Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inventory PIE (Principles of Industrial Engineering) Assignment
Inventory PIE (Principles of Industrial Engineering) Assignment
Uploaded by
akhila varma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesThe document discusses inventory management concepts through 4 questions about determining optimal order quantities, inventory levels, holding and setup costs for different companies. It examines scenarios for a company producing EPROMs, an online retailer of vitamins, a carpet store stocking different brands, and a retailer considering smaller order quantities under just-in-time purchasing. Optimal order sizes, inventory levels, number of orders, and total inventory costs are calculated based on information about demand, ordering costs, holding costs, and shortage costs provided in each question.
Original Description:
Original Title
Inventory PIE (principles of industrial engineering) assignment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses inventory management concepts through 4 questions about determining optimal order quantities, inventory levels, holding and setup costs for different companies. It examines scenarios for a company producing EPROMs, an online retailer of vitamins, a carpet store stocking different brands, and a retailer considering smaller order quantities under just-in-time purchasing. Optimal order sizes, inventory levels, number of orders, and total inventory costs are calculated based on information about demand, ordering costs, holding costs, and shortage costs provided in each question.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesInventory PIE (Principles of Industrial Engineering) Assignment
Inventory PIE (Principles of Industrial Engineering) Assignment
Uploaded by
akhila varmaThe document discusses inventory management concepts through 4 questions about determining optimal order quantities, inventory levels, holding and setup costs for different companies. It examines scenarios for a company producing EPROMs, an online retailer of vitamins, a carpet store stocking different brands, and a retailer considering smaller order quantities under just-in-time purchasing. Optimal order sizes, inventory levels, number of orders, and total inventory costs are calculated based on information about demand, ordering costs, holding costs, and shortage costs provided in each question.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
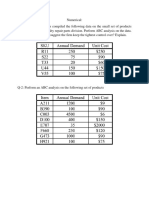
INVENTORY MANAGEMENT (TUTORIAL 3)
Q1. A local company produces a programmable EPROM (erasable programmable read-only
memory) for several industrial clients. They have experienced a relatively flat demand of 2500
units per year for the product. The EPROM is produced at a rate of 10000 units per year. The
accounting department has estimated that it costs $50 to initiate a production run, each unit costs
the company1$2 to manufacture, and the cost of holding is based on a 30% annual interest rate.
Determine the optimal size of a production run, the length of each production run, and the average
annual cost of holding and setup. What is the maximum level of on-hand inventory of the
EPROMs?
Q2. Drugs online (DO) is an online retailer of prescription drugs and health supplements. Vitamins
represent a significant percentage of its sales. Demand for vitamins is 10,000 bottles per month.
DO incurs a fixed order placement, transportation and receiving cost of $150 each times an order
for vitamins is placed with the manufacturer. Do incurs a holding cost of $0.75/bottle/month and
Shortage cost of $2/bottle/month. Find out the optimal order quantity, shortage level and maximum
inventory level and total inventory cost?
Time during which inventory is on hand t1 Q S
D
Time during which there is a shortage t2 S
D
Q3. The I-75 Carpet Discount Store in North Georgia stocks carpet in its warehouse and sells it
through an adjoining showroom. The store keeps several brands and styles of carpet in stock;
however, its biggest seller is Super Shag carpet. The store wants to determine the optimal order
size and total inventory cost for this brand of carpet given an estimated annual demand of 10,000
yards of carpet, an annual carrying cost of $0.75 per yard, and an ordering cost of $150. The store
would also like to know the number of orders that will be made annually and the time between
orders (i.e., the order cycle) given that the store is open every day except Sunday, Thanksgiving
Day, and Christmas Day (which is not on a Sunday). Now if store person allowed back-ordering
with back-oreder cost $200, then what is the new optimal order size.
Q4. A retailer estimates her fixed cost for placing an order at $1,000. Presently she orders in
optimal quantities of 400 units. She has, however, heard of the benefits of just-in-time purchasing
– a principle that advocates purchasing goods in smaller lots as a means of keeping inventory
down. If she wishes to order in lots no larger than 50, what should be her fixed ordering costs?
You might also like
- VAS - GIS 2024 Converted From ExcelDocument10 pagesVAS - GIS 2024 Converted From Excelmarkanthony031986No ratings yet
- DocDocument3 pagesDocsaurabhmanitNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Homework Template - 13thDocument11 pagesWeek 7 Homework Template - 13thalgadilan0% (2)
- Inventory NumericalDocument2 pagesInventory NumericaljehadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 QuestionDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 QuestionJanarthanan Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document7 pagesCH 12Fadila Elsa PrimNo ratings yet
- CASE 2 - Brushing Up On Inventory ControlDocument20 pagesCASE 2 - Brushing Up On Inventory ControlVõ MartinNo ratings yet
- OM PS2 InventoryDocument3 pagesOM PS2 InventoryNavneeth KrishnaNo ratings yet
- US Dollar Store Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesUS Dollar Store Consumer BehaviourTryden Royce D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Inventory AssignmentDocument3 pagesInventory AssignmentMuhammad Bilal100% (1)
- EOQ ProblemsDocument3 pagesEOQ ProblemsTushar MehndirattaNo ratings yet
- 15 ExercisesDocument3 pages15 ExercisesAravind ShankarNo ratings yet
- Suggested Solution To Assignment 2 Part 1: November 10, 2011Document7 pagesSuggested Solution To Assignment 2 Part 1: November 10, 2011sojoud shorbajiNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain & Logistics Analytics - Session 5 Analytics in Inventory Management MOQ, EOQ, Inventory OptimizationDocument31 pagesSupply Chain & Logistics Analytics - Session 5 Analytics in Inventory Management MOQ, EOQ, Inventory OptimizationArya KeoliyaNo ratings yet
- II.3 Management of InventoriesDocument44 pagesII.3 Management of InventoriesKin SaysonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Vi. Inventory Models Part 1Document36 pagesChapter Vi. Inventory Models Part 1pekka172No ratings yet
- Üretim Servis Çalışma SorularıDocument10 pagesÜretim Servis Çalışma SorularıEzgi Su KilitNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 1Document5 pagesPractice Problems 1Murtaza PoonawalaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 QuestionsDocument1 pageQuiz 3 Questionsmahnoor javaidNo ratings yet
- Problem Set and Quiz in or 2Document1 pageProblem Set and Quiz in or 2Ryan Jeffrey Padua CurbanoNo ratings yet
- 3 Inventory Management - CompressDocument5 pages3 Inventory Management - Compressforacademicfiles.01No ratings yet
- The DDL Is 5 April, Please Write Clearly Your Name and ID in The Answer SheetDocument2 pagesThe DDL Is 5 April, Please Write Clearly Your Name and ID in The Answer SheetФилипп СибирякNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Pactice QuestionsDocument8 pagesOperations Management Pactice QuestionsHumphrey OsaigbeNo ratings yet
- Formula and Calculation of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)Document7 pagesFormula and Calculation of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)harpominder100% (1)
- Quantech: InventoryDocument15 pagesQuantech: InventoryJem Carstairs67% (3)
- SCM Numerical 2011Document13 pagesSCM Numerical 2011arvindpmNo ratings yet
- Case Study 8Document1 pageCase Study 8eviegonzalez211No ratings yet
- Seminar Materials: Management Analytics 1 Global MBA Ou Tang October 2014Document8 pagesSeminar Materials: Management Analytics 1 Global MBA Ou Tang October 2014Vicky SinhaNo ratings yet
- Final Practice 2 QDocument2 pagesFinal Practice 2 QraymondNo ratings yet
- OM - Sessions 18 - 23 - Inventory ManagementDocument64 pagesOM - Sessions 18 - 23 - Inventory ManagementSiddhant SinghNo ratings yet
- Bài tập tồn khoDocument2 pagesBài tập tồn khoduyentran.31211024068No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015Document5 pagesChapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015Jharr699No ratings yet
- Mathematics For Retail Buying-Inventory ManagementDocument27 pagesMathematics For Retail Buying-Inventory ManagementBhavyata ChavdaNo ratings yet
- GW4 - Quantity and InventoryDocument1 pageGW4 - Quantity and InventoryPhương TrầnNo ratings yet
- 3 - Inventory ManagementDocument5 pages3 - Inventory ManagementAngela Shaine Castro GarciaNo ratings yet
- InventoryDocument27 pagesInventoryAmaresh JhaNo ratings yet
- Required:: Financial ManagementDocument5 pagesRequired:: Financial ManagementBKS Sannyasi100% (1)
- Min Max LevelsDocument7 pagesMin Max LevelsUday JoshiNo ratings yet
- IE323 Study Set 2Document5 pagesIE323 Study Set 2Mehmet ŞahinNo ratings yet
- Why Is Inventory Turnover Important?: ... It Measures How Hard Your Inventory Investment Is WorkingDocument6 pagesWhy Is Inventory Turnover Important?: ... It Measures How Hard Your Inventory Investment Is WorkingabhiNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management - HandoutsDocument4 pagesProduction and Operations Management - HandoutsGhilman HabibNo ratings yet
- Managing Working Capital Inventory ManagementDocument10 pagesManaging Working Capital Inventory ManagementAjay Kumar TakiarNo ratings yet
- Inventory Tutorial1Document1 pageInventory Tutorial1Aldiz NatsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Managing Working Capital - GUI HVDocument44 pagesChapter 5 - Managing Working Capital - GUI HVTấn Phú LêNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Class 2 - 5409456 - 2024 - 01 - 18 - 20 - 01Document34 pagesModule 2-Class 2 - 5409456 - 2024 - 01 - 18 - 20 - 01Shajathkhan Bin Syed UsmanNo ratings yet
- Inventory MGMT ComprehensiveDocument4 pagesInventory MGMT ComprehensivebigbaekNo ratings yet
- Store IhmDocument17 pagesStore IhmAnupam royNo ratings yet
- EOQ Group-2Document2 pagesEOQ Group-2Ella CunananNo ratings yet
- Fixed-OrderQuantity and Fixed-TimePeriod ExercisesDocument1 pageFixed-OrderQuantity and Fixed-TimePeriod ExercisesIris Descent0% (1)
- Chapter 20 Exercise: RequiredDocument5 pagesChapter 20 Exercise: RequiredNitinNo ratings yet
- 2 Class - Exercise - Question - 1 DR - HyattDocument5 pages2 Class - Exercise - Question - 1 DR - Hyattnurfarhana6789No ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Company ProfileDocument9 pagesChapter-1: Company ProfileTryden Royce D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Inventory: Critical Thinking ExecisesDocument2 pagesInventory: Critical Thinking ExecisesBùi Nguyễn Hoàng VânNo ratings yet
- Suede-Mart Case StudyDocument17 pagesSuede-Mart Case Studyprasadvkamath100% (1)
- Assignment 2: Mega BhattaraiDocument6 pagesAssignment 2: Mega BhattaraimegaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Basics StimulationDocument2 pagesInventory Basics Stimulationswarnima biswariNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution CasesDocument3 pagesNormal Distribution Casesjaiveer gurjarNo ratings yet
- SC FinalsDocument6 pagesSC Finalsacctsecret70No ratings yet
- Inventory Management AssignmentDocument2 pagesInventory Management AssignmentPravin MandoraNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Inventory ManagementDocument3 pagesExercises On Inventory ManagementHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1 Lesson 4-5Document32 pagesFabm 1 Lesson 4-5Dionel RizoNo ratings yet
- HW#10 11.2 and 11.5 Implicit Diff and Application - MATH 104 - Fall 2023, Fall 2023 WebAssignDocument1 pageHW#10 11.2 and 11.5 Implicit Diff and Application - MATH 104 - Fall 2023, Fall 2023 WebAssignAbdullah AlaamNo ratings yet
- Value Cocreationn Vega-Vazquez2013Document13 pagesValue Cocreationn Vega-Vazquez2013Sonila ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Assessment E - Bistro Reports - V2-1Document3 pagesAssessment E - Bistro Reports - V2-1littlebambiNo ratings yet
- Mockboard 1Document100 pagesMockboard 1Joseph AsisNo ratings yet
- Annual Report BataDocument18 pagesAnnual Report BataVenna PavanNo ratings yet
- FabmDocument28 pagesFabmHanissandra Franz V. DalanNo ratings yet
- Big Bazaar Strategic AnalysisDocument16 pagesBig Bazaar Strategic Analysisprakashprabum0% (1)
- A Study On Social Media For Innovative Marketing StrategiesDocument83 pagesA Study On Social Media For Innovative Marketing Strategiesankur kumarNo ratings yet
- 2022 ICTSI Balance Sheet Income Statement - pg.53Document1 page2022 ICTSI Balance Sheet Income Statement - pg.53loveartxoxo.commissionNo ratings yet
- Sweta E-Commerce Project 8Document44 pagesSweta E-Commerce Project 8SUSHIL GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Question Bank of Financial and Management Accounting - 2 MarkDocument28 pagesQuestion Bank of Financial and Management Accounting - 2 MarklakkuMS100% (1)
- An Industrial Report On Balaji WafersDocument31 pagesAn Industrial Report On Balaji Wafersrohan amrutiyaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Studies On Neuromarketing PR EspañolDocument20 pagesA Review of Studies On Neuromarketing PR EspañolAnalia BenitezNo ratings yet
- PartnershipDocument24 pagesPartnershipPranavNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management - Session 08-09Document56 pagesProduction and Operations Management - Session 08-09Manik KapoorNo ratings yet
- Demand Management DraftDocument31 pagesDemand Management DraftTAHIR TINWALANo ratings yet
- CH 07Document63 pagesCH 07Ivhy Cruz Estrella100% (5)
- AFA Model Question PaperDocument17 pagesAFA Model Question PaperWinner ANo ratings yet
- Terracog GPS Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesTerracog GPS Case AnalysisZohair AhmedNo ratings yet
- QTM AssignmentDocument4 pagesQTM AssignmentLoveesh SinglaNo ratings yet
- CV - Srikanth VarmaDocument2 pagesCV - Srikanth VarmaChandanNo ratings yet
- Integrated Marketing Communications As A Tool ForDocument12 pagesIntegrated Marketing Communications As A Tool ForBeatriz FerreiraNo ratings yet
- EEMA Membership List 7Document8 pagesEEMA Membership List 7Manishh Venkateshwara RaoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Steps in The Selling Process of VeetDocument5 pagesAdvanced Steps in The Selling Process of VeetMoeed SaeedNo ratings yet
- Accounting For ManufacturingDocument36 pagesAccounting For ManufacturingMhico Mateo0% (1)
- Real Estate SalesDocument29 pagesReal Estate SalesAniruddha SahaNo ratings yet
- Marginal Cost Questions - Past ExamDocument3 pagesMarginal Cost Questions - Past ExamLouisa HasfordNo ratings yet
- Valuation ParableDocument7 pagesValuation ParableVico Ahmad RisyadNo ratings yet