Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Crane-Hydra-deployment For Lifting-Lowering-Risk Assessment
Crane-Hydra-deployment For Lifting-Lowering-Risk Assessment
Uploaded by
Ahmed El-sherpiniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Crane-Hydra-deployment For Lifting-Lowering-Risk Assessment
Crane-Hydra-deployment For Lifting-Lowering-Risk Assessment
Uploaded by
Ahmed El-sherpiniCopyright:
Available Formats
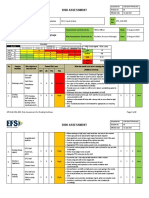
RISK ASSESSMENT
Activity: Crane-Hydra-Deployment for Lifting-Lowering
Location: Department: Date of Assessment:
RA Reference: Revision: 00 PTW Reference:
Assessment Team: Supporting Documents: Reference Documents:
(Method Statement/Drawings) (Standards/Procedures/Manuals)
Approval granted for work to proceed
Approval NOT granted for work to proceed. Please revise the Risk Assessment to include additional safeguards
Name: Designation: Signatures:
Distribution:
General Guidelines: Hierarchy of Hazard Controls:
1. Risk Assessment (also called Job Safety Analysis) is a qualitative hazard identification technique used for (In order from most effective to least effective)
identifying, assessing and controlling major hazard(s) associated with a specific task or operation where Elimination (by design or process changes)
Permit to Work (PTW) precautions are deemed insufficient to execute the job safely. Substitution (with less hazardous material or equipment)
2. No such work should be allowed to proceed until the Risk Assessment has been completed and approved by Isolation (with barriers, machine guards)
a competent authority (normally Site Manager/Superintendent). Engineering Controls (interlocks, ESD system)
3. Risk Assessment should be carried out by a competent person and conducted in a team environment, Administrative Controls (procedures, job rotations,
involving all relevant parties. training)
4. Only trained and experienced staff should be deployed to execute high-risk jobs. Warning Systems (signs, labels)
5. Conduct RA well in advance as part of the work planning process. Personal Protective Equipment
6. Address all direct and indirect hazards associated with the task.
7. This RA shall be conducted in conjunction with the above referenced PTW. A copy of the approved Risk Abbreviations:
Assessment must be attached to the permit throughout the work duration. ALARP : As Low as Reasonably Practicable
8. Use the 5x5 Risk Assessment Matrix (provided separately) to assess the potential risks.
PTW : Permit to Work
9. When determining safeguards, consider the ‘Hierarchy of Hazard Controls’ provided on this page.
10. Communicate RA to all relevant personnel through meetings/toolbox talks before starting work. ESD : Emergency Shutdown
11. Record Risk Assessment and revise if necessary. RA : Risk Assessment
P : Probability (Likelihood)
C : Consequences
R : Risk (H = High, M = Medium, L = Low)
Page 1 of 4 HSE DOCUMENTS
RISK ASSESSMENT
S/ Initial Risk Residual Risk
Hazards Safeguards Action by
N P C R (Low/ALARP)
1 1. Preparation and checking before entry Fire extension due Crane/ Hydra must have a valid permit for entry Project ALARP Level
2. Entry inside plant to spark generated E 4 V inside red roads Engineer/supervi
3. Preparation and checking before H sor/HSE in charge
Damage due to Crane/ Hydra must be certified for use by the P&M
Lifting hitting against department
4. Lifting/ Lowering of the load pipe/equipment Driver must have a safe driving licence. Spark
Injury to people arrestor must be healthy
around Check LEL in the proposed route of the Crane/
Property damage / Hydra. Switch off the engine and evaluate if the
Exposure to toxic F&G alarm is sounded
release/ fire due Crane/ Hydra will move with a speed of less than 10
to falling of lifted Kmph
load/ crane Identify all pits near to the route, barricaded
toppling due to /highlight if required
improper usage of Use wheel jammers to prevent accidental
the crane movement of the Crane /Hydra
Exposure to Keep the Crane / Hydra on gear when parked.
HC/toxic release Follow Vehicle entry procedure
due to Crane rope Do not leave the crane / Hydra unattended when
getting entangled parked near plant and machinery
with a small-bore Do not allow to move people in the route of Crane/
connection Hydra
Property damage / Crane/ Hydra reverse horn must be working and
toxic release/fire assistant to guide while reversing
due to dropping of
the load to Following things are to be ascertained before lifting:
slippage of slings, Object load;
rupture of slings, lift radius;
crane brake load height;
load centre of gravity;
failure, rupture of
load suspension point;
crane rope wire,
Slew Limitation;
slippage of rope
counterweight;
wire from the
Bearing load on the ground;
anchor point Safe working load;
Property damage/ Object dimension (if more than 25m2), safe
exposure to toxic approach. Also, give the request form to P&M
release/fire due to depth so that the correct crane is allocated
toppling or Check on Crane /Hydra:
collapse on the Crane load test certificate, Daily log sheet,
Page 2 of 4 HSE DOCUMENTS
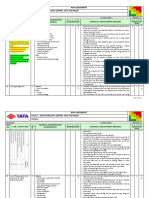
RISK ASSESSMENT
Fortnightly / monthly service and inspection
checklist must be available and updated. The safe
load indicator (SLI) is working. If not working
capacity loading will not exceed 60%
All limit switches are functioning. The free-fall
system is blocked. No hydraulic oil leakage
Lifting plan to be prepared if: load wt is more than
15T or Boom length above 55m or two cranes used
for single lift or capacity loading more than 85% or
using mobile crane rated above 200T
Identification and marking any small SBC at risk and
pointing out the risk to the crane operator and
signaler
Lifting weight to be with guide rope. Optimal setting
crane of the crane and restricting crane movement. Also
Electrical shock barricade the crane
hazard due to Crane has undergone regular and competent
entangling with service, inspection
overhead Control of slings wear and tear and the attachment
electrical cables to the load
Hazard due to high Crane capacity loading (85 % with working SLI, 60 %
wind velocity if SLI is not working)
Load weight and lifting radius must be known and
within crane capacity
The area must be barricaded; people should not be
allowed under lifted load
low-capacity loading, working SLI, setting of crane
outriggers on the solid foundation
Proper operators under the outriggers required.
The outriggers must always be extended in their full
length
Elec. Overhead line is at least 6.0 m above from tip
of the crane
Wind speed should be less than 19.4 knots (35
km/hr). For personnel lifting wind speed should be
less than 14 knots
Page 3 of 4 HSE DOCUMENTS
RISK ASSESSMENT
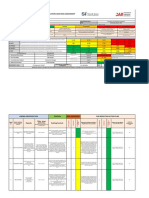
The Risk Matrix Likelihood
Consequences People Assets Environmen Reputation A B C D E
t
5-Catastrophic Multiple Fatalities Extensive damage Extensive Effect International impact VERY
HIGH
4-Severe Single fatality or Permanent total Severe damage Severe Effect National impact
disability
3-Critical Major injury or health effects (long Major damage Major Effect Major impact
term or permanent partial disability) MEDIUM HIGH
2-Marginal Minor injury or health effects leading to Minor effect Minor Effect Minor impact
LTI/RWC/MTC
1-Negligible Single injury or health effects, requiring Slight effect Slight Effect Slight impact
first aid LOW
Likelihood Descriptor to assist in Qualitative Assessment of Likelihood/Frequency of Occurrence.
A Has occurred in a similar industry worldwide, or judged likely to have occurred.
B Has occurred regionally within a similar industry, or judged likely to have occurred.
C Has occurred at [worksite], or judged likely to have occurred.
D Has occurred several times at [worksite], or judged likely to have occurred.
E It May occurred several times at the same [worksite], Location or judged likely to have occurred.
Assessed by: Date: Signature:
Reviewed by: Date: Signature:
Page 4 of 4 HSE DOCUMENTS
You might also like
- Risk Assessment Fire Hydrant Installation Testing CommissioningDocument11 pagesRisk Assessment Fire Hydrant Installation Testing CommissioningAmie GTunedNo ratings yet
- GENERAL JOURNAL Tugas Akuntansi 4Document9 pagesGENERAL JOURNAL Tugas Akuntansi 4Sultan Fathulhaq100% (2)
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityDocument6 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityAnthony MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Demolition ChecklistDocument1 pageDemolition ChecklistAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- Contractor Ehs Risk Assessment For NDT TestingDocument6 pagesContractor Ehs Risk Assessment For NDT TestingBernard PenuliarNo ratings yet
- JHA Maintenance Tech HVACDocument2 pagesJHA Maintenance Tech HVACMdavaNo ratings yet
- Olifantsvlei: General Site Operations - Flame CuttingDocument4 pagesOlifantsvlei: General Site Operations - Flame CuttinggrantNo ratings yet
- Cultural LagDocument3 pagesCultural LagJona D'john100% (1)
- Backfilling and Compaction MVLDocument3 pagesBackfilling and Compaction MVLLawrence adeleke OmisakinNo ratings yet
- CRA For Beam Stregthening WorksDocument4 pagesCRA For Beam Stregthening WorksVikki P ReddiNo ratings yet
- HEMP-006 Operation of Wood Cutting & Grooving Machine Rev.1 PDFDocument7 pagesHEMP-006 Operation of Wood Cutting & Grooving Machine Rev.1 PDFsaravana.bNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of Trees MaintenanceDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment of Trees Maintenanceطارق رضوان100% (1)
- Jsa For Installation, Testing and Commissioning of Sewer and Strom Water Drainage System at 14 Nos. of Alijarah Warehouse.Document67 pagesJsa For Installation, Testing and Commissioning of Sewer and Strom Water Drainage System at 14 Nos. of Alijarah Warehouse.jafar mohdNo ratings yet
- RA Excavation For Trial TrenchDocument9 pagesRA Excavation For Trial TrenchSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- EFS-SLB-SRA-006 Risk Assessment For General Waste CollectionDocument2 pagesEFS-SLB-SRA-006 Risk Assessment For General Waste Collectionmohammed ayazNo ratings yet
- EFS-SLB-SRA-005 Risk Assessment For Dusting Surfaces of SignagesDocument2 pagesEFS-SLB-SRA-005 Risk Assessment For Dusting Surfaces of Signagesmohammed ayazNo ratings yet
- RA Pump TemoraryDocument11 pagesRA Pump TemoraryCarlos ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- ARA - For Emergency Diesel GeneratorDocument4 pagesARA - For Emergency Diesel GeneratorShaikh AftabNo ratings yet
- Work at Height ProcedureDocument36 pagesWork at Height ProcedureShams JogNo ratings yet
- Lifting OperationDocument8 pagesLifting OperationFILE 1131No ratings yet
- 9 - Risk Assessment - PaintingDocument8 pages9 - Risk Assessment - Paintingmahmoud nadaNo ratings yet
- DOD-MST-AKG-2-E-012 (Rev-A) Installation of TransformerDocument4 pagesDOD-MST-AKG-2-E-012 (Rev-A) Installation of TransformerProfessional TrustNo ratings yet
- 7.OHS-PR-09-03-F02 HIRA - 30 Hydro Testing of Gas PipelineDocument5 pages7.OHS-PR-09-03-F02 HIRA - 30 Hydro Testing of Gas PipelineabbasNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis For Pump Installation in Ts3 Area: Hcu & Lobs Revamp ProjectDocument5 pagesJob Safety Analysis For Pump Installation in Ts3 Area: Hcu & Lobs Revamp ProjectShilpiengg SafetyNo ratings yet
- General Risk Assessment FormDocument8 pagesGeneral Risk Assessment FormmkmusaNo ratings yet
- Welspun Enterprises Limited Project: Am2 Group Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesWelspun Enterprises Limited Project: Am2 Group Risk AssessmentDwijendra ChanumoluNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Rebar Shifting Using BHDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment - Rebar Shifting Using BHLeoniv Arviz LiboroNo ratings yet
- Ra of Manual Excavation For Trench of Telephone CableDocument5 pagesRa of Manual Excavation For Trench of Telephone CableRaza Muhammad SoomroNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis & Risk Assessment For Scrapping and Grading ActivityDocument1 pageJob Safety Analysis & Risk Assessment For Scrapping and Grading ActivityAzhar Mushtaq100% (1)
- Lift Accessories Lift Measure Risk Assessment Form BaseDocument6 pagesLift Accessories Lift Measure Risk Assessment Form Basebalusandeep20No ratings yet
- RA For Snake BiteDocument5 pagesRA For Snake Biteshamroz khan100% (1)
- Lock Out Tag Out-Permit To Work Process Flow Chart: EPC Sub-ContractorDocument1 pageLock Out Tag Out-Permit To Work Process Flow Chart: EPC Sub-ContractorShailendraNo ratings yet
- CSCEC HSE-F-01 Risk Assessment Form - Excavation& Backfilling - RA-02Document12 pagesCSCEC HSE-F-01 Risk Assessment Form - Excavation& Backfilling - RA-02Dan SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Coring WorksDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment For Coring WorksFaizan Tanveer100% (1)
- HSE Risk Assessment For Hot Work ActivityDocument8 pagesHSE Risk Assessment For Hot Work ActivityDarseen RNo ratings yet
- Scaffold Erection and DismantlingDocument5 pagesScaffold Erection and DismantlingFosu DicksonNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment LiftingDocument2 pagesHazard Identification and Risk Assessment LiftingHariharan Muthukrishanan100% (1)
- 02 - R.A. Working On ScaffoldsDocument2 pages02 - R.A. Working On ScaffoldspremNo ratings yet
- EFS-SLB-SRA-004 Risk Assessment For Bodily Fluid Spillage CleansDocument2 pagesEFS-SLB-SRA-004 Risk Assessment For Bodily Fluid Spillage Cleansmohammed ayazNo ratings yet
- P-985-SH-AHA-003. AHA For Outage Lock Our Tag OutDocument3 pagesP-985-SH-AHA-003. AHA For Outage Lock Our Tag OutPatrick Bibila NdansiNo ratings yet
- PCR-LP-362-Tower Crane Dismantling (LTM1450-8.1)Document17 pagesPCR-LP-362-Tower Crane Dismantling (LTM1450-8.1)Geethika SandaruwanNo ratings yet
- Mobile Equipment Hazards-ADocument25 pagesMobile Equipment Hazards-ALuis PallerosNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of Fabrication, Welding, Cutting WorkDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment of Fabrication, Welding, Cutting WorkAbdul MujeebNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - Carpentry Works DateDocument1 pageJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - Carpentry Works DatenabeelNo ratings yet
- LITE Manual Handling Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesLITE Manual Handling Risk AssessmentTina fu GeeNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - House and BuildingDocument1 pageRisk Assessment - House and Buildingnayanahari0% (1)
- Diesel Generator Hazard Assessment PDF Master HireDocument6 pagesDiesel Generator Hazard Assessment PDF Master HireMuhammad MalikNo ratings yet
- FMSA 69970 Aspect-Impact EnvironmentDocument11 pagesFMSA 69970 Aspect-Impact EnvironmentAhmad Assad mredn0% (1)
- JSA #19 - Heavy Lifting in Hazardous AreaDocument1 pageJSA #19 - Heavy Lifting in Hazardous AreaMock ProjectNo ratings yet
- Survey Work HSE Risk AssessmentsDocument2 pagesSurvey Work HSE Risk AssessmentsSarfraz RandhawaNo ratings yet
- SWMS - Blind IstallationDocument12 pagesSWMS - Blind IstallationParasNo ratings yet
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Overall Risk Assessment Code (RAC) (Use Highest Code)Document4 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Overall Risk Assessment Code (RAC) (Use Highest Code)Anthony MacatangayNo ratings yet
- F5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Foul Sewer - Manhole ConstructionDocument11 pagesF5B-BMJV-0001-AHA-HSE 00 AHA For Foul Sewer - Manhole ConstructionTaiwo OshinNo ratings yet
- Code of PracticeDocument26 pagesCode of PracticeS Khan100% (2)
- RMR-HSMS-P-001 Hazard Identification Risk Assessment and Risk ManagementDocument14 pagesRMR-HSMS-P-001 Hazard Identification Risk Assessment and Risk ManagementkamranNo ratings yet
- HSE-RA-023 Site Establishment - Rev 0Document17 pagesHSE-RA-023 Site Establishment - Rev 0عمروNo ratings yet
- Contractor's EHSS Evaluation by PMT EHSS PK CLC Project FMO Jan 2020Document5 pagesContractor's EHSS Evaluation by PMT EHSS PK CLC Project FMO Jan 2020ManPower RecruitingNo ratings yet
- Site Inspection Workplace Trasport ChecklistDocument6 pagesSite Inspection Workplace Trasport ChecklisttipuNo ratings yet
- PTW Evcavation ENDocument1 pagePTW Evcavation ENATSI HadjilaNo ratings yet
- Lifting Operations Planning Risk Assessment PDFDocument1 pageLifting Operations Planning Risk Assessment PDFulisses costaNo ratings yet
- CIV510 - Management of Temporary WorksDocument14 pagesCIV510 - Management of Temporary Worksezzularab100% (1)
- Daily Pre Start ChecklistDocument1 pageDaily Pre Start ChecklistAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry ProcedureDocument2 pagesConfined Space Entry ProcedureAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Hazards Assessment FormDocument3 pagesConfined Space Hazards Assessment FormAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- Compactor Daily Inspection ChecklistDocument1 pageCompactor Daily Inspection ChecklistAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- Workers Related Safety Inspection Checklist With PPEDocument5 pagesWorkers Related Safety Inspection Checklist With PPEAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- Building Materials Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesBuilding Materials Risk AssessmentAhmed El-sherpiniNo ratings yet
- Prioritizing Nursing ProblemsDocument10 pagesPrioritizing Nursing ProblemsAnonymous iG0DCOfNo ratings yet
- E290 Procedure Feb 2024Document3 pagesE290 Procedure Feb 2024I weld with hot glueNo ratings yet
- Column GuideDocument52 pagesColumn GuideDr. Ghulam FareedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 3 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial Chapter 3 PDFToukaNo ratings yet
- Root Canals: What To Expect During A ROOT CANALDocument3 pagesRoot Canals: What To Expect During A ROOT CANALKuntum Khaira UmmahNo ratings yet
- Msds Shell Coolant Longlife PlusDocument19 pagesMsds Shell Coolant Longlife Plusanother.faldyNo ratings yet
- Heizka Catalogue Cat6 24awg Utp 2Document2 pagesHeizka Catalogue Cat6 24awg Utp 2votinh20687No ratings yet
- Guntan - Assignment No. 15 (SHP 303)Document5 pagesGuntan - Assignment No. 15 (SHP 303)Dimasalang PerezNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Test Report: Calibration Test Report - Pressure Recorder SATR-A-2004 22-Jan-18 MechDocument2 pagesSaudi Aramco Test Report: Calibration Test Report - Pressure Recorder SATR-A-2004 22-Jan-18 MechaneeshNo ratings yet
- Chromatography 1686504920Document21 pagesChromatography 1686504920Annisa JuliayantiNo ratings yet
- Design & Analysis of Line Impedance Stabilization Network Using RLC Components For ITE PDFDocument5 pagesDesign & Analysis of Line Impedance Stabilization Network Using RLC Components For ITE PDFEbubekir KeskinkılıçNo ratings yet
- Md. Faruqul IslamDocument110 pagesMd. Faruqul Islamjaxad78743No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeTownship TownshipNo ratings yet
- Rossi Cholodny TechniqueDocument11 pagesRossi Cholodny TechniqueAyesha Khan50% (2)
- Legal MEdicineDocument29 pagesLegal MEdicineMuktar CabangcalaNo ratings yet
- Beneheart D1: DefibrillatorDocument3 pagesBeneheart D1: DefibrillatorNicolae MaicanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 036012859390003W Main PDFDocument82 pages1 s2.0 036012859390003W Main PDFAnonymous pv63gnBMAZNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Male and Female Genitals During Coitus and Female Sexual ArousalDocument6 pagesMagnetic Resonance Imaging of Male and Female Genitals During Coitus and Female Sexual Arousalapi-3738541100% (1)
- Fine Motor SkillSDocument52 pagesFine Motor SkillSHemant Kumar100% (1)
- Bala Murugan E - , MSC Nursing AIIMSDocument33 pagesBala Murugan E - , MSC Nursing AIIMSBalaMuruganNo ratings yet
- Lbe Diskusi 16 Tambahan FixDocument4 pagesLbe Diskusi 16 Tambahan FixRayhan Al FaiqNo ratings yet
- MBA Unemployment ReportDocument19 pagesMBA Unemployment ReportShiva NandNo ratings yet
- Open Circuit Axial Piston Pumps: Series 45 Frame K and LDocument33 pagesOpen Circuit Axial Piston Pumps: Series 45 Frame K and LRomeo Lemus LainezNo ratings yet
- Gut-Focused Hypnotherapy Protocol For Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Background To The Manchester Protocol and RationaleDocument10 pagesGut-Focused Hypnotherapy Protocol For Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Background To The Manchester Protocol and RationaleΦωτεινή ΜαρίνηNo ratings yet
- IA - Consumer Electronics Servicing CGDocument25 pagesIA - Consumer Electronics Servicing CGGlenn TotzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HW SolnDocument10 pagesChapter 5 HW SolnthemangoburnerNo ratings yet
- SBS Basalt 101Document4 pagesSBS Basalt 101kelvinyeohNo ratings yet
- Is PresentationDocument15 pagesIs PresentationFaria KhanNo ratings yet