Professional Documents
Culture Documents
30 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
30 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
Gagne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageA rectifier converts alternating current to direct current. It allows power to flow from the AC input to the DC output, and in some cases can operate in reverse as an inverter. Rectifiers are classified by the components used, circuit topology, number of phases, and control mechanism. All rectifiers produce unwanted harmonics at the output and input. Single phase uncontrolled half wave rectifiers have a low average output voltage and poor ripple factor, while full wave rectifiers have a higher average output voltage and better ripple factor, especially with inductive loads. A bridge rectifier generates a higher DC voltage than a split supply rectifier but uses more diodes.
Original Description:
Original Title
30_L-9(DK)(PE) ((EE)NPTEL)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA rectifier converts alternating current to direct current. It allows power to flow from the AC input to the DC output, and in some cases can operate in reverse as an inverter. Rectifiers are classified by the components used, circuit topology, number of phases, and control mechanism. All rectifiers produce unwanted harmonics at the output and input. Single phase uncontrolled half wave rectifiers have a low average output voltage and poor ripple factor, while full wave rectifiers have a higher average output voltage and better ripple factor, especially with inductive loads. A bridge rectifier generates a higher DC voltage than a split supply rectifier but uses more diodes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 page30 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
30 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneA rectifier converts alternating current to direct current. It allows power to flow from the AC input to the DC output, and in some cases can operate in reverse as an inverter. Rectifiers are classified by the components used, circuit topology, number of phases, and control mechanism. All rectifiers produce unwanted harmonics at the output and input. Single phase uncontrolled half wave rectifiers have a low average output voltage and poor ripple factor, while full wave rectifiers have a higher average output voltage and better ripple factor, especially with inductive loads. A bridge rectifier generates a higher DC voltage than a split supply rectifier but uses more diodes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Module Summary
• A rectifier is a power electronic converter which converts ac voltage or current sources to
dc voltage and current.
• In a rectifier, electrical power flows from the ac input to the dc output.
• In many rectifier circuits, power can also flow from the dc side to the ac side, where
upon, the rectifier is said to be operating in the “inverter mode”.
• Rectifiers can be classified based on the type of device they use, the converter circuit
topology, number of phases and the control mechanism.
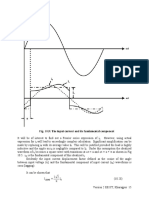
• All rectifiers produce unwanted harmonies both at the out put and the input. Performance
of a rectifier is judged by the relative magnitudes of these harmonies with respect to the
desired output.
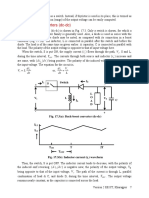
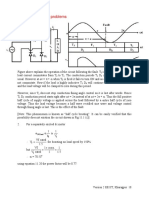
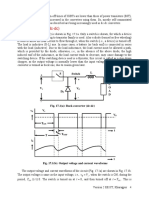
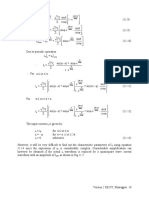
• For a given input voltage and load, the output voltage (current) of an uncontrolled
rectifier can not be varied. However, the output voltage may vary considerably with load.
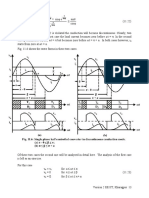
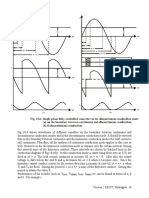
• Single phase uncontrolled half wave rectifier with resistive or inductive load have low
average output voltage, high from factor and poor ripple factor of the output voltage
waveform.
• Single phase uncontrolled full wave rectifier have higher average output voltage and
improved ripple factor compared to a half wave rectifier with resistive and inductive load.
• With highly inductive load the output voltage waveform of a full wave rectifier may be
independent of the load parameters.
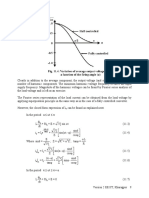
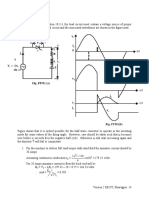
• With a capacitive load the output voltage form factor approaches unity with increasing
capacitance value for both the half wave and the full wave rectifiers. However, THD of
the input current also increases.
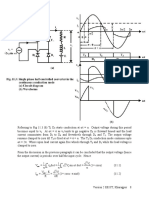
• A full wave bridge rectifier generates higher average dc voltage compared to a split
supply full wave rectifier. However it also uses more number of diodes.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 30
You might also like
- Split Supply Single Phase Uncontrolled Full Wave Rectifier (Ass PE)Document3 pagesSplit Supply Single Phase Uncontrolled Full Wave Rectifier (Ass PE)Miz AelyfhaNo ratings yet
- Power Supply and Zener Diode (Canvas)Document95 pagesPower Supply and Zener Diode (Canvas)Aaron Jacob ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument29 pagesPower SupplyavallenjosephviiiaNo ratings yet
- Eet 06206 HandoutDocument40 pagesEet 06206 HandoutMohammed ShabanNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 Wind0.02Document25 pagesAss 2 Wind0.02Šämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- NAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034Document22 pagesNAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034BARUN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Power Plant and BatteryDocument34 pagesPower Plant and BatteryAnanya100% (2)
- SUBTOPIC 1 - Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesSUBTOPIC 1 - Power ElectronicsJasperNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Power SupplyDocument81 pagesLecture On Power SupplyMATE0100% (2)
- Introduction Power Supply PPT 1Document51 pagesIntroduction Power Supply PPT 1Abdul Qawie Jumaan100% (4)
- AC and DC Conversion BasicsDocument19 pagesAC and DC Conversion BasicsSandeep SolankiNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Gate Drivers and Uncontrolled RectifierDocument30 pagesWeek 10 Gate Drivers and Uncontrolled RectifierAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- SIMULINKDocument5 pagesSIMULINKshresth.gupta.ug22No ratings yet
- EE301: Electronic Circuits: Unit 1: Linear DC Power SupplyDocument53 pagesEE301: Electronic Circuits: Unit 1: Linear DC Power SupplySadrina MahamudNo ratings yet
- Introduction Power Supply PPT 1Document51 pagesIntroduction Power Supply PPT 1Rokiah Juman0% (1)
- Experiment 3 Eng NaderDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 WindDocument10 pagesAss 2 WindŠämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument13 pagesRectifiersInfidragon GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers: Alternating Current (AC) To Direct Current (DC)Document20 pagesRectifiers: Alternating Current (AC) To Direct Current (DC)Golu SinghNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic NotesDocument142 pagesPower Electronic Notesjosphat mbathaNo ratings yet
- Beng BenggsssDocument11 pagesBeng BenggsssBeth PartozaNo ratings yet
- 4 2 PDFDocument32 pages4 2 PDFAkoto BlessNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Overview of Power ElectronicsDocument64 pagesUnit 2 - Overview of Power ElectronicsKakumbi Shukhovu ChitiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT by Shadan AlamDocument17 pagesPower Electronics PPT by Shadan Alamshadan alamNo ratings yet
- An Electronic System Power Supply ExampleDocument20 pagesAn Electronic System Power Supply Examplegenesis serominesNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase RectificationDocument30 pages3 Phase RectificationKobby Brine100% (1)
- Generation of High Direct Current VoltagesDocument68 pagesGeneration of High Direct Current VoltagesMaria JoseeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument21 pagesUnit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringAJAY SNo ratings yet
- 7th Sem Major ProjectDocument23 pages7th Sem Major ProjectArjun BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- RECTIFIERDocument15 pagesRECTIFIERAni AniNo ratings yet
- Full Wave ContentDocument6 pagesFull Wave ContentAkshaya chandra sekarNo ratings yet
- (Industrial Electronics) : ECE 312aDocument7 pages(Industrial Electronics) : ECE 312aRon DomanaisNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Unit-4 InverterDocument31 pagesPower Electronics: Unit-4 Invertershikha prakashNo ratings yet
- Design of Power SupplyDocument25 pagesDesign of Power SupplySaadah100% (1)
- Introduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) CircuitsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Circuits9chand3100% (1)
- Advantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterLemuel C. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Interleaved Voltage Boosting Circuit and Power Factor CorrectionDocument9 pagesInterleaved Voltage Boosting Circuit and Power Factor Correctiontejaputta1616No ratings yet
- Lab 5Document16 pagesLab 5msania654No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 DC To DC ConvertersDocument68 pagesLecture 10 DC To DC Convertersprabhash anandNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDC Power Supplyweaam raedNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDC Power Supplyweaam raedNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 (Power Supply Unit)Document82 pagesTOPIC 1 (Power Supply Unit)AR de Souza100% (1)
- Rectifire SummaryDocument4 pagesRectifire SummaryajjjindoreNo ratings yet
- Microgrid Integration 5Document15 pagesMicrogrid Integration 5LaallNo ratings yet
- Physics Project01 (N6)Document12 pagesPhysics Project01 (N6)nilu royNo ratings yet
- Q. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Document5 pagesQ. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Huidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- An Electronic System Power SupplyDocument17 pagesAn Electronic System Power Supplyjisha r krishnanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (A) : Controlled RectifiersDocument22 pagesModule 4 (A) : Controlled RectifiersAishwarya PKamatagiNo ratings yet
- RACTIFIERDocument19 pagesRACTIFIERDhananjay Aghara100% (1)
- Rectifiers: Marino, Christian Rey G. ECEA101L-E02 MARCH 11, 2020Document17 pagesRectifiers: Marino, Christian Rey G. ECEA101L-E02 MARCH 11, 2020Christian MarinoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractDocument20 pagesEmergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractAakash SheelvantNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply CircuitDocument7 pagesDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- REEEFFFSESDocument6 pagesREEEFFFSESezradural99No ratings yet
- Physics Project01Document12 pagesPhysics Project01nilu royNo ratings yet
- Unit-3: REGULATORS:Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple FactorDocument12 pagesUnit-3: REGULATORS:Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple FactorShinde SaikiranNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument16 pagesRectifiersJaiom JoshiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Wk4Document65 pagesPower Electronics Wk4Pang MaronNo ratings yet
- CS CepDocument8 pagesCS Cepfaizan habibNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet