglena to move towards the light. It
has lots of chloroplasts to trap light for photosynthesis. (3 marks)
6 This is a QWC question. Students should be marked on the use of good English,
organisation of information, spelling and grammar, and correct use of specialist scientific
terms. The best answers will be organised in a logical sequence, with detail of how to
use the microscope (maximum of 6 marks).
Examples of correct scientific points:
State source of cells (onion skin and animal source, e.g., skin cell). Indication that the
sample needs to be very thin.
Reference to use of stain/dye. Reference to use of a microscope.
Use of lowest level of magnification first. Focus by turning fine/coarse focus knob. Any
other relevant microscope detail.
Draw a labelled diagram of the structures you observe. Indicate the magnification used
on the diagram drawn.
Answer guide for Big Write
Developing Secure Extending
1–2 marks 3–4 marks 5–6 marks
● The article is not presented in a ● The article is clearly presented. ● The article is clearly presented
logical way, and little attention and engaging, paying attention
● The student has described
has been paid to the rules of to the rules of this text type.
at least two similarities and
this text type.
two differences in the ● The student has clearly
● The student has stated at least structure and function of explained a number of
one difference and one an amoeba and a human. similarities and differences in
similarity between an amoeba the structure and functions of
and a human. an amoeba and a human.
© Oxford University Press 2014 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
You might also like
- b1 Cell Structure and Transport Exam QsDocument38 pagesb1 Cell Structure and Transport Exam QsMary Ann MaherNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz100% (1)
- Activate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz100% (1)
- AQA Biology: 1 Biological Molecules Exam-Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesAQA Biology: 1 Biological Molecules Exam-Style QuestionsreneehandsNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 Physics Chapter1 AnswersDocument5 pagesActivate 1 Physics Chapter1 AnswersPapi Parikh100% (1)
- Hostel Allocation System C++ ProjectDocument18 pagesHostel Allocation System C++ ProjectSuruchi Jha100% (1)
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 Chemistry Chapter1 AnswersDocument5 pagesActivate 1 Chemistry Chapter1 AnswersAlex Lim100% (1)
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Student Book Answers - Physics 1 Chapter 2Document5 pagesStudent Book Answers - Physics 1 Chapter 2Mhmd AlrashedNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Questions StudentDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Questions Studentapi-299996815No ratings yet
- The Robots Are Coming The Robots Are ComingDocument5 pagesThe Robots Are Coming The Robots Are Comingapi-272551013No ratings yet
- 9Bb-6 Leaves and RootsDocument1 page9Bb-6 Leaves and RootsHAMAD NoorNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz0% (1)
- Activate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- 4 - Unicellular Structural AdaptationsDocument12 pages4 - Unicellular Structural AdaptationsNayani Snigdha0% (1)
- P3 Chapter 1 End-Of-Chapter Test (Foundation)Document6 pagesP3 Chapter 1 End-Of-Chapter Test (Foundation)Paul LloydNo ratings yet
- Topic 8: Transport in PlantsDocument18 pagesTopic 8: Transport in PlantsCOXMIC FNNo ratings yet
- Biology IGCSE CellDocument30 pagesBiology IGCSE CellUmm ArafaNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocument51 pages12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- Test 1 Chapter 5: Cell Division Sub Topic: Mitosis: BPK/Biology Item /Method1-Analogy & Role Play1/MitosisDocument3 pagesTest 1 Chapter 5: Cell Division Sub Topic: Mitosis: BPK/Biology Item /Method1-Analogy & Role Play1/MitosisYan MLNo ratings yet
- Specialised-Cells-Worksheet - Combined ScienceDocument3 pagesSpecialised-Cells-Worksheet - Combined ScienceBachittar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Use The Table Above To Fill in The ChartDocument5 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet Use The Table Above To Fill in The ChartRachel Ann EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- KS3 Light 2Document46 pagesKS3 Light 2Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- 2.1 Formative Assessment Biology BookDocument1 page2.1 Formative Assessment Biology Bookabdullah adNo ratings yet
- Amoeba, Euglena, Spirogyra, Paramecium: CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesAmoeba, Euglena, Spirogyra, Paramecium: CharacteristicsMac SensNo ratings yet
- Specialised CellsDocument9 pagesSpecialised CellsJanah Pauline AbunganNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Light and SoundDocument11 pagesYear 8 Light and SoundCinara RahimovaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Digestion and Absorption Revision Notes PDFDocument24 pagesBiology - Digestion and Absorption Revision Notes PDFanna robertsonNo ratings yet
- Interdependence and Food WebsDocument3 pagesInterdependence and Food WebsArchieNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFDocument50 pagesCell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFRozel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells - WorksheetDocument4 pagesPlant and Animal Cells - WorksheetsabaNo ratings yet
- Checked - Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene Technology - Exam BookletDocument63 pagesChecked - Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene Technology - Exam BookletEllane leeNo ratings yet
- 3.2 MicroscopeDocument30 pages3.2 Microscopesudirman0103651972No ratings yet
- Sats QuestionsDocument9 pagesSats Questionsapi-3800318No ratings yet
- Chem12015 ExamDocument16 pagesChem12015 ExamAAVANINo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet: (Assume That The Sugar Molecules Can Pass Through The Cell Membrane in Each Case.)Document2 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Worksheet: (Assume That The Sugar Molecules Can Pass Through The Cell Membrane in Each Case.)Cavene Scott100% (1)
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Periodic Table ks3Document3 pagesWorksheet Periodic Table ks3Miku ChanNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Cell Membranes and Transport Worksheet: Name: - Class: XI SCIENCEDocument5 pagesAs-Level Biology Cell Membranes and Transport Worksheet: Name: - Class: XI SCIENCEDina Anggraini Pramitasari100% (2)
- Cie Alevel BiologyDocument24 pagesCie Alevel BiologyArun Ghatan100% (2)
- Living and Nonliving NotesDocument2 pagesLiving and Nonliving NotesRobNo ratings yet
- Patterns of InheritanceDocument26 pagesPatterns of InheritanceVidhya NairNo ratings yet
- Electricity Worksheet Page 2Document1 pageElectricity Worksheet Page 2Laura LucumiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 SCIENCE QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesGrade 9 SCIENCE QUESTIONSSharreah LimNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument14 pagesActive TransportRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument32 pagesStates of MatterKeith BansrajNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision GuideDocument22 pagesBiology Revision GuidePoornima AthikariNo ratings yet
- Biology As A2 CombinedDocument253 pagesBiology As A2 CombinedKulsoom JawedNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemAbdurahmaan RaikarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1Document14 pagesEdexcel Intl A Levels Biology Unit 2 Wbi12 v1seif nimerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Science Module Form 1 - Chapter 2Document13 pagesChapter 2: Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Science Module Form 1 - Chapter 2Thiba KrishnanNo ratings yet
- How Can We Study The Living WorldDocument9 pagesHow Can We Study The Living WorldFarah TaimoorNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Organism (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDocument16 pagesOrganisation of The Organism (Multiple Choice) 1 QPNatalie RossetteNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument14 pagesTransport in PlantsMuhammad Faizan KaleemNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesRumaisa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 November 1999Document5 pagesPaper 2 November 1999MSHNo ratings yet
- Science Equipments Mathematics Equipment: Item Description Qty. UnitDocument5 pagesScience Equipments Mathematics Equipment: Item Description Qty. UnitJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Science Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12From EverandScience Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12No ratings yet
- GR 9 NS Cell Worksheet MemoDocument4 pagesGR 9 NS Cell Worksheet MemoSyrus ZambiaNo ratings yet
- BC Science 8 Workbook AnswersDocument22 pagesBC Science 8 Workbook Answersi. zNo ratings yet
- 7 SolubilityDocument4 pages7 SolubilityJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Mynard JoDocument13 pagesMynard JoJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W9Document1 pageT1W9John LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W4 (Revision)Document4 pagesT1W4 (Revision)John LebizNo ratings yet
- T1W10Document1 pageT1W10John LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 3 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Booking Confirmation - 28342216136Document2 pagesBooking Confirmation - 28342216136John LebizNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Physics Worksheet 1Document3 pagesGrade 7 Physics Worksheet 1John LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter2 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Chemistry Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz0% (1)
- Activate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersDocument6 pagesActivate 2 Physics Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- NPS International SchoolDocument2 pagesNPS International SchoolJohn LebizNo ratings yet
- 1a (I) (1) (A) (Ii) (1) (A) (Iii) (1) (Iv) (1) B (1) (1) (1) Number Mark 2 (A)Document2 pages1a (I) (1) (A) (Ii) (1) (A) (Iii) (1) (Iv) (1) B (1) (1) (1) Number Mark 2 (A)John LebizNo ratings yet
- Practice Abstract Reasoning Test 1 - With ExplanationsDocument9 pagesPractice Abstract Reasoning Test 1 - With ExplanationsEliah Lopez0% (1)
- Astrovega May 2024Document44 pagesAstrovega May 2024VARA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Final1 PDFDocument10 pagesFinal1 PDFAngelica SantiagoNo ratings yet
- JD Asistent Manager - ENDocument4 pagesJD Asistent Manager - ENMihaela RaduNo ratings yet
- PA - StocksDocument36 pagesPA - Stocksikolev57No ratings yet
- Xii CH 1 PPT 1Document92 pagesXii CH 1 PPT 1jiyanshi yadavNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Heineken BeerDocument13 pagesPresentation On Heineken BeerΣόλα ΚαρίμοβαNo ratings yet
- Bradburn Et Al v. North Central Regional Library District - Document No. 57Document28 pagesBradburn Et Al v. North Central Regional Library District - Document No. 57Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering ActivitiesDocument3 pagesData Gathering ActivitiesKyla PapaNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On Shri Ram Piston and Rings LimitedDocument89 pagesSummer Training Report On Shri Ram Piston and Rings LimitedKevin Joy75% (4)
- CONFIRMALDocument50 pagesCONFIRMALSri SaiNo ratings yet
- PPC DrainDocument6 pagesPPC Drainherysyam1980No ratings yet
- BT1 Handout - 01 Concrete (REV20210114)Document11 pagesBT1 Handout - 01 Concrete (REV20210114)Jano AgbigayNo ratings yet
- PROCESS AND ART. OSKAR HANSEN AND HIS CONCEPT OF VARIABLE ARCHITECTURE - Contemporary Lynx - Promoting Polish Art in The WorldDocument13 pagesPROCESS AND ART. OSKAR HANSEN AND HIS CONCEPT OF VARIABLE ARCHITECTURE - Contemporary Lynx - Promoting Polish Art in The WorldBen GreenNo ratings yet
- EG III Generator Unit ManualDocument15 pagesEG III Generator Unit ManualLIVIANo ratings yet
- Active Certificates: A Framework For DelegationDocument39 pagesActive Certificates: A Framework For DelegationBruno CrispoNo ratings yet
- Access 4 TEST MODULE 1Document5 pagesAccess 4 TEST MODULE 1Stai4eNo ratings yet
- Stage 1 English Curriculum Framework PDFDocument2 pagesStage 1 English Curriculum Framework PDFMangunatun KhasanahNo ratings yet
- APICS BSCM Chapter 1 NotesDocument11 pagesAPICS BSCM Chapter 1 NotesvayugaramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NematodesDocument5 pagesChapter 8 NematodesJuju GalangNo ratings yet
- Session-10 Assignment Name: Dharmi Javiya Enroll No: 92100133058Document3 pagesSession-10 Assignment Name: Dharmi Javiya Enroll No: 92100133058Dharmi JaviyaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Beauty Parlour Managment' She Guided Us in Preparation of The Project andDocument23 pagesAcknowledgement: Beauty Parlour Managment' She Guided Us in Preparation of The Project andKomal DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 5070 s12 QP 21 PDFDocument20 pages5070 s12 QP 21 PDFNeural Spark Physics CieNo ratings yet
- Bohemian Rhapsody (Ukulele Tab)Document4 pagesBohemian Rhapsody (Ukulele Tab)crojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Interstate-Mcbee Sensors: Serving The Diesel and Natural Gas Industry For Over 60 YearsDocument1 pageInterstate-Mcbee Sensors: Serving The Diesel and Natural Gas Industry For Over 60 YearsRicardoNo ratings yet
- NFL Network ResumeDocument2 pagesNFL Network Resumeapi-314448476No ratings yet
- En - mb997 F407VGT6 E01 SchematicDocument9 pagesEn - mb997 F407VGT6 E01 SchematicBharath Kumar Reddy MNo ratings yet
- 'NEXtCARE Corporate Profile 5Document1 page'NEXtCARE Corporate Profile 5Rajesh PotluriNo ratings yet