Professional Documents
Culture Documents
17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PX5202 - SSDC Question BankDocument21 pagesPX5202 - SSDC Question BankRoja50% (2)
- Chapter 4Document60 pagesChapter 4Vince Dominich MadroneroNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Buck Boost ConverterDocument4 pagesSimulation of Buck Boost Converterganeshkurapati_15512No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - NewDocument61 pagesUnit 2 - NewMonster AmanNo ratings yet
- Rectifire SummaryDocument4 pagesRectifire SummaryajjjindoreNo ratings yet
- L4-Controlled RectifiersDocument36 pagesL4-Controlled Rectifiershamza malikNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamDocument31 pagesElectrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamSaif Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 15EC73 - PE - Mod 3 - QB - 12102019 PDFDocument35 pages15EC73 - PE - Mod 3 - QB - 12102019 PDFAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Class DutyDocument58 pagesClass DutyHarsha AnantwarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Chapter 2-2: Applications of Semiconductor DevicesDocument18 pagesPower Electronics Chapter 2-2: Applications of Semiconductor DevicestesfuNo ratings yet
- Mcqs (Transformers) : Electrical Machine Final RevisionDocument5 pagesMcqs (Transformers) : Electrical Machine Final Revisionmoooo yii trrhjNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation +autotransformerDocument10 pagesVoltage Regulation +autotransformerShaikh Zia ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- D Unit 3Document11 pagesD Unit 3Abhishek ShyamalNo ratings yet
- Viva EM LabDocument4 pagesViva EM LabcoolrajeeeNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Kawalan MotorDocument20 pagesLab 6 Kawalan MotorMohd FiqrieNo ratings yet
- Answers of Power Electronics NewDocument9 pagesAnswers of Power Electronics NewSyed ZabiullahNo ratings yet
- Buck BoostDocument11 pagesBuck Boostkima lachgarNo ratings yet
- WEST COAST MAGNETICS - Application Notes: Alnt 1440, Revision 1 Flyback Converter DesignDocument6 pagesWEST COAST MAGNETICS - Application Notes: Alnt 1440, Revision 1 Flyback Converter DesignkhsniperNo ratings yet
- Electric DrivesDocument16 pagesElectric DrivesElie KabangaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To All The Teacher's Of: SmitDocument30 pagesWelcome To All The Teacher's Of: Smitsrvdhar100% (2)
- Question BankDocument11 pagesQuestion BankRohini MukunthanNo ratings yet
- Flyback ConverterDocument5 pagesFlyback ConverterAlin PopescuNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT by HEMANTDocument9 pagesPower Electronics PPT by HEMANTshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slide - Single Phase Transformer (Part I)Document24 pagesLecture Slide - Single Phase Transformer (Part I)plshamburger17No ratings yet
- MTS-231 Actuating Systems: Kanwal NaveedDocument38 pagesMTS-231 Actuating Systems: Kanwal NaveedARSLAN FALAKNo ratings yet
- AutotransformerDocument16 pagesAutotransformerKuzma John PadriqueNo ratings yet
- Power Factor CorrectionDocument43 pagesPower Factor Correctionravirnjn88No ratings yet
- 6 - L-21 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-21 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 Wind0.02Document25 pagesAss 2 Wind0.02Šämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- Autotransformer Connection ExplaineDocument6 pagesAutotransformer Connection ExplaineNepoliyanNo ratings yet
- 30 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page30 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Ssemd PPT1Document205 pagesSsemd PPT1control 4uonlyNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 peDocument16 pagesMODULE 4 penandhuramesh71No ratings yet
- Autotransformers: Made By: Prankit Mishra 141CC00007 Submitted To: Mr. Gaurav BhandariDocument16 pagesAutotransformers: Made By: Prankit Mishra 141CC00007 Submitted To: Mr. Gaurav BhandariAtul DahiyaNo ratings yet
- PSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Document8 pagesPSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Vishal BhatNo ratings yet
- Current and Voltage Transformer: Module - 6Document24 pagesCurrent and Voltage Transformer: Module - 6mansi jagtapNo ratings yet
- Power Converters FED DC Drives Aug16Document22 pagesPower Converters FED DC Drives Aug16Ashwini SinghNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Machine: Dr. Sushma Gupta Professor Department of Electrical Engineering MANIT, BhopalDocument73 pagesSpeed Control of DC Machine: Dr. Sushma Gupta Professor Department of Electrical Engineering MANIT, BhopalVenomNo ratings yet
- NAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034Document22 pagesNAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034BARUN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Two-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingDocument8 pagesTwo-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingRakeshconclaveNo ratings yet
- Transformer Gec228 2024 2Document26 pagesTransformer Gec228 2024 2eerandomstuff1211No ratings yet
- Ed Lab ManualDocument27 pagesEd Lab ManualBonnieNo ratings yet
- Dual Converter: PR Epar Ed By: Guided byDocument16 pagesDual Converter: PR Epar Ed By: Guided byRavinandan PathakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Det50063 - Speed Control of DC MotorDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Det50063 - Speed Control of DC MotorFara Fara100% (1)
- Resonance Mode Converters PDFDocument105 pagesResonance Mode Converters PDFprakashbuddha99No ratings yet
- Effect of Source InductanceDocument10 pagesEffect of Source Inductancemeeravali_snNo ratings yet
- Article 50 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Document6 pagesArticle 50 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Pradyumna PooskuruNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-Lecture 3 Chopper Fed DC DrivesDocument23 pagesUNIT 1-Lecture 3 Chopper Fed DC Drivesanandlm710No ratings yet
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDocument9 pagesFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- Cyclo Converter 1Document46 pagesCyclo Converter 1basabNo ratings yet
- 06 Auto TransformerDocument19 pages06 Auto TransformerMuhammad NaguibNo ratings yet
- Tap Changing TransformerDocument16 pagesTap Changing Transformer[5013] Dorathi Christine100% (1)
- An 7517Document9 pagesAn 7517MallickarjunaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDocument5 pagesPower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- Unit4 EDCDocument15 pagesUnit4 EDCKarthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion 4Document35 pagesEnergy Conversion 4kapsicumadNo ratings yet
- 53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - DC Motors PDFDocument56 pages53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - DC Motors PDFDora TengNo ratings yet
- How An Smps Works: Rectifier StageDocument7 pagesHow An Smps Works: Rectifier StageImran AshrafNo ratings yet
- 23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
17 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
GagneCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Summary
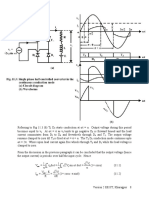
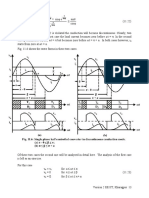
• Single phase half controlled converters are obtained from fully controlled converters by
replacing two thyristors by two diodes.
• Two thyristors of one phase leg or one group (top or bottom) can be replaced resulting in
two different topologies of the half controlled converter. From the operational point of
view these two topologies are identical.
• In a half controlled converter the output voltage does not become negative and hence the
converter cannot operate in the inverter mode.
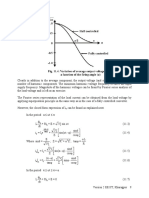
• For the same firing angle and input voltage the half controlled converter in the continuous
conduction mode gives higher output voltage compared to a fully controlled converter.
• For the same input voltage, firing angle and load parameters the half controlled converter
has better output voltage and current form factor compared to a fully controlled
converter.
• For the same firing angle and load current the half controlled converter in the continuous
conduction mode has better input power factor compared to a fully controlled converter.
• Half controlled converters are most favored in applications requiring unidirectional
output voltage and current.
Practice Problems and Answers
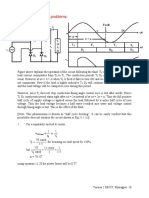
Q1. The thyristor T3 of Fig 1.1(b) fails to turn on at the desired instant. Describe how this
circuit will work in the presence of the fault.
Q2. A single phase half controlled converter is used to boost the no load speed of a
separately excited dc machine by weakening its field supply. At α = 0° the half
controlled converter produces the rated field voltage. If the field inductance is large enough
to make the field current almost ripple face what will be the input power factor when the dc
motor no load speed is bossed to 150%?
Q3. A single phase half controlled converter supplies a 220V, 1500rpm, 20A dc motor from a
230V 50HZ single phase supply. The motor has a armature resistance of 1.0Ω and
inductance of 50mH. What will be the operating modes and torques for α = 30°; and
speed of 1400 RPM.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 17
You might also like
- PX5202 - SSDC Question BankDocument21 pagesPX5202 - SSDC Question BankRoja50% (2)
- Chapter 4Document60 pagesChapter 4Vince Dominich MadroneroNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Buck Boost ConverterDocument4 pagesSimulation of Buck Boost Converterganeshkurapati_15512No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - NewDocument61 pagesUnit 2 - NewMonster AmanNo ratings yet
- Rectifire SummaryDocument4 pagesRectifire SummaryajjjindoreNo ratings yet
- L4-Controlled RectifiersDocument36 pagesL4-Controlled Rectifiershamza malikNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamDocument31 pagesElectrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamSaif Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 15EC73 - PE - Mod 3 - QB - 12102019 PDFDocument35 pages15EC73 - PE - Mod 3 - QB - 12102019 PDFAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Class DutyDocument58 pagesClass DutyHarsha AnantwarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Chapter 2-2: Applications of Semiconductor DevicesDocument18 pagesPower Electronics Chapter 2-2: Applications of Semiconductor DevicestesfuNo ratings yet
- Mcqs (Transformers) : Electrical Machine Final RevisionDocument5 pagesMcqs (Transformers) : Electrical Machine Final Revisionmoooo yii trrhjNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation +autotransformerDocument10 pagesVoltage Regulation +autotransformerShaikh Zia ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- D Unit 3Document11 pagesD Unit 3Abhishek ShyamalNo ratings yet
- Viva EM LabDocument4 pagesViva EM LabcoolrajeeeNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Kawalan MotorDocument20 pagesLab 6 Kawalan MotorMohd FiqrieNo ratings yet
- Answers of Power Electronics NewDocument9 pagesAnswers of Power Electronics NewSyed ZabiullahNo ratings yet
- Buck BoostDocument11 pagesBuck Boostkima lachgarNo ratings yet
- WEST COAST MAGNETICS - Application Notes: Alnt 1440, Revision 1 Flyback Converter DesignDocument6 pagesWEST COAST MAGNETICS - Application Notes: Alnt 1440, Revision 1 Flyback Converter DesignkhsniperNo ratings yet
- Electric DrivesDocument16 pagesElectric DrivesElie KabangaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To All The Teacher's Of: SmitDocument30 pagesWelcome To All The Teacher's Of: Smitsrvdhar100% (2)
- Question BankDocument11 pagesQuestion BankRohini MukunthanNo ratings yet
- Flyback ConverterDocument5 pagesFlyback ConverterAlin PopescuNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT by HEMANTDocument9 pagesPower Electronics PPT by HEMANTshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slide - Single Phase Transformer (Part I)Document24 pagesLecture Slide - Single Phase Transformer (Part I)plshamburger17No ratings yet
- MTS-231 Actuating Systems: Kanwal NaveedDocument38 pagesMTS-231 Actuating Systems: Kanwal NaveedARSLAN FALAKNo ratings yet
- AutotransformerDocument16 pagesAutotransformerKuzma John PadriqueNo ratings yet
- Power Factor CorrectionDocument43 pagesPower Factor Correctionravirnjn88No ratings yet
- 6 - L-21 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-21 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 Wind0.02Document25 pagesAss 2 Wind0.02Šämęh ËšśämNo ratings yet
- Autotransformer Connection ExplaineDocument6 pagesAutotransformer Connection ExplaineNepoliyanNo ratings yet
- 30 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page30 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Ssemd PPT1Document205 pagesSsemd PPT1control 4uonlyNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 peDocument16 pagesMODULE 4 penandhuramesh71No ratings yet
- Autotransformers: Made By: Prankit Mishra 141CC00007 Submitted To: Mr. Gaurav BhandariDocument16 pagesAutotransformers: Made By: Prankit Mishra 141CC00007 Submitted To: Mr. Gaurav BhandariAtul DahiyaNo ratings yet
- PSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Document8 pagesPSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Vishal BhatNo ratings yet
- Current and Voltage Transformer: Module - 6Document24 pagesCurrent and Voltage Transformer: Module - 6mansi jagtapNo ratings yet
- Power Converters FED DC Drives Aug16Document22 pagesPower Converters FED DC Drives Aug16Ashwini SinghNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Machine: Dr. Sushma Gupta Professor Department of Electrical Engineering MANIT, BhopalDocument73 pagesSpeed Control of DC Machine: Dr. Sushma Gupta Professor Department of Electrical Engineering MANIT, BhopalVenomNo ratings yet
- NAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034Document22 pagesNAVEEN KUMAR CgOLLEGE ROLL NO - 237094034BARUN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Two-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingDocument8 pagesTwo-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingRakeshconclaveNo ratings yet
- Transformer Gec228 2024 2Document26 pagesTransformer Gec228 2024 2eerandomstuff1211No ratings yet
- Ed Lab ManualDocument27 pagesEd Lab ManualBonnieNo ratings yet
- Dual Converter: PR Epar Ed By: Guided byDocument16 pagesDual Converter: PR Epar Ed By: Guided byRavinandan PathakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Det50063 - Speed Control of DC MotorDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Det50063 - Speed Control of DC MotorFara Fara100% (1)
- Resonance Mode Converters PDFDocument105 pagesResonance Mode Converters PDFprakashbuddha99No ratings yet
- Effect of Source InductanceDocument10 pagesEffect of Source Inductancemeeravali_snNo ratings yet
- Article 50 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Document6 pagesArticle 50 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Pradyumna PooskuruNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-Lecture 3 Chopper Fed DC DrivesDocument23 pagesUNIT 1-Lecture 3 Chopper Fed DC Drivesanandlm710No ratings yet
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDocument9 pagesFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- Cyclo Converter 1Document46 pagesCyclo Converter 1basabNo ratings yet
- 06 Auto TransformerDocument19 pages06 Auto TransformerMuhammad NaguibNo ratings yet
- Tap Changing TransformerDocument16 pagesTap Changing Transformer[5013] Dorathi Christine100% (1)
- An 7517Document9 pagesAn 7517MallickarjunaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDocument5 pagesPower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- Unit4 EDCDocument15 pagesUnit4 EDCKarthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion 4Document35 pagesEnergy Conversion 4kapsicumadNo ratings yet
- 53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - DC Motors PDFDocument56 pages53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - DC Motors PDFDora TengNo ratings yet
- How An Smps Works: Rectifier StageDocument7 pagesHow An Smps Works: Rectifier StageImran AshrafNo ratings yet
- 23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-17 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page24 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page22 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page23 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page19 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page18 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-11 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page16 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-10 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet